Lists
- 1. CHAPTER 4 LISTS All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed “Fundamentals of Data Structures in C”, Computer Science Press, 1992. CHAPTER 4 1
- 2. Introduction Array successive items locate a fixed distance disadvantage • data movements during insertion and deletion • waste space in storing n ordered lists of varying size possible solution • linked list CHAPTER 4 2
- 3. Pointer Review (1) Pointer Can Be Dangerous int i, *pi; 1000 2000 i ? pi ? pi = &i; i 1000 2000 *pi ? pi 1000 i = 10 or *pi = 10 i 1000 2000 *pi 10 pi 1000 CHAPTER 4 3
- 4. Pointer Review (2) typedef struct list_node *list_pointer; typedef struct list_node { int data; list_pointer link; } list_pointer ptr = NULL; 1000 ptr NULL ptr->data(*ptr).data ptr = malloc(sizeof(list_node)); 1000 2000 *ptr ptr 2000 data link CHAPTER 4 4
- 5. 4.1.2 Using Dynamically Allocated Storage int i, *pi; float f, *pf; pi = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int)); request memory pf = (float *) malloc (sizeof(float)); *pi =1024; *pf =3.14; printf(”an integer = %d, a float = %fn”, *pi, *pf); free(pi); return memory free(pf); *Program4.1:Allocation and deallocation of pointers (p.138) CHAPTER 4 5
- 6. 4.2 SINGLY LINKED LISTS bat cat sat vat NULL *Figure 4.1: Usual way to draw a linked list (p.139) CHAPTER 4 6
- 7. Insertion bat cat sat vat NULL mat *Figure 4.2: Insert mat after cat (p.140) CHAPTER 4 7
- 8. bat cat mat sat vat NULL dangling reference *Figure 4.3: Delete mat from list (p.140) CHAPTER 4 8
- 9. Example 4.1: create a linked list of words Declaration typedef struct list_node, *list_pointer; typedef struct list_node { char data [4]; list_pointer link; }; Creation list_pointer ptr =NULL; Testing #define IS_EMPTY(ptr) (!(ptr)) Allocation ptr=(list_pointer) malloc (sizeof(list_node)); CHAPTER 4 9
- 10. e -> name (*e).name strcpy(ptr -> data, “bat”); ptr -> link = NULL; address of ptr data ptr link first node b a t 0 NULL ptr *Figure 4.4:Referencing the fields of a node(p.142) CHAPTER 4 10
- 11. Example: create a two-node list ptr 10 20 NULL typedef struct list_node *list_pointer; typedef struct list_node { int data; list_pointer link; }; list_pointer ptr =NULL Example 4.2: (p.142) CHAPTER 4 11
- 12. list_pointer create2( ) { /* create a linked list with two nodes */ list_pointer first, second; first = (list_pointer) malloc(sizeof(list_node)); second = ( list_pointer) malloc(sizeof(list_node)); second -> link = NULL; second -> data = 20; ptr first -> data = 10; first ->link = second; return first; 10 20 NULL } *Program 4.2:Create a tow-node list (p.143) CHAPTER 4 12
- 13. List Insertion: Insert a node after a specific node void insert(list_pointer *ptr, list_pointer node) { /* insert a new node with data = 50 into the list ptr after node */ list_pointer temp; temp = (list_pointer) malloc(sizeof(list_node)); if (IS_FULL(temp)){ fprintf(stderr, “The memory is fulln”); exit (1); } CHAPTER 4 13
- 14. temp->data = 50; if (*ptr) { noempty list temp->link =node ->link; node->link = temp; ptr } else { empty list 10 20 NULL temp->link = NULL; node *ptr =temp; } 50 } temp *Program 4.3:Simple insert into front of list (p.144) CHAPTER 4 14
