Lecture slides stats1.13.l03.air
- 1. Statistics One Lecture 3 Variables, Distributions, & Scales 1
- 2. Three segments • Variables • Distributions • Scales 2
- 3. Lecture 3 ~ Segment 1 Types of variables 3
- 4. Variables • Variables can take on multiple values • In contrast, a constant has only one value 4
- 6. Variables • The size, shape, weight, and type of apple are all variables • Gravity, or gravitational force, is a constant on Earth 6
- 9. Types of variables • Nominal variables – Used to assign individual cases to categories • For example, Coursera students come from many different countries • Country of Origin is a nominal variable 9
- 10. Types of variables • Ordinal variables – Used to rank order cases • For example, countries may be ranked according to overall population • Ranking is an ordinal variable 10
- 11. Types of variables • Interval variables – Used to rank order cases and the distance, or interval, between each value is equal • For example, each country has a longitude and latitude • Longitude and Latitude are interval variables 11
- 13. Types of variables • Ratio variables – The same as interval variables but they have a “true zero” • For example, Population (Population = 0 = extinct) • For example, Age (Age = 0 literally means NO age) • For example, Temperature K° (the Kelvin scale) 13
- 15. Types of variables • Preview of variables in this course – Nominal variables • Independent variables in experimental research – For example, treatment to prevent polio (vaccine, placebo) • Quasi-independent variables in correlational research – For example, gender (female, male) 15
- 16. Types of variables • Preview of variables in this course – Interval and Ratio variables • Dependent variables in experimental research – For example, rate of polio in a community • Measured variables in correlational research – For example, intelligence test scores 16
- 17. Types of variables • Preview of variables in this course – Discrete vs. continuous variables • Nominal variables are discrete (categorical) • Interval and ratio variables are continuous • Ordinal variables are technically discrete but they are often treated as continuous in statistical analyses (more on this later) 17
- 18. Segment summary • Types of variables – Nominal – Ordinal – Interval – Ratio 18
- 19. END SEGMENT 19
- 20. Lecture 3 ~ Segment 2 Distributions: Histograms 20
- 21. Histograms • A histogram is a type of graph used to display a distribution 21
- 22. Histograms • Why start with histograms? – To overcome the natural tendency to rely upon summary information, such as an average 22
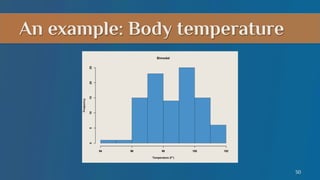
- 23. An example: Body temperature 23
- 24. An example: Body temperature 24
- 25. Histograms • Histograms can reveal information not captured by summary statistics – Suppose a few children in a school are sick with influenza (flu) and have a high temperature • The distribution will be positively skewed 25
- 26. An example: Body temperature 26
- 27. An example: Body temperature 27
- 28. Histograms • Not all distributions are normal – Suppose one group of children had the flu a week prior to a second sick group of children – Assume the first group received antiobiotics, which temporarily caused their body temperatures to be slightly below normal, while the second group was still above normal 28
- 29. An example: Body temperature Normal, below average Normal, above average 29
- 30. An example: Body temperature 30
- 31. An example: Body temperature Normal, below average Normal, above average 31
- 32. An example: Body temperature 32
- 33. Histograms • Not all distributions are normal – Simply viewing a histogram often reveals whether a distribution is normal or not normal – However, sometimes it is hard to determine • Summary statistics help in such cases 33
- 34. Histograms • Not all distributions are normal – As you view more and more distributions you will get a better sense of what is normal and what is not normal – So, let’s look at more distributions 34
- 35. Wine tasting! 35
- 36. An example: Wine ratings • Suppose that 100 wine experts rated the overall quality of 8 different wines on a scale of 1 to 100 – Higher scores indicate higher quality 36
- 37. An example: Wine ratings • Suppose four countries submitted two wines each, one red and one white – Argentina – Australia – France – USA 37
- 38. An example: Wine ratings Malbec & Chardonnay Shiraz & Pinot Grigio 38
- 39. An example: Wine ratings Bourdeaux & Sauvignon Blanc Cabarnet & Reisling 39
- 40. An example: Wine ratings • Preview – The ratings of the red wines are normal – The ratings of the whites are not normal 40
- 41. An example: Wine ratings Red, Argentina Red, Australia 41
- 42. Four histograms Red, France Red, USA 42
- 43. An example: Wine ratings White, Argentina White, Australia 43
- 44. An example: Wine ratings White, France White, USA 44
- 45. Segment summary • Histograms are used to display distributions • Many distributions are normal 45
- 46. Segment summary • Some distributions are not normal, for example: – Bi-modal – Positively skewed – Negatively skewed – Uniform (platykurtic) – Leptokurtic 46
- 51. END SEGMENT 51
- 52. Lecture 3 ~ Segment 3 Scales of measurement 52
- 53. Scales • Scales of measurement – For example, in the last segment body temperature was presented in both Fahrenheit and in Celsius • Different scales but both measure temperature • F° can be converted to C° and vice-versa 53
- 54. Scales • In statistics, there is a standard scale – The Z scale • Any score from any scale can be converted – To Z scores • Allows for efficient communication 54
- 55. Z scores • Z = (X – M) / SD • X is a score on an original scale (raw score) • M is the mean • SD is the standard deviation 55
- 56. Z scores • Z = (X – M) / SD • The mean Z-score is Z = 0 • Positive Z scores are above average • Negative Z scores are below average 56
- 60. Z scores • For example, assume M = 98.6, SD = .5 • Suppose an individual, X = 99.6 • Convert X to Z 60
- 61. Z scores • Convert X to Z • Z = (X – M) / SD • Z = (99.6 – 98.6) / .5 = 2 • Z = 2 61
- 62. Percentile rank • Percentile rank – The percentage of scores that fall at or below a score in a distribution • Assume a normal distribution • If Z = 0 then the percentile rank = 50th • 50 percent of the distribution falls below the mean 62
- 64. Segment summary • The Z-scale is the standard scale in statistics • Raw scores can be converted to Z-scores • Z-scores can be used to find percentile rank • Raw score ~ Z-score ~ Percentile rank 64
- 65. END SEGMENT 65
- 66. END LECTURE 3 66