Jdk 7 4-forkjoin
Download as PPTX, PDF5 likes1,177 views
This document discusses Fork/Join framework in Java 7. It explains that Fork/Join is designed to maximize usage of multiple processors by recursively splitting large tasks into smaller subtasks. It uses work-stealing algorithm where idle workers can steal tasks from busy workers' queues to balance load. An example of calculating Fibonacci numbers using Fork/Join is provided where the task is split recursively until the subproblem size is smaller than threshold, at which point it is computed directly.
1 of 27
Download to read offline












![Main14public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("Number of processors: " + Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());intn = 7;StopWatchstopWatch = new StopWatch(); FibonacciProblembigProblem = new FibonacciProblem(n);FibonacciTasktask = new FibonacciTask(bigProblem);ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();pool.invoke(task);long result = task.result;System.out.println("Computed Result: " + result);stopWatch.stop();System.out.println("Elapsed Time: " + stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis());System.out.println("Steal Count : " + pool.getStealCount());}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdk7-4-forkjoin-110729035045-phpapp02/85/Jdk-7-4-forkjoin-14-320.jpg)










![Phaser예제25public static void main(String[] args) {runDevelopment(Arrays.asList(new Developer(), new Developer(), new Developer(), new Developer()));}private static void runDevelopment(Iterable<Developer> team) { final Phasermanager = new Phaser(1); //"1" to register selfSystem.out.println("mgr: assign all developers, then start coding"); for (final Developer developer : team) { final String dev = developer.toString();System.out.println("mgr: assigns a new unarrived " + dev + " to the project");manager.register(); new Thread() { public void run() {System.out.println("mgr: " + dev + ", please await all developers");manager.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); // await all creationSystem.out.println("mgr: " + dev + ", OK to start coding");developer.run();} }.start();}System.out.println("mgr: all assigned, start coding after all arrive");manager.arriveAndDeregister();}class Developer implements Runnable { private final static AtomicIntegeridSource = new AtomicInteger(); private final int id = idSource.incrementAndGet(); public void run() { System.out.println(toString() + ": coding"); } public String toString() { return "developer #" + id; }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdk7-4-forkjoin-110729035045-phpapp02/85/Jdk-7-4-forkjoin-25-320.jpg)


Ad
Recommended
Jersey framework



Jersey frameworkknight1128 The document summarizes Jersey Framework, a Java REST framework. It provides an overview of Jersey's features such as supporting JAX-RS APIs, Servlet 3.0, JSON/JAXB, and integration with Spring. A code sample demonstrates a simple "hello world" RESTful service using Jersey with annotations like @Path, @GET and @Produces. The document also covers additional Jersey concepts like request/response processing, URI building, exception handling, and security.
Jdk(java) 7 - 6 기타기능



Jdk(java) 7 - 6 기타기능knight1128 This document summarizes new features in JDK 7 including updates to XML stack, JDBC, RowSet, class loading, JVM performance improvements, garbage collection, I/O, graphics APIs, collections, and strict class file checking. It also previews planned features for JDK 8 such as support for modular programming, annotations, collections improvements, lambda expressions, and modularization.
Project Coin



Project CoinBalamurugan Soundararajan The document summarizes the key new features introduced in each version of Java from JDK 1.0 to Java SE 8. Some major enhancements included strings in switch statements in Java 7, binary and underscore literals, multi-catch exceptions, try-with-resources for automatic resource management, and lambda expressions in Java 8.
NIO and NIO2



NIO and NIO2Balamurugan Soundararajan This document provides an overview of new features in NIO 2 and asynchronous I/O in Java. It discusses buffers, channels, selectors, file system APIs, file change notification, and asynchronous operations using futures and completion handlers. The key aspects covered include non-blocking I/O, readiness selection, file locking, memory mapping, and file attributes.
Bytecode manipulation with Javassist and ASM



Bytecode manipulation with Javassist and ASMashleypuls The document discusses a presentation titled "Living in the Matrix with Bytecode Manipulation". It provides an overview of bytecode and frameworks for manipulating bytecode. Specifically, it discusses what bytecode is, reasons for manipulating bytecode, frameworks for doing so, and examines logging as an example use case. The presentation outlines how to add logging to methods by annotating them and transforming the bytecode at runtime using a Java agent.
Voxxed Days Vilnius 2015 - Having fun with Javassist



Voxxed Days Vilnius 2015 - Having fun with JavassistAnton Arhipov The document discusses using Javassist, a Java bytecode engineering library, to dynamically generate Java proxies at runtime. It provides examples of using Javassist with a Java agent to transform class files and generate proxies within a ClassFileTransformer. It also summarizes how Javassist is used within the JRebel application reload agent to refresh configurations and notify plugins of class reloading.
Software Testing - Invited Lecture at UNSW Sydney



Software Testing - Invited Lecture at UNSW Sydneyjulien.ponge This document provides an overview of software testing concepts and the JUnit testing framework. It discusses the importance of testing, different types of testing, unit testing with JUnit, best practices for writing tests, integrating tests into builds with Ant and Maven, and logging. Examples of JUnit tests are also provided. The key points covered are:
- Why testing is important to find bugs, prevent regressions, and allow for refactoring
- Unit testing, functional testing, and other types of testing
- How to write automated unit tests with JUnit
- Best practices like testing edge cases, achieving good code coverage
- Integrating tests into builds with Ant and Maven
- Using logging frameworks like Log
Java and OpenJDK: disecting the ecosystem



Java and OpenJDK: disecting the ecosystemRafael Winterhalter With its ninth version, the Java platform has shifted gear and introduced biyearly releases. This was followed by a license change where Oracle, the steward of Java, now publishes a commercial and a non-commercial release of the Java virtual machine while other vendors took more space to promote their alternative builds of the OpenJDK. And in another flood of news, the Java EE specification was terminated and resolved into the Jakarta EE namespace.
A lot has been happening in the traditionally conservative Java ecosystem, to say the least, and many users are wondering if they still can rely on the platform. This talk gives an overview of the Java ecosystem, summarizes the changes that have been, that to expect and why the evolution of the platform is good news to the community.
Java 10, Java 11 and beyond



Java 10, Java 11 and beyondRafael Winterhalter A lookout on the upcoming Java releases, on breaking functionality and projects that will come after the current schedule.
Riga Dev Day 2016 - Having fun with Javassist



Riga Dev Day 2016 - Having fun with JavassistAnton Arhipov The document discusses using Javassist, an open-source bytecode engineering library, for bytecode instrumentation and generation of Java proxies. It provides examples of using Javassist's ClassPool and CtClass APIs to dynamically generate and modify classes, such as adding a print statement before a method or generating a class from metadata. The key uses of Javassist mentioned are generating proxies, bytecode instrumentation, and dynamic class generation.
GeeCON 2017 - TestContainers. Integration testing without the hassle



GeeCON 2017 - TestContainers. Integration testing without the hassleAnton Arhipov TestContainers is a Java library that supports JUnit tests, providing lightweight, throwaway instances of common databases, Selenium web browsers, or anything else that can run in a Docker container.
Java 7 LavaJUG



Java 7 LavaJUGjulien.ponge This document summarizes new features and enhancements in Java 7 including Project Coin, NIO.2, invokedynamic, Fork/Join framework, and concurrency utilities. It discusses how these features make threads, parallelism, and concurrency easier to work with in Java. Code examples are provided to illustrate the use of ForkJoinPool, Callable, and try-with-resources statements.
Java 7 Launch Event at LyonJUG, Lyon France. Fork / Join framework and Projec...