- 15. List Deletion Delete the first node. ptr trail node ptr 10 50 20 NULL 50 20 NULL (a) before deletion (b)after deletion Delete node other than the first node. ptr trail node ptr 10 50 20 NULL 10 20 NULL CHAPTER 4 15
- 16. void delete(list_pointer *ptr, list_pointer trail, list_pointer node) { /* delete node from the list, trail is the preceding node ptr is the head of the list */ trail node if (trail) trail->link = node->link; 10 50 20 NULL else *ptr = (*ptr) ->link; 10 20 NULL free(node); } ptr node ptr 10 50 20 NULL 50 20 NULL CHAPTER 4 16
- 17. Print out a list (traverse a list) void print_list(list_pointer ptr) { printf(“The list ocntains: “); for ( ; ptr; ptr = ptr->link) printf(“%4d”, ptr->data); printf(“n”); } *Program 4.5: Printing a list (p.146) CHAPTER 4 17
- 18. 4.3 DYNAMICALLY LINKED STACKS AND QUEUES top element link NULL (a) Linked Stack front rear element link NULL (b) Linked queue *Figure 4.10: Linked Stack and queue (p.147) CHAPTER 4 18
- 19. Represent n stacks #define MAX_STACKS 10 /* maximum number of stacks */ typedef struct { int key; /* other fields */ } element; typedef struct stack *stack_pointer; typedef struct stack { element item; stack_pointer link; }; stack_pointer top[MAX_STACKS]; CHAPTER 4 19
- 20. Represent n queues #define MAX_QUEUES 10 /* maximum number of queues */ typedef struct queue *queue_pointer; typedef struct queue { element item; queue_pointer link; }; queue_pointer front[MAX_QUEUE], rear[MAX_QUEUES]; CHAPTER 4 20
- 21. Push in the linked stack void add(stack_pointer *top, element item) { /* add an element to the top of the stack */ stack_pointer temp = (stack_pointer) malloc (sizeof (stack)); if (IS_FULL(temp)) { fprintf(stderr, “ The memory is fulln”); exit(1); } temp->item = item; temp->link = *top; *top= temp; * Program 4.6:Add to a linked stack (p.149) } CHAPTER 4 21
- 22. pop from the linked stack element delete(stack_pointer *top) { /* delete an element from the stack */ stack_pointer temp = *top; element item; if (IS_EMPTY(temp)) { fprintf(stderr, “The stack is emptyn”); exit(1); } item = temp->item; *top = temp->link; free(temp); return item; } *Program 4.7: Delete from a linked stack (p.149) CHAPTER 4 22
- 23. enqueue in the linked queue void addq(queue_pointer *front, queue_pointer *rear, element item) { /* add an element to the rear of the queue */ queue_pointer temp = (queue_pointer) malloc(sizeof (queue)); if (IS_FULL(temp)) { fprintf(stderr, “ The memory is fulln”); exit(1); } temp->item = item; temp->link = NULL; if (*front) (*rear) -> link = temp; else *front = temp; *rear = temp; } CHAPTER 4 23
- 24. dequeue from the linked queue (similar to push) element deleteq(queue_pointer *front) { /* delete an element from the queue */ queue_pointer temp = *front; element item; if (IS_EMPTY(*front)) { fprintf(stderr, “The queue is emptyn”); exit(1); } item = temp->item; *front = temp->link; free(temp); return item; } CHAPTER 4 24
- 25. Polynomials A( x ) =a m − x e 1 m−1 + m− x e a 2 m−2 + + 0xe ... a 0 Representation typedef struct poly_node *poly_pointer; typedef struct poly_node { int coef; int expon; poly_pointer link; }; poly_pointer a, b, c; coef expon link CHAPTER 4 25
- 26. Examples a = 3x + 2 x +1 14 8 a 3 14 2 8 1 0 null b = 8 x 14 − 3x 10 +10 x 6 b 8 14 -3 10 10 6 null CHAPTER 4 26
