java script functions, classes
- 1. Java Script Functions, Classes, Regular Expressions
- 2. Java Script Functions ● A function is a block of JavaScript code that is defined once but may be executed, or invoked, any number of times. ● Functions can have optional parameters and optional return value. ● In JavaScript, functions are objects, – they can be manipulated by programs, – set properties – invoke methods – assign to variables – pass them to other functions as parameters
- 3. Function invocation ● Function invocations provide arguments, for the function’s parameter, which are used to compute a return value that becomes the value of the function-invocation expression. ● Each function invocation has another value— the invocation context—that is the value of the this keyword
- 4. Function definition in statement form ● Functions are defined with function function_name(arguements) { statements;} ● Example: Function to Compute distance between points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2). function distance(x1, y1, x2, y2) { var dx = x2 – x1; var dy = y2 - y1; return Math.sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy); } ● A recursive function to compute factorial function factorial(x) { if (x <= 1) return 1; return x * factorial(x-1); }
- 5. Functions in expression form ● The function name is optional for functions defined as expressions, and is suitable for one-time usage. Example: – This expression defines a function that squares its argument, and the return value is assigned to a variable var square = function(x) { return x*x; } – Function expressions can also be used as arguments to other functions: data.sort(function(a,b) { return a-b; }); – Function expressions defined and immediately invoked: var tensquared = (function(x) {return x*x;}(10));
- 6. Return Values ● The return statement causes the function to stop executing and to return the value of its expression (if any) to the caller. ● If the return statement does not have an associated expression, it returns the undefined value. ● If a function does not contain a return statement, it simply executes each statement in the function body and returns the undefined value to the caller.
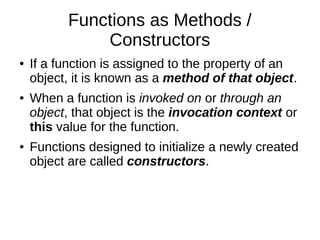
- 7. Functions as Methods / Constructors ● If a function is assigned to the property of an object, it is known as a method of that object. ● When a function is invoked on or through an object, that object is the invocation context or this value for the function. ● Functions designed to initialize a newly created object are called constructors.
- 8. Invoking Functions ● JavaScript functions can be invoked in four ways: – as functions, – as methods, – as constructors, and – indirectly through their call() and apply() methods.
- 9. Function Invocation ● Functions are invoked as functions or as methods with an invocation expression ● An invocation expression consists of a function expression that evaluates to a function object '(' comma-separated list of zero or more argument expressions ')' ● If the function is the property of an object or an element of an array—then it is a method invocation expression.
- 10. Function Invocation ● var total = distance(0,0,2,1) + distance(2,1,3,5); ● var probability = factorial(5)/factorial(13);
- 11. Method Invocation ● A method is a JavaScript function that is stored in a property of an object. ● A function f to act as a method m of an object o: o.m = f; – invoke it using: o.m(); – Or with arguements o.m(x, y); ● Method invocations differ from function invocations in the invocation context – Obejct o is the invocation context, which will be returned when using 'this' keyword in the method body
- 12. Method Invocation Example var calculator = { operand1: 1, operand2: 1, add: function() { // The this keyword refers to this object. this.result = this.operand1 + this.operand2; } }; calculator.add(); // A method invocation to compute 1+1. calculator.result // => 2
- 13. Method Invocation using [ ] ● Property access expressions that use square brackets cause method invocation. o["m"](x,y); // Another way to write o.m(x,y).
- 14. Constructor Invocation ● If a function or method invocation is preceded by the keyword new, then it is a constructor invocation. ● Constructor invocations differ from regular function and method invocations in their handling of arguments, invocation context, and return value.
- 15. Constructor Invocation ● We can always omit a pair of empty parentheses in a constructor invocation. Example both the following invocation works: – var obj = new Object(); – var obj = new Object; ● A constructor invocation creates a new, empty object that inherits from the prototype property of the constructor. ● Constructor functions are intended to initialize objects and this newly created object is used as the invocation context, so the constructor function can refer to it with the this keyword.
- 16. Constructor Invocation – Return Values ● Constructor functions do not normally use the return keyword, and the new object created is returned implicitly, which gets stored in constructor invocation expression (obj) ● Constructor explicitly used the return statement to return an object, then that object becomes the value of the invocation expression. ● If the constructor uses return with no value, or if it returns a primitive value, that return value is ignored and the new object is used as the value of the invocation.
- 17. Indirect Invocation ● Methods - call() and apply(), invoke the function indirectly. ● The first argument to both call() and apply() is the object on which the function is to be invoked; this argument is the invocation context and becomes the value of the this keyword within the body of the function. ● To invoke the function f() as a method of the object o (passing no arguments): – f.call(o); – f.apply(o); ● To invoke the function f() and pass 2 arguements (for apply() arguments are passed in arrays – suitable for variable length arguments) – f.call(o, 1, 2); – f.apply(o, [1,2]);
