Lecture_1.1.pptx introduction to cloud ar
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes27 views
Configuring availability and reliability-related mechanisms. Managing credentials for developers and cloud resource administrators using IAM.
1 of 23
Download to read offline






















Ad
Recommended
CloudBus



CloudBusAshis Kumar Chanda The presentation is based on the speech of Rajkumar Buyya on Cloud Bus Toolkit.
Amit Kumar Nath (CSE, DU) and I made this presentation to provide a brief description about some useful cloud bus toolkit, such as, Aneka, CloudSim, Broker, Cloud Maker, Workflow.
Understanding Cloud Computing



Understanding Cloud ComputingMohammed Sajjad Ali “This chapter provide an overview of introductory cloud computing topics. It begins with a brief history of cloud computing along with short descriptions of its business and technology drivers. This is followed by definitions of basic concepts and terminology, in addition to explanations of the primary benefits and challenges of cloud computing adoption.”
ICC1_Module 1_Fundamentals of Cloud Computing.pptx



ICC1_Module 1_Fundamentals of Cloud Computing.pptxDeepakGour17 This document introduces cloud computing and discusses its fundamentals. It begins by explaining what cloud computing is and discussing its history and evolution from early concepts of time-sharing to modern cloud platforms. It then outlines the key characteristics of cloud computing like on-demand access, resource pooling, and measured service. The document also describes the major cloud deployment models including public, private, hybrid and community clouds. Finally, it discusses how traditional data centers evolved into private clouds through increased virtualization and automation.
Data centers are typically comprised of the following technologies and compon...



Data centers are typically comprised of the following technologies and compon...Radhika R Virtualization
Standardization and Modularity
Automation
Remote Operation and Management
High Availability
Facilities
Computing Hardware
Storage Hardware
introduction to cloud computing and basic



introduction to cloud computing and basicRadhika R Cloud Computing is a general term used to describe a new class of network based computing that takes place over the Internet,
basically a step on from Utility Computing
a collection/group of integrated and networked hardware, software and Internet infrastructure (called a platform).
Using the Internet for communication and transport provides hardware, software and networking services to clients
Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services)
These platforms hide the complexity and details of the underlying infrastructure from users and applications by providing very simple graphical interface or API (Applications Programming Interface).
Cloud Computing is a general term used to describe a new class of network bas...



Cloud Computing is a general term used to describe a new class of network bas...Radhika R Cloud Computing is a general term used to describe a new class of network based computing that takes place over the Internet,
basically a step on from Utility Computing
a collection/group of integrated and networked hardware, software and Internet infrastructure (called a platform).
Using the Internet for communication and transport provides hardware, software and networking services to clients
Cloud Computing_Unit 1- Part 1.pptx



Cloud Computing_Unit 1- Part 1.pptxVivek Shelke Cloud Computing at a Glance, the Vision of Cloud Computing, Defining a Cloud, A Closer Look, Cloud Computing Reference Model, Characteristics and Benefits, Challenges Ahead, Historical Developments. Virtualization: Introduction, Characteristics of Virtualized Environment, Taxonomy of Virtualization Techniques, Virtualization and Cloud computing, Pros and Cons of Virtualization, Technology Examples- VMware and Microsoft Hyper-V.
Security & privacy issues of cloud & grid computing networks



Security & privacy issues of cloud & grid computing networksijcsa Cloud computing is a new field in Internet computing that provides novel perspectives in internetworking
technologies. Cloud computing has become a significant technology in field of information technology.
Security of confidential data is a very important area of concern as it can make way for very big problems
if unauthorized users get access to it. Cloud computing should have proper techniques where data is
segregated properly for data security and confidentiality. This paper strives to compare and contrast cloud
computing with grid computing, along with the Tools and simulation environment & Tips to store data and
files safely in Cloud.
Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internet



Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internetharendraj2ee Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internet based development and services
A number of characteristics define cloud data, applications services and infrastructure:
Remotely hosted: Services or data are hosted on remote infrastructure.
Ubiquitous: Services or data are available from anywhere.
Commodified: The result is a utility computing model similar to traditional that of traditional utilities, like gas and electricity - you pay for what you would want!
Cloud computing Review over various scheduling algorithms