- 27. Adding Polynomials 3 14 2 8 1 0 a 8 14 -3 10 10 6 b 11 14 a->expon == b->expon d 3 14 2 8 1 0 a 8 14 -3 10 10 6 b 11 14 -3 10 a->expon < b->expon d CHAPTER 4 27
- 28. Adding Polynomials (Continued) 3 14 2 8 1 0 a 8 14 -3 10 10 6 b 11 14 -3 10 2 8 d a->expon > b->expon CHAPTER 4 28
- 29. Alogrithm for Adding Polynomials poly_pointer padd(poly_pointer a, poly_pointer b) { poly_pointer front, rear, temp; int sum; rear =(poly_pointer)malloc(sizeof(poly_node)); if (IS_FULL(rear)) { fprintf(stderr, “The memory is fulln”); exit(1); } front = rear; while (a && b) { switch (COMPARE(a->expon, b->expon)) { CHAPTER 4 29
- 30. case -1: /* a->expon < b->expon */ attach(b->coef, b->expon, &rear); b= b->link; break; case 0: /* a->expon == b->expon */ sum = a->coef + b->coef; if (sum) attach(sum,a->expon,&rear); a = a->link; b = b->link; break; case 1: /* a->expon > b->expon */ attach(a->coef, a->expon, &rear); a = a->link; } } for (; a; a = a->link) attach(a->coef, a->expon, &rear); for (; b; b=b->link) attach(b->coef, b->expon, &rear); rear->link = NULL; temp = front; front = front->link; free(temp); return front; } Delete extra initial node. CHAPTER 4 30
- 31. Analysis (1) coefficient additions 0 ≤ additions ≤ min(m, n) where m (n) denotes the number of terms in A (B). (2) exponent comparisons extreme case em-1 > fm-1 > em-2 > fm-2 > … > e0 > f0 m+n-1 comparisons (3) creation of new nodes extreme case m + n new nodes summary O(m+n) CHAPTER 4 31
- 32. Attach a Term void attach(float coefficient, int exponent, poly_pointer *ptr) { /* create a new node attaching to the node pointed to by ptr. ptr is updated to point to this new node. */ poly_pointer temp; temp = (poly_pointer) malloc(sizeof(poly_node)); if (IS_FULL(temp)) { fprintf(stderr, “The memory is fulln”); exit(1); } temp->coef = coefficient; temp->expon = exponent; (*ptr)->link = temp; *ptr = temp; } CHAPTER 4 32
- 33. A Suite for Polynomials e(x) = a(x) * b(x) + d(x) poly_pointer a, b, d, e; read_poly() ... a = read_poly(); print_poly() b = read_poly(); padd() d = read_poly(); temp = pmult(a, b); psub() e = padd(temp, d); pmult() print_poly(e); temp is used to hold a partial result. By returning the nodes of temp, we may use it to hold other polynomials CHAPTER 4 33
- 34. Erase Polynomials void earse(poly_pointer *ptr) { /* erase the polynomial pointed to by ptr */ poly_pointer temp; while (*ptr) { temp = *ptr; *ptr = (*ptr)->link; free(temp); } } O(n) CHAPTER 4 34
- 35. Circular Linked Lists circular list vs. chain ptr 3 14 2 8 1 0 avail ptr temp avail ... CHAPTER 4 35
- 36. Maintain an Available List poly_pointer get_node(void) { poly_pointer node; if (avail) { node = avail; avail = avail->link: } else { node = (poly_pointer)malloc(sizeof(poly_node)); if (IS_FULL(node)) { printf(stderr, “The memory is fulln”); exit(1); } } return node; } CHAPTER 4 36
- 37. Maintain an Available List (Continued) Insert ptr to the front of this list void ret_node(poly_pointer ptr) { ptr->link = avail; avail = ptr; } Erase a circular list (see next page) void cerase(poly_pointer *ptr) { poly_pointer temp; if (*ptr) { temp = (*ptr)->link; (*ptr)->link = avail; (1) avail = temp; (2) *ptr = NULL; } } Independent of # of nodes in a list O(1) constant time CHAPTER 4 37
