ITERATIVE model in software engineering.pptx
- 1. ITERATIVE MODEL DR. SUCHITA BHOVAR
- 2. ITERATIVE MODEL • In this Model, you can start with some of the software specifications and develop the first version of the software. • After the first version if there is a need to change the software, then a new version of the software is created with a new iteration. • Every release of the Iterative Model finishes in an exact and fixed period that is called iteration. • The Iterative Model allows the accessing earlier phases, in which the variations made respectively. • The final output of the project renewed at the end of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process.
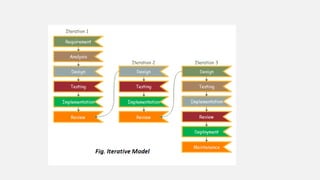
- 4. THE VARIOUS PHASES OF ITERATIVE MODEL ARE AS FOLLOWS: 1. Requirement gathering & analysis: In this phase, requirements are gathered from customers and check by an analyst whether requirements will fulfil or not. Analyst checks that need will achieve within budget or not. After all of this, the software team skips to the next phase. 2. Design: In the design phase, team design the software by the different diagrams like Data Flow diagram, activity diagram, class diagram, state transition diagram, etc.
- 5. THE VARIOUS PHASES OF ITERATIVE MODEL ARE AS FOLLOWS: 3. Implementation: In the implementation, requirements are written in the coding language and transformed into computer programmes which are called Software. 4. Testing: After completing the coding phase, software testing starts using different test methods. There are many test methods, but the most common are white box, black box, and grey box test methods. 5. Deployment: After completing all the phases, software is deployed to its work environment.
- 6. THE VARIOUS PHASES OF ITERATIVE MODEL ARE AS FOLLOWS: 6. Review: In this phase, after the product deployment, review phase is performed to check the behaviour and validity of the developed product. And if there are any error found then the process starts again from the requirement gathering. 7. Maintenance: In the maintenance phase, after deployment of the software in the working environment there may be some bugs, some errors or new updates are required. Maintenance involves debugging and new addition options.
- 7. WHEN TO USE THE ITERATIVE MODEL? 1.When requirements are defined clearly and easy to understand. 2.When the software application is large. 3.When there is a requirement of changes in future.
- 8. ADVANTAGE(PROS) OF ITERATIVE MODEL: 1.Testing and debugging during smaller iteration is easy. 2.A Parallel development can plan. 3.It is easily acceptable to ever-changing needs of the project. 4.Risks are identified and resolved during iteration. 5.Limited time spent on documentation and extra time on designing.
- 9. DISADVANTAGE(CONS) OF ITERATIVE MODEL: 1.It is not suitable for smaller projects. 2.More Resources may be required. 3.Design can be changed again and again because of imperfect requirements. 4.Requirement changes can cause over budget. 5.Project completion date not confirmed because of changing requirements.
- 10. THANK YOU