Java 7 Launch Event at LyonJUG, Lyon France. Fork / Join framework and Projec...julien.ponge The document discusses new features in Java SE 7 including the Fork/Join framework for parallel programming, language evolutions through Project Coin such as try-with-resources statements, and diamond syntax for generic types which simplifies generic class instance creation. It also covers varargs syntax simplification and restrictions on using diamond syntax with anonymous inner classes.
JVM



JVMMurali Pachiyappan The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is an abstract computing machine that executes Java bytecode. It has several core components including a class loader, memory areas like the heap and stack, and an execution engine. The execution engine initially interprets bytecode instructions but can optimize performance by just-in-time compiling frequently used bytecode into native machine code. The JVM provides a layer of abstraction between Java applications and the underlying hardware or operating system.
Java Concurrency by Example



Java Concurrency by ExampleGanesh Samarthyam The document discusses various Java concurrency concepts including threads, locks, semaphores, and concurrent collections. It provides examples to illustrate thread synchronization issues like race conditions and deadlocks. It also demonstrates how to use various concurrency utilities from java.util.concurrent package like CountDownLatch, Exchanger, PriorityBlockingQueue to synchronize thread execution and communication between threads. The examples show how to simulate real world scenarios involving multiple threads accessing shared resources in a synchronized manner.
Java Bytecode for Discriminating Developers - JavaZone 2011



Java Bytecode for Discriminating Developers - JavaZone 2011Anton Arhipov The document discusses Java bytecode and provides examples of decompiling a simple "Hello World" Java program to bytecode using the javap tool. It summarizes the structure of bytecode, including one-byte instructions, opcode taxonomy involving stack manipulation, flow control, and object models. The document demonstrates how javap can be used to disassemble a class file into bytecode instructions and interpret the constant pool references.
A topology of memory leaks on the JVM



A topology of memory leaks on the JVMRafael Winterhalter While most bugs reveal their cause within their stack trace, Java’s OutOfMemoryError is less talkative and therefore regarded as being difficult to debug by a majority of developers. With the right techniques and tools, memory leaks in Java programs can however be tackled like any other programming error. This talks discusses how a JVM stores data, categorizes different types of memory leaks that can occur in a Java program and presents techniques for fixing such errors. Furthermore, we will have a closer look at lambda expressions and their considerable potential of introducing memory leaks when they are used incautiously.
201913046 wahyu septiansyah network programing



201913046 wahyu septiansyah network programingwahyuseptiansyah The document describes a network programming report on a Java chat application. It includes the code for a Server class that implements a threaded server to handle multiple client connections simultaneously. The server opens a port to listen for clients and spins up a new thread for each accepted connection. It then reads and writes data between the server and client over buffered input/output streams. The report notes issues with messages from one client not being visible to others and connection errors that can occur between the client and server.
Oredev 2015 - Taming Java Agents



Oredev 2015 - Taming Java AgentsAnton Arhipov Java agents are pluggable self contained components that run embedded in a JVM and intercept the classloading process. They were introduced in Java 5 along with the powerful java.lang.instrument package. Java agents can be loaded statically at startup or dynamically (programmatically) at runtime to attach to a running process.
Java agents were an awesome addition to the JVM as it opened a lot of opportunities for tool designers and changed Java tooling landscape quite drastically. In conjunction with Java bytecode manipulation libraries it is now possible to do amazing things to Java classes: we can experiment with programming models, redefine classes at runtime, record execution flow, etc.
I’d like to give an overview of Java agents’ functionality along with the usage examples and real world experiences. You will learn, how to implement an agent and apply Instrumentation API in combination with bytecode manipulation libraries to solve interesting tasks.
Server1



Server1FahriIrawan3 The document describes a Java program that implements a chat server and client. It includes classes for the server and client frames, with methods for network connections and message handling. The server is capable of accepting multiple simultaneous client connections and running them in separate threads. Methods are provided for tasks like initializing GUI components, sending and receiving messages, and disconnecting clients.
Jenkins 2を使った究極のpipeline ~ 明日もう一度来てください、本物のpipelineをお見せしますよ ~



Jenkins 2を使った究極のpipeline ~ 明日もう一度来てください、本物のpipelineをお見せしますよ ~ikikko This document contains code for a Jenkins pipeline that defines stages for compiling, testing, packaging, deploying, and smoke testing a build. It also contains code to send notifications to Typetalk if the build fails. Additional code shows how to fetch pull request branches from a Git remote and check if a pull request is open for a given branch.
15 tips to improve your unit tests (Droidcon Berlin 2016 Barcamp)



15 tips to improve your unit tests (Droidcon Berlin 2016 Barcamp)Danny Preussler 1. The document provides 15 tips for improving unit tests, focusing on readability, consistent naming conventions, using matchers over basic asserts, moving setup code out of test methods, adding matchers for custom models, using null objects to reduce test garbage, and writing tests that fail to ensure quality code.
2. Key tips include giving tests readable names, reducing noise in tests, implementing equals on test models, using reflection code fluently, and inverting control for testability even if it breaks encapsulation.
3. The document emphasizes that tests should prioritize readability and maintainability over strict adherence to "unit" sizes, and that if all tests pass without failing, better tests need to be written to
Down to Stack Traces, up from Heap Dumps



Down to Stack Traces, up from Heap DumpsAndrei Pangin Глубже стек-трейсов, шире хип-дампов
Stack trace и heap dump - не просто инструменты отладки; это потайные дверцы к самым недрам виртуальной Java машины. Доклад будет посвящён малоизвестным особенностям JDK, так или иначе связанным с обоходом хипа и стеками потоков.
Мы разберём:
- как снимать дампы в продакшне без побочных эффектов;
- как работают утилиты jmap и jstack изнутри, и в чём хитрость forced режима;
- почему все профилировщики врут, и как с этим бороться;
- познакомимся с новым Stack-Walking API в Java 9;
- научимся сканировать Heap средствами JVMTI;
- узнаем о недокументированных функциях Хотспота и других интересных штуках.
모던자바의 역습



모던자바의 역습DoHyun Jung 어느덧 스무살이 된 자바. 좋든싫든 프로그래밍의 세계에 몸담고 있는 이상 부딪히지 않을 수 없는 언어인데요, 이 자바에 대한 올바른 모습의 이해화 앞으로 나아가야 할 방향을 모색해본다는 의미에서 "모던 자바의 역습"이라는 타이틀로 실시한 온라인 세미나의 슬라이드 자료입니다.
진행자: 김대우(http://lekdw.blogspot.kr/)
정도현(http://moreagile.net)
이번 세미나는 게임개발자이신 김대우님을 모시고 진행하게 되었는데요 자바 언어와 관련 하여 다음과 같은 주제로 두시간에 걸쳐 발표를 진행합니다.
- 간단히 살펴보는 자바20년의 발자취
- 자바를 둘러싼 진실 혹은 거짓(성능,생산성,품질)
- SI영역 이외에서 자바의 가치
- 모던자바의 역습: 자바8과 함수형 프로그래밍
- 자바 개발의 새로운 패러다임들
Java Bytecode For Discriminating Developers - GeeCON 2011



