Ad
Lecture 9 key distribution and user authentication
- 2. Overview • Symmetric Key Distribution using Symmetric Encryption Kerberos • Key Distribution using Asymmetric Encryption X.509 Certificates 2 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 3. Symmetric Key Distribution • Two parties must share same key Protected from the access of others Frequent key exchange to limit amount of data compromised • Key can be exchanged 1. Physical delivery to B 2. A third party physically deliver it to A and B 3. Re-usage of old key to exchange new key 4. A & B both communicate securely with C, C delivers the key For option 1 & 2 require manual delivery For option 3 link encryption or end-to-end encryption, What if old key is compromised 3 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 4. Symmetric Key Distribution For option 4 two kinds of keys are used – Session Key: One time key – Permanent Key: for distributing session key. – Necessary element, Key Distribution Center (KDC): determines which systems are allowed to communicate with each other. – Operation of KDC • A wish to communicate B, transmits request to KDC. Communication is encrypted using a master key • KDC approves connection and creates one time session key. Session key is encrypted with permanent keys of A & B and delivered to A & B. • A & B set up logical connection and uses session key. Most widely application to use this approach is KERBEROS 4 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 5. Security Concerns • Key concerns are confidentiality and timeliness • To provide confidentiality must encrypt identification and session key info which requires the use of previously shared private or public keys • Need timeliness to prevent replay attacks • Provided by using sequence numbers or timestamps or challenge/response 5 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 6. KERBEROS In Greek mythology, a many headed dog, the guardian of the entrance of Hades 6 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 7. KERBEROS • Users wish to access services on servers. • Three threats exist: User pretend to be another user. User alter the network address of a workstation. User eavesdrop on exchanges and use a replay attack. 7 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 8. KERBEROS • Assumes a distributed client/server architecture • Provides a centralized authentication server to authenticate users to servers and servers to users. • Relies on conventional encryption, making no use of public- key encryption • Two versions: version 4 and 5 • Version 4 makes use of DES 8 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 9. Requirements for Kerberos • Secure: Eavesdropper should not be able to obtain the necessary information to impersonate a user • Reliable: Kerberos should employ a distributed server architecture, systems backing up each other • Transparent: User should not be aware that authentication is taking place • Scalable: The system should be capable of supporting large number of clients and servers 9 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 10. Overview of Kerberos • AS = Authentication Server • SS = Service Server • TGS = Ticket-Granting Server • TGT = Ticket Granting Ticket • User Client-based Logon A user enters a username and password on the client machine. The client performs a one-way function (hash usually) on the entered password, and this becomes the secret key of the client/user. 10 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 11. Overview of Kerberos • Client Authentication The client sends a clear text message of the user ID to the AS requesting services on behalf of the user. (Note: Neither the secret key nor the password is sent to the AS.) – The AS generates the secret key by hashing the password of the user found at the database. The AS checks client rights in its database. If valid, the AS sends back the following two messages to the client: – Message A: Client/TGS Session Key encrypted using the secret key of the client/user. – Message B: Ticket-to Get-Ticket (which includes the client ID, client network address, ticket validity period, and the client/TGS session key) encrypted using the secret key of the TGS. 11 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 12. Overview of Kerberos Client receives messages A and B, and decrypt message A to obtain the Client/TGS Session Key. – The session key is used for further communications with the TGS. (Note: The client cannot decrypt Message B, as it is encrypted using TGS's secret key.) 12 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 13. Overview of Kerberos • Client Service Authorization When requesting services, the client sends the following two messages to the TGS: – Message C: Composed of the TGT from message B and the ID of the requested service. – Message D: Authenticator (which is composed of the client ID and the timestamp), encrypted using the Client/TGS Session Key. TGS retrieves message B out of message C. It decrypts message B using the TGS secret key to have "client/TGS session key". Using this key, the TGS decrypts message D (Authenticator) and sends