Lecture 2
Download as PPT, PDF6 likes12,360 views
This document discusses key concepts and terminologies related to parallel computing. It defines tasks, parallel tasks, serial and parallel execution. It also describes shared memory and distributed memory architectures as well as communications and synchronization between parallel tasks. Flynn's taxonomy is introduced which classifies parallel computers based on instruction and data streams as Single Instruction Single Data (SISD), Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD), Multiple Instruction Single Data (MISD), and Multiple Instruction Multiple Data (MIMD). Examples are provided for each classification.
1 of 18
Downloaded 357 times

















Ad
Recommended
Parallel processing



Parallel processingSyed Zaid Irshad Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or the execution of processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has been employed for many years, mainly in high-performance computing, but interest in it has grown lately due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling. As power consumption (and consequently heat generation) by computers has become a concern in recent years, parallel computing has become the dominant paradigm in computer architecture, mainly in the form of multi-core processors.
Flynns classification



Flynns classificationYasir Khan Michael Flynn proposed a taxonomy in 1966 to classify computer architectures based on the number of instruction streams and data streams. The four classifications are: SISD (single instruction, single data stream), SIMD (single instruction, multiple data streams), MISD (multiple instructions, single data stream), and MIMD (multiple instructions, multiple data streams). SISD corresponds to the traditional von Neumann architecture, SIMD is used for array processing, MIMD describes most modern parallel computers, and MISD has never been implemented.
Parallel processing



Parallel processingrajshreemuthiah The document provides an overview of parallel processing and multiprocessor systems. It discusses Flynn's taxonomy, which classifies computers as SISD, SIMD, MISD, or MIMD based on whether they process single or multiple instructions and data in parallel. The goals of parallel processing are to reduce wall-clock time and solve larger problems. Multiprocessor topologies include uniform memory access (UMA) and non-uniform memory access (NUMA) architectures.
Virtual memory



Virtual memoryAnuj Modi The document discusses the concept of virtual memory. Virtual memory allows a program to access more memory than what is physically available in RAM by storing unused portions of the program on disk. When a program requests data that is not currently in RAM, it triggers a page fault that causes the needed page to be swapped from disk into RAM. This allows the illusion of more memory than physically available through swapping pages between RAM and disk as needed by the program during execution.
Parallel programming model



Parallel programming modeleasy notes The document discusses several parallel programming models:
1. The shared variable model uses shared memory and variables for inter-process communication but has issues around critical sections, memory consistency, and synchronization.
2. The message passing model uses message passing between processes instead of shared memory, avoiding synchronization issues but introducing delays. It describes synchronous and asynchronous variants.
3. The data parallel model partitions data across processes, which perform similar operations in parallel. It is well-suited to regular problems like matrix operations.
4. Other models discussed include object-oriented, functional, and logic programming models.
advanced computer architesture-conditions of parallelism



advanced computer architesture-conditions of parallelismPankaj Kumar Jain This PPT contains Data and Resource Dependencies,Control Dependence,Resource Dependence,Bernstein’s Conditions ,Hardware And Software Parallelism,Types of Software Parallelism
Introduction to Parallel and Distributed Computing



Introduction to Parallel and Distributed ComputingSayed Chhattan Shah Introduction
Parallel Computer Memory Architectures
Parallel Programming Models
Design Parallel Programs
Distributed Systems
Distributed computing



Distributed computingshivli0769 This document summarizes distributed computing. It discusses the history and origins of distributed computing in the 1960s with concurrent processes communicating through message passing. It describes how distributed computing works by splitting a program into parts that run simultaneously on multiple networked computers. Examples of distributed systems include telecommunication networks, network applications, real-time process control systems, and parallel scientific computing. The advantages of distributed computing include economics, speed, reliability, and scalability while the disadvantages include complexity and network problems.
Asynchronous data transfer



Asynchronous data transferpriya Nithya This document discusses asynchronous data transfer between independent units. It describes two methods for asynchronous transfer - strobe control and handshaking. Strobe control uses a single control line to time each transfer, while handshaking introduces a second control signal to provide confirmation between units. Specifically, it details the handshaking process, which involves control signals like "data valid" and "data accepted" or "ready for data" to coordinate placing data on the bus and accepting data between a source and destination unit.
Multi Processors And Multi Computers



Multi Processors And Multi ComputersNemwos In this presentation, you will learn the fundamentals of Multi Processors and Multi Computers in only a few minutes.
Meanings, features, attributes, applications, and examples of multiprocessors and multi computers.
So, let's get started. If you enjoy this and find the information beneficial, please like and share it with your friends.
Computer architecture pipelining



Computer architecture pipeliningMazin Alwaaly Computer Architecture Pipelining seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Operating Systems: Device Management



Operating Systems: Device ManagementDamian T. Gordon The document discusses device management and storage devices. It describes the main functions of a device manager as monitoring device status, enforcing allocation policies, and allocating and deallocating devices to processes. It then covers different types of storage devices like hard disks, optical disks, and RAID arrays. Specific topics discussed include mobile-head vs fixed-head hard disks, writing data to disk surfaces vs tracks, and key performance metrics for optical disks.
CISC & RISC Architecture 



CISC & RISC Architecture Suvendu Kumar Dash This document discusses the history and characteristics of CISC and RISC architectures. It describes how CISC architectures were developed in the 1950s-1970s to address hardware limitations at the time by allowing instructions to perform multiple operations. RISC architectures emerged in the late 1970s-1980s as hardware improved, focusing on simpler instructions that could be executed faster through pipelining. Common RISC and CISC processors used commercially are also outlined.
Cache coherence



Cache coherencePriyam Pandey Cache coherence is an issue that arises in multiprocessing systems where multiple processors have cached copies of shared memory locations. If a processor modifies its local copy, it can create an inconsistent global view of memory.
There are two main approaches to maintaining cache coherence - snoopy bus protocols and directory schemes. Snoopy bus protocols use a shared bus for processors to monitor memory transactions and invalidate local copies when needed. Directory schemes track which processors are sharing each block of data using a directory structure.
One common snoopy protocol is MESI, which uses cache states of Modified, Exclusive, Shared, and Invalid to track the ownership of cache lines and ensure coherency is maintained when a line is modified.
Producer consumer problem operating system



Producer consumer problem operating systemAl Mamun In computing, the producer–consumer problem (also known as the bounded-buffer problem) is a classic example of a multi-process synchronization problem. The problem describes two processes, the producer and the consumer, who share a common, fixed-size buffer used as a queue.
Superscalar & superpipeline processor