Java Bytecode For Discriminating Developers - GeeCON 2011Anton Arhipov The document discusses Java bytecode and how it is used to represent compiled Java code. It provides an overview of bytecode basics like the bytecode instruction set and taxonomy. It then gives examples of decompiling simple "Hello World" Java code and analyzing the resulting bytecode instructions. Key details like the stack-based execution model and how frames are used are also outlined.
Monitoring distributed (micro-)services



Monitoring distributed (micro-)servicesRafael Winterhalter micro(-service) components. While this approach to building software - if done correctly - can improve a system's maintainability and scalability, distributed applications also introduce challanges for operations. Where monolithic applications typically offered direct access to extensive monitoring dashbords, such easy overview is no longer available when multitude services are loosly connected over a network. But how to keep track of a system of such dynamic state?
Distributed tracing is a method of connecting interaction of different services on a network. Collecting and processing such tracing information again allows for the observation of a distributed system in its entirety. This talk shares the presenter's insights gained by working on the JVM-support of distributed tracing for the APM tool Instana. Doing so, it introduces the landscape of distributed tracing on the JVM, discussing popular approaches such as Dapper, Zipkin or Brave/OpenTracing. In the process, it is discussed how byte code instrumentation can be used to capture systems without requiring a user to set up the software under observation. The presentation finishes with a discussion of typical problems of distributed tracing solutions and carefully examines the performance penalties APM tools entail.
JEEConf 2017 - The hitchhiker’s guide to Java class reloading



JEEConf 2017 - The hitchhiker’s guide to Java class reloadingAnton Arhipov In Java, a typical workflow involves restarting the application (almost) with every class change. For some applications it is not a problem at all, for some – it is a disaster.
From HotSwap to agent-based reloading. In this session, we are going to take a look at the options available for Java class reloading. There is plenty of tools that you can use for this task: rely on standard JVM HotSwap, redesign your application to rely on dynamic class loaders, to comprehend the Zen of OSGi, or to integrate a reloading agent. Every option has its own drawbacks and benefits and we’re going to take a deep dive on the subject.
Finally, there are also the conceptual challenges in reloading Java classes. What to do with the state? What should happen with the static initialisers? What if super class changes? Join this session to gain a better understanding of class reloading technologies and become more productive Java developer.
Con-FESS 2015 - Having Fun With Javassist



Con-FESS 2015 - Having Fun With JavassistAnton Arhipov This document discusses using Javassist, a bytecode manipulation library, for tasks like adding logging to existing code without modifying the source code. It provides examples of using Javassist to inject logging into a method and creating a Java agent to manipulate bytecode. The document also summarizes how Javassist works under the hood to modify class files and how frameworks like JRebel use it to reload configurations without restarts.
Java 8 Stream API. A different way to process collections.



Java 8 Stream API. A different way to process collections.David Gómez García A look on one of the features of Java 8 hidden behind the lambdas. A different way to iterate Collections. You'll never see the Collecions the same way.
These are the slides I used on my talk at the "Tech Thursday" by Oracle in June in Madrid.
JavaOne 2016 - Learn Lambda and functional programming



JavaOne 2016 - Learn Lambda and functional programmingHenri Tremblay This tutorial walks through tons of examples. You will learn everything you need to know about lambdas and functional programming in Java 8. I'm the supplier. You’re the consumer (and you will get the joke after the session).
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Java 10, Java 11 and beyond



Java 10, Java 11 and beyondRafael Winterhalter A lookout on the upcoming Java releases, on breaking functionality and projects that will come after the current schedule.
Riga Dev Day 2016 - Having fun with Javassist



Riga Dev Day 2016 - Having fun with JavassistAnton Arhipov The document discusses using Javassist, an open-source bytecode engineering library, for bytecode instrumentation and generation of Java proxies. It provides examples of using Javassist's ClassPool and CtClass APIs to dynamically generate and modify classes, such as adding a print statement before a method or generating a class from metadata. The key uses of Javassist mentioned are generating proxies, bytecode instrumentation, and dynamic class generation.
GeeCON 2017 - TestContainers. Integration testing without the hassle



GeeCON 2017 - TestContainers. Integration testing without the hassleAnton Arhipov TestContainers is a Java library that supports JUnit tests, providing lightweight, throwaway instances of common databases, Selenium web browsers, or anything else that can run in a Docker container.
Java 7 LavaJUG



Java 7 LavaJUGjulien.ponge This document summarizes new features and enhancements in Java 7 including Project Coin, NIO.2, invokedynamic, Fork/Join framework, and concurrency utilities. It discusses how these features make threads, parallelism, and concurrency easier to work with in Java. Code examples are provided to illustrate the use of ForkJoinPool, Callable, and try-with-resources statements.
Java 7 Launch Event at LyonJUG, Lyon France. Fork / Join framework and Projec...



Java 7 Launch Event at LyonJUG, Lyon France. Fork / Join framework and Projec...julien.ponge The document discusses new features in Java SE 7 including the Fork/Join framework for parallel programming, language evolutions through Project Coin such as try-with-resources statements, and diamond syntax for generic types which simplifies generic class instance creation. It also covers varargs syntax simplification and restrictions on using diamond syntax with anonymous inner classes.
JVM



JVMMurali Pachiyappan The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is an abstract computing machine that executes Java bytecode. It has several core components including a class loader, memory areas like the heap and stack, and an execution engine. The execution engine initially interprets bytecode instructions but can optimize performance by just-in-time compiling frequently used bytecode into native machine code. The JVM provides a layer of abstraction between Java applications and the underlying hardware or operating system.
Java Concurrency by Example



Java Concurrency by ExampleGanesh Samarthyam The document discusses various Java concurrency concepts including threads, locks, semaphores, and concurrent collections. It provides examples to illustrate thread synchronization issues like race conditions and deadlocks. It also demonstrates how to use various concurrency utilities from java.util.concurrent package like CountDownLatch, Exchanger, PriorityBlockingQueue to synchronize thread execution and communication between threads. The examples show how to simulate real world scenarios involving multiple threads accessing shared resources in a synchronized manner.
Java Bytecode for Discriminating Developers - JavaZone 2011



Java Bytecode for Discriminating Developers - JavaZone 2011Anton Arhipov The document discusses Java bytecode and provides examples of decompiling a simple "Hello World" Java program to bytecode using the javap tool. It summarizes the structure of bytecode, including one-byte instructions, opcode taxonomy involving stack manipulation, flow control, and object models. The document demonstrates how javap can be used to disassemble a class file into bytecode instructions and interpret the constant pool references.
A topology of memory leaks on the JVM