the following two messages to the client: – Message E: Client-to-server ticket (which includes the client ID, client network address, validity period and Client/Server Session Key) encrypted using the service's secret key. – Message F: Client/server session key encrypted with the Client/TGS Session Key. 13 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 14. Overview of Kerberos • Client Service Authorization For requesting services, the client sends the following two messages to the TGS: – Message C: Composed of the TGT from message B and the ID of the requested service. – Message D: Authenticator (which is composed of the client ID and the timestamp), encrypted using the Client/TGS Session Key. TGS retrieves message B out of message C. – It decrypts message B using the TGS secret key. This gives it the "client/TGS session key". Using this key, the TGS decrypts message D (Authenticator) and sends the following two messages to the client: • Message E: Client-to-server ticket (which includes the client ID, client network address, validity period and Client/Server Session Key) encrypted using the service's secret key. • Message F: Client/server session key encrypted with the Client/TGS Session Key. 14 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 15. Overview of Kerberos • Client Service Request Client receives messages E and F from TGS. The client connects to the SS and sends the following two messages: – Message E from the previous step (the client-to-server ticket, encrypted using service's secret key). – Message G: a new Authenticator, which includes the client ID, timestamp and is encrypted using client/server session key. The SS decrypts the ticket using its own secret key to retrieve the Client/Server Session Key. Using the sessions key, SS decrypts the Authenticator and sends the following message to the client to confirm its true identity and willingness to serve the client: – Message H: the timestamp found in client's Authenticator plus 1, encrypted using the Client/Server Session Key. ƒ The client decrypts the confirmation using the Client/Server Session Key and checks whether the timestamp is correctly updated. If so, then the client can trust the server and can start issuing service requests to the server. 15 The server provides the requested services to the client. Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 16. Overview of Kerberos 16 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 17. Kerberos Version 4 • Terms: C = Client AS = authentication server V = server IDc = identifier of user on C IDv = identifier of V Pc = password of user on C ADc = network address of C Kv = secret encryption key shared by AS and V TS = timestamp || = concatenation 17 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 18. A Simple Authentication Dialogue (1) C AS: IDc || Pc || IDv (2) AS C: Ticket (3) C V: IDc || Ticket • Ticket = EKv[IDc || Pc || IDv] 18 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 19. Remaining problems 2. Number of times that a user has to enter a password 4. Plain-text transmission of password 19 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 20. More secure Authentication Dialogue Once per user logon session: • C AS: IDC || IDtgs • AS C: EKc [ Tickettgs ] Once per type of service: (3) C TGS: IDC || IDV ||Tickettgs (4) TGS C: TicketV Once per service session: (5) C V: IDC || TicketV 20 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 21. Remaining problems 3. The lifetime associated with the ticket-granting ticket 5. Servers are not able to authenticate themselves 21 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 22. Version 4 Authentication Dialogue Authentication Service Exhange: To obtain Ticket-Granting Ticket • C AS: IDc || IDtgs ||TS1 • AS C: EKc [Kc,tgs|| IDtgs || TS2 || Lifetime2 || Tickettgs] Ticket-Granting Service Echange: To obtain Service-Granting Ticket (3) C TGS: IDv ||Tickettgs ||Authenticatorc (4) TGS C: EKc [Kc,¨v|| IDv || TS4 || Ticketv] Client/Server Authentication Exhange: To Obtain Service (5) C V: Ticketv || Authenticatorc (6) V C: EKc,v[TS5 +1] 22 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 23. Version 4 Authentication Dialogue • Problems: Lifetime associated with the ticket-granting ticket If to short repeatedly asked for password If to long greater opportunity to replay • The threat is that an opponent will steal the ticket and use it before it expires 23 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 24. Overview of Kerberos 24 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 25. Request for Service in Another Realm 25 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 26. Difference Between Version 4 and 5 • Encryption system dependence (V.4 DES) • IP - Internet protocol dependence • Message byte ordering • Ticket lifetime • Authentication forwarding • Inter realm authentication 26 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 27. Kerberos - in practice • Currently have two Kerberos versions: 4 : restricted to a single realm 5 : allows inter-realm authentication, in beta test • Kerberos v5 is an Internet standard • Specified in