Superscalar & superpipeline processorMuhammad Ishaq This document discusses superscalar and super pipeline approaches to improving processor performance. Superscalar processors execute multiple independent instructions in parallel using multiple pipelines. Super pipelines break pipeline stages into smaller stages to reduce clock period and increase instruction throughput. While superscalar utilizes multiple parallel pipelines, super pipelines perform multiple stages per clock cycle in each pipeline. Super pipelines benefit from higher parallelism but also increase potential stalls from dependencies. Both approaches aim to maximize parallel instruction execution but face limitations from true data and other dependencies.
Parallel computing persentation



Parallel computing persentationVIKAS SINGH BHADOURIA Parallel computing is computing architecture paradigm ., in which processing required to solve a problem is done in more than one processor parallel way.
Parallel processing



Parallel processingPraveen Kumar Domain Decomposition, Ecosystem Modeling, Signal Processing, Parallelism in Uniprocessor Systems,Parallelism in Multiprocessor Systems,fynns classification, parallel computing.
multiprocessors and multicomputers



multiprocessors and multicomputersPankaj Kumar Jain Categories of Parallel Computers,Shared-Memory Multiprocessors, uma, numa , coma,Vector Processor Models,SIMD Supercomputers
operating system structure



operating system structureWaseem Ud Din Farooqui The document discusses key components and concepts related to operating system structures. It describes common system components like process management, memory management, file management, I/O management, and more. It then provides more details on specific topics like the role of processes, main memory management, file systems, I/O systems, secondary storage, networking, protection systems, and command interpreters in operating systems. Finally, it discusses operating system services, system calls, and how parameters are passed between programs and the operating system.
Paging and segmentation



Paging and segmentationPiyush Rochwani This document summarizes and compares paging and segmentation, two common memory management techniques. Paging divides physical memory into fixed-size frames and logical memory into same-sized pages. It maps pages to frames using a page table. Segmentation divides logical memory into variable-sized segments and uses a segment table to map segment numbers to physical addresses. Paging avoids external fragmentation but can cause internal fragmentation, while segmentation avoids internal fragmentation but can cause external fragmentation. Both approaches separate logical and physical address spaces but represent different models of how a process views memory.
INTER PROCESS COMMUNICATION (IPC).pptx



INTER PROCESS COMMUNICATION (IPC).pptxLECO9 Inter-process communication (IPC) allows processes to communicate and synchronize. Common IPC methods include pipes, message queues, shared memory, semaphores, and mutexes. Pipes provide unidirectional communication while message queues allow full-duplex communication through message passing. Shared memory enables processes to access the same memory region. Direct IPC requires processes to explicitly name communication partners while indirect IPC uses shared mailboxes.
Operating System - Monitors (Presentation)



Operating System - Monitors (Presentation)Experts Desk This document discusses monitors and their use in interprocess communication and synchronization. It contains the following key points:
1. Monitors provide mutual exclusion and condition variables to avoid race conditions when processes access shared resources. They allow processes to block when they cannot proceed.
2. Semaphores can be used to implement monitors, with a binary semaphore controlling entry to the monitor and additional semaphores for condition variables.
3. Monitors can also implement semaphores and messages, providing a higher-level construct than semaphores for synchronization between processes. Counters and linked lists are used to track semaphore values and message queues.
Cache memory



Cache memoryAnuj Modi Cache memory is a small, fast memory located between the CPU and main memory. It stores copies of frequently used instructions and data to accelerate access and improve performance. There are different mapping techniques for cache including direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping. When the cache is full, replacement algorithms like LRU and FIFO are used to determine which content to remove. The cache can write to main memory using either a write-through or write-back policy.
Applications of paralleL processing



Applications of paralleL processingPage Maker This document discusses various applications of parallel processing. It describes how parallel processing is used in numeric weather prediction to forecast weather by processing large amounts of observational data. It is also used in oceanography and astrophysics to study oceans and conduct particle simulations. Other applications mentioned include socioeconomic modeling, finite element analysis, artificial intelligence, seismic exploration, genetic engineering, weapon research, medical imaging, remote sensing, energy exploration, and more. The document also discusses loosely coupled and tightly coupled multiprocessors and the differences between the two approaches.
Aca2 01 new



Aca2 01 newSumit Mittu This document is a chapter summary for "CSE539: Advanced Computer Architecture" taught by Sumit Mittu, Assistant Professor at Lovely Professional University. The chapter discusses parallel computer models and covers topics like the evolution of computing through generations of computers, parallel computer classifications like multiprocessors and multicomputers, and theoretical parallel models like PRAM. It provides examples of parallel systems from each generation and model. The goal is to introduce students to parallel architectures and taxonomy.
Von Neumann vs Harvard Architecture



Von Neumann vs Harvard ArchitectureOLSON MATUNGA The Von Neumann and Harvard architectures are two common computer architectures. The Von Neumann architecture uses a single memory to store both programs and data, accessed via a shared bus, while the Harvard architecture separates memory and uses two separate buses for program and data access. The Von Neumann architecture has advantages of simpler design and lower cost while the Harvard allows parallel instruction and data processing but has higher development costs. They differ primarily in their memory structure and bus configurations.
Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computing



Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computingVajira Thambawita This gives you an introduction to parallel and distributed computing. More details: https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials
Parallel & Distributed processing



Parallel & Distributed processingSyed Zaid Irshad The document provides an introduction to high performance computing architectures. It discusses the von Neumann architecture that has been used in computers for over 40 years. It then explains Flynn's taxonomy, which classifies parallel computers based on whether their instruction and data streams are single or multiple. The main categories are SISD, SIMD, MISD, and MIMD. It provides examples of computer architectures that fall under each classification. Finally, it discusses different parallel computer memory architectures, including shared memory, distributed memory, and hybrid models.
Lec 2 (parallel design and programming)



Lec 2 (parallel design and programming)Sudarshan Mondal This document discusses parallel computing architectures and concepts. It begins by describing Von Neumann architecture and how parallel computers follow the same basic design but with multiple units. It then covers Flynn's taxonomy which classifies computers based on their instruction and data streams as Single Instruction Single Data (SISD), Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD), Multiple Instruction Single Data (MISD), or Multiple Instruction Multiple Data (MIMD). Each classification is defined. The document also discusses parallel terminology, synchronization, scalability, and Amdahl's law on the costs and limits of parallel programming.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Asynchronous data transfer



