Line coding
- 1. A Seminar On: Line Coding Presented by: Miss Rina Ahire ME(ETC) 1
- 2. Objectives: •Need of Line Coding •Introduction of Line Coding •Properties of Line Coding •Types of Line Coding •Advantages and Disadvantages •Power Spectral Density • PSD of Line Coding •Comparison of Line Coding 2
- 3. Need Of Line Coding: •Various Techniques •Other Way: From Computers •Information: Inherently discrete in nature •Transmitted over band-limited channel: Signal gets Dispersed •Causes: Overlap and Distortion •Distortion: Intersymbol Interference(ISI) 3
- 4. To avoid all these problems we are going for Line Coding 4
- 5. Introduction: •Binary Data: Pulses •Line Coding: A pair of pulses to represent symbols 1 and 0 5
- 6. Properties of Line Coding: •Transmission Bandwidth: as small as possible • Power Efficiency: As small as possible for given BW and probability of error • Error Detection and Correction capability: Ex: Bipolar • Favorable power spectral density: dc=0 • Adequate timing content: Extract timing from pulses • Transparency: Prevent long strings of 0s or 1s 6
- 7. Types of Line Coding: 7
- 8. Unipolar Signaling: •On-Off keying ie OOK •Pulse 0: Absence of pulse •Pulse1 : Presence of pulse There are two common variations of unipolar signalling: 1. Non-Return to Zero (NRZ) 2. Return to Zero (RZ) 8
- 9. Unipolar Non-Return to Zero (NRZ): •Duration of the MARK pulse (Ƭ ) is equal to the duration (To) of the symbol slot. 9
- 10. Advantages: •Simplicity in implementation • Doesn‟t require a lot of bandwidth for transmission. Disadvantages: •Presence of DC level (indicated by spectral line at 0 Hz). •Contains low frequency components. Causes “Signal Droop” •Does not have any error correction capability. •Does not posses any clocking component for ease of synchronisation. •Is not Transparent. Long string of zeros causes loss of synchronisation. 10
- 11. Unipolar Return to Zero (RZ): •MARK pulse (Ƭ ) is less than the duration (To) of the symbol slot. •Fills only the first half of the time slot, returning to zero for the second half. 11
- 12. Advantages: •Simplicity in implementation. •Presence of a spectral line at symbol rate which can be used as symbol timing clock signal. Disadvantages: •Presence of DC level (indicated by spectral line at 0 Hz). •Continuous part is non-zero at 0 Hz. Causes “Signal Droop”. •Does not have any error correction capability. •Occupies twice as much bandwidth as Unipolar NRZ. •Is not Transparent 12
- 13. Polar Signalling: •Polar RZ •Polar NRZ Polar NRZ: •A binary 1 is represented by a pulse g1(t) •A binary 0 by the opposite (or antipodal) pulse g0(t) = -g1(t). 13
- 14. Advantages: •Simplicity in implementation. •No DC component. Disadvantages: •Continuous part is non-zero at 0 Hz. Causes “Signal Droop”. •Does not have any error correction capability. •Does not posses any clocking component for ease of synchronisation. •Is not transparent. 14
- 15. Polar RZ: •A binary 1: A pulse g1(t) •A binary 0: The opposite (or antipodal) pulse g0(t) = -g1(t). •Fills only the first half of the time slot, returning to zero for the second half. 15
- 16. Advantages: •Simplicity in implementation. •No DC component. Disadvantages: •Continuous part is non-zero at 0 Hz. Causes “Signal Droop”. •Does not have any error correction capability. •Occupies twice as much bandwidth as Polar NRZ. 16
- 17. Bipolar Signalling: •Alternate mark inversion (AMI) •Uses three voltage levels (+V, 0, -V) •0: Absence of a pulse •1: Alternating voltage levels of +V and –V 17
- 18. Bipolar NRZ: Bipolar RZ: 18
- 19. Advantages: •No DC component. •Occupies less bandwidth than unipolar and polar NRZ schemes. •Does not suffer from signal droop (suitable for transmission over AC coupled lines). •Possesses single error detection capability. Disadvantages: •Does not posses any clocking component for ease of synchronisation. •Is not Transparent. 19
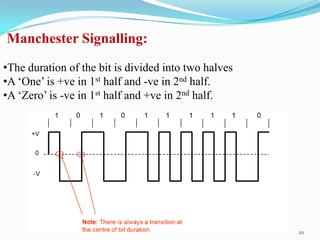
- 20. Manchester Signalling: •The duration of the bit is divided into two halves •A „One‟ is +ve in 1st half and -ve in 2nd half. •A „Zero‟ is -ve in 1st half and +ve in 2nd half. 20
- 21. Advantages: •No DC component. •Does not suffer from signal droop (suitable for transmission over AC coupled lines). •Easy to synchronise. •Is Transparent. Disadvantages: •Because of the greater number of transitions it occupies a significantly large bandwidth. •Does not have error detection capability. 21
- 22. Power Spectral Density: •The function which gives distribution of power of a signal at various frequencies in frequency domain. •PSD is the Fourier Transform of autocorrelation •Rectangular pulse and its spectrum 22
- 23. PSD Derivation: • We now need to derive the time autocorrelation of a power signal x(t) _-- • Since x(t) consists of impulses, is found by • Recognizing for real signals, we have 23
- 24. •Since the pulse filter has the spectrum of , we have • Now, we can use this to find the PSD of various line codes. 24
- 25. PSD of Polar Signalling: • In polar signalling, Binary “1” is transmitted by a pulse f(t) Binary “0” is transmitted by a pulse –f(t) • In this case, is equally likely to be 1 or -1 and is always 1. Where, There are N pulses and for each one. The summation on the right-hand side of the above equation is N. • Moreover, both and are either 1 or -1. So, is either 1 or -1. They are equally likely to be 1 or -1 on the average, out of N terms the product is equal to 1 for N/2 terms and is equal to -1 for the remaining N/2 terms. 25
- 26. PSD of Bipolar Signalling: •To calculate the PSD, we have •On the average, half of the are 0, and the remaining half are either 1 or -1, with . Therefore, 26
- 27. •To compute R1, we consider the pulse strength product . -Four possible equally likely sequences of two bits:11,10,01,00. -Since bit 0 encoded by no pulse , the product for the last three of these sequences. This means that, on the average, 3N/4 combinations have and only N/4 combinations have non zero . Because of the bipolar rule, the bit sequence 11 can only be encoded by two consecutive pulse of opposite polarities. This means the product for the N/4 combinations. 27
- 28. PSD of Lines Codes: 28
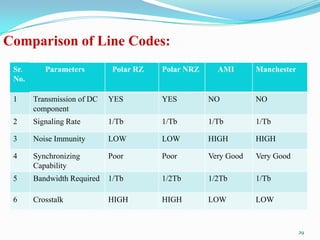
- 29. Comparison of Line Codes: Sr. Parameters Polar RZ Polar NRZ AMI Manchester No. 1 Transmission of DC YES YES NO NO component 2 Signaling Rate 1/Tb 1/Tb 1/Tb 1/Tb 3 Noise Immunity LOW LOW HIGH HIGH 4 Synchronizing Poor Poor Very Good Very Good Capability 5 Bandwidth Required 1/Tb 1/2Tb 1/2Tb 1/Tb 6 Crosstalk HIGH HIGH LOW LOW 29
- 30. Thank You 30