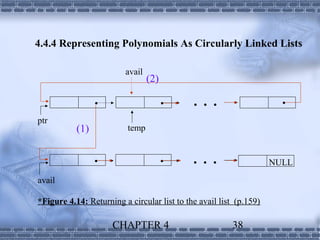
- 38. 4.4.4 Representing Polynomials As Circularly Linked Lists avail (2) ptr (1) temp NULL avail *Figure 4.14: Returning a circular list to the avail list (p.159) CHAPTER 4 38
- 39. Head Node Represent polynomial as circular list. (1) zero a -1 Zero polynomial (2) others a -1 3 14 2 8 1 0 a = 3x + 2 x +1 14 8 CHAPTER 4 39
- 40. Another Padd poly_pointer cpadd(poly_pointer a, poly_pointer b) { poly_pointer starta, d, lastd; int sum, done = FALSE; starta = a; a = a->link; Set expon field of head node to -1. b = b->link; d = get_node(); d->expon = -1; lastd = d; do { switch (COMPARE(a->expon, b->expon)) { case -1: attach(b->coef, b->expon, &lastd); b = b->link; break; CHAPTER 4 40
- 41. Another Padd (Continued) case 0: if (starta == a) done = TRUE; else { sum = a->coef + b->coef; if (sum) attach(sum,a->expon,&lastd); a = a->link; b = b->link; } break; case 1: attach(a->coef,a->expon,&lastd); a = a->link; } } while (!done); lastd->link = d; return d; Link last node to } first CHAPTER 4 41
- 42. Additional List Operations typedef struct list_node *list_pointer; typedef struct list_node { char data; list_pointer link; }; Invert single linked lists Concatenate two linked lists CHAPTER 4 42
- 43. Invert Single Linked Lists Use two extra pointers: middle and trail. list_pointer invert(list_pointer lead) { list_pointer middle, trail; middle = NULL; while (lead) { trail = middle; middle = lead; lead = lead->link; middle->link = trail; } return middle; } 0: null 1: lead ... ≥2: lead CHAPTER 4 43
- 44. Concatenate Two Lists list_pointer concatenate(list_pointer ptr1, list_pointer ptr2) { list_pointer temp; if (IS_EMPTY(ptr1)) return ptr2; else { if (!IS_EMPTY(ptr2)) { for (temp=ptr1;temp->link;temp=temp->link); temp->link = ptr2; } return ptr1; } } O(m) where m is # of elements in the first list CHAPTER 4 44
- 45. 4.5.2 Operations For Circularly Linked List What happens when we insert a node to the front of a circular linked list? X1 X2 X3 a Problem: move down the whole list. *Figure 4.16: Example circular list (p.165) CHAPTER 4 45
- 46. A possible solution: X1 X2 X3 a Note a pointer points to the last node. *Figure 4.17: Pointing to the last node of a circular list (p.165) CHAPTER 4 46
- 47. Operations for Circular Linked Lists void insert_front (list_pointer *ptr, list_pointer node) { if (IS_EMPTY(*ptr)) { *ptr= node; node->link = node; } else { node->link = (*ptr)->link; (1) (*ptr)->link = node; (2) } } X1 X2 X3 ptr (2) (1) CHAPTER 4 47
- 48. Length of Linked List int length(list_pointer ptr) { list_pointer temp; int count = 0; if (ptr) { temp = ptr; do { count++; temp = temp->link; } while (temp!=ptr); } return count; } CHAPTER 4 48
- 49. Equivalence Relations A relation over a set, S, is said to be an equivalence relation over S iff it is symmertric( 对称 ), reflexive( 自反 ), and transitive( 传递 ) over S. reflexive, x=x symmetric, if x=y, then y=x transitive, if x=y and y=z, then x=z CHAPTER 4 49
- 50. Examples 0=4, 3=1, 6=10, 8=9, 7=4, 6=8, 3=5, 2=11, 11=1 three equivalent classes {0,2,4,7,11}; {1,3,5}; {6,8,9,10} CHAPTER 4 50