Asynchronous data transferpriya Nithya This document discusses asynchronous data transfer between independent units. It describes two methods for asynchronous transfer - strobe control and handshaking. Strobe control uses a single control line to time each transfer, while handshaking introduces a second control signal to provide confirmation between units. Specifically, it details the handshaking process, which involves control signals like "data valid" and "data accepted" or "ready for data" to coordinate placing data on the bus and accepting data between a source and destination unit.
Multi Processors And Multi Computers



Multi Processors And Multi ComputersNemwos In this presentation, you will learn the fundamentals of Multi Processors and Multi Computers in only a few minutes.
Meanings, features, attributes, applications, and examples of multiprocessors and multi computers.
So, let's get started. If you enjoy this and find the information beneficial, please like and share it with your friends.
Computer architecture pipelining



Computer architecture pipeliningMazin Alwaaly Computer Architecture Pipelining seminar
Mustansiriya University
Department of Education
Computer Science
Operating Systems: Device Management



Operating Systems: Device ManagementDamian T. Gordon The document discusses device management and storage devices. It describes the main functions of a device manager as monitoring device status, enforcing allocation policies, and allocating and deallocating devices to processes. It then covers different types of storage devices like hard disks, optical disks, and RAID arrays. Specific topics discussed include mobile-head vs fixed-head hard disks, writing data to disk surfaces vs tracks, and key performance metrics for optical disks.
CISC & RISC Architecture 



CISC & RISC Architecture Suvendu Kumar Dash This document discusses the history and characteristics of CISC and RISC architectures. It describes how CISC architectures were developed in the 1950s-1970s to address hardware limitations at the time by allowing instructions to perform multiple operations. RISC architectures emerged in the late 1970s-1980s as hardware improved, focusing on simpler instructions that could be executed faster through pipelining. Common RISC and CISC processors used commercially are also outlined.
Cache coherence



Cache coherencePriyam Pandey Cache coherence is an issue that arises in multiprocessing systems where multiple processors have cached copies of shared memory locations. If a processor modifies its local copy, it can create an inconsistent global view of memory.
There are two main approaches to maintaining cache coherence - snoopy bus protocols and directory schemes. Snoopy bus protocols use a shared bus for processors to monitor memory transactions and invalidate local copies when needed. Directory schemes track which processors are sharing each block of data using a directory structure.
One common snoopy protocol is MESI, which uses cache states of Modified, Exclusive, Shared, and Invalid to track the ownership of cache lines and ensure coherency is maintained when a line is modified.
Producer consumer problem operating system



Producer consumer problem operating systemAl Mamun In computing, the producer–consumer problem (also known as the bounded-buffer problem) is a classic example of a multi-process synchronization problem. The problem describes two processes, the producer and the consumer, who share a common, fixed-size buffer used as a queue.
Superscalar & superpipeline processor



Superscalar & superpipeline processorMuhammad Ishaq This document discusses superscalar and super pipeline approaches to improving processor performance. Superscalar processors execute multiple independent instructions in parallel using multiple pipelines. Super pipelines break pipeline stages into smaller stages to reduce clock period and increase instruction throughput. While superscalar utilizes multiple parallel pipelines, super pipelines perform multiple stages per clock cycle in each pipeline. Super pipelines benefit from higher parallelism but also increase potential stalls from dependencies. Both approaches aim to maximize parallel instruction execution but face limitations from true data and other dependencies.
Parallel computing persentation



Parallel computing persentationVIKAS SINGH BHADOURIA Parallel computing is computing architecture paradigm ., in which processing required to solve a problem is done in more than one processor parallel way.
Parallel processing



Parallel processingPraveen Kumar Domain Decomposition, Ecosystem Modeling, Signal Processing, Parallelism in Uniprocessor Systems,Parallelism in Multiprocessor Systems,fynns classification, parallel computing.
multiprocessors and multicomputers



multiprocessors and multicomputersPankaj Kumar Jain Categories of Parallel Computers,Shared-Memory Multiprocessors, uma, numa , coma,Vector Processor Models,SIMD Supercomputers
operating system structure



operating system structureWaseem Ud Din Farooqui The document discusses key components and concepts related to operating system structures. It describes common system components like process management, memory management, file management, I/O management, and more. It then provides more details on specific topics like the role of processes, main memory management, file systems, I/O systems, secondary storage, networking, protection systems, and command interpreters in operating systems. Finally, it discusses operating system services, system calls, and how parameters are passed between programs and the operating system.
Paging and segmentation



Paging and segmentationPiyush Rochwani This document summarizes and compares paging and segmentation, two common memory management techniques. Paging divides physical memory into fixed-size frames and logical memory into same-sized pages. It maps pages to frames using a page table. Segmentation divides logical memory into variable-sized segments and uses a segment table to map segment numbers to physical addresses. Paging avoids external fragmentation but can cause internal fragmentation, while segmentation avoids internal fragmentation but can cause external fragmentation. Both approaches separate logical and physical address spaces but represent different models of how a process views memory.
INTER PROCESS COMMUNICATION (IPC).pptx



INTER PROCESS COMMUNICATION (IPC).pptxLECO9 Inter-process communication (IPC) allows processes to communicate and synchronize. Common IPC methods include pipes, message queues, shared memory, semaphores, and mutexes. Pipes provide unidirectional communication while message queues allow full-duplex communication through message passing. Shared memory enables processes to access the same memory region. Direct IPC requires processes to explicitly name communication partners while indirect IPC uses shared mailboxes.
Operating System - Monitors (Presentation)



Operating System - Monitors (Presentation)Experts Desk This document discusses monitors and their use in interprocess communication and synchronization. It contains the following key points:
1. Monitors provide mutual exclusion and condition variables to avoid race conditions when processes access shared resources. They allow processes to block when they cannot proceed.
2. Semaphores can be used to implement monitors, with a binary semaphore controlling entry to the monitor and additional semaphores for condition variables.
3. Monitors can also implement semaphores and messages, providing a higher-level construct than semaphores for synchronization between processes. Counters and linked lists are used to track semaphore values and message queues.
Cache memory



Cache memoryAnuj Modi Cache memory is a small, fast memory located between the CPU and main memory. It stores copies of frequently used instructions and data to accelerate access and improve performance. There are different mapping techniques for cache including direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping. When the cache is full, replacement algorithms like LRU and FIFO are used to determine which content to remove. The cache can write to main memory using either a write-through or write-back policy.
Applications of paralleL processing