Cloud computing Review over various scheduling algorithmsIJEEE Cloud computing has taken an importantposition in the field of research as well as in thegovernment organisations. Cloud computing uses virtualnetwork technology to provide computer resources tothe end users as well as to the customer’s. Due tocomplex computing environment the use of high logicsand task scheduler algorithms are increase which resultsin costly operation of cloud network. Researchers areattempting to build such kind of job scheduling algorithms that are compatible and applicable in cloud computing environment.In this paper, we review research work which is recently proposed by researchers on the base of energy saving scheduling techniques. We also studying various scheduling algorithms and issues related to them in cloud computing.
Cloud computing



Cloud computingArar Fahem This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including:
- A definition of cloud computing as networked hardware and software resources delivered as a service over the Internet.
- A brief history of cloud computing origins dating back to the 1960s with milestones like Amazon Web Services launching in 2002.
- Descriptions of cloud computing characteristics like on-demand self-service, broad network access, and resource pooling.
- Explanations of cloud service models including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
- Reasons for the popularity of cloud services like scalability, reliability, and reducing costs compared to owning infrastructure.
Cloud ppt for college students for their projects



Cloud ppt for college students for their projectsragunayaka4361 Good cloud security controls and procedures
The Riisk and Challllenges off Clloud Computtiing



The Riisk and Challllenges off Clloud ComputtiingIJERA Editor Cloud computing is a computing technology aiming to share storage, computation, and services transparently
among a massive users. Current cloud computing systems pose serious limitation to protecting the confidentiality
of user data. Since the data share and stored is presented in unencrypted forms to remote machines owned and
operated by third party service providers despite it sensitivity (example contact address, mails), the risks of
disclosing user confidential data by service providers may be quite high and the risk of attacking cloud storage
by third party is also increasing. The purpose of this study is to review researches done on this technology,
identify the security risk and explore some techniques for protecting users‟ data from attackers in the cloud.
Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt



Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptNastyaM6 Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt
Distributed system.pptx



Distributed system.pptxMeymunaMohammed1 This document provides an overview of distributed computing paradigms such as cloud computing, jungle computing, and fog computing. It defines distributed computing as utilizing multiple autonomous computers located across different areas to solve large problems. Cloud computing is described as internet-based computing using shared online resources and data storage. Jungle computing combines distributed systems for high performance, while fog computing extends cloud computing to network edges for low latency applications. The document discusses characteristics, architectures, advantages and disadvantages of these paradigms.
Cloud computing



Cloud computingRipal Ranpara The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its key concepts and components. It discusses the different deployment models (public, private, hybrid, community clouds), service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), characteristics, benefits, history and evolution. Communication protocols used in cloud computing like HTTP, HTTPS and various RPC implementations are also mentioned. The role of open standards in cloud architecture including virtualization, SOA, open-source software and web services is assessed.
Cloud Computing (Lecture 1 & 2).pptx



Cloud Computing (Lecture 1 & 2).pptxMuhammadArslan799356 Introduction of Cloud Computing & Historical Background
Cloud Service Models & Cloud Deployment Models
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Risks and Challenges
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
Edge Computing, Serverless Computing, AI & Machine Learning in Cloud, Security and
Compliance
Needs and Obstacles for Cloud Deployment
Conclusion
Ad
More Related Content
Similar to Lecture_1.1.pptx introduction to cloud ar (20)
Cloud Computing_Unit 1- Part 1.pptx



Cloud Computing_Unit 1- Part 1.pptxVivek Shelke Cloud Computing at a Glance, the Vision of Cloud Computing, Defining a Cloud, A Closer Look, Cloud Computing Reference Model, Characteristics and Benefits, Challenges Ahead, Historical Developments. Virtualization: Introduction, Characteristics of Virtualized Environment, Taxonomy of Virtualization Techniques, Virtualization and Cloud computing, Pros and Cons of Virtualization, Technology Examples- VMware and Microsoft Hyper-V.
Security & privacy issues of cloud & grid computing networks



