Java input Scanner
- 1. University of Kufa Collage of Computer Science and Mathematics Lecture 3 م . االمين الحسن عبد هدى م
- 2. The Scanner class is used to get user input, and it is found in the java.util package. To use the Scanner class, create an object of the class and use any of the available methods found in the Scanner class documentation. In our examples, we will use the nextLine() method, which is used to read Strings: Java User Input (Scanner) the nextInt () method, which is used to read int the nextLine () method, which is used to read string
- 3. Java User Input (Scanner) import java.util.Scanner; // Import the Scanner class class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object System.out.println("Enter username"); String userName = myObj.nextLine(); // Read user input System.out.println("Username is: " + userName); // Output user input } }
- 4. Java User Input (Scanner) import java.util.Scanner; // Import the Scanner class class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object System.out.println("Enter username"); String userName = myObj.nextLine(); // Read user input System.out.println("Username is: " + userName); // Output user input } }
- 5. Java User Input (Scanner)
- 6. Java User Input (Scanner)
- 7. Some programming statements allow us to make decisions and perform repetitions These decisions are based on boolean expressions (also called conditions) that evaluate to true or false The order of statement execution is called the flow of control Flow of Control
- 8. A conditional statement lets us choose which statement will be executed next They are sometimes called selection statements Conditional statements give us the power to make basic decisions The Java conditional statements are the: if and if-else statement switch statement Flow of Control
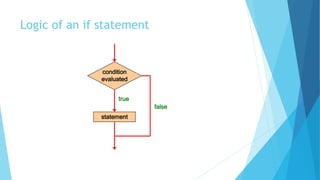
- 9. The if Statement Let's now look at the if statement in more detail The if statement has the following syntax: if ( condition ) statement; if is a Java reserved word The condition must be a boolean expression. It must evaluate to either true or false. If the condition is true, the statement is executed. If it is false, the statement is skipped.
- 10. Logic of an if statement condition evaluated false statement true
- 11. A condition often uses one of Java's equality operators or relational operators, which all return boolean results: ==equal to !=not equal to < less than > greater than <=less than or equal to >=greater than or equal to Note the difference between the equality operator (==) and the assignment operator (=) Boolean Expressions
- 12. An if statement with its boolean condition: if (sum > MAX) delta = sum – MAX; First, the condition is evaluated: the value of sum is either greater than the value of MAX, or it is not If the condition is true, the assignment statement is executed; if it isn't, it is skipped Boolean Expressions
- 13. //******************************************************************** // Age.java Author: Lewis/Loftus // // Demonstrates the use of an if statement. //******************************************************************** import java.util.Scanner; public class Age { //----------------------------------------------------------------- // Reads the user's age and prints comments accordingly. //----------------------------------------------------------------- public static void main (String[] args) { final int MINOR = 21; Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in); System.out.print ("Enter your age: "); int age = scan.nextInt(); continue
- 14. continue System.out.println ("You entered: " + age); if (age < MINOR) System.out.println ("Youth is a wonderful thing. Enjoy."); System.out.println ("Age is a state of mind."); } }
- 15. continue System.out.println ("You entered: " + age); if (age < MINOR) System.out.println ("Youth is a wonderful thing. Enjoy."); System.out.println ("Age is a state of mind."); } } Sample Run Enter your age: 47 You entered: 47 Age is a state of mind. Another Sample Run Enter your age: 12 You entered: 12 Youth is a wonderful thing. Enjoy. Age is a state of mind.
- 16. Logical Operators Boolean expressions can also use the following logical operators: ! Logical NOT && Logical AND || Logical OR They all take boolean operands and produce boolean results Logical NOT is a unary operator (it operates on one operand) Logical AND and logical OR are binary operators (each operates on two operands)
- 17. Logical NOT The logical NOT operation is also called logical negation or logical complement If some boolean condition a is true, then !a is false; if a is false, then !a is true Logical expressions can be shown using a truth table: a !a true false false true
- 18. Logical AND and Logical OR The logical AND expression a && b is true if both a and b are true, and false otherwise The logical OR expression a || b is true if a or b or both are true, and false otherwise
- 19. Logical AND and Logical OR A truth table shows all possible true-false combinations of the terms Since && and || each have two operands, there are four possible combinations of conditions a and b a b a && b a || b true true True true true false false true false true false true false false false false
- 20. Logical Operators Expressions that use logical operators can form complex conditions if (total < MAX+5 && !found) System.out.println ("Processing…"); All logical operators have lower precedence than the relational operators The ! operator has higher precedence than && and ||
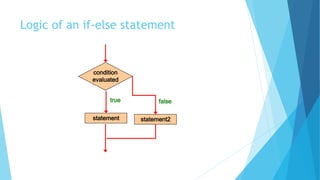
- 21. The if-else Statement An else clause can be added to an if statement to make an if-else statement if ( condition ) statement1; else statement2; If the condition is true, statement1 is executed; if the condition is false, statement2 is executed One or the other will be executed, but not both
- 23. Logic of an if-else statement condition evaluated false statement2 statement true
- 24. Nested if Statements The statement executed as a result of an if or else clause could be another if statement These are called nested if statements An else clause is matched to the last unmatched if (no matter what the indentation implies) Braces can be used to specify the if statement to which an else clause belongs See MinOfThree.java
- 28. Switch Case statement Switch case statement is used when we have number of options (or choices) and we may need to perform a different task for each choice. The syntax of Switch case statement looks like this
- 29. Switch Case statement: Example
- 30. Switch Case statement: Example
- 31. Switch Case Flow Diagram First the variable, value or expression which is provided in the switch parenthesis is evaluated and then based on the result, the corresponding case block is executed that matches the result.
- 33. Break statement in Switch Case Break statement is optional in switch case but you would use it almost every time you deal with switch case. Before we discuss about break statement, Let’s have a look at the example below where I am not using the break statement:
- 34. Break statement in Switch Case: Example
- 35. Break statement in Switch Case: Example
- 36. Break statement in Switch Case: Example In the above program, we have passed integer value 2 to the switch, so the control switched to the case 2 , revewoh ew nod ’ t have break statement after the case 2 that caused the flow to pass to the subsequent cases till the end . The solution to this problem is break statement Break statements are used when you want your program-flow to come out of the switch body. Whenever a break statement is encountered in the switch body, the execution flow would directly come out of the switch, ignoring rest of the cases Let’s take the same example but this time with break statement.


![Java User Input (Scanner)
import java.util.Scanner; // Import the Scanner class
class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object
System.out.println("Enter username");
String userName = myObj.nextLine(); // Read user input
System.out.println("Username is: " + userName); // Output user input } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation3-211028071537/85/Java-input-Scanner-3-320.jpg)
![Java User Input (Scanner)
import java.util.Scanner; // Import the Scanner class
class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object
System.out.println("Enter username");
String userName = myObj.nextLine(); // Read user input
System.out.println("Username is: " + userName); // Output user input } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation3-211028071537/85/Java-input-Scanner-4-320.jpg)







![//********************************************************************
// Age.java Author: Lewis/Loftus
//
// Demonstrates the use of an if statement.
//********************************************************************
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Age
{
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Reads the user's age and prints comments accordingly.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public static void main (String[] args)
{
final int MINOR = 21;
Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.print ("Enter your age: ");
int age = scan.nextInt();
continue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation3-211028071537/85/Java-input-Scanner-13-320.jpg)