Applications of paralleL processingPage Maker This document discusses various applications of parallel processing. It describes how parallel processing is used in numeric weather prediction to forecast weather by processing large amounts of observational data. It is also used in oceanography and astrophysics to study oceans and conduct particle simulations. Other applications mentioned include socioeconomic modeling, finite element analysis, artificial intelligence, seismic exploration, genetic engineering, weapon research, medical imaging, remote sensing, energy exploration, and more. The document also discusses loosely coupled and tightly coupled multiprocessors and the differences between the two approaches.
Aca2 01 new



Aca2 01 newSumit Mittu This document is a chapter summary for "CSE539: Advanced Computer Architecture" taught by Sumit Mittu, Assistant Professor at Lovely Professional University. The chapter discusses parallel computer models and covers topics like the evolution of computing through generations of computers, parallel computer classifications like multiprocessors and multicomputers, and theoretical parallel models like PRAM. It provides examples of parallel systems from each generation and model. The goal is to introduce students to parallel architectures and taxonomy.
Von Neumann vs Harvard Architecture



Von Neumann vs Harvard ArchitectureOLSON MATUNGA The Von Neumann and Harvard architectures are two common computer architectures. The Von Neumann architecture uses a single memory to store both programs and data, accessed via a shared bus, while the Harvard architecture separates memory and uses two separate buses for program and data access. The Von Neumann architecture has advantages of simpler design and lower cost while the Harvard allows parallel instruction and data processing but has higher development costs. They differ primarily in their memory structure and bus configurations.
Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computing



Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computingVajira Thambawita This gives you an introduction to parallel and distributed computing. More details: https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials
Similar to Lecture 2 (20)
Parallel & Distributed processing



Parallel & Distributed processingSyed Zaid Irshad The document provides an introduction to high performance computing architectures. It discusses the von Neumann architecture that has been used in computers for over 40 years. It then explains Flynn's taxonomy, which classifies parallel computers based on whether their instruction and data streams are single or multiple. The main categories are SISD, SIMD, MISD, and MIMD. It provides examples of computer architectures that fall under each classification. Finally, it discusses different parallel computer memory architectures, including shared memory, distributed memory, and hybrid models.
Lec 2 (parallel design and programming)



Lec 2 (parallel design and programming)Sudarshan Mondal This document discusses parallel computing architectures and concepts. It begins by describing Von Neumann architecture and how parallel computers follow the same basic design but with multiple units. It then covers Flynn's taxonomy which classifies computers based on their instruction and data streams as Single Instruction Single Data (SISD), Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD), Multiple Instruction Single Data (MISD), or Multiple Instruction Multiple Data (MIMD). Each classification is defined. The document also discusses parallel terminology, synchronization, scalability, and Amdahl's law on the costs and limits of parallel programming.
unit 4.pptx



unit 4.pptxSUBHAMSHARANRA211100 This document provides an overview of parallelism, including the need for parallelism, types of parallelism, applications of parallelism, and challenges in parallelism. It discusses instruction level parallelism and data level parallelism in software. It describes Flynn's classification of computer architectures and the categories of SISD, SIMD, MISD, and MIMD. It also covers hardware multi-threading, uni-processors vs multi-processors, multi-core processors, memory in multi-processor systems, cache coherency, and the MESI protocol.
unit 4.pptx



unit 4.pptxSUBHAMSHARANRA211100 This document provides an overview of parallelism and parallel computing architectures. It discusses the need for parallelism to improve performance and throughput. The main types of parallelism covered are instruction level parallelism, data parallelism, and task parallelism. Flynn's taxonomy is introduced for classifying computer architectures based on their instruction and data streams. Common parallel architectures like SISD, SIMD, MIMD are explained. The document also covers memory architectures for multi-processor systems including shared memory, distributed memory, and cache coherency protocols.
Parallel architecture &programming



Parallel architecture &programmingIsmail El Gayar This document discusses parallel architecture and parallel programming. It begins with an introduction to von Neumann architecture and serial computation. Then it defines parallel architecture, outlines its benefits, and describes classifications of parallel processors including multiprocessor architectures. It also discusses parallel programming models, how to design parallel programs, and examples of parallel algorithms. Specific topics covered include shared memory and distributed memory architectures, message passing and data parallel programming models, domain and functional decomposition techniques, and a case study on developing parallel web applications using Java threads and mobile agents.
Parallel architecture-programming



Parallel architecture-programmingShaveta Banda This document discusses parallel architecture and parallel programming. It begins by introducing the traditional von Neumann architecture and serial computation model. It then defines parallel architecture, noting its use of multiple processors to solve problems concurrently by breaking work into discrete parts that can execute simultaneously. Key concepts in parallel programming models are also introduced, including shared memory, message passing, and data parallelism. The document outlines approaches for designing parallel programs, such as automatic and manual parallelization, as well as domain and functional decomposition. It concludes by mentioning examples of parallel algorithms and case studies in parallel application development using Java mobile agents and threads.
CSA unit5.pptx



CSA unit5.pptxAbcvDef Parallel computing involves using multiple processing units simultaneously to solve computational problems. It can save time by solving large problems or providing concurrency. The basic design involves memory storing program instructions and data, and a CPU fetching instructions from memory and sequentially performing them. Flynn's taxonomy classifies computer systems based on their instruction and data streams as SISD, SIMD, MISD, or MIMD. Parallel architectures can also be classified based on their memory arrangement as shared memory or distributed memory systems.
Week # 1.pdf



Week # 1.pdfgiddy5 This document provides an overview of the topics that will be covered in the CS 3006 Parallel and Distributed Computing course. It introduces the course instructor, textbook, schedule, evaluation criteria, and pre-requisites. The first three lectures are also summarized, covering introduction and definitions, shared and distributed memory systems, parallel execution terms and definitions, overhead in parallel computing, speed-up and Amdahl's law, and Flynn's taxonomy of computer architectures.
Aca module 1



Aca module 1Avinash_N Rao This document provides an overview of parallel computing models and the evolution of computer hardware and software. It discusses:
1) Flynn's taxonomy which classifies computer architectures based on whether they have a single or multiple instruction/data streams. This includes SISD, SIMD, MISD, and MIMD models.
2) The attributes that influence computer performance such as hardware technology, algorithms, data structures, and programming tools. Performance is measured by turnaround time, clock rate, and cycles per instruction.
3) A brief history of computing from mechanical devices to modern electronic computers organized into generations defined by advances in hardware and software.
Multiprocessor.pptx