Security & privacy issues of cloud & grid computing networksijcsa Cloud computing is a new field in Internet computing that provides novel perspectives in internetworking
technologies. Cloud computing has become a significant technology in field of information technology.
Security of confidential data is a very important area of concern as it can make way for very big problems
if unauthorized users get access to it. Cloud computing should have proper techniques where data is
segregated properly for data security and confidentiality. This paper strives to compare and contrast cloud
computing with grid computing, along with the Tools and simulation environment & Tips to store data and
files safely in Cloud.
Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internet



Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internetharendraj2ee Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internet based development and services
A number of characteristics define cloud data, applications services and infrastructure:
Remotely hosted: Services or data are hosted on remote infrastructure.
Ubiquitous: Services or data are available from anywhere.
Commodified: The result is a utility computing model similar to traditional that of traditional utilities, like gas and electricity - you pay for what you would want!
Cloud computing Review over various scheduling algorithms



Cloud computing Review over various scheduling algorithmsIJEEE Cloud computing has taken an importantposition in the field of research as well as in thegovernment organisations. Cloud computing uses virtualnetwork technology to provide computer resources tothe end users as well as to the customer’s. Due tocomplex computing environment the use of high logicsand task scheduler algorithms are increase which resultsin costly operation of cloud network. Researchers areattempting to build such kind of job scheduling algorithms that are compatible and applicable in cloud computing environment.In this paper, we review research work which is recently proposed by researchers on the base of energy saving scheduling techniques. We also studying various scheduling algorithms and issues related to them in cloud computing.
Cloud computing



Cloud computingArar Fahem This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including:
- A definition of cloud computing as networked hardware and software resources delivered as a service over the Internet.
- A brief history of cloud computing origins dating back to the 1960s with milestones like Amazon Web Services launching in 2002.
- Descriptions of cloud computing characteristics like on-demand self-service, broad network access, and resource pooling.
- Explanations of cloud service models including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
- Reasons for the popularity of cloud services like scalability, reliability, and reducing costs compared to owning infrastructure.
Cloud ppt for college students for their projects



Cloud ppt for college students for their projectsragunayaka4361 Good cloud security controls and procedures
The Riisk and Challllenges off Clloud Computtiing



The Riisk and Challllenges off Clloud ComputtiingIJERA Editor Cloud computing is a computing technology aiming to share storage, computation, and services transparently
among a massive users. Current cloud computing systems pose serious limitation to protecting the confidentiality
of user data. Since the data share and stored is presented in unencrypted forms to remote machines owned and
operated by third party service providers despite it sensitivity (example contact address, mails), the risks of
disclosing user confidential data by service providers may be quite high and the risk of attacking cloud storage
by third party is also increasing. The purpose of this study is to review researches done on this technology,
identify the security risk and explore some techniques for protecting users‟ data from attackers in the cloud.
Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt



Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptNastyaM6 Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.pptIrfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt Irfan Jalal Bhat.ppt
Distributed system.pptx



Distributed system.pptxMeymunaMohammed1 This document provides an overview of distributed computing paradigms such as cloud computing, jungle computing, and fog computing. It defines distributed computing as utilizing multiple autonomous computers located across different areas to solve large problems. Cloud computing is described as internet-based computing using shared online resources and data storage. Jungle computing combines distributed systems for high performance, while fog computing extends cloud computing to network edges for low latency applications. The document discusses characteristics, architectures, advantages and disadvantages of these paradigms.
Cloud computing



Cloud computingRipal Ranpara The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its key concepts and components. It discusses the different deployment models (public, private, hybrid, community clouds), service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), characteristics, benefits, history and evolution. Communication protocols used in cloud computing like HTTP, HTTPS and various RPC implementations are also mentioned. The role of open standards in cloud architecture including virtualization, SOA, open-source software and web services is assessed.
Cloud Computing (Lecture 1 & 2).pptx



Cloud Computing (Lecture 1 & 2).pptxMuhammadArslan799356 Introduction of Cloud Computing & Historical Background
Cloud Service Models & Cloud Deployment Models
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Risks and Challenges
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
Edge Computing, Serverless Computing, AI & Machine Learning in Cloud, Security and
Compliance
Needs and Obstacles for Cloud Deployment
Conclusion
More from Radhika R (20)
module4 cloud provider and consumer persp



module4 cloud provider and consumer perspRadhika R Controlling scalability features such as usage quotas, active instance thresholds, and the configuration and deployment of the automated scaling listener and load balancer mechanisms.
containers-in-cloud.pptx introduction part



containers-in-cloud.pptx introduction partRadhika R Many SaaS offerings are provided free of charge, although these cloud services often come with data collecting sub-programs that harvest usage data for the benefit of the cloud provider (what benefits?).
containerization1. introduction to contain



containerization1. introduction to containRadhika R SaaS-based cloud services are almost always accompanied by refined and generic APIs, they are usually designed to be incorporated as part of larger distributed solutions.
moThese platforms hide the complexity and details of the underlying infrastru...



moThese platforms hide the complexity and details of the underlying infrastru...Radhika R These platforms hide the complexity and details of the underlying infrastructure from users and applications by providing very simple graphical interface or API (Applications Programming Interface).
Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access ...



Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access ...Radhika R Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources
a collection/group of integrated and networked hardware, software and Interne...



a collection/group of integrated and networked hardware, software and Interne...Radhika R a collection/group of integrated and networked hardware, software and Internet infrastructure (called a platform).
containers-in-cloud introduction to ppts



containers-in-cloud introduction to pptsRadhika R Why Containers?
What are Containers?
History of Containers
Docker
Orchestration
Docker Swarm
containerization with example module and



containerization with example module andRadhika R DTGO -a public organization that specializes in IT infrastructure and technology
services for public sector organization.
• DTGOV has virtualized its network infrastructure to produce a logical network
layout favoring network segmentation and isolation.
• Figure 7.4 depicts the logical network perimeter implemented at each DTGOV data
center. A logical network layout is established through a set of logical network
perimeters using various firewalls and virtual networks.
containers-in-cloud introduction example



containers-in-cloud introduction exampleRadhika R The cloud consumer’s on-premise environment and a cloud provider’s
cloud-based environment, connected through VPN and protect
communications. Figure 7.3
Virtualization technology and virtualization



Virtualization technology and virtualizationRadhika R Logical Network Perimeter
• Isolation of a network environment from the rest of a communications
network
• Establishes a virtual network boundary Figure 7.1
that can encompass and isolate a group of related cloud-based IT
resources
• This mechanism can be implemented to: – isolate IT resources in a cloud from non-authorized users – isolate IT resources in a cloud from non-users – isolate IT resources in a cloud from cloud consumers – control the bandwidth that is available to isolated IT resources
introduction to web technology and web application



introduction to web technology and web applicationRadhika R Enable multiple users (tenants) to access the same
application simultaneously
• Multitenant applications ensure that tenants do
not have access to data and configuration
information that is not their own
Introduction to cloud delivery models of paas



Introduction to cloud delivery models of paasRadhika R Cloud computing relies on internet.
• Web technology is generally used as both the
implementation medium and the managUniform resource locator (URL)
Commonly informally referred to as a web address
a reference to a web resource that specifies its location
on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving
it
Example: http://www.example.com/index.html
• Hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP)
Primary communication protocol used to exchange
content
• Markup languages (HTML, XML)
16
Express Web‐centric data and metadata
Virtualization Technology Hardware Independence Server Consolidation



Virtualization Technology Hardware Independence Server ConsolidationRadhika R Virtualization is the process of converting a physical IT resource into a virtual IT
resource.
Most types of IT resources can be virtualized, including:
Servers
Storage
Network
Power
Computing hardware technologies include Rackamount form factor server with in...



Computing hardware technologies include Rackamount form factor server with in...Radhika R Support for different hardware processing architecture
A number of characteristics define cloud data, applications services and infr...



A number of characteristics define cloud data, applications services and infr...Radhika R Remotely hosted: Services or data are hosted on remote infrastructure.
Ubiquitous: Services or data are available from anywhere.
Commodified: The result is a utility computing model similar to traditional that of traditional utilities, like gas and electricity - you pay for what you would want!
Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internet based developme...



Cloud computing is an umbrella term used to refer to Internet based developme...Radhika R A number of characteristics define cloud data, applications services and infrastructure:
Remotely hosted: Services or data are hosted on remote infrastructure.
Ubiquitous: Services or data are available from anywhere.
Commodified: The result is a utility computing model similar to traditional that of traditional utilities, like gas and electricity - you pay for what you would want!
lecture4.ppt is no sql database introduction



lecture4.ppt is no sql database introductionRadhika R In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a
transformative force, reshaping the way businesses and individuals interact with digital resources.
By offering scalable, on-demand access to computing power, storage, and various applications,
cloud computing provides unprecedented flexibility and efficiency.
Module – 1
Introduction: Understanding Cloud Computing: Origins and Influences, Basic Concepts and
Introduction about NoSQL which gives the detailed
Terminology, Goals and Benefits, Risks and Challenges.
Chapter-3 (8 Hours)
Module – 2
Fundamental Concepts and Models: Roles and Boundaries, Cloud Characteristics, Cloud
Delivery Models, Cloud Deployment Models.
Chapter-4 (8 Hours)
Module – 3
Cloud-Enabling Technology: Broadband Networks and Internet Architecture, Data Centre
Technology, Virtualization Technology, Web Technology, Multitenant Technology,
Containerization.
Chapter-5 (8 Hours)
Module – 4
Cloud Infrastructure Mechanisms: Logical Network Perimeter, Virtual Server, Cloud Storage Device,
Cloud Usage Monitor, Resource Replication, Ready-Made Environment.
Cloud Delivery Model Considerations: Cloud Delivery Models: The Cloud Provider Perspective.
Chapter-7, Chapter-14 (8 Hours)
Module – 5
Cloud Delivery Model Considerations: Cloud Delivery Models: The Cloud Consumer Perspective.
Fundamental Cloud
Terminology, Goals and Benefits, Risks and Challenges.
Chapter-3 (8 Hours)
Module – 2
Fundamental Concepts and Models: Roles and Boundaries, Cloud Characteristics, Cloud
Delivery Models, Cloud Deployment Models.
Chapter-4 (8 Hours)
Module – 3
Cloud-Enabling Technology: Broadband Networks and Internet Architecture, Data Centre
Technology, Virtualization Technology, Web Technology, Multitenant Technology,
Containerization.
Chapter-5 (8 Hours)
Module – 4
Cloud Infrastructure Mechanisms: Logical Network Perimeter, Virtual Server, Cloud Storage Device,
Cloud Usage Monitor, Resource Replication, Ready-Made Environment.
Cloud Delivery Model Considerations: Cloud Delivery Models: The Cloud Provider Perspective.
Chapter-7, Chapter-14 (8 Hours)
Module – 5
Cloud Delivery Model Considerations: Cloud Delivery Models: The Cloud Consumer Perspective.
Fundamental Cloud Security: Basic Terms and Concepts, Threat Agents, Cloud Security Threats,
Additional Considerations.
Chapter-14, Chapter-6 (8 Hours)
Course outcomes:
The students will be able to:
1. Understand the basic concepts and terminologies of cloud computing
2. Apply the concept of cloud computing to different real word examples
3. Analysis the cloud frameworks and technologies for different IT Industry
4. Design real word cloud applications
5. Study the framework of Aneka cloud for data intensive Application
Text Books
1.Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture, by Zaigham Mahmood, Ricardo
Puttini, Thomas Erl, Released May 2013, Publisher(s): Pearson, ISBN: 9780133387568
References
1. Dan C. Marinescu, Morgan Kaufmann, Cloud Computing Theory and Practice
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Structural Response of Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Deep Beam Using Fi...



Structural Response of Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Deep Beam Using Fi...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering Analysis of reinforced concrete deep beam is based on simplified approximate method due to the complexity of the exact analysis. The complexity is due to a number of parameters affecting its response. To evaluate some of this parameters, finite element study of the structural behavior of the reinforced self-compacting concrete deep beam was carried out using Abaqus finite element modeling tool. The model was validated against experimental data from the literature. The parametric effects of varied concrete compressive strength, vertical web reinforcement ratio and horizontal web reinforcement ratio on the beam were tested on eight (8) different specimens under four points loads. The results of the validation work showed good agreement with the experimental studies. The parametric study revealed that the concrete compressive strength most significantly influenced the specimens’ response with the average of 41.1% and 49 % increment in the diagonal cracking and ultimate load respectively due to doubling of concrete compressive strength. Although the increase in horizontal web reinforcement ratio from 0.31 % to 0.63 % lead to average of 6.24 % increment on the diagonal cracking load, it does not influence the ultimate strength and the load-deflection response of the beams. Similar variation in vertical web reinforcement ratio leads to an average of 2.4 % and 15 % increment in cracking and ultimate load respectively with no appreciable effect on the load-deflection response.
some basics electrical and electronics knowledge



some basics electrical and electronics knowledgenguyentrungdo88 This chapter discribe about common electrical divices such as passive component, the internaltional system unit and international system prefixes.
Degree_of_Automation.pdf for Instrumentation and industrial specialist



Degree_of_Automation.pdf for Instrumentation and industrial specialistshreyabhosale19 degree of Automation for industrial and Instrumentation learners.
Value Stream Mapping Worskshops for Intelligent Continuous Security



Value Stream Mapping Worskshops for Intelligent Continuous SecurityMarc Hornbeek This presentation provides detailed guidance and tools for conducting Current State and Future State Value Stream Mapping workshops for Intelligent Continuous Security.
"Boiler Feed Pump (BFP): Working, Applications, Advantages, and Limitations E...



"Boiler Feed Pump (BFP): Working, Applications, Advantages, and Limitations E...Infopitaara A Boiler Feed Pump (BFP) is a critical component in thermal power plants. It supplies high-pressure water (feedwater) to the boiler, ensuring continuous steam generation.
⚙️ How a Boiler Feed Pump Works
Water Collection:
Feedwater is collected from the deaerator or feedwater tank.
Pressurization:
The pump increases water pressure using multiple impellers/stages in centrifugal types.
Discharge to Boiler:
Pressurized water is then supplied to the boiler drum or economizer section, depending on design.
🌀 Types of Boiler Feed Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps (most common):
Multistage for higher pressure.
Used in large thermal power stations.
Positive Displacement Pumps (less common):
For smaller or specific applications.
Precise flow control but less efficient for large volumes.
🛠️ Key Operations and Controls
Recirculation Line: Protects the pump from overheating at low flow.
Throttle Valve: Regulates flow based on boiler demand.
Control System: Often automated via DCS/PLC for variable load conditions.
Sealing & Cooling Systems: Prevent leakage and maintain pump health.
⚠️ Common BFP Issues
Cavitation due to low NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head).
Seal or bearing failure.
Overheating from improper flow or recirculation.
Lidar for Autonomous Driving, LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars.pptx



Lidar for Autonomous Driving, LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars.pptxRishavKumar530754 LiDAR-Based System for Autonomous Cars
Autonomous Driving with LiDAR Tech
LiDAR Integration in Self-Driving Cars
Self-Driving Vehicles Using LiDAR
LiDAR Mapping for Driverless Cars
DATA-DRIVEN SHOULDER INVERSE KINEMATICS YoungBeom Kim1 , Byung-Ha Park1 , Kwa...



DATA-DRIVEN SHOULDER INVERSE KINEMATICS YoungBeom Kim1 , Byung-Ha Park1 , Kwa...charlesdick1345 This paper proposes a shoulder inverse kinematics (IK) technique. Shoulder complex is comprised of the sternum, clavicle, ribs, scapula, humerus, and four joints.
AI-assisted Software Testing (3-hours tutorial)



AI-assisted Software Testing (3-hours tutorial)Vəhid Gəruslu Invited tutorial at the Istanbul Software Testing Conference (ISTC) 2025 https://iststc.com/
Data Structures_Linear data structures Linked Lists.pptx



Data Structures_Linear data structures Linked Lists.pptxRushaliDeshmukh2 Concept of Linear Data Structures, Array as an ADT, Merging of two arrays, Storage
Representation, Linear list – singly linked list implementation, insertion, deletion and searching operations on linear list, circularly linked lists- Operations for Circularly linked lists, doubly linked
list implementation, insertion, deletion and searching operations, applications of linked lists.
Development of MLR, ANN and ANFIS Models for Estimation of PCUs at Different ...



Development of MLR, ANN and ANFIS Models for Estimation of PCUs at Different ...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering Passenger car unit (PCU) of a vehicle type depends on vehicular characteristics, stream characteristics, roadway characteristics, environmental factors, climate conditions and control conditions. Keeping in view various factors affecting PCU, a model was developed taking a volume to capacity ratio and percentage share of particular vehicle type as independent parameters. A microscopic traffic simulation model VISSIM has been used in present study for generating traffic flow data which some time very difficult to obtain from field survey. A comparison study was carried out with the purpose of verifying when the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), artificial neural network (ANN) and multiple linear regression (MLR) models are appropriate for prediction of PCUs of different vehicle types. From the results observed that ANFIS model estimates were closer to the corresponding simulated PCU values compared to MLR and ANN models. It is concluded that the ANFIS model showed greater potential in predicting PCUs from v/c ratio and proportional share for all type of vehicles whereas MLR and ANN models did not perform well.
Compiler Design_Lexical Analysis phase.pptx



Compiler Design_Lexical Analysis phase.pptxRushaliDeshmukh2 The role of the lexical analyzer
Specification of tokens
Finite state machines
From a regular expressions to an NFA
Convert NFA to DFA
Transforming grammars and regular expressions
Transforming automata to grammars
Language for specifying lexical analyzers
15th International Conference on Computer Science, Engineering and Applicatio...



15th International Conference on Computer Science, Engineering and Applicatio...IJCSES Journal #computerscience #programming #coding #technology #programmer #python #computer #developer #tech #coder #javascript #java #codinglife #html #code #softwaredeveloper #webdeveloper #software #cybersecurity #linux #computerengineering #webdevelopment #softwareengineer #machinelearning #hacking #engineering #datascience #css #programmers #pythonprogramming
How to use nRF24L01 module with Arduino



How to use nRF24L01 module with ArduinoCircuitDigest Learn how to wirelessly transmit sensor data using nRF24L01 and Arduino Uno. A simple project demonstrating real-time communication with DHT11 and OLED display.
Structural Response of Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Deep Beam Using Fi...



Structural Response of Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Deep Beam Using Fi...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering
Development of MLR, ANN and ANFIS Models for Estimation of PCUs at Different ...



Development of MLR, ANN and ANFIS Models for Estimation of PCUs at Different ...Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering
Ad
Lecture_1.1.pptx introduction to cloud ar
- 2. 2 Part 1 Reference Text • Thomas Erl, Zaigham Mahmood, and Ricardo Puttini, Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture, Prentice Hall, May 20, 2013, ISBN: 978-0133387520
- 3. 3 Outline 1. A brief history 2. Definition 3. Motivation, Benefit, Risk 4. Concepts
- 4. 4 Outline 1. A brief history 2. Definition 3. Motivation, Benefit, Risk 4. Concepts
- 5. 5 Brief History • Computer scientist John McCarthy publicly proposed in 1961 If computers of the kind I have advocated become the computers of the future, then computing may someday be organized as a public utility just as the telephone system is a public utility. … The computer utility could become the basis of a new and important industry • Leonard Kleinrock, a chief scientist of the ARPANET project, in 1969 As of now, computer networks are still in their infancy, but as they grow up and become sophisticated, we will probably see the spread of ‘computer utilities’ …
- 6. 6 Brief History • Internet-based computer utilities since the mid-1990s Search engines Email services Open publishing platforms: MySpace, YouTube Social media: Facebook, Twitter • In the late 1990s, Salesforce.com pioneered the notion of bringing remotely provisioned services into the enterprise • In 2002, Amazon.com launched the Amazon Web Services (AWS) platform Remotely provisioned storage, computing resources, and business functionality
- 7. 7 Brief History • The term “cloud computing” emerged in the commercial arena in 2006 Amazon launched its Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) services “lease” computing capacity and processing power to run their enterprise applications Google Apps also began providing browser-based enterprise applications
- 8. 8 Outline 1. A brief history 2. Definition 3. Motivation, Benefit, Risk 4. Concepts
- 9. 9 Definitions • Wikipedia Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources
- 10. 10 Definitions • NIST (National Institute of Standard and Technology) Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models • A concise definition Cloud computing is a specialized form of distributed computing that introduces utilization models for remotely provisioning scalable and measured resources
- 11. 11 Outline 1. A brief history 2. Definition 3. Motivation, Benefit, Risk 4. Concepts
- 12. 12 Business Drivers • Capacity planning Process of determining and fulfilling future demands of an organization’s IT resources, products, and services Lead Strategy - adding capacity to an IT resource in anticipation of demand Lag Strategy - adding capacity when the IT resource reaches its full capacity Match Strategy - adding IT resource capacity in small increments, as demand increases Planning for capacity can be challenging • Cost Reduction Cost of acquiring new infrastructure Cost of its ongoing ownership • Organizational Agility Measure of an organization’s responsiveness to change
- 13. 13 Benefits • Reduced Investments and Proportional Costs • Increased Scalability • Increased Availability and Reliability
- 14. 14 Risks and Challenges • Increased Security Vulnerabilities • Limited Portability Between Cloud Providers • Multi-Regional Compliance and Legal Issues Some UK laws require personal data belonging to UK citizens to be kept within the United Kingdom
- 15. 15 A cloud consumer’s application has a decreased level of portability when assessing a potential migration from Cloud A to Cloud B, because the cloud provider of Cloud B does not support the same security technologies as Cloud A.
- 16. 16 Outline 1. A brief history 2. Definition 3. Motivation, Benefit, Risk 4. Concepts
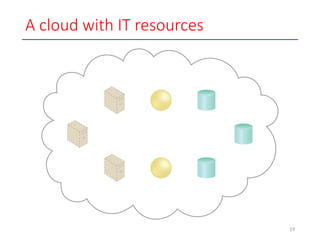
- 17. 17 Basic concepts: cloud • A cloud refers to a distinct IT environment that is designed for the purpose of remotely provisioning scalable and measured IT resources
- 18. 18 Basic concepts: IT resource • An IT resource is a physical or virtual IT-related artifact that can be either software based, such as a virtual server or a custom software program, or hardware-based, such as a physical server or a network device
- 19. 19 A cloud with IT resources
- 20. 20 Cloud Consumers and Cloud Providers • Cloud provider The party that provides cloud-based IT resources • Cloud consumer The party that uses cloud-based IT resources
- 21. 21 Cloud service • A cloud service (or cloud product) is any IT resource that is made remotely accessible via a cloud
- 22. 22 Service-level agreement (SLA) • Cloud service usage conditions are typically expressed in a service-level agreement (SLA) • A service contract between a cloud provider and cloud consumer Describes QoS features, behaviors, and limitations of a cloud-based service or other provisions Provides details of various measurable characteristics related to IT outcomes Uptime, security characteristics, and other specific QoS features, including availability, reliability, and performance
- 23. 23 Cloud service consumer • The cloud service consumer is a temporary runtime role assumed by a software program when it accesses a cloud service Examples of cloud service consumers. Depending on the nature of a given diagram, an artifact labeled as a cloud service consumer may be a software program or a hardware device (in which case it is implied that it is running a software program capable of acting as a cloud service consumer).

![Cloud-Computing-32-40[1].pptx...,..........](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/cloud-computing-32-401-241120164825-adcc70bb-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

