A topology of memory leaks on the JVMRafael Winterhalter While most bugs reveal their cause within their stack trace, Java’s OutOfMemoryError is less talkative and therefore regarded as being difficult to debug by a majority of developers. With the right techniques and tools, memory leaks in Java programs can however be tackled like any other programming error. This talks discusses how a JVM stores data, categorizes different types of memory leaks that can occur in a Java program and presents techniques for fixing such errors. Furthermore, we will have a closer look at lambda expressions and their considerable potential of introducing memory leaks when they are used incautiously.
201913046 wahyu septiansyah network programing



201913046 wahyu septiansyah network programingwahyuseptiansyah The document describes a network programming report on a Java chat application. It includes the code for a Server class that implements a threaded server to handle multiple client connections simultaneously. The server opens a port to listen for clients and spins up a new thread for each accepted connection. It then reads and writes data between the server and client over buffered input/output streams. The report notes issues with messages from one client not being visible to others and connection errors that can occur between the client and server.
Oredev 2015 - Taming Java Agents



Oredev 2015 - Taming Java AgentsAnton Arhipov Java agents are pluggable self contained components that run embedded in a JVM and intercept the classloading process. They were introduced in Java 5 along with the powerful java.lang.instrument package. Java agents can be loaded statically at startup or dynamically (programmatically) at runtime to attach to a running process.
Java agents were an awesome addition to the JVM as it opened a lot of opportunities for tool designers and changed Java tooling landscape quite drastically. In conjunction with Java bytecode manipulation libraries it is now possible to do amazing things to Java classes: we can experiment with programming models, redefine classes at runtime, record execution flow, etc.
I’d like to give an overview of Java agents’ functionality along with the usage examples and real world experiences. You will learn, how to implement an agent and apply Instrumentation API in combination with bytecode manipulation libraries to solve interesting tasks.
Server1



Server1FahriIrawan3 The document describes a Java program that implements a chat server and client. It includes classes for the server and client frames, with methods for network connections and message handling. The server is capable of accepting multiple simultaneous client connections and running them in separate threads. Methods are provided for tasks like initializing GUI components, sending and receiving messages, and disconnecting clients.
Jenkins 2を使った究極のpipeline ~ 明日もう一度来てください、本物のpipelineをお見せしますよ ~



Jenkins 2を使った究極のpipeline ~ 明日もう一度来てください、本物のpipelineをお見せしますよ ~ikikko This document contains code for a Jenkins pipeline that defines stages for compiling, testing, packaging, deploying, and smoke testing a build. It also contains code to send notifications to Typetalk if the build fails. Additional code shows how to fetch pull request branches from a Git remote and check if a pull request is open for a given branch.
15 tips to improve your unit tests (Droidcon Berlin 2016 Barcamp)



15 tips to improve your unit tests (Droidcon Berlin 2016 Barcamp)Danny Preussler 1. The document provides 15 tips for improving unit tests, focusing on readability, consistent naming conventions, using matchers over basic asserts, moving setup code out of test methods, adding matchers for custom models, using null objects to reduce test garbage, and writing tests that fail to ensure quality code.
2. Key tips include giving tests readable names, reducing noise in tests, implementing equals on test models, using reflection code fluently, and inverting control for testability even if it breaks encapsulation.
3. The document emphasizes that tests should prioritize readability and maintainability over strict adherence to "unit" sizes, and that if all tests pass without failing, better tests need to be written to
Down to Stack Traces, up from Heap Dumps



Down to Stack Traces, up from Heap DumpsAndrei Pangin Глубже стек-трейсов, шире хип-дампов
Stack trace и heap dump - не просто инструменты отладки; это потайные дверцы к самым недрам виртуальной Java машины. Доклад будет посвящён малоизвестным особенностям JDK, так или иначе связанным с обоходом хипа и стеками потоков.
Мы разберём:
- как снимать дампы в продакшне без побочных эффектов;
- как работают утилиты jmap и jstack изнутри, и в чём хитрость forced режима;
- почему все профилировщики врут, и как с этим бороться;
- познакомимся с новым Stack-Walking API в Java 9;
- научимся сканировать Heap средствами JVMTI;
- узнаем о недокументированных функциях Хотспота и других интересных штуках.
모던자바의 역습



모던자바의 역습DoHyun Jung 어느덧 스무살이 된 자바. 좋든싫든 프로그래밍의 세계에 몸담고 있는 이상 부딪히지 않을 수 없는 언어인데요, 이 자바에 대한 올바른 모습의 이해화 앞으로 나아가야 할 방향을 모색해본다는 의미에서 "모던 자바의 역습"이라는 타이틀로 실시한 온라인 세미나의 슬라이드 자료입니다.
진행자: 김대우(http://lekdw.blogspot.kr/)
정도현(http://moreagile.net)
이번 세미나는 게임개발자이신 김대우님을 모시고 진행하게 되었는데요 자바 언어와 관련 하여 다음과 같은 주제로 두시간에 걸쳐 발표를 진행합니다.
- 간단히 살펴보는 자바20년의 발자취
- 자바를 둘러싼 진실 혹은 거짓(성능,생산성,품질)
- SI영역 이외에서 자바의 가치
- 모던자바의 역습: 자바8과 함수형 프로그래밍
- 자바 개발의 새로운 패러다임들
Java Bytecode For Discriminating Developers - GeeCON 2011



Java Bytecode For Discriminating Developers - GeeCON 2011Anton Arhipov The document discusses Java bytecode and how it is used to represent compiled Java code. It provides an overview of bytecode basics like the bytecode instruction set and taxonomy. It then gives examples of decompiling simple "Hello World" Java code and analyzing the resulting bytecode instructions. Key details like the stack-based execution model and how frames are used are also outlined.
Monitoring distributed (micro-)services



Monitoring distributed (micro-)servicesRafael Winterhalter micro(-service) components. While this approach to building software - if done correctly - can improve a system's maintainability and scalability, distributed applications also introduce challanges for operations. Where monolithic applications typically offered direct access to extensive monitoring dashbords, such easy overview is no longer available when multitude services are loosly connected over a network. But how to keep track of a system of such dynamic state?
Distributed tracing is a method of connecting interaction of different services on a network. Collecting and processing such tracing information again allows for the observation of a distributed system in its entirety. This talk shares the presenter's insights gained by working on the JVM-support of distributed tracing for the APM tool Instana. Doing so, it introduces the landscape of distributed tracing on the JVM, discussing popular approaches such as Dapper, Zipkin or Brave/OpenTracing. In the process, it is discussed how byte code instrumentation can be used to capture systems without requiring a user to set up the software under observation. The presentation finishes with a discussion of typical problems of distributed tracing solutions and carefully examines the performance penalties APM tools entail.
JEEConf 2017 - The hitchhiker’s guide to Java class reloading



JEEConf 2017 - The hitchhiker’s guide to Java class reloadingAnton Arhipov In Java, a typical workflow involves restarting the application (almost) with every class change. For some applications it is not a problem at all, for some – it is a disaster.
From HotSwap to agent-based reloading. In this session, we are going to take a look at the options available for Java class reloading. There is plenty of tools that you can use for this task: rely on standard JVM HotSwap, redesign your application to rely on dynamic class loaders, to comprehend the Zen of OSGi, or to integrate a reloading agent. Every option has its own drawbacks and benefits and we’re going to take a deep dive on the subject.
Finally, there are also the conceptual challenges in reloading Java classes. What to do with the state? What should happen with the static initialisers? What if super class changes? Join this session to gain a better understanding of class reloading technologies and become more productive Java developer.
Con-FESS 2015 - Having Fun With Javassist



Con-FESS 2015 - Having Fun With JavassistAnton Arhipov This document discusses using Javassist, a bytecode manipulation library, for tasks like adding logging to existing code without modifying the source code. It provides examples of using Javassist to inject logging into a method and creating a Java agent to manipulate bytecode. The document also summarizes how Javassist works under the hood to modify class files and how frameworks like JRebel use it to reload configurations without restarts.
Viewers also liked (14)
Java 8 Stream API. A different way to process collections.