- 51. A Rough Algorithm to Find Equivalence Classes void equivalenec() { initialize; while (there are more pairs) { Phase 1 read the next pair <i,j>; process this pair; } initialize the output; do { output a new equivalence class; Phase 2 } while (not done); } What kinds of data structures are adopted? CHAPTER 4 51
- 52. First Refinement #include <stdio.h> #include <alloc.h> #define MAX_SIZE 24 #define IS_FULL(ptr) (!(ptr)) #define FALSE 0 #define TRUE 1 void equivalence() { initialize seq to NULL and out to TRUE while (there are more pairs) { read the next pair, <i,j>; put j on the seq[i] list; put i on the seq[j] list; } for (i=0; i<n; i++) if (out[i]) { direct equivalence out[i]= FALSE; output this equivalence class; } } Compute indirect equivalence using transitivity CHAPTER 4 52
- 53. Lists After Pairs are input [0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] 0≡4 seq 3≡1 6 ≡ 10 8≡9 11 3 11 5 7 3 8 4 6 8 6 0 7≡4 NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL 6≡8 3≡5 2 ≡ 11 4 1 0 10 9 2 11 ≡ 0 NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL typedef struct node *node_pointer ; typedef struct node { int data; node_pointer link; }; CHAPTER 4 53
- 54. Final Version for Finding Equivalence Classes void main(void) { short int out[MAX_SIZE]; node_pointer seq[MAX_SIZE]; node_pointer x, y, top; int i, j, n; printf(“Enter the size (<= %d) “, MAX_SIZE); scanf(“%d”, &n); for (i=0; i<n; i++) { out[i]= TRUE; seq[i]= NULL; } printf(“Enter a pair of numbers (-1 -1 to quit): “); scanf(“%d%d”, &i, &j); Phase 1: input the equivalence pairs: CHAPTER 4 54
- 55. while (i>=0) { x = (node_pointer) malloc(sizeof(node)); if (IS_FULL(x)) fprintf(stderr, “memory is fulln”); exit(1); } Insert x to the top of lists seq[i] x->data= j; x->link= seq[i]; seq[i]= x; if (IS_FULL(x)) fprintf(stderr, “memory is fulln”); exit(1); } Insert x to the top of lists seq[j] x->data= i; x->link= seq[j]; seq[j]= x; printf(“Enter a pair of numbers (-1 -1 to quit): “); scanf(“%d%d”, &i, &j); } CHAPTER 4 55
- 56. Phase 2: output the equivalence classes for (i=0; i<n; i++) { if (out[i]) { printf(“nNew class: %5d”, i); out[i]= FALSE; x = seq[i]; top = NULL; for (;;) { while (x) { j = x->data; if (out[j]) { printf(“%5d”, j); push out[j] = FALSE; y = x->link; x->link = top; top = x; x = y; } else x = x->link; } if (!top) break; pop x = seq[top->data]; top = top->link; } } } CHAPTER 4 56
- 57. 4.7 Sparse Matrices 0 0 11 0 12 0 0 0 0 −4 0 0 0 0 0 − 15 inadequates of sequential schemes (1) # of nonzero terms will vary after some matrix computation (2) matrix just represents intermediate results new scheme Each column (row): a circular linked list with a head node CHAPTER 4 57
- 58. Revisit Sparse Matrices # of head nodes = max{# of rows, # of columns} 連 down head right 連同一列元素 head node 同 next 一 行 down entry row col right entry node 元 value 素 entry i j aij aij CHAPTER 4 58
- 59. Linked Representation for Matrix 4 4 0 2 11 1 0 1 1 12 5 2 1 -4 3 3 -15 CircularCHAPTER 4 linked list 59
- 60. #define MAX_SIZE 50 /* size of largest matrix */ typedef enum {head, entry} tagfield; typedef struct matrix_node *matrix_pointer; typedef struct entry_node { int row; int col; int value; }; typedef struct matrix_node { matrix_pointer down; matrix_pointer right; tagfield tag; CHAPTER 4 60
- 61. union { matrix_pointer next; entry_node entry; } u; }; matrix_pointer hdnode[MAX_SIZE]; CHAPTER 4 61
