Ldap intro
- 1. Introduction to LDAP Yousry Ibrahim Mabrouk ©2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
- 2. AGENDA • Understanding LDAP. • LDAP Servers. • Information Structure. • Protocol overview. • LDAP Operations. • How to use LDAP? • Using JNDI For LDAP Thursday, October 25, 2 2012
- 3. Understanding LDAP • Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. • open network protocol standard designed to provide access to distributed directories. • using TCP/IP protocols. • The phrase “write once read many times“ describes the best use of LDAP. • standard and allowing directories to be managed. • No transactions, No rollback Thursday, October 25, 3 2012
- 4. LDAP Servers • 389 Directory Server (formerly Fedora/Red Hat Directory Server) • Active Directory from Microsoft • Apache Directory Server • Apple Open Directory • FreeIPA • IBM Tivoli Directory Server • Mandriva Directory Server • Novell eDirectory • OpenDJ - A fork of the OpenDS project • OpenDS • OpenLDAP • Optimal IdM • Oracle Internet Directory • Radiant Logic VDS • Sun Java System Directory Server Thursday, October 25, 4 2012
- 5. Information Structure • Presents information in the form of a hierarchical tree structure called a DIT (Directory Information Tree). Thursday, October 25, 5 2012
- 6. Information Structure (con) • Each information, called Entry (or even DSE, Directory Service Entry). • Each entry in the LDAP directory relates to an abstract or real object (for example a person, a piece of hardware, parameters, etc.). • Each entry is made up of a collection of key/value pairs called attributes. • Types of attributes : • Normal attributes: these are the usual attributes (cn, name,o, ...) distinguishing the object. • Operational attributes: these are the attributes which only the server can access in order to manipulate the directory data (modification dates, etc,). Thursday, October 25, 6 2012
- 7. Information Structure (con II) • Every entry in the directory has a distinguished name (DN). • DN is made up of attribute=value pairs, separated by commas, for example: • dn:o=hp,ou=people,[email protected] • Some keys which are generally used: o Organization ou Organizational unit cn Common name sn Surname givenname First name uid Userid mail Email address Thursday, October 25, 7 2012
- 8. Information Structure (con III) HP Directory Information Tree (DIT). Thursday, October 25, 8 2012
- 9. Protocol overview • client starts an LDAP session by connecting to an LDAP server. • The default TCP port is 389. • Bind to the server (think of this as authentication). • client then sends an operation request to the server. • the server sends responses in return. Thursday, October 25, 9 2012
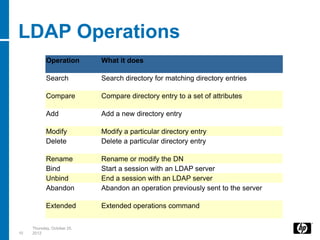
- 10. LDAP Operations Operation What it does Search Search directory for matching directory entries Compare Compare directory entry to a set of attributes Add Add a new directory entry Modify Modify a particular directory entry Delete Delete a particular directory entry Rename Rename or modify the DN Bind Start a session with an LDAP server Unbind End a session with an LDAP server Abandon Abandon an operation previously sent to the server Extended Extended operations command Thursday, October 25, 10 2012
- 11. How to use LDAP? • Can use any Java LDAP SDK, for example: • JNDI LDAP : standard . • Spring LDAP: http://www.springsource.org/ldap − (it is better to use it when using spring framework) • LDAP API: from apache http://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/LDAPA PI/Index • NetScape LDAP : http://www- archive.mozilla.org/directory/javasdk.html Thursday, October 25, 11 2012
- 12. Using JNDI For LDAP 1- Connect to the server: − you must obtain a reference to an object that implements the DirContext interface. − In most applications, this is done by using an InitialDirContext object that takes a Hashtable as an argument. − The Hashtable contains various entries, such as the hostname, port, and JNDI service provider classes to use: Thursday, October 25, 12 2012
- 13. Using JNDI For LDAP (con) 2- Bind to the Server: - Once connected, the client may need to authenticate itself; this process is also known as binding to the server. - in LDAP version 2, all clients had to authenticate while connecting, but version 3 defaults to anonymous and, if the default values are used, the connections are anonymous as well - LDAP supports three different security types: - Simple: Authenticates fast using plain text usernames and passwords. - SSL: Authenticates with SSL encryption over the network. - SASL: Uses MD5/Kerberos mechanisms. SASL is a simple authentication and security layer-based scheme Thursday, October 25, 13 2012
- 14. Using JNDI For LDAP (conII) 3- Search: -Search Scopes: - Sub Tree Scope: search of the entire subtree searches the named object and all of its descendants. - Object Scope: search the named object. This is useful, for example, to test whether the named object satisfies a search filter -OnLevel Scope (default): specifies that the search is to be performed in the named context -Filters :Used to filter the search results according to attribute’s value. Thursday, October 25, 14 2012
- 15. Examples ….. Let’s work. Thursday, October 25, 15 2012
- 16. Thursday, October 25, 16 2012