java slides
- 1. Object Oriented Programming in JAVA
- 2. JAVA Basics
- 3. Why Java is Important • Two reasons : – Trouble with C/C++ language is that they are not portable and are not platform independent languages. – Emergence of World Wide Web, which demanded portable programs • Portability and security necessitated the invention of Java
- 4. History • James Gosling • Co founder – Vinod Khosla • JDK Evolutions – JDK 1.0 (January 23, 1996) – JDK 1.1 (February 19, 1997) – J2SE 1.2 (December 8, 1998) – J2SE 1.3 (May 8, 2000) – J2SE 1.4 (February 6, 2002) – J2SE 5.0 (September 30, 2004) – Java SE 6 (December 11, 2006) – Java SE 7 (July 28, 2011)
- 5. Cont.. • Java Editions. J2SE(Java 2 Standard Edition) - to develop client-side standalone applications or applets. J2ME(Java 2 Micro Edition ) - to develop applications for mobile devices such as cell phones. J2EE(Java 2 Enterprise Edition ) - to develop server-side applications such as Java serves and Java Server Pages.
- 6. What is java? • A general-purpose object-oriented language. • Write Once Run Anywhere (WORA). • Designed for easy Web/Internet applications.
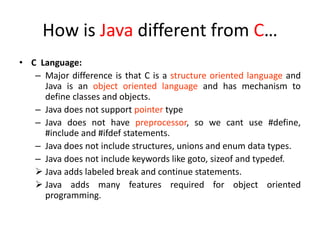
- 7. How is Java different from C… • C Language: – Major difference is that C is a structure oriented language and Java is an object oriented language and has mechanism to define classes and objects. – Java does not support pointer type – Java does not have preprocessor, so we cant use #define, #include and #ifdef statements. – Java does not include structures, unions and enum data types. – Java does not include keywords like goto, sizeof and typedef. Java adds labeled break and continue statements. Java adds many features required for object oriented programming.
- 8. How is Java different from C++… • C++ language Features removed in java: Java doesn’t support pointers to avoid unauthorized access of memory locations. Java does not include structures, unions and enum data types. Java does not support operator over loading. Preprocessor eliminated entirely in java.
- 9. Cont… Java does not support global variables. Every method and variable is declared within a class and forms part of that class. Java does not support inheritance of multiple super classes by a sub class (i.e., multiple inheritance). This is accomplished by using ‘interface’ concept. It is not possible to declare unsigned integers(Unsigned can hold a larger positive value, and no negative value. In java objects are passed by reference only. In C++ objects may be passed by value or reference.
- 10. Cont … New features added in Java: Multithreading, that allows two or more pieces of the same program to execute concurrently. C++ has a set of library functions that use a common header file. But java replaces it with its own set of API(Application Programming Interface) classes. It adds packages and interfaces. Java supports automatic garbage collection.
- 11. Cont … Features that differ: Though C++ and java supports Boolean data type, C++ takes any nonzero value as true and zero as false. True and false in java are predefined literals that are values for a boolean expression. Java has replaced the destructor function with a finalize() function. C++ supports exception handling that is similar to java's.
- 12. Characteristics of Java • Java is simple • Java is object-oriented • Java is robust • Java is secure • Java is architecture-neutral • Java is portable • Java’s performance • Java is multithreaded • Java platform Independent
- 13. • Simple According to Sun, Java language is simple because syntax is based on C++ (so easier for programmers to learn it after C++). It removed many confusing and/or rarely-used features e.g. operator overloading etc. • Object-oriented Object-oriented means we organize our software as a combination of different types of objects that incorporates both data and behavior. Object-oriented programming(OOPs) is a methodology that simplify software development and maintenance by providing some rules. • Platform Independent A platform is the hardware or software environment in which a program runs. There are two types of platforms software-based and hardware-based. Java provides software-based platform. The Java platform differs from most other platforms in the sense that it is a software- based platform that runs on the top of other hardware-based platforms. 8/30/2022 Object Oriented Programming using JAVA 13
- 14. • Secured Java is secured because: No pointer Java Programs run inside virtual machine sandbox • Robust Robust simply means strong. Java uses strong memory management. There are lack of pointers that avoids security problem. There is automatic garbage collection in java. There is exception handling and type checking mechanism in java. All these points makes java robust. 8/30/2022 Object Oriented Programming using JAVA 14
- 15. • Architecture-neutral In C programming, in data type occupies 2 bytes of memory for 32-bit architecture and 4 bytes of memory for 64-bit architecture. But in java, it occupies 4 bytes of memory for both 32 and 64 bit architectures. 8/30/2022 Object Oriented Programming using JAVA 15
- 16. • Portable We may carry the java bytecode to any platform. • High-performance Java is faster than traditional interpretation since byte code is "close" to native code still somewhat slower than a compiled language (e.g., C++) • Multi-threaded A thread is like a separate program, executing concurrently. We can write Java programs that deal with many tasks at once by defining multiple threads. The main advantage of multi-threading is that it doesn't occupy memory for each thread. It shares a common memory area. Threads are important for multi-media, Web applications etc. 8/30/2022 Object Oriented Programming using JAVA 16
- 17. Java Environment • Java includes many development tools, classes and methods – Development tools are part of Java Development Kit (JDK) and – The classes and methods are part of Java Standard Library (JSL), also known as Application Programming Interface (API). • JDK constitutes of tools like java compiler, java interpreter and many. • API includes hundreds of classes and methods grouped into several packages according to their functionality.
- 18. Example • File: HelloWorldApp.java public class HelloWorldApp{ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello world"); } }
- 19. Things to remember • Name of file must match name of class – It is case sensitive • Processing starts in main – public static void main(String[] args) • Printing is done with System.out – System.out.println, System.out.print
- 20. An idiom explained • You will see the following line of code often: – public static void main(String args[]) { …} • About main() – “main” is the function from which your program starts – Why public? • So that run time can call it from outside – Why static ? • it is made static so that we can call it without creating an object – What is String args[] ? • Way of specifying input at startup of application
- 21. Things to Remember • “+” operator when used with Strings concatenates them – System.out.pritln(“Hello” + “World”) will produce Hello World on console – String concatenated with any other data type such as int will also convert that datatype to String and the result will be a concatenated String displayed on console • For Example – int i = 4 – int j = 5 ; – System .out.println (“Hello” + i) // will print Hello 4 on screen • However – System,.out..println( i+j) ; // will print 9 on the console – For comparing Strings never use == operator, use equals methos. • E.g string1.equals(string2)
- 22. public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 4; int j = 5; System.out.println("Hello" + i); System.out.println(i + j); String s1 = new String (“pakistan”); String s2 = “pakistan”; if (s1 == s2) { System.out.println(“comparing string using == operator”); } if (s1.equals( s2) ) { System.out.println(“comparing string using equal method”); } } } String Concatenation
- 23. Primitives
- 24. Primitives • Primitive Data Types – 8 Primitive Data types of java • boolean, byte 1 byte • char, short 2 bytes • int, float 4 bytes • long, double 8 bytes • Primitive data types are generally used for local variables, parameters and instance variables (properties of an object)
- 25. Primitives (cont) • For all built-in primitive data types java uses lowercase. E.g. int , float etc. • Primitives can be stored in arrays • You cannot get a reference to a primitive
- 26. Input / Output
- 27. Java Inputting 8/30/2022 Object Oriented Programming using JAVA 27 There are various ways to read input from the keyboard, the java.util.Scanner class is one of them. The Java Scanner class breaks the input into tokens using a delimiter that is whitespace by default. It provides many methods to read and parse various primitive values. Java Scanner class is widely used to parse text for string
- 28. Console based Output System.out • System class – Out represents the screen • System.out.println() – Prints the string followed by an end of line • System.out.print() – Does not print the end of line
- 29. 8/30/2022 Object Oriented Programming using JAVA 29















![Example
• File: HelloWorldApp.java
public class HelloWorldApp{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect1java1-220830193958-22114396/85/java-slides-18-320.jpg)
![Things to remember
• Name of file must match name of class
– It is case sensitive
• Processing starts in main
– public static void main(String[] args)
• Printing is done with System.out
– System.out.println, System.out.print](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect1java1-220830193958-22114396/85/java-slides-19-320.jpg)
![An idiom explained
• You will see the following line of code often:
– public static void main(String args[]) { …}
• About main()
– “main” is the function from which your program starts
– Why public?
• So that run time can call it from outside
– Why static ?
• it is made static so that we can call it without creating an object
– What is String args[] ?
• Way of specifying input at startup of application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect1java1-220830193958-22114396/85/java-slides-20-320.jpg)

![public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 4;
int j = 5;
System.out.println("Hello" + i);
System.out.println(i + j);
String s1 = new String (“pakistan”);
String s2 = “pakistan”;
if (s1 == s2) {
System.out.println(“comparing string using == operator”);
}
if (s1.equals( s2) ) {
System.out.println(“comparing string using equal method”);
}
}
}
String Concatenation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect1java1-220830193958-22114396/85/java-slides-22-320.jpg)