Java 8 Stream API. A different way to process collections.David Gómez García A look on one of the features of Java 8 hidden behind the lambdas. A different way to iterate Collections. You'll never see the Collecions the same way.
These are the slides I used on my talk at the "Tech Thursday" by Oracle in June in Madrid.
JavaOne 2016 - Learn Lambda and functional programming



JavaOne 2016 - Learn Lambda and functional programmingHenri Tremblay This tutorial walks through tons of examples. You will learn everything you need to know about lambdas and functional programming in Java 8. I'm the supplier. You’re the consumer (and you will get the joke after the session).
Spring MVC 3 Restful



Spring MVC 3 Restfulknight1128 Spring 3 MVC can be used to build RESTful web services. It supports annotations like @Controller, @RequestMapping and @PathVariable to map HTTP requests to controller methods. Requests and responses can be in various formats like JSON, XML, RSS using ContentNegotiatingViewResolver. Custom converters can be used to convert request parameters to Java objects. Exceptions can be handled using @ExceptionHandler.
Apache Thrift



Apache Thriftknight1128 Thrift is a software framework that allows for efficient cross-language communication. It provides features such as RPC, code generation, and serialization to make it easy to define and develop services that can be used across multiple languages. Supported languages include C++, Java, Python, PHP and more. Thrift handles low-level details like data serialization while providing an interface definition language to define services and data structures.
Ad
Similar to Jdk 7 4-forkjoin (20)
JVM Mechanics: When Does the JVM JIT & Deoptimize?



JVM Mechanics: When Does the JVM JIT & Deoptimize?Doug Hawkins HotSpot promises to do the "right" thing for us by identifying our hot code and compiling "just-in-time", but how does HotSpot make those decisions?
This presentation aims to detail how HotSpot makes those decisions and how it corrects its mistakes through a series of demos that you run yourself.
Parallel Programming With Dot Net



Parallel Programming With Dot NetNeeraj Kaushik The document discusses parallel programming in .NET. It covers two main strategies for parallelism - data parallelism and task parallelism. For data parallelism, it describes using Parallel.For to partition work over collections. For task parallelism, it discusses using the Task Parallel Library to create and run independent tasks concurrently, allowing work to be distributed across multiple processors. It provides examples of creating tasks implicitly with Parallel.Invoke and explicitly by instantiating Task objects and passing delegates.
Silicon Valley JUG: JVM Mechanics



Silicon Valley JUG: JVM MechanicsAzul Systems, Inc. The JVM JIT compiler and deoptimizer are triggered under certain conditions like method invocation counts, changes in program behavior, and hot spots. The JIT initially compiles code to generate fast machine instructions while the deoptimizer reverts back to interpreted execution if needed.
Java Concurrency



Java ConcurrencyCarol McDonald Carol McDonald gave a presentation on Java concurrency utilities introduced in J2SE 5.0. She discussed motivation for improved concurrency tools, common concurrency issues, and key utilities like Executor framework, locks, synchronizers, and concurrent collections. The utilities make concurrent programming easier and improve performance of multithreaded Java applications.
RxJava on Android



RxJava on AndroidDustin Graham An exploration into RxJava on Android for the experienced, yet uninitiated software engineer. This presentation explores Declarative vs Imperative programming paradigms and expands the discussion into Functional Reactive Programming. It explains the benefits of the observer contract, high-order functions, and schedulers available in RxJava. It also explains the purpose of the Android integration libraries: RxAndroid, RxLifecycle, and RxBindings.
Global Interpreter Lock: Episode I - Break the Seal



Global Interpreter Lock: Episode I - Break the SealTzung-Bi Shih PyCon APAC 2015 discusses the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) in CPython and ways to work around it to achieve higher performance on multi-processor systems. It provides examples of using multiprocessing, pp (Parallel Python), and releasing the GIL using C extensions to allow concurrent execution across multiple CPU cores. Releasing the GIL allows taking advantage of additional CPUs for processor-intensive tasks, while multiprocessing and pp allow running I/O-bound tasks in parallel across multiple processes to improve throughput.
Java util concurrent



Java util concurrentRoger Xia This document discusses concurrency and concurrent programming in Java. It introduces the built-in concurrency primitives like wait(), notify(), synchronized, and volatile. It then discusses higher-level concurrency utilities and data structures introduced in JDK 5.0 like Executors, ExecutorService, ThreadPools, Future, Callable, ConcurrentHashMap, CopyOnWriteArrayList that provide safer and more usable concurrency constructs. It also briefly covers topics like Java Memory Model, memory barriers, and happens-before ordering.
#JavaFX.forReal() - ElsassJUG



#JavaFX.forReal() - ElsassJUGThierry Wasylczenko REX about JavaFX8 used in SlideshowFX. This presentation covers concept from JavaFX as well as technologies like OSGi, Vert.x, LeapMotion, nashorn and friends in order to make them communicate inside one application developed in JavaFX.
This presentation was made at the ElsassJUG
Construire une application JavaFX 8 avec gradle



Construire une application JavaFX 8 avec gradleThierry Wasylczenko JavaFX 8 est disponible depuis mars 2014 et apporte son lot de nouveautés. Gradle est en version 2 depuis juillet 2014. Deux technologies plus que prometteuses: JavaFX donne un coup de jeune au développement d’applications desktop en Java en apportant un navigateur web intégré, le support des WebSockets, de la 3D, et bien d’autres. Gradle est l’outil de d’automatisation de build à la mode, apportant de superbes possibilités par rapport rapport à maven, outil vieillissant, grâce à l’engouement de la communauté vis à vis de cet outil mais aussi par le fait de la technologie utilisée en son sein: groovy. Venez découvrir comment il est possible de réaliser rapidement une application à la mode en JavaFX avec un outil à la mode également. Bref venez à une session trendy.
Whats new in_csharp4



Whats new in_csharp4Abed Bukhari The document summarizes new features in C# 4.0 including optional and named parameters, dynamic typing, tuples, complex numbers, parallel programming, and thread-safe data structures. It also mentions code contracts, memory-mapped files, and the Managed Extensibility Framework.
Fork and join framework