RFC1510, and used by many utilities • To use Kerberos: need to have a Key Distribution Center (KDC) on your network need to have Kerberised applications running on all participating systems major problem - US export restrictions Kerberos cannot be directly distributed outside the US in source format (& binary versions must obscure crypto routine entry points and have no encryption) else crypto libraries must be re-implemented locally 27 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 28. Key Distribution using Asymmetric Encryption • Problem : The distribution of Public Keys What if a fake user imparsionate to be a legitimate user and distribute his keys • Solution : Public-Key Certificates Consists of a public key + User ID of the key owner with whole block signed by a trusted third party Third party is a Certificate Authority (CA), trusted by user community User deliver public key to CA in a secure manner and obtain a certificate User publish the certificate Anyone needing this user’s public key can obtain the certificate and verify it by attached trusted signature X.509 Certificates 28 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 29. Key Distribution using Asymmetric Encryption 29 Public-Key Certificate Use Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 30. X.509 Certificates • Standard for a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Set of hardware, software, people, policies and procedures needed to create, manage, store, distribute and revoke digital certificates based on asymmetric cryptography • Distributed set of servers that maintains a database about users. • Assumes a strict hierarchical system of certificate authorities (CAs) for issuing the certificates • Each certificate contains the public key of a user and is signed with the private key of a CA. • Is used in S/MIME, IP Security, SSL/TLS and SET. 30 • RSA is recommended to use. Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 31. X.509 Certificates • A certification authority issues a certificate binding a public key to a particular distinguished user A certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity which issues digital certificates for use by other parties. It is an example of a trusted third party. There are many commercial CAs that charge for their services. Institutions and governments may have their own CAs, and there are free CAs. • An organization's trusted root certificates can be distributed to all employees so that they can use the company PKI system • X.509 also includes standards for certificate revocation list (CRL) implementations 31 Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 32. X.509 Certificates 32 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 33. X.509 Certificates 33 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
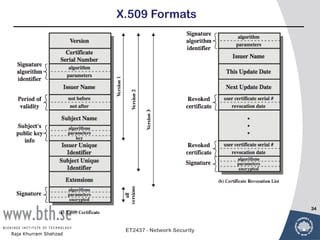
- 34. X.509 Formats 34 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 35. Obtaining a User’s Certificate • Characteristics of certificates generated by CA: Any user with access to the public key of the CA can recover the user public key that was certified. No part other than the CA can modify the certificate without this being detected. 35 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 36. Revocation of Certificates • Reasons for revocation: The users secret key is assumed to be compromised. The user is no longer certified by this CA. The CA’s certificate is assumed to be compromised. 36 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad
- 37. 37 ET2437 - Network Security Raja Khurram Shahzad

















![A Simple Authentication Dialogue
(1) C AS: IDc || Pc || IDv
(2) AS C: Ticket
(3) C V: IDc || Ticket
• Ticket = EKv[IDc || Pc || IDv]
18
ET2437 - Network Security
Raja Khurram Shahzad](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture9-keydistributionanduserauthentication0-2-120612174534-phpapp01/85/Lecture-9-key-distribution-and-user-authentication-18-320.jpg)

![More secure Authentication Dialogue
Once per user logon session:
• C AS: IDC || IDtgs
• AS C: EKc [ Tickettgs ]
Once per type of service:
(3) C TGS: IDC || IDV ||Tickettgs
(4) TGS C: TicketV
Once per service session:
(5) C V: IDC || TicketV
20
ET2437 - Network Security
Raja Khurram Shahzad](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture9-keydistributionanduserauthentication0-2-120612174534-phpapp01/85/Lecture-9-key-distribution-and-user-authentication-20-320.jpg)

![Version 4 Authentication Dialogue
Authentication Service Exhange: To obtain Ticket-Granting
Ticket
• C AS: IDc || IDtgs ||TS1
• AS C: EKc [Kc,tgs|| IDtgs || TS2 || Lifetime2 || Tickettgs]
Ticket-Granting Service Echange: To obtain Service-Granting
Ticket
(3) C TGS: IDv ||Tickettgs ||Authenticatorc
(4) TGS C: EKc [Kc,¨v|| IDv || TS4 || Ticketv]
Client/Server Authentication Exhange: To Obtain Service
(5) C V: Ticketv || Authenticatorc
(6) V C: EKc,v[TS5 +1]
22
ET2437 - Network Security
Raja Khurram Shahzad](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture9-keydistributionanduserauthentication0-2-120612174534-phpapp01/85/Lecture-9-key-distribution-and-user-authentication-22-320.jpg)