Lecture1_introduction to python.pptx
- 1. Eng. Mohammed AL-Yemeni Winter-2022 Modern Specialized College Faculty of Engineering Mechatronics Engineering Department 4th Level Practical Lab Lab 1- Introduction to Python Programming Language
- 2. What is Python? • Python is a popular high-level programming language. • It can handle various programming tasks such as numerical computation, web development, database programming, network programming, parallel processing, etc. • Official website: http://www.python.org • Python official documentation: http://docs.python.org/
- 3. Python Features Python is popular for various reasons including: • It is free. • Available on all the popular operating systems such as Windows, Mac or Linux. • It is an interpreted language (no need for compiling or linking). • Highly readable and easier to debug. It gives the ability to program faster. • Programs written in Python can be run on various OS or platforms with little or no change. • It is a dynamically typed language (No need for declaration) • It has a dedicated developer and user community and is kept up to date. • Used in Raspberry pi programming.
- 4. Python Applications • Web Development and Gaming • Cyber Security and Networks • Artificial Intelligent • Internet of Things • Automation • Data Science
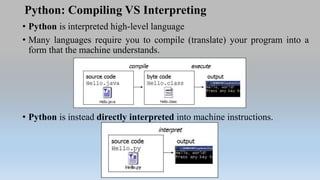
- 5. Python: Compiling VS Interpreting • Python is interpreted high-level language • Many languages require you to compile (translate) your program into a form that the machine understands. • Python is instead directly interpreted into machine instructions.
- 6. Python Environments • Python Shell –running 'python' from the Command Line opens this interactive shell • Python IDLE is an Integrated Development Environment for Python, typically used on Windows, Multi-window text editor with syntax highlighting, auto-completion, smart indent and other. • The Jupyter Notebook is an interactive computing environment that enables users to author notebook documents that include: -Live code - Interactive widgets -Plots -Narrative text -Equations -Images -Video • Pycharm • Anaconda
- 8. Installing Anaconda • So to use anaconda download it first • Go to anaconda site https://www.anacond a.com/distribution/ .
- 10. Different Python Environments •Hello World using IDLE (Python 3.7) •Hello World using Spyder • Hello World using Jupyter Notebook
- 11. Anaconda conditional free and open-source distribution of the Python programming languages for scientific computing (data science, machine learning applications, large-scale data processing, predictive analytics, etc.), that aims to simplify package management and deployment.
- 13. Installing Jupyter Notebook Prerequisite: Python While Jupyter runs code in many programming languages, Python is a requirement (Python 3.3 or greater, or Python 2.7) for installing the Jupyter Notebook.
- 14. Installing Jupyter using Anaconda and conda Use the following installation steps: • Download Anaconda. We recommend downloading Anaconda’s latest Python 3 version (currently Python 3.5). • Install the version of Anaconda which you downloaded, following the instructions on the download page.
- 15. Print • print: Produces text output on the console. • Syntax: print ("Message") print (Expression) • Prints the given text message or expression value on the console, and moves the cursor down to the next line. print (Item1, Item2, ..., ItemN) • Prints several messages and/or expressions on the same line. Examples: • Code: age = 45 print ("You have", 65 -age, "years until retirement“) • Output: You have 20 years until retirement
- 16. User Input • input: Reads a number from user input. • We can instruct Python to pause and read data from the user using the input() function • You can assign (store) the result of input into a variable. • The input() function returns a string Example: • Code: name = input('Who are you?') print('Welcome', name) • Output: Who are you? Ali Welcome Ali
- 17. String Conversions • You can also use int() and float() to convert between strings and integers >>> x = '123' >>> type(x) <class 'str’> >>> x = int(x) >>> type(x) <class 'int'> • You will get an error if the string does not contain numeric characters
- 18. Variables, Expressions, and Statements • Fixed values such as numbers, letters, and strings, are called “constants” because their value does not change • Numeric constants are as you expect • String constants use single quotes (') or double quotes (")
- 19. Reserved Words • You cannot use reserved words as variable names / identifiers
- 20. Variables • A variable is a named place in the memory where a programmer can store data and later retrieve the data using the variable “name”. •Programmers get to choose the names of the variables. • You can change the contents of a variable in a later statement.
- 21. Basic Python Statements and Data Types (Cont.) • Variables Python is a dynamic language and hence you do not need to specify the variable type as in C/C++. The values can be an integer, float, string, lists, tuples, dictionary, set, etc. >>> a = 1 #integer >>> a = 10.0 #float >>> a = “hello” # String
- 22. Basic Python Statements and Data Types (Cont.) • Comments All code should contain comments that describe what it does In Python, lines beginning with a # sign are comment lines You can also have comments on the same line as a statement # This entire line is a comment x=5# Set up loop counter For multiline comments, use """triple quotes"""
- 23. Type Conversions • When you put an integer and floating point in an expression, the integer is implicitly converted to a float. • You can control this with the built-in functions int() and float() >>> print(float(99) + 100) 199.0 >>> i = 42 >>> type(i) <class'int'> >>> f = float(i) >>> print(f) 42.0 >>> type(f) <class'float'>
- 24. Exercise • Write a program to prompt the user for hours and rate per hour to compute gross pay. • Enter Hours: 35 • Enter Rate: 2.75 Pay: 96.25
- 25. Basic Python Statements and Data Types (Cont.) • if-else statement All code should contain comments that describe what it does if a<10 : print(a is less than 10) elif if a<20 : print(a is between 10 and 20) else: print(a is greater than 20)
- 26. Basic Python Statements and Data Types (Cont.) for Loop: Repeats a set of statements over a group of values. • Syntax: for variableName in groupOfValues : statements We indent the statements to be repeated with tabs or spaces. variableName gives a name to each value, so you can refer to it in the statements. groupOfValues can be a range of integers, specified with the range function. • Example: for x in range(1, 6): print (x, "squared is", x * x) Output: 1 squared is 1 2 squared is 4 3 squared is 9 4 squared is 16 5 squared is 25
- 28. Operators Many logical expressions use relational operators: Modules
- 29. Modules • Modules are additional pieces of code that further extend Python’s functionality • A module typically has a specific functionality import module: import fibo Can import specific methods from module: from fibo import fib, fib2 Can import all names defined by module: from fiboi mport *
- 30. Math Module Commands • Python has useful commands for performing calculations. • To use many of these commands, you must write the following at the top of your Python program: from math import *
- 31. For the next lab • Make sure Anaconda packages are installed properly • Install NUMPY using the anaconda prompt conda install numpy • When finished, run Juyter notebook and test the installation of numpy using importing it and performing any operation
- 32. For the next lab • Make sure Anaconda packages are installed properly • Install scipy using the anaconda prompt conda install scipy • When finished, run Juyter notebook and test the installation of scipy using importing it and performing any operation using the import Import scipy
- 33. Any Questions ?
Editor's Notes
- #9: What is Anaconda python ? It is a free and open source distribution of python and R programming languages. Used for scientific computing (data science, machine learning applications ,large scale data processing , predictive analytics, etc…). It aims to simplify package management and deployment. It includes more than 1500 packages suitable for windows, Linux and macos.
- #18: age = int(input("How old are you? "))
- #27: Exercise Print even numbers from a range you specify
- #29: Remember: “=” is used for assignment. Boolean expressions ask a question and produce a Yes or No result which we use to control program flow Boolean expressions using comparison operators evaluate to True / False or Yes / No Comparison operators look at variables but do not change the variables