Multiprocessor.pptxMuhammad54342 Flynn's taxonomy classifies computer architectures based on the number of instruction and data streams. The main categories are:
1) SISD - Single instruction, single data stream (von Neumann architecture)
2) SIMD - Single instruction, multiple data streams (vector/MMX processors)
3) MIMD - Multiple instruction, multiple data streams (most multiprocessors including multi-core)
Multiprocessor architectures can be organized as shared memory (SMP/UMA) or distributed memory (message passing/DSM). Shared memory allows automatic sharing but can have memory contention issues, while distributed memory requires explicit communication but scales better. Achieving high parallel performance depends on minimizing sequential
Computer Architecture CSN221_Lec_37_SpecialTopics.pdf



Computer Architecture CSN221_Lec_37_SpecialTopics.pdfssuser034ce1 Computer Architecture CSN221_Lec_37_SpecialTopics.pdf
CA UNIT IV.pptx



CA UNIT IV.pptxssuser9dbd7e Unit IV discusses parallelism and parallel processing architectures. It introduces Flynn's classifications of parallel systems as SISD, MIMD, SIMD, and SPMD. Hardware approaches to parallelism include multicore processors, shared memory multiprocessors, and message-passing systems like clusters, GPUs, and warehouse-scale computers. The goals of parallelism are to increase computational speed and throughput by processing data concurrently across multiple processors.
Computing notes



Computing notesthenraju24 This document provides an overview of distributed computing. It discusses key concepts like distributed systems having computers with separate memories that communicate over a network. Distributed computing involves splitting a program into parts that run simultaneously on multiple computers. The document also covers the history of distributed computing, examples like grid and cloud computing, motivations like performance and fault tolerance, and challenges around complexity and security.
Parallel Processors (SIMD) 



Parallel Processors (SIMD) Ali Raza This document discusses parallel processors, specifically single instruction multiple data (SIMD) processors. It provides details on vector processors and array processors. Vector processors utilize vector instructions that operate on arrays of data called vectors. They have vector registers, functional units, and load/store units. Array processors perform parallel computations on large data arrays using multiple identical processing elements. The document describes dedicated memory and global memory organizations for array processors. It provides examples of early SIMD machines like ILLIAC IV.
Parallel Processors (SIMD) 



Parallel Processors (SIMD) Ali Raza SIMD (single instruction, multiple data) parallel processors exploit data-level parallelism by performing the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously using a single instruction. Vector processors are a type of SIMD parallel processor that operate on 1D arrays of data called vectors. They contain vector registers that can hold multiple data elements and functional units that perform arithmetic and logical operations in a pipelined fashion on entire vectors. Array processors are another type of SIMD machine composed of multiple identical processing elements that perform computations in lockstep under the control of a single instruction unit. Early examples include the ILLIAC IV and Cray X1 supercomputers. Multimedia extensions like MMX provide SIMD integer operations to improve performance of multimedia applications.
Parallel computing



Parallel computingVinay Gupta Parallel computing involves solving computational problems simultaneously using multiple processors. It can save time and money compared to serial computing and allow larger problems to be solved. Parallel programs break problems into discrete parts that can be solved concurrently on different CPUs. Shared memory parallel computers allow all processors to access a global address space, while distributed memory systems require communication between separate processor memories. Hybrid systems combine shared and distributed memory architectures.
High performance computing



High performance computingpunjab engineering college, chandigarh This document provides an overview of high performance computing infrastructures. It discusses parallel architectures including multi-core processors and graphical processing units. It also covers cluster computing, which connects multiple computers to increase processing power, and grid computing, which shares resources across administrative domains. The key aspects covered are parallelism, memory architectures, and technologies used to implement clusters like Message Passing Interface.
intro, definitions, basic laws+.pptx



intro, definitions, basic laws+.pptxssuser413a98 The document discusses the importance and applications of high performance computing (HPC). It provides examples of when HPC is needed, such as to perform time-consuming operations more quickly or handle high volumes of data/transactions. It also outlines what HPC studies, including hardware components like computer architecture and networks, as well as software elements like programming paradigms and languages. Additionally, it notes the international competition around developing exascale supercomputers and some of the research areas that utilize HPC, such as finance, weather forecasting, and health care applications involving large datasets.
Ad
More from Mr SMAK (20)
Fyp list batch-2009 (project approval -rejected list)



Fyp list batch-2009 (project approval -rejected list)Mr SMAK This document lists 29 final year projects for computer science students in the BS (CS) Batch of 2009 at Sir Syed University of Engineering & Technology in Karachi, Pakistan. It provides the roll numbers, names, project titles and assigned supervisors for each group of students. The remarks column notes whether project ideas were accepted, rejected or required revisions and additional consultation with supervisors.
Assigments2009



Assigments2009Mr SMAK The document contains 8 questions for an assignment on wireless application protocol. The questions cover topics such as comparing circuit-switched and packet-switched networks, frequency division multiplexing of voice channels, spread spectrum techniques, calculating bandwidth requirements for frequency division multiplexing with guard bands, advantages and disadvantages of bursty versus continuous data transmission in wireless systems, and disadvantages of wireless LANs compared to wired LANs. The last question discusses applications where the disadvantages of wireless LANs may be outweighed or override the advantages of wireless mobility.
Week1



Week1Mr SMAK This document provides an introduction to wireless communication and wireless application protocol (WAP). It discusses the benefits of wireless communication like freedom from wires and global coverage. It also covers some of the technical challenges in wireless communication like efficient use of spectrum, mobility support, and maintaining quality of service over unreliable links. It defines wireless communication and differentiates between wireless and mobile. It also describes various types of wireless technologies and their limitations.
Evaluation of cellular network



Evaluation of cellular networkMr SMAK The document summarizes the evolution of wireless networks from 1G to 4G. 1G networks used analog signals and standards like NMT, AMPS, and TACS. 2G introduced digital cellular and standards like GSM, CDMA, and IS-136. 2.5G provided upgrades like GPRS, EDGE, and CDMA2000 1x to support higher data rates. 3G networks supported broadband data and included W-CDMA and CDMA2000. 4G aims to provide fully integrated IP services with speeds over 100 Mbps.
Common protocols



Common protocolsMr SMAK Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) allows devices to access the Internet over wireless networks. There are three main categories of protocols for managing shared access to wireless networks: fixed assignment, demand assignment, and random assignment. Fixed assignment divides resources like frequency bands or time slots and allocates them exclusively. Demand assignment allocates resources only to nodes that need them. Random assignment does not preallocate resources and relies on collision detection and retransmission to manage shared access. Common protocols that fall under these categories include FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, ALOHA, and CSMA.
Cellular network