- 18. Nesting Functions ● JavaScript function definitions can be nested within other functions, and they have access to any variables that are in scope where they are defined, not the variable scope that is in effect when they are invoked. ● This combination of a function object and the scope (a set of variable bindings) in which it was defined is known as a closure
- 19. Nesting Functions ● Example, the inner function square() can read and write the parameters a and b defined by the outer function hypotenuse() function hypotenuse(a, b) { function square(x) { return x*x; } return Math.sqrt(square(a) + square(b)); }
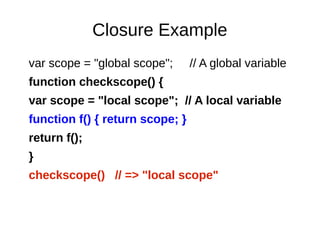
- 20. Closure Example var scope = "global scope"; // A global variable function checkscope() { var scope = "local scope"; // A local variable function f() { return scope; } return f(); } checkscope() // => "local scope"
- 21. Closure Example var scope = "global scope"; // A global variable function checkscope() { var scope = "local scope"; // A local variable function f() { return scope; } return f; } checkscope()() // return value?
- 22. Closure Example ● checkscope()() returns “local scope ● The nested function f() was defined under a scope chain in which the variable scope was bound to the value “local scope.” ● That binding is still in effect when f is executed, wherever it is executed from.
- 23. Function Object Properties, Methods, Constructors ● Function as an Object – The typeof operator returns the string “function” when applied to a function – call() and apply() are some methods of function objects – bind() - to bind a function to an object. – toString() - return the complete source code for the function, built in functions return – length Property – arity of function, no of parameters defined for the function return like “[native code]” as the function body – prototype property - refers to the prototype object of the function
- 24. Function Object Properties, Methods, Constructors – arguments.length - specifies the number of arguments that were passed to the function, when accessed within the function body – Function() constructor can also be used to create new function objects. var f = new Function("x", "y", "return x*y;"); ● Equivalent to var f = function(x, y) { return x*y; }
- 25. Classes ● Class of objects share certain properties. ● Members, or instances, of the class have their own properties to hold or define their state, but they also have properties (typically methods) that define their behavior, which is defined by the class and is shared by all instances. ● In JavaScript, classes are based on JavaScript’s prototype-based inheritance mechanism. ● If two objects inherit properties from the same prototype object, then we say that they are instances of the same class.
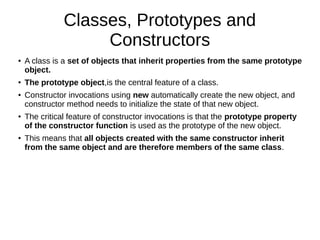
- 26. Classes, Prototypes and Constructors ● A class is a set of objects that inherit properties from the same prototype object. ● The prototype object,is the central feature of a class. ● Constructor invocations using new automatically create the new object, and constructor method needs to initialize the state of that new object. ● The critical feature of constructor invocations is that the prototype property of the constructor function is used as the prototype of the new object. ● This means that all objects created with the same constructor inherit from the same object and are therefore members of the same class.
- 27. Class Example ● // range2.js: Another class representing a range of values. ● // This is a constructor function that initializes new Range objects. Note that it does not create or return the object. It just initializes this. function Range(from, to) { // Store the start and end points (state) of this new range object. These are noninherited properties that are unique to this object. this.from = from; this.to = to; }
- 28. Class Example ● // All Range objects inherit from this object. Note that the property name must be "prototype". Range.prototype = { // Return true if x is in the range, false otherwise includes: function(x) { return this.from <= x && x <= this.to; }, // Invoke f once for each integer in the range. foreach: function(f) { for(var x=Math.ceil(this.from); x <= this.to; x++) f(x); }, // Return a string representation of the range toString: function() { return "(" + this.from + "..." + this.to + ")"; } };
- 29. Class Example ● //Example uses of a range object var r = new Range(1,3); // Create a range object ● r.includes(2); // => true: 2 is in the range
- 30. instanceOf Operator ● instanceof operator is used when testing objects for membership in a class ● // true if r inherits from Range.prototype ● r instanceof Range
- 31. Regular Expressions ● A regular expression is an object that describes a pattern of characters. ● The JavaScript RegExp class represents regular expressions.
- 32. Describing Patterns with Regular Expressions ● RegExp objects may be created with the RegExp() constructor using a special literal syntax (regular expression literals are specified as characters within a pair of slash (/) characters.) ● Example to create a pattern to match a string ending with s - var pattern = new RegExp("s$");
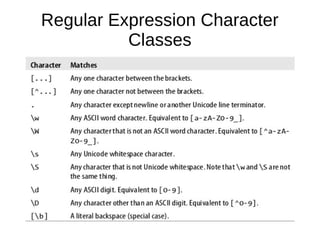
- 33. Character Classes ● Individual literal characters can be combined into character classes by placing them within square brackets. ● A character class matches any one character that is contained within it. Eg: the regular expression /[abc]/ matches any one of the letters a, b, or c
- 35. Repetition
- 36. Examples ● /d{2,4}/ - Between two and four digits ● /w{3}d?/ - Three word characters + optional digit ● /s+javas+/ - "java" with spaces before and after ● /[^(]*/ - zero or more chars that are not '('
- 37. Refer JavaScript Pocket Reference ● Apart from these topics please study : – Other Regular Expression techniques for pattern matching – Accessing the DOM elements through various methods .Eg: ● document.getElementById("id1");, ● document.getElementsByName("color"); ● document.getElementsByTagName("span"); ● document.getElementsByClassName("warning"); – Events, Cookies, Networking, Client Side Storage












![Method Invocation using [ ]
● Property access expressions that use square
brackets cause method invocation.
o["m"](x,y); // Another way to write o.m(x,y).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10javascriptfunctionsclasses-140716154314-phpapp01/85/java-script-functions-classes-13-320.jpg)



![Indirect Invocation
● Methods - call() and apply(), invoke the function indirectly.
● The first argument to both call() and apply() is the object on which the
function is to be invoked; this argument is the invocation context and
becomes the value of the this keyword within the body of the function.
● To invoke the function f() as a method of the object o (passing no
arguments):
– f.call(o);
– f.apply(o);
● To invoke the function f() and pass 2 arguements (for apply() arguments
are passed in arrays – suitable for variable length arguments)
– f.call(o, 1, 2);
– f.apply(o, [1,2]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10javascriptfunctionsclasses-140716154314-phpapp01/85/java-script-functions-classes-17-320.jpg)




![Function Object Properties,
Methods, Constructors
● Function as an Object
– The typeof operator returns the string “function” when
applied to a function
– call() and apply() are some methods of function objects
– bind() - to bind a function to an object.
– toString() - return the complete source code for the function,
built in functions return
– length Property – arity of function, no of parameters defined
for the function return like “[native code]” as the function body
– prototype property - refers to the prototype object of the
function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10javascriptfunctionsclasses-140716154314-phpapp01/85/java-script-functions-classes-23-320.jpg)








![Character Classes
● Individual literal characters can be combined
into character classes by placing them
within square brackets.
● A character class matches any one character
that is contained within it. Eg: the regular
expression /[abc]/ matches any one of the
letters a, b, or c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10javascriptfunctionsclasses-140716154314-phpapp01/85/java-script-functions-classes-33-320.jpg)

![Examples
● /d{2,4}/ - Between two and four digits
● /w{3}d?/ - Three word characters + optional
digit
● /s+javas+/ - "java" with spaces before and
after
● /[^(]*/ - zero or more chars that are not '('](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10javascriptfunctionsclasses-140716154314-phpapp01/85/java-script-functions-classes-36-320.jpg)
