Ad
LinuxTraining_26_Sept_2021.ppt
- 1. Advanced System Programming Advanced System Programming 1
- 2. Classification of Programming Languages 2
- 5. Introduction to Linux 5 In the early 1990s, Torvalds became interested in a freeware product called Minix were written by Andrew S. Tanenbaum. Developed by Andrew S.Tanenbaum, Minix was a clone of the commercial UNIX operating system. Linux version 0.02, released on October 5, 1991, consisted of only the Linux kernel and three utilities: bash : a command-line interface update : a utility for flushing file system buffers gcc : a C++ compiler Today used on 7-10 million computers with 1000’s of programmers working to enhance it around the world.
- 6. Introduction to Linux 6 GNU Project: Richard Stallman on September 27th 1983. The GNU Project was launched in 1984 to develop a complete Unix-like operating system which is free software: the GNU system. GNU's kernel isn't finished, so GNU is used with the kernel Linux. The combination of GNU and Linux is the GNU/Linux operating system, now used by millions.
- 7. What is Linux 7 A fully-networked 32/64-Bit Unix-like Operating System Unix Tools Like sed, awk, and grep (explained later) Compilers Like C, C++, Fortran, Smalltalk, Ada Network Tools Like telnet, ftp, ping, traceroute Multi-user, Multitasking, Multiprocessor Has the X Windows GUI Coexists with other Operating Systems Runs on multiple platforms Includes the Source Code
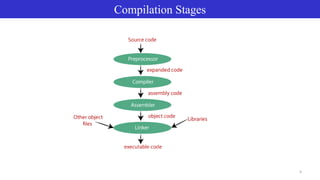
- 8. Component of Linux 8 The Linux Kernel Libraries Utilities User Interface
- 10. Linux Kernel 10 Libraries are pre-written code “pieces” that application programmers use in their programs. Utilities maintaining the file system, editing text files, managing running processes, and installing new software packages. User Interface command-line interface (CLI) and a graphical user interface (GUI).
- 11. Kernel Space and User Space 11 The Concept of kernel space and user space is all about memory and access rights. It is a feature of modern CPU, allowing it to operate either in privileged or unprivileged mode. One ,may consider kernel to be privileged and user apps are restricted.
- 12. Kernel Space and User Space 12
- 13. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 13 The Linux File Hierarchy Structure or the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) defines the directory structure and directory contents in Unix-like operating systems. It is maintained by the Linux Foundation. • In the FHS, all files and directories appear under the root directory /, even if they are stored on different physical or virtual devices. • Some of these directories only exist on a particular system if certain subsystems, such as the X Window System, are installed. • Most of these directories exist in all UNIX operating systems and are generally used in much the same way; however, the descriptions here are those used specifically for the FHS and are not considered authoritative for platforms other than Linux.
- 15. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 15 / (root) • Primary hierarchy root and is the first directory and the root directory of the entire file system hierarchy. • It contains all other directories i.e. the sub directories. • Only the root user has the permissions to write here. • This is not the home directory for the root user /bin (user binaries) • It contains binary executables. • Binary executables of common linux commands used by all users in single-user mode are located in this directory. • Some files present in this directory are: ls, cp, grep, ping, cat, etc.
- 16. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 16 /boot (boot loader files) • It contains boot loader files. • kernel, initrd, grub, and other files and directories are located in this directory. • e.g. vmlinux-2.7.31.25-generic, initrd.img-2.3.32.24-generic, etc. /dev (device files) • It contains the essential files related to the devices attached to the system. • This includes terminal devices, USB, network devices and any other devices that are attached to the system. • e.g. /dev/usbmon0 , /dev/tty1 , /dev/null , etc.
- 17. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 17 /etc (configuration files) • etc stands for ‘edit to config’ • This directory contains the configuration files that are required by the installed programs. • The files are host-specific and system-wide configurations needed for the proper functioning of the system. • This directory also contains shell scripts for system startup and system shutdown that are used to start or stop individual programs. • The files in this directory should not be edited without proper knowledge of system configuration as improper configuration could brick the system. • e.g. /etc/passwd , /etc/shadow , /etc/group , /etc/resolv.conf , etc.
- 18. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 18 /home (home directories) • This directory contains user’s home directories, containing saved files and personal settings. • Each user will have an separate directory with their username under this directory except the root user because every time a new user is created, a directory is created in the name of the user within the home directory. • e.g. /home/user , /home/sage , /home/guest , etc. /lib (system libraries) • This directory contains libraries that are essential for the binaries in /bin and /sbin • Library filenames are either ld* or lib*.so.* • e.g. ld-2.11.1.so , etc. /media (removable media devices) • Temporary mount directory for removable media such as CD-ROM. • e.g. /media/cdrom for CD-ROM ; /media/floppy for floppy drives ; /media/cdrecorder for CD writer ; etc.
- 19. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 19 /mnt (mount directory) • Temporary mount directory where system administrator can mount file systems. /opt (optional application software packages) • This directory contains add-on applications from individual vendors. /proc (process information) • This is a virtual filesystem providing process and kernel information. This files in this directory are automatically generated, populated and deleted by the system. In Linux, corresponds to a procfs mount. • This directory contains information about the processes running in the system. • This directory also contains text information about running processes. e.g. /proc/uptime • e.g. /proc/{pid} directory contains information about the process with that particular pid that will be mentioned within the brackets.
- 20. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 20 /root (root directory) • This is the home directory for the root user. /sbin (system binaries) • This directory contains essential system binaries. • The linux commands that are located in this directory are used by system administrator, for system maintenance and configuration purpose. e.g. fsck , reboot , fdisk , ifconfig , init , etc.
- 21. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 21 /root (root directory) • This is the home directory for the root user. /sbin (system binaries) • This directory contains essential system binaries. • The linux commands that are located in this directory are used by system administrator, for system maintenance and configuration purpose. e.g. fsck , reboot , fdisk , ifconfig , init , etc. /srv (service data) • This directory contains site-specific data served by the system, such as data and scripts for web servers, data offered by FTP servers, and repositories for version control systems i.e. server specific services related data. e.g. /srv/cvs contains CVS related data , etc.
- 22. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 22 /sys (system) • This directory contains information about devices, drivers, and some kernel features. /tmp (temporary files) • This directory contains temporary files created by system and the users that will be rebooted when the system is rebooted. /usr (user programs) • This directory contains read-only user data like binaries, libraries, documentation and source-code for second level programs like user utilities and applications. • /usr/bin → contains binary files for user programs. If you can’t find a user binary under /bin, then we should look under /usr/bin. • /usr/include → contains standard include files.
- 23. Linux Filesystem Hierarchy 23 • /usr/lib → contains libraries for the binaries in /usr/bin and /usr/sbin • /usr/local → tertiary hierarchy for local data. contains users programs that you install from source. e.g., when you install apache, it goes under /usr/local/apache2 • /usr/sbin → /usr/sbin contains binary files for system administrators. If you can’t find a system binary under /sbin, then you should look under /usr/sbin. It also contains non- essential system binaries. e.g. daemons for network-services. /var (variable files) • This directory contains files whose content is expected to continually change during normal operation of the system—such as logs, spool files, and temporary e-mail file. • /var/log → contains system log files.
- 24. Thank you 24


































![Tahir Ashraf [Linux file system herarchy].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/tahirashraflinuxfilesystemherarchy-240302163436-9981e4ca-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)



