Cellular networkMr SMAK Wireless cellular networks divide geographic areas into cells served by base stations to allow for frequency reuse. As users travel between cells, their calls are handed off seamlessly. Cellular systems improve capacity by allocating unique frequency groups to each cell and reusing the same frequencies in cells sufficiently distant from each other. Larger networks connect multiple base stations and mobile switching centers to facilitate roaming and complete calls between mobile and fixed users.
Lecture 6.1



Lecture 6.1Mr SMAK This chapter discusses shared memory architecture and classifications of shared memory systems. It describes Uniform Memory Access (UMA), Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA), and Cache Only Memory Architecture (COMA). It also covers bus-based symmetric multiprocessors and basic cache coherency methods like write-through, write-back, write-invalidate, and write-update. Finally, it discusses snooping protocols for maintaining cache coherency, including write-invalidate and write-through, write-invalidate and write-back, write-once, write-update and partial write-through, and write-update and write-back.
Lecture 6



Lecture 6Mr SMAK This document discusses parallel computer memory architectures, including shared memory, distributed memory, and hybrid architectures. Shared memory architectures allow all processors to access a global address space, but lack scalability. Distributed memory assigns separate memory to each processor requiring explicit communication between tasks. Hybrid architectures combine shared memory within nodes and distributed memory between nodes for scalability.
Parallel architecture



Parallel architectureMr SMAK This document discusses parallel computers and architectures. It defines parallel computers as collections of processing elements that cooperate and communicate to solve problems fast. It then examines questions about parallel computers, different types of parallelism, and opportunities for parallel computing in scientific and commercial applications. Finally, it discusses fundamental issues in parallel architectures, including naming, synchronization, latency and bandwidth, and different parallel frameworks and models like shared memory, message passing, and data parallelism.
Lecture 3



Lecture 3Mr SMAK This document provides an overview of parallel computing and parallel processing. It discusses:
1. The three types of concurrent events in parallel processing: parallel, simultaneous, and pipelined events.
2. The five fundamental factors for projecting computer performance: clock rate, cycles per instruction (CPI), execution time, million instructions per second (MIPS) rate, and throughput rate.
3. The four programmatic levels of parallel processing from highest to lowest: job/program level, task/procedure level, interinstruction level, and intrainstruction level.
Lecture 1



Lecture 1Mr SMAK This document provides an overview of a course on parallel computing for undergraduates. It outlines the theoretical and practical components of the course, including concepts that will be covered pre- and post-midterm. It also details assessment criteria, reading resources, and codes of conduct for the class.
Lecture 6



Lecture 6Mr SMAK This document discusses parallel computer memory architectures, including shared memory, distributed memory, and hybrid architectures. Shared memory architectures allow all processors to access a global address space, but lack scalability. Distributed memory assigns separate memory to each processor requiring explicit communication between tasks. Hybrid architectures combine shared memory within nodes and distributed memory between nodes for scalability.
Lecture 6.1



Lecture 6.1Mr SMAK This chapter discusses shared memory architecture and classifications of shared memory systems. It describes Uniform Memory Access (UMA), Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA), and Cache Only Memory Architecture (COMA). It also covers basic cache coherency methods like write-through, write-back, write-invalidate, and write-update. Finally, it discusses snooping protocols and cache coherency techniques used in shared memory systems.
Chapter 2 ASE



Chapter 2 ASEMr SMAK Planning and scheduling involves fundamental engineering principles of first analyzing a problem and then developing a solution to meet defined needs. Key objectives include effective time management, optimizing the sequence of events, and defining necessary resources to ensure timely project progress. Gantt charts and PERT charts are common tools used to plan and schedule projects, with Gantt charts focusing more on calendar timelines and PERT charts emphasizing task dependencies. Function point analysis is an alternative technique for estimating the time and effort required for a software project based on identifying and weighting various user-requested application components and functionalities.
Structure of project plan and schedule



Structure of project plan and scheduleMr SMAK The document outlines a project plan structure covering 5 sections: 1) the software engineering process model and team roles, 2) risk analysis and management methods, 3) tasks and scheduling, 4) resources, costs and estimates, and 5) monitoring and management methods to track the project. A sample project plan is attached for reference.
Proposal format



Proposal formatMr SMAK The document outlines guidelines for formatting a final year project proposal. It includes sections for the project title, student names and roll numbers, main text formatting, headings formatting, figures and tables, and references. Guidelines are provided for font type, size, indentation, spacing, capitalization, and other formatting rules to maintain a consistent structure and appearance.
Proposal announcement batch2009



Proposal announcement batch2009Mr SMAK Students of the final year 2009 batch at Sir Syed University of Engineering & Technology are advised to submit 3 copies of their final year project proposals by March 03, 2012. The proposals can be in the areas of artificial intelligence, expert systems, communication & networking, 3D applications, mobile computing, or web applications. Proposals should be submitted to faculty members Naheed Khan, Shardha Nand, Asharaf Ali Waseem, or M. Kashif Khan. Projects must be completed by groups of 3 to 4 students, who will later defend their proposal to the final year project committee.
List ofsuparco projectsforuniversities



List ofsuparco projectsforuniversitiesMr SMAK This document outlines 29 potential projects for university students to undertake with SUPARCO. The projects range from designing components of small satellites to analyzing aerodynamic properties to developing encryption systems. SUPARCO will provide funding and engineering support for selected projects. Students will gain hands-on experience working on challenges relevant to SUPARCO's objectives.
Fyp timeline & assessment policy batch 2009



Fyp timeline & assessment policy batch 2009Mr SMAK The document outlines the timeline and assessment policy for final year projects (FYP) for computer science students graduating in 2009 from Sir Syed University of Engineering & Technology in Karachi, Pakistan. Key dates are provided for submitting registration forms, proposals, requirements documents, design documents, progress reviews, reports and presentations. The assessment policy breaks down the project into components like requirements, design, presentations and reviews, allocating marks between supervisor and evaluation committee assessments with the total project marks equalling 200.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Role of Data Annotation Services in AI-Powered Manufacturing



Role of Data Annotation Services in AI-Powered ManufacturingAndrew Leo From predictive maintenance to robotic automation, AI is driving the future of manufacturing. But without high-quality annotated data, even the smartest models fall short.
Discover how data annotation services are powering accuracy, safety, and efficiency in AI-driven manufacturing systems.
Precision in data labeling = Precision on the production floor.
Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...



Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...Impelsys Inc. Impelsys provided a robust testing solution, leveraging a risk-based and requirement-mapped approach to validate ICU Connect and CritiXpert. A well-defined test suite was developed to assess data communication, clinical data collection, transformation, and visualization across integrated devices.
Rock, Paper, Scissors: An Apex Map Learning Journey



Rock, Paper, Scissors: An Apex Map Learning JourneyLynda Kane Slide Deck from Presentations to WITDevs (April 2021) and Cleveland Developer Group (6/28/2023) on using Rock, Paper, Scissors to learn the Map construct in Salesforce Apex development.
Manifest Pre-Seed Update | A Humanoid OEM Deeptech In France



Manifest Pre-Seed Update | A Humanoid OEM Deeptech In Francechb3 The latest updates on Manifest's pre-seed stage progress.
Technology Trends in 2025: AI and Big Data Analytics



Technology Trends in 2025: AI and Big Data AnalyticsInData Labs At InData Labs, we have been keeping an ear to the ground, looking out for AI-enabled digital transformation trends coming our way in 2025. Our report will provide a look into the technology landscape of the future, including:
-Artificial Intelligence Market Overview
-Strategies for AI Adoption in 2025
-Anticipated drivers of AI adoption and transformative technologies
-Benefits of AI and Big data for your business
-Tips on how to prepare your business for innovation
-AI and data privacy: Strategies for securing data privacy in AI models, etc.
Download your free copy nowand implement the key findings to improve your business.
Into The Box Conference Keynote Day 1 (ITB2025)



Into The Box Conference Keynote Day 1 (ITB2025)Ortus Solutions, Corp This is the keynote of the Into the Box conference, highlighting the release of the BoxLang JVM language, its key enhancements, and its vision for the future.
Network Security. Different aspects of Network Security.



Network Security. Different aspects of Network Security.gregtap1 Network Security. Different aspects of Network Security.
What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...



What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...Vishnu Singh Chundawat The MCP (Model Context Protocol) is a framework designed to manage context and interaction within complex systems. This SlideShare presentation will provide a detailed overview of the MCP Model, its applications, and how it plays a crucial role in improving communication and decision-making in distributed systems. We will explore the key concepts behind the protocol, including the importance of context, data management, and how this model enhances system adaptability and responsiveness. Ideal for software developers, system architects, and IT professionals, this presentation will offer valuable insights into how the MCP Model can streamline workflows, improve efficiency, and create more intuitive systems for a wide range of use cases.
Procurement Insights Cost To Value Guide.pptx



Procurement Insights Cost To Value Guide.pptxJon Hansen Procurement Insights integrated Historic Procurement Industry Archives, serves as a powerful complement — not a competitor — to other procurement industry firms. It fills critical gaps in depth, agility, and contextual insight that most traditional analyst and association models overlook.
Learn more about this value- driven proprietary service offering here.
Drupalcamp Finland – Measuring Front-end Energy Consumption



Drupalcamp Finland – Measuring Front-end Energy ConsumptionExove How to measure web front-end energy consumption using Firefox Profiler. Presented in DrupalCamp Finland on April 25th, 2025.
Learn the Basics of Agile Development: Your Step-by-Step Guide



Learn the Basics of Agile Development: Your Step-by-Step GuideMarcel David New to Agile? This step-by-step guide is your perfect starting point. "Learn the Basics of Agile Development" simplifies complex concepts, providing you with a clear understanding of how Agile can improve software development and project management. Discover the benefits of iterative work, team collaboration, and flexible planning.
Cyber Awareness overview for 2025 month of security



Cyber Awareness overview for 2025 month of securityriccardosl1 Cyber awareness training educates employees on risk associated with internet and malicious emails
Buckeye Dreamin' 2023: De-fogging Debug Logs



Buckeye Dreamin' 2023: De-fogging Debug LogsLynda Kane Slide Deck from Buckeye Dreamin' 2023: De-fogging Debug Logs which went over how to capture and read Salesforce Debug Logs
Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdf



Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdfSoftware Company Explore the benefits and features of advanced logistics management software for businesses in Riyadh. This guide delves into the latest technologies, from real-time tracking and route optimization to warehouse management and inventory control, helping businesses streamline their logistics operations and reduce costs. Learn how implementing the right software solution can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and provide a competitive edge in the growing logistics sector of Riyadh.
The Evolution of Meme Coins A New Era for Digital Currency ppt.pdf



The Evolution of Meme Coins A New Era for Digital Currency ppt.pdfAbi john Analyze the growth of meme coins from mere online jokes to potential assets in the digital economy. Explore the community, culture, and utility as they elevate themselves to a new era in cryptocurrency.
How Can I use the AI Hype in my Business Context?



How Can I use the AI Hype in my Business Context?Daniel Lehner 𝙄𝙨 𝘼𝙄 𝙟𝙪𝙨𝙩 𝙝𝙮𝙥𝙚? 𝙊𝙧 𝙞𝙨 𝙞𝙩 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙜𝙖𝙢𝙚 𝙘𝙝𝙖𝙣𝙜𝙚𝙧 𝙮𝙤𝙪𝙧 𝙗𝙪𝙨𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙨𝙨 𝙣𝙚𝙚𝙙𝙨?
Everyone’s talking about AI but is anyone really using it to create real value?
Most companies want to leverage AI. Few know 𝗵𝗼𝘄.
✅ What exactly should you ask to find real AI opportunities?
✅ Which AI techniques actually fit your business?
✅ Is your data even ready for AI?
If you’re not sure, you’re not alone. This is a condensed version of the slides I presented at a Linkedin webinar for Tecnovy on 28.04.2025.
Dev Dives: Automate and orchestrate your processes with UiPath Maestro



Dev Dives: Automate and orchestrate your processes with UiPath MaestroUiPathCommunity This session is designed to equip developers with the skills needed to build mission-critical, end-to-end processes that seamlessly orchestrate agents, people, and robots.
📕 Here's what you can expect:
- Modeling: Build end-to-end processes using BPMN.
- Implementing: Integrate agentic tasks, RPA, APIs, and advanced decisioning into processes.
- Operating: Control process instances with rewind, replay, pause, and stop functions.
- Monitoring: Use dashboards and embedded analytics for real-time insights into process instances.
This webinar is a must-attend for developers looking to enhance their agentic automation skills and orchestrate robust, mission-critical processes.
👨🏫 Speaker:
Andrei Vintila, Principal Product Manager @UiPath
This session streamed live on April 29, 2025, 16:00 CET.
Check out all our upcoming Dev Dives sessions at https://community.uipath.com/dev-dives-automation-developer-2025/.
DevOpsDays Atlanta 2025 - Building 10x Development Organizations.pptx



DevOpsDays Atlanta 2025 - Building 10x Development Organizations.pptxJustin Reock Building 10x Organizations with Modern Productivity Metrics
10x developers may be a myth, but 10x organizations are very real, as proven by the influential study performed in the 1980s, ‘The Coding War Games.’
Right now, here in early 2025, we seem to be experiencing YAPP (Yet Another Productivity Philosophy), and that philosophy is converging on developer experience. It seems that with every new method we invent for the delivery of products, whether physical or virtual, we reinvent productivity philosophies to go alongside them.
But which of these approaches actually work? DORA? SPACE? DevEx? What should we invest in and create urgency behind today, so that we don’t find ourselves having the same discussion again in a decade?
What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...