- 62. [0] [1] [2] [0] 4 4 4 [1] 0 2 11 [2] 1 0 12 [3] 2 1 -4 [4] 3 3 -15 *Figure 4.22: Sample input for sparse matrix (p.174) CHAPTER 4 62
- 63. Read in a Matrix matrix_pointer mread(void) { /* read in a matrix and set up its linked list. An global array hdnode is used */ int num_rows, num_cols, num_terms; int num_heads, i; int row, col, value, current_row; matrix_pointer temp, last, node; printf(“Enter the number of rows, columns and number of nonzero terms: “); CHAPTER 4 63
- 64. scanf(“%d%d%d”, &num_rows, &num_cols, &num_terms); num_heads = (num_cols>num_rows)? num_cols : num_rows; /* set up head node for the list of head nodes */ node = new_node(); node->tag = entry; node->u.entry.row = num_rows; node->u.entry.col = num_cols; if (!num_heads) node->right = node; else { /* initialize the head nodes */ for (i=0; i<num_heads; i++) { term= new_node(); hdnode[i] = temp; hdnode[i]->tag = head; O(max(n,m)) hdnode[i]->right = temp; hdnode[i]->u.next = temp; } CHAPTER 4 64
- 65. current_row= 0; last= hdnode[0]; for (i=0; i<num_terms; i++) { printf(“Enter row, column and value:”); scanf(“%d%d%d”, &row, &col, &value); if (row>current_row) { last->right= hdnode[current_row]; current_row= row; last=hdnode[row]; } ... temp = new_node(); temp->tag=entry; temp->u.entry.row=row; temp->u.entry.col = col; temp->u.entry.value = value; last->right = temp;/*link to row list */ last= temp; /* link to column list */ hdnode[col]->u.next->down = temp; hdnode[col]=>u.next = temp; } 利用 next field 存放 column 的 last node CHAPTER 4 65
- 66. /*close last row */ last->right = hdnode[current_row]; /* close all column lists */ for (i=0; i<num_cols; i++) hdnode[i]->u.next->down = hdnode[i]; /* link all head nodes together */ for (i=0; i<num_heads-1; i++) hdnode[i]->u.next = hdnode[i+1]; hdnode[num_heads-1]->u.next= node; node->right = hdnode[0]; } return node; } O(max{#_rows, #_cols}+#_terms) CHAPTER 4 66
- 67. Write out a Matrix void mwrite(matrix_pointer node) { /* print out the matrix in row major form */ int i; matrix_pointer temp, head = node->right; printf(“n num_rows = %d, num_cols= %dn”, node->u.entry.row,node->u.entry.col); printf(“The matrix by row, column, and value:nn”); O(#_rows+#_terms) for (i=0; i<node->u.entry.row; i++) { for (temp=head->right;temp!=head;temp=temp->right) printf(“%5d%5d%5dn”, temp->u.entry.row, temp->u.entry.col, temp->u.entry.value); head= head->u.next; /* next row */ } } CHAPTER 4 67
- 68. Free the entry and head nodes by row. Erase a Matrix void merase(matrix_pointer *node) { int i, num_heads; matrix_pointer x, y, head = (*node)->right; for (i=0; i<(*node)->u.entry.row; i++) { y=head->right; while (y!=head) { x = y; y = y->right; free(x); } x= head; head= head->u.next; free(x); } y = head; while (y!=*node) { x = y; y = y->u.next; free(x); } free(*node); *node = NULL; } O(#_rows+#_cols+#_terms) Alternative: 利用 Fig 4.14 的技巧,把一列資料 erase (constant time) CHAPTER 4 68
- 69. 4.8 Doubly Linked List Move in forward and backward direction. Singly linked list (in one direction only) How to get the preceding node during deletion or insertion? Using 2 pointers Node in doubly linked list consists of: 1. left link field (llink) 2. data field (item) 3. right link field (rlink) