Java 9 Module System Introduction
- 1. Java 9 Module System Introduction Dan Stine Software Architecture, Development and Integration Meetup Newton, MA October 19, 2017
- 2. About Me • Software Architect • Library Author and Maintainer • Build Process Designer • Enterprise Dependency Graph Wrangler dstine at copyright.com sw at stinemail.com github.com/dstine 10/20/20172
- 3. About You • Java version • Java build tool • Any familiarity with new module system? 10/20/20173
- 5. Java 9 • GA on September 21, 2017 – Exactly four weeks ago • Not immediately enticing for many individual coders – Compared to Java 8: Streams! Lambdas!! • Java Platform Module System (JPMS) – Driving feature of Java 9 – Project Jigsaw initiated in 2008 – Promises to impact system architecture and software evolution 10/20/20175
- 6. Why Does Java Need a Module System? • Multitude of open-source libraries and frameworks – Covering immense number of use cases • Organizations develop internal shared libraries – Consumed by systems managed by other people • Build tools and artifact repositories to manage all of this – Easily (?) 10/20/20176
- 7. Exposed Internals 10/20/20177 That type is in the “internal” package; I’m sure no one will import it That class uses the “Impl” suffix; I’m sure everyone will code to the interface instead
- 8. API Management Problems • No mechanism to clearly define a library’s API • No mechanism to enforce a library’s API • Library evolution suffers • www.semver.org Clause 1: Software using Semantic Versioning MUST declare a public API. This API could be declared in the code itself or exist strictly in documentation. However it is done, it should be precise and comprehensive. 10/20/20178
- 9. Applications • These issues also apply to applications • Layering and partitioning are common techniques – UI services repositories data access – Bounded contexts for various subdomains – Client libraries for service consumers – Shared utilities • Layering and partitioning = modularization • How do you ensure “the rules” are followed? 10/20/20179
- 10. Collaboration Difficulty 10/20/201710 It’s covered in the project wiki We wrote some custom static analysis Alice reviews everyone’s code
- 11. Lack of Encapsulation • Traditional JAR • All types and packages exported to all consumers • All dependencies exported to all consumers • All runtime dependencies exported to compile classpath of all consumers 10/20/201711
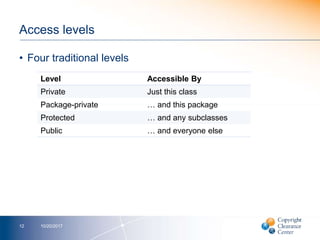
- 12. Access levels • Four traditional levels 10/20/201712 Level Accessible By Private Just this class Package-private … and this package Protected … and any subclasses Public … and everyone else
- 13. Dependency Configuration • At build time, our tooling uses a non-trivial degree of sophistication to manage dependencies • But much of the information known at build time is discarded • All JARs are on the runtime classpath; all classes are available to all others 10/20/201713
- 15. Modules • Java 9 provides a new abstraction – the module • “A set of packages designed for reuse” – Oracle • Stronger encapsulation than traditional JAR files – Finer-grained access control – At the package and module levels • Reliable dependency configuration – Explicit notion of dependencies between modules 10/20/201715
- 16. Module Declaration • New special file: module-info.java • Module name – Reverse domain name convention strongly encouraged – Single global namespace • Declares dependencies on other modules • Declares exported packages module [MODULE_NAME] { requires [OTHER_MODULE_NAME]; exports [PACKAGE_NAME]; } 10/20/201716
- 17. Example: Internal Package 10/20/201717 com.example.lib Foo of(String s) of(Integer i) com.example.lib.internal StringToFoo IntegerToFoo com.example.app uses com.example.lib module lib { exports com.example.lib } module app { requires lib } app cannot compile against com.example.lib.internal
- 18. Example: Internal Third-Party Dependency 10/20/201718 com.example.app uses com.example.lib module app { requires lib } com.example.lib Foo of(String s) of(Integer i) com.example.lib.internal StringToFoo uses Guava IntegerToFoo module lib { requires com.google.common exports com.example.lib } app cannot compile against com.google.common
- 19. Example: Third-Party Dependency in API 10/20/201719 com.example.app uses com.example.lib module app { requires lib } com.example.lib Foo of(String s) of(Integer i) of(UnsignedInteger ui) com.example.lib.internal StringToFoo IntegerToFoo UnsignedIntegerToFoo module lib { requires transitive com.google.common exports com.example.lib } app may compile against com.google.common
- 20. Module Path • Classpath replaced by module path – Supported by javac (compile time) and java (runtime) • module-info.java is compiled to module-info.class • Placed at root of modular JAR 10/20/201720
- 21. Module System Guarantees • All module dependencies are satisfied • Declared package visibility is enforced • No split packages • No cyclic dependencies 10/20/201721
- 22. Access Levels • Two new levels; protected and public effectively redefined (Qualified exports enables another two variations beyond these) 10/20/201722 Level Accessible Private Just this class Package-private … and this package Protected … and any subclasses in this module Protected (exported) … and any subclasses in other modules Public … and any classes in this module Public (exported) … and any classes in other modules
- 23. Additional Benefits • Faster class loading – Build time: fewer dependencies to load – Runtime: don’t need to scan every JAR on classpath • Shorter (re-)compile times – Recompile only if API of a dependency has changed – API is now clearly defined (packages and dependencies) • More responsive IDEs – Auto-complete, “Open Type” dialog, suggested imports 10/20/201723
- 25. JDK Itself is Now Modular • Monolithic JDK had tangled complex dependency graph • Refactored (starting in Java 7 timeframe) • Now officially partitioned into modules – http://openjdk.java.net/projects/jigsaw/doc/jdk-modularization.html • User modules must now explicitly declare a dependency on each required JDK platform module 10/20/201725
- 26. JDK Platform Modules • Base platform module – Name = java.base – Packages = java.io, java.lang, java.net, java.util, …. – Implicit in all module declarations • Other platform modules – Names = java.sql, java.logging, java.xml, … – Must be explicitly declared • JDK documentation – Lists all modules with exported packages and dependencies 10/20/201726
- 27. Example: JDK Platform Module Dependency 10/20/201727 module app { requires lib } com.example.app uses com.example.lib com.example.lib Foo of(String s) of(Integer i) of(Document doc) com.example.lib.internal StringToFoo IntegerToFoo DocumentToFoo module lib { requires transitive java.xml exports com.example.lib }
- 29. Adopting Modules • Could wait – Classpath has not been removed – Classpath ignores module-info.class • Could slowly work dependency graph from the bottom up – Wait for all dependencies to modularize – Shared company libraries – All third-party libraries, and their dependencies 10/20/201729
- 30. Top Down Adoption • Start modularizing at the top of the dependency graph • Take advantage of automatic modules (next slide) • Reap some benefits immediately • Gain more as the ecosystem catches up 10/20/201730
- 31. Automatic Modules • Put traditional (non-modular) JARs on the module path • These are treated as automatic modules • Receive auto-generated module name – Based on file name without version – E.g. commons-lang3-3.1.jar commons-lang3 – Use this in module-info.java • Like JARs on the classpath, automatic modules: – Export all their packages – “Require” all other modules 10/20/201731
- 32. Other Components of the Module System • Qualified exports • jdeps command line tool • Automatic-Module-Name JAR manifest entry • Illegal access & JDK internals • Services (java.util.ServiceLoader) • Modular runtime images (including jlink tool) • Layers 10/20/201732
- 33. Summary • Module system addresses several pain points in building and maintaining software systems – Strong encapsulation via explicit package exports – Reliable configuration via explicit module dependencies • Module is “a set of packages designed for reuse” • Module path replaces classpath • JDK itself is now composed of platform modules • Can begin top-down adoption now 10/20/201733
- 34. References • JDK 9 javadoc – http://download.java.net/java/jdk9/docs/api/overview- summary.html • State of the Module System – http://openjdk.java.net/projects/jigsaw/spec/sotms/ – Slightly outdated; update is promised • Jigsaw / JPMS / JSR 376 – http://openjdk.java.net/projects/jigsaw/spec/ – Includes JLS and JVMS diffs 10/20/201734
- 35. Thank you!
- 36. Qualified Exports • Share (some of) API with a known set of other modules • Package export can be qualified with to keyword 10/20/201736
- 37. Access Levels • Eight levels 10/20/201737 Level Accessible By Private Just this class Package-private … and this package Protected … and any subclasses in this module Protected (exported to) … and any subclasses in particular modules Protected (exported) … and any subclasses in all modules Public … and any classes in this module Public (exported to) … and any classes in particular modules Public (exported) … and any classes in all modules
- 38. jdeps • Command line tool for dependency analysis • Appeared in Java 8, improved in Java 9 • Report on JDK internal dependencies • Report on module graph • Generate module-info.java • Etc. 10/20/201738
- 39. Automatic-Module-Name • Modularization can take some effort • Library maintainer can declare the intended module name immediately • Add Automatic-Module-Name entry to JAR manifest • For example, Guava has declared com.google.common 10/20/201739
- 40. Illegal Access & JDK Internals • One goal of JPMS is to properly hide JDK internals – Allow for faster / better evolution • But many libraries use the internals – Who has heard of sun.misc.Unsafe • Command line flag --illegal-access – Default is permit to provide more gradual cutover – Default will eventually be deny – http://mail.openjdk.java.net/pipermail/jigsaw-dev/2017- June/012841.html 10/20/201740
- 41. Services • java.util.ServiceLoader introduced in Java 6 • Module A declares use of an interface • Modules B and C can declare implementations • Module A does not have to declare dependency on B or C – Doesn’t know about them – B and C are managed independently 10/20/201741
- 42. Service Example module java.sql { ... uses java.sql.Driver; } module com.mysql.jdbc { ... provides java.sql.Driver with com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; } module org.postgresql { ... provides java.sql.Driver with org.postgresql.Driver; } 10/20/201742
- 43. Modular Runtime Images • Java has always had dynamic (runtime) linking • Now Java has optional static linking • New tool jlink creates a custom runtime image – All required JAR modules – Only the required JDK modules • More efficient use of compute resources – Scale up: large public web service resource requirements – Scale down: mobile devices 10/20/201743
- 44. Layers • Application servers host applications • Hosted applications might require different versions of modules than those used by the server • Hosted applications might require new or different services than those used by the server • Application servers can create new layers in which to host individual applications 10/20/201744
- 45. Formal Syntax (JLS § 7.7) ModuleDeclaration: {Annotation} [open] module Identifier {. Identifier} { {ModuleDirective} } ModuleDirective: requires {RequiresModifier} ModuleName; exports PackageName [to ModuleName {, ModuleName}] ; opens PackageName [to ModuleName {, ModuleName}] ; uses TypeName; provides TypeName with TypeName {, TypeName} ; RequiresModifier: (one of) transitive static 10/20/201745















![Module Declaration
• New special file: module-info.java
• Module name
– Reverse domain name convention strongly encouraged
– Single global namespace
• Declares dependencies on other modules
• Declares exported packages
module [MODULE_NAME] {
requires [OTHER_MODULE_NAME];
exports [PACKAGE_NAME];
}
10/20/201716](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/software-architecture-meetup-jdk-9-171020172621/85/Java-9-Module-System-Introduction-16-320.jpg)




























![Formal Syntax (JLS § 7.7)
ModuleDeclaration:
{Annotation} [open] module Identifier {. Identifier}
{ {ModuleDirective} }
ModuleDirective:
requires {RequiresModifier} ModuleName;
exports PackageName [to ModuleName {, ModuleName}] ;
opens PackageName [to ModuleName {, ModuleName}] ;
uses TypeName;
provides TypeName with TypeName {, TypeName} ;
RequiresModifier:
(one of)
transitive static
10/20/201745](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/software-architecture-meetup-jdk-9-171020172621/85/Java-9-Module-System-Introduction-45-320.jpg)