What is Model Context Protocol(MCP) - The new technology for communication bw...Vishnu Singh Chundawat
Lecture 2
- 1. Parallel Computing Concepts and Terminologies
- 2. Terminologies • Task – A logically discrete section of computational work. A task is typically a program or program-like set of instructions that is executed by a processor. • Parallel Task – A task that can be executed by multiple processors safely (yields correct results) • Serial Execution – Execution of a program sequentially, one statement at a time. In the simplest sense, this is what happens on a one processor machine. However, virtually all parallel tasks will have sections of a parallel program that must be executed serially. • Parallel Execution – Execution of a program by more than one task, with each task being able to execute the same or different statement at the same moment in time.
- 3. Terminologies • Shared Memory – From a strictly hardware point of view, describes a computer architecture where all processors have direct (usually bus based) access to common physical memory. In a programming sense, it describes a model where parallel tasks all have the same "picture" of memory and can directly address and access the same logical memory locations regardless of where the physical memory actually exists. • Distributed Memory – In hardware, refers to network based memory access for physical memory that is not common. As a programming model, tasks can only logically "see" local machine memory and must use communications to access memory on other machines where other tasks are executing
- 4. Terminologies • Communications – Parallel tasks typically need to exchange data. There are several ways this can be accomplished, such as through a shared memory bus or over a network, however the actual event of data exchange is commonly referred to as communications regardless of the method employed. • Synchronization – The coordination of parallel tasks in real time, very often associated with communications. Often implemented by establishing a synchronization point within an application where a task may not proceed further until another task(s) reaches the same or logically equivalent point. Synchronization usually involves waiting by at least one task, and can therefore cause a parallel application's wall clock execution time to increase
- 5. Terminologies • Granularity – In parallel computing, granularity is a qualitative measure of the ratio of computation to communication. • Coarse: relatively large amounts of computational work are done between communication events • Fine: relatively small amounts of computational work are done between communication events • Observed Speedup – Observed speedup of a code which has been parallelized, defined as: wall-clock time of serial execution / wall-clock time of parallel execution – One of the simplest and most widely used indicators for
- 6. von Neumann Architecture • For over 40 years, virtually all computers have followed a common machine model known as the von Neumann computer. Named after the Hungarian mathematician John von Neumann. • A von Neumann computer uses the stored- program concept. The CPU executes a stored program that specifies a sequence of read and write operations on the memory.
- 7. von Neumann Architecture • Memory is used to store both program and data instructions • Program instructions are coded data which tell the computer to do something • Data is simply information to be used by the program • A central processing unit (CPU) gets instructions and/or data from memory, decodes the instructions and then sequentially performs them
- 8. Flynn's Classical Taxonomy • There are different ways to classify parallel computers. One of the more widely used classifications, in use since 1966, is called Flynn's Taxonomy. • Flynn's taxonomy distinguishes multi-processor computer architectures according to how they can be classified along the two independent dimensions of Instruction and Data. Each of these dimensions can have only one of two possible states: Single or Multiple.
- 9. Flynn's Classical Taxonomy • The matrix below defines the 4 possible classifications according to Flynn. •S I S D •S I M D •Single Instruction, Single Data •Single Instruction, Multiple Data •M I S D •M I M D •Multiple Instruction, Single •Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data Data
- 10. Single Instruction, Single Data (SISD) • A serial (non-parallel) computer • Single instruction: only one instruction stream is being acted on by the CPU during any one clock cycle • Single data: only one data stream is being used as input during any one clock cycle • Deterministic execution • This is the oldest and until recently, the most prevalent form of computer • Eg: most PCs, single CPU workstations and mainframes
- 11. Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD): • A type of parallel computer • Single instruction: All processing units execute the same instruction at any given clock cycle • Multiple data: Each processing unit can operate on a different data element • This type of machine typically has an instruction dispatcher, a very high-bandwidth internal network, and a very large array of very small- capacity instruction units.
- 12. Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD):
- 13. Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD): • Best suited for specialized problems characterized by a high degree of regularity,such as image processing. • Synchronous (lockstep) and deterministic execution • Two varieties: Processor Arrays and Vector Pipelines • Examples (some extinct): o Processor Arrays: Connection Machine CM-2, Maspar MP-1, MP-2 o Vector Pipelines: IBM 9000, Cray C90, Fujitsu VP, NEC SX-2, Hitachi S820
- 14. Multiple Instruction, Single Data (MISD): • Few actual examples of this class of parallel computer have ever existed • Some conceivable examples might be: – multiple frequency filters operating on a single signal stream – multiple cryptography algorithms attempting to crack a single coded message.
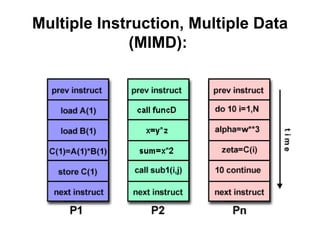
- 15. Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data (MIMD): • Currently, the most common type of parallel computer • Multiple Instruction: every processor may be executing a different instruction stream • Multiple Data: every processor may be working with a different data stream • Execution can be synchronous or asynchronous, deterministic or non- deterministic • Examples: most current supercomputers, networked parallel computer "grids" and multi-processor SMP computers - including some types of PCs.
- 16. Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data (MIMD):
- 18. scalar sequential Lookahead Functional I/E overlap parallelism Multiple Func. Units Pipeline Implicit Explicit Vector vector Mem-to-Mem Reg-to-Reg SIMD MIMD Assoc. Processor Multicomputer Multiprocessor Processor Array