Fork and join frameworkMinh Tran The fork/join framework, which is based on the ForkJoinPool class, is an implementation of the Executor interface. It is designed to efficiently run a large number of tasks using a pool of worker threads. A work-stealing technique is used to keep all the worker threads busy, to take full advantage of multiple processors
Multithreading in Java



Multithreading in JavaAppsterdam Milan The document discusses multithreading in Java, including the evolution of threading support across Java releases and examples of implementing multithreading using Threads, ExecutorService, and NIO channels. It also provides examples of how to make operations thread-safe using locks and atomic variables when accessing shared resources from multiple threads. References are included for further reading on NIO-based servers and asynchronous channel APIs introduced in Java 7.
Os lab final



Os lab finalLakshmiSarvani6 The document outlines the schedule and objectives for an operating systems lab course over 10 weeks. The first few weeks focus on writing programs using Unix system calls like fork, exec, wait. Later weeks involve implementing I/O system calls, simulating commands like ls and grep, and scheduling algorithms like FCFS, SJF, priority and round robin. Students are asked to display Gantt charts, compute waiting times and turnaround times for each algorithm. The final weeks cover inter-process communication, the producer-consumer problem, and memory management techniques.
Microkernel Development



Microkernel DevelopmentRodrigo Almeida Apresentação sobre o desenvolvimento de um microkernel para sistemas embarcados. Apresentada no TDC SP
Counter Wars (JEEConf 2016)



Counter Wars (JEEConf 2016)Alexey Fyodorov The talks is about several ways to implement thread-safe counters. And about implementations performance.
Rx workshop



Rx workshopRyan Riley Workshop slides from the Alt.Net Seattle 2011 workshop. Presented by Wes Dyer and Ryan Riley. Get the slides and the workshop code at http://rxworkshop.codeplex.com/
00_Introduction to Java.ppt



00_Introduction to Java.pptHongAnhNguyn285885 The document provides an introduction to the Java programming language. It discusses Java's history and key editions. It also covers basic Java concepts like compiling and running a simple "Hello World" program, primitive data types, variables, operators, conditional statements like if/else, and iterative structures like the for loop. Examples are provided throughout to demonstrate syntax and output.
13multithreaded Programming



13multithreaded ProgrammingAdil Jafri This document discusses multithreaded programming in Java. It covers two main approaches for creating threads: extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface. Common thread problems like race conditions are addressed, as are techniques for synchronizing access to shared resources using synchronized blocks and methods. The thread lifecycle and useful thread methods like start(), sleep(), join(), etc. are outlined. Signaling with wait() and notify() is demonstrated as a way for threads to communicate. Overall, the document provides an overview of multithreaded concepts in Java and best practices for writing multithreaded programs.
Java Fundamentals



Java FundamentalsShalabh Chaudhary Learn about the basic fundamentals of java and important for the different company's interview. Topics like JRE, JDK, Java Keywords, Primitive DataTypes, Types of Variables, Logical, Shift and Bitwise Operator working, Command Line Argument, Handling Arrays, Array Copy, and different programs and output based programs.
Tools and Techniques for Understanding Threading Behavior in Android



Tools and Techniques for Understanding Threading Behavior in AndroidIntel® Software The document discusses tools and techniques for understanding threading behavior in Android. It summarizes several performance analysis tools for Android including Intel VTune, Linux Perf, Nvidia System Profiler, Google Systrace, and ARM DS-5. It then provides examples of simple, communicating, simultaneously executing, and lazy threads. It demonstrates these threading concepts on devices and analyzes the results from the tools. It finally discusses the concept of false sharing between threads accessing different parts of the same cache line.
Ad
More from knight1128 (7)
Hancom MDS Conference - KAKAO DEVOPS Practice (카카오 스토리의 Devops 사례)



Hancom MDS Conference - KAKAO DEVOPS Practice (카카오 스토리의 Devops 사례)knight1128 카카오 스토리는 한국의 대표적인 SNS 서비스이다.
카카오스토리에서 대용량, NoSQL, Devops, CI/CD 환경을 소개한다.
속도체크



속도체크knight1128 This document compares different methods for measuring performance and timing logic in Java, including System.currentTimeMillis(), System.nanoTime(), the StopWatch class from Apache Commons Lang, and the StopWatch utility from Spring Core. Code examples are provided for each method to demonstrate how to use it and sample output is shown. The Spring and Commons StopWatch implementations are then compared in terms of functionality.
Recently uploaded (20)
Procurement Insights Cost To Value Guide.pptx



Procurement Insights Cost To Value Guide.pptxJon Hansen Procurement Insights integrated Historic Procurement Industry Archives, serves as a powerful complement — not a competitor — to other procurement industry firms. It fills critical gaps in depth, agility, and contextual insight that most traditional analyst and association models overlook.
Learn more about this value- driven proprietary service offering here.
Mobile App Development Company in Saudi Arabia



Mobile App Development Company in Saudi ArabiaSteve Jonas EmizenTech is a globally recognized software development company, proudly serving businesses since 2013. With over 11+ years of industry experience and a team of 200+ skilled professionals, we have successfully delivered 1200+ projects across various sectors. As a leading Mobile App Development Company In Saudi Arabia we offer end-to-end solutions for iOS, Android, and cross-platform applications. Our apps are known for their user-friendly interfaces, scalability, high performance, and strong security features. We tailor each mobile application to meet the unique needs of different industries, ensuring a seamless user experience. EmizenTech is committed to turning your vision into a powerful digital product that drives growth, innovation, and long-term success in the competitive mobile landscape of Saudi Arabia.
Build Your Own Copilot & Agents For Devs



Build Your Own Copilot & Agents For DevsBrian McKeiver May 2nd, 2025 talk at StirTrek 2025 Conference.
Noah Loul Shares 5 Steps to Implement AI Agents for Maximum Business Efficien...



Noah Loul Shares 5 Steps to Implement AI Agents for Maximum Business Efficien...Noah Loul Artificial intelligence is changing how businesses operate. Companies are using AI agents to automate tasks, reduce time spent on repetitive work, and focus more on high-value activities. Noah Loul, an AI strategist and entrepreneur, has helped dozens of companies streamline their operations using smart automation. He believes AI agents aren't just tools—they're workers that take on repeatable tasks so your human team can focus on what matters. If you want to reduce time waste and increase output, AI agents are the next move.
Quantum Computing Quick Research Guide by Arthur Morgan



Quantum Computing Quick Research Guide by Arthur MorganArthur Morgan This is a Quick Research Guide (QRG).
QRGs include the following:
- A brief, high-level overview of the QRG topic.
- A milestone timeline for the QRG topic.
- Links to various free online resource materials to provide a deeper dive into the QRG topic.
- Conclusion and a recommendation for at least two books available in the SJPL system on the QRG topic.
QRGs planned for the series:
- Artificial Intelligence QRG
- Quantum Computing QRG
- Big Data Analytics QRG
- Spacecraft Guidance, Navigation & Control QRG (coming 2026)
- UK Home Computing & The Birth of ARM QRG (coming 2027)
Any questions or comments?
- Please contact Arthur Morgan at [email protected].
100% human made.
Transcript: #StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tec...



Transcript: #StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tec...BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, presentation slides, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Increasing Retail Store Efficiency How can Planograms Save Time and Money.pptx



Increasing Retail Store Efficiency How can Planograms Save Time and Money.pptxAnoop Ashok In today's fast-paced retail environment, efficiency is key. Every minute counts, and every penny matters. One tool that can significantly boost your store's efficiency is a well-executed planogram. These visual merchandising blueprints not only enhance store layouts but also save time and money in the process.
How analogue intelligence complements AI



How analogue intelligence complements AIPaul Rowe
Artificial Intelligence is providing benefits in many areas of work within the heritage sector, from image analysis, to ideas generation, and new research tools. However, it is more critical than ever for people, with analogue intelligence, to ensure the integrity and ethical use of AI. Including real people can improve the use of AI by identifying potential biases, cross-checking results, refining workflows, and providing contextual relevance to AI-driven results.
News about the impact of AI often paints a rosy picture. In practice, there are many potential pitfalls. This presentation discusses these issues and looks at the role of analogue intelligence and analogue interfaces in providing the best results to our audiences. How do we deal with factually incorrect results? How do we get content generated that better reflects the diversity of our communities? What roles are there for physical, in-person experiences in the digital world?
Designing Low-Latency Systems with Rust and ScyllaDB: An Architectural Deep Dive



Designing Low-Latency Systems with Rust and ScyllaDB: An Architectural Deep DiveScyllaDB Want to learn practical tips for designing systems that can scale efficiently without compromising speed?
Join us for a workshop where we’ll address these challenges head-on and explore how to architect low-latency systems using Rust. During this free interactive workshop oriented for developers, engineers, and architects, we’ll cover how Rust’s unique language features and the Tokio async runtime enable high-performance application development.
As you explore key principles of designing low-latency systems with Rust, you will learn how to:
- Create and compile a real-world app with Rust
- Connect the application to ScyllaDB (NoSQL data store)
- Negotiate tradeoffs related to data modeling and querying
- Manage and monitor the database for consistently low latencies
AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global Trends



AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global TrendsInData Labs In this infographic, we explore how businesses can implement effective governance frameworks to address AI data privacy. Understanding it is crucial for developing effective strategies that ensure compliance, safeguard customer trust, and leverage AI responsibly. Equip yourself with insights that can drive informed decision-making and position your organization for success in the future of data privacy.
This infographic contains:
-AI and data privacy: Key findings
-Statistics on AI data privacy in the today’s world
-Tips on how to overcome data privacy challenges
-Benefits of AI data security investments.
Keep up-to-date on how AI is reshaping privacy standards and what this entails for both individuals and organizations.
Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...



Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...Impelsys Inc. Impelsys provided a robust testing solution, leveraging a risk-based and requirement-mapped approach to validate ICU Connect and CritiXpert. A well-defined test suite was developed to assess data communication, clinical data collection, transformation, and visualization across integrated devices.
Into The Box Conference Keynote Day 1 (ITB2025)



Into The Box Conference Keynote Day 1 (ITB2025)Ortus Solutions, Corp This is the keynote of the Into the Box conference, highlighting the release of the BoxLang JVM language, its key enhancements, and its vision for the future.
Special Meetup Edition - TDX Bengaluru Meetup #52.pptx



Special Meetup Edition - TDX Bengaluru Meetup #52.pptxshyamraj55 We’re bringing the TDX energy to our community with 2 power-packed sessions:
🛠️ Workshop: MuleSoft for Agentforce
Explore the new version of our hands-on workshop featuring the latest Topic Center and API Catalog updates.
📄 Talk: Power Up Document Processing
Dive into smart automation with MuleSoft IDP, NLP, and Einstein AI for intelligent document workflows.
Andrew Marnell: Transforming Business Strategy Through Data-Driven Insights



Andrew Marnell: Transforming Business Strategy Through Data-Driven InsightsAndrew Marnell With expertise in data architecture, performance tracking, and revenue forecasting, Andrew Marnell plays a vital role in aligning business strategies with data insights. Andrew Marnell’s ability to lead cross-functional teams ensures businesses achieve sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Linux Support for SMARC: How Toradex Empowers Embedded Developers



Linux Support for SMARC: How Toradex Empowers Embedded DevelopersToradex Toradex brings robust Linux support to SMARC (Smart Mobility Architecture), ensuring high performance and long-term reliability for embedded applications. Here’s how:
• Optimized Torizon OS & Yocto Support – Toradex provides Torizon OS, a Debian-based easy-to-use platform, and Yocto BSPs for customized Linux images on SMARC modules.
• Seamless Integration with i.MX 8M Plus and i.MX 95 – Toradex SMARC solutions leverage NXP’s i.MX 8 M Plus and i.MX 95 SoCs, delivering power efficiency and AI-ready performance.
• Secure and Reliable – With Secure Boot, over-the-air (OTA) updates, and LTS kernel support, Toradex ensures industrial-grade security and longevity.
• Containerized Workflows for AI & IoT – Support for Docker, ROS, and real-time Linux enables scalable AI, ML, and IoT applications.
• Strong Ecosystem & Developer Support – Toradex offers comprehensive documentation, developer tools, and dedicated support, accelerating time-to-market.
With Toradex’s Linux support for SMARC, developers get a scalable, secure, and high-performance solution for industrial, medical, and AI-driven applications.
Do you have a specific project or application in mind where you're considering SMARC? We can help with Free Compatibility Check and help you with quick time-to-market
For more information: https://www.toradex.com/computer-on-modules/smarc-arm-family
Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD



Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure ADVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD
Role of Data Annotation Services in AI-Powered Manufacturing



Role of Data Annotation Services in AI-Powered ManufacturingAndrew Leo From predictive maintenance to robotic automation, AI is driving the future of manufacturing. But without high-quality annotated data, even the smartest models fall short.
Discover how data annotation services are powering accuracy, safety, and efficiency in AI-driven manufacturing systems.
Precision in data labeling = Precision on the production floor.
Rusty Waters: Elevating Lakehouses Beyond Spark



Rusty Waters: Elevating Lakehouses Beyond Sparkcarlyakerly1 Spark is a powerhouse for large datasets, but when it comes to smaller data workloads, its overhead can sometimes slow things down. What if you could achieve high performance and efficiency without the need for Spark?
At S&P Global Commodity Insights, having a complete view of global energy and commodities markets enables customers to make data-driven decisions with confidence and create long-term, sustainable value. 🌍
Explore delta-rs + CDC and how these open-source innovations power lightweight, high-performance data applications beyond Spark! 🚀
Jdk 7 4-forkjoin
- 1. JDK 7 출시 기념 (2011.7)JDK 7 소개 #4 ConcurrentyFork & Join (jsr166y)김용환knight76.tistory.comKnight76 at gmail.com1
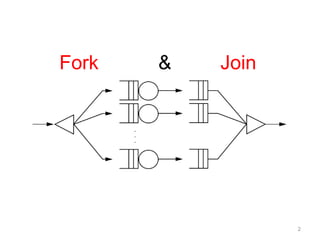
- 2. Fork & Join2
- 3. Multicore-friendly lightweight parallel frameworkJSR166y (maintenance)목적놀고 있는 여러 개의 processor를 최대한 활용을 위해서 디자인됨병렬처리 필요MapReduce와 비슷하지만, 더 세분화할 수 있다. Work-stealing 알고리즘을 기반.3
- 4. Fork/JoinForkRecursively큰 단위의 작업을 작은 단위로 쪼갬Join결과를 Recursive하게모음Doug Lee(뉴욕 주립대 교수)http://gee.cs.oswego.edu/dl/papers/fj.pdfhttp://g.oswego.edu/dl/concurrency-interest/4
- 5. Map Reduce와 비교Map ReduceNode 기반의 Cluster 기반Single forkFork / Join하나의장비안에서 여러 개의 CPU를 사용하려는 하나의 JVMRecursive forkWork Stealing5
- 6. Work StealingCilk에서개념을 채용 (논문)MIT에서 만든 멀티쓰레드 프로그래밍 언어예약어 조금 + C언어(http://supertech.csail.mit.edu/cilk/manual-5.4.6.pdf)특징각 worker 는 DeQueue(double-ended queue)를 가지고 있음 worker가 idle일 때, 바쁜 Worker의 Queue에 쌓인 task 를 steal.왜?여러 개의 processor(core)에서 동작 가능로드 밸런스 (작은 task로 나눌 수 있도록 함)6
- 7. Work Stealing7ForkJoinPool클래스에구현되어 있음출처 : http://karlsenchoi.blogspot.com/2011/02/threadpool-work-stealing.html
- 9. Pseudo code9if (my portion of the work is small enough)dothe work directlyelsesplit my work into two piecesinvokethe two pieces and wait for the results
- 10. Java pseudo code 10class OOOTaskextends RecursiveTask { @Override public void compute() {// small enough if (problem.size< THRESHOLD) { // do directlyproblem.solve(); } else {// split Task worker1 = new OOOTask(new Problem(problem.size - 1)); Task worker2 = new OOOTask(new Problem(problem.size- 2));// invokeinvokeAll(worker1, worker2); } }}
- 11. 예제피보나치 계산Fib(7) 계산CPU는 411
- 12. FibonacciProblem12class FibonacciProblem {public int n; public FibonacciProblem(int n) {this.n = n; } public long solve() { return fibonacci(n); } private long fibonacci(int n) {System.out.println("Thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " calculates " + n); if (n <= 1) { return n;} else {return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2); } }}
- 13. FibonacciTask13@SuppressWarnings("serial")class FibonacciTask extends RecursiveTask<Long> { private static final intTHRESHOLD = 5; private FibonacciProblem problem; public long result; public FibonacciTask(FibonacciProblem problem) {this.problem = problem; } @Override public Long compute() { if (problem.n < THRESHOLD) { result = problem.solve(); } else {FibonacciTask worker1 = new FibonacciTask( new FibonacciProblem(problem.n - 1));FibonacciTask worker2 = new FibonacciTask( new FibonacciProblem(problem.n - 2));worker1.fork(); result = worker2.compute() + worker1.join(); } return result; }}
- 14. Main14public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("Number of processors: " + Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());intn = 7;StopWatchstopWatch = new StopWatch(); FibonacciProblembigProblem = new FibonacciProblem(n);FibonacciTasktask = new FibonacciTask(bigProblem);ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();pool.invoke(task);long result = task.result;System.out.println("Computed Result: " + result);stopWatch.stop();System.out.println("Elapsed Time: " + stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis());System.out.println("Steal Count : " + pool.getStealCount());}
- 15. 실행 결과15No of processors: 4Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1 calculates 3Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 4Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 4Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 3Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 2Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 3Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 2Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 3Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 2Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1 calculates 2Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 0Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 0Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 0Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1 calculates 0Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 2Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 2Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3 calculates 0Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2 calculates 0Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 4Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 3Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 2Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 0Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 2Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 1Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-4 calculates 0Computed Result: 13Elapsed Time: 4Steal Count : 4
- 17. API (RecursiveAction)17public abstract class RecursiveAction<V> extends ForkJoinTask<V> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 5232453952276485270L; protected abstract V compute(); public final void getRawResult() { return null; } protected final void setRawResult(V value) { } protected final boolean exec() { compute(); return true; }}
- 18. API (RecursiveTask)18public abstract class RecursiveTaskextends ForkJoinTask<Void> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 5232453952276485270L; V result; protected abstract V compute(); public final V getRawResult() { return result; } protected final void setRawResult(V value) { result = value; } protected final boolean exec() { result = compute(); return true; }}
- 21. ForkJoinPool21
- 22. 기타22
- 23. ThreadLocalRandom멀티쓰레드상에서Random 은 contention과 overhead가 존재. Random 내부에서 thread를 isolation을 함ForkJoinPool에서 Random 사용시 이슈가 속도가 저하되기 때문에 이를 해결할 수 있는 클래스23long f = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong();System.out.println("1 : " + f);f = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong();System.out.println("2 : " + f);1 : 42322372 : 767956431209526212
- 24. Phaser특징쓰레드를 동시 시작/종료시킬 수 있도록 함CyclicBarrier와 CountDownLatch클래스를 보다 유연함좋은 자료http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/Phaser.htmlhttp://olegignatenko.livejournal.com/16771.html24
- 25. Phaser예제25public static void main(String[] args) {runDevelopment(Arrays.asList(new Developer(), new Developer(), new Developer(), new Developer()));}private static void runDevelopment(Iterable<Developer> team) { final Phasermanager = new Phaser(1); //"1" to register selfSystem.out.println("mgr: assign all developers, then start coding"); for (final Developer developer : team) { final String dev = developer.toString();System.out.println("mgr: assigns a new unarrived " + dev + " to the project");manager.register(); new Thread() { public void run() {System.out.println("mgr: " + dev + ", please await all developers");manager.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); // await all creationSystem.out.println("mgr: " + dev + ", OK to start coding");developer.run();} }.start();}System.out.println("mgr: all assigned, start coding after all arrive");manager.arriveAndDeregister();}class Developer implements Runnable { private final static AtomicIntegeridSource = new AtomicInteger(); private final int id = idSource.incrementAndGet(); public void run() { System.out.println(toString() + ": coding"); } public String toString() { return "developer #" + id; }}
- 26. Phaser결과26mgr: assign all developers, then start codingmgr: assigns a new unarrived developer #1 to the projectmgr: assigns a new unarrived developer #2 to the projectmgr: developer #1, please await all developersmgr: assigns a new unarrived developer #3 to the projectmgr: assigns a new unarrived developer #4 to the projectmgr: developer #3, please await all developersmgr: all assigned, start coding after all arrivemgr: developer #4, please await all developersmgr: developer #2, please await all developersmgr: developer #2, OK to start codingdeveloper #2: codingmgr: developer #1, OK to start codingdeveloper #1: codingmgr: developer #3, OK to start codingdeveloper #3: codingmgr: developer #4, OK to start codingdeveloper #4: coding
- 27. To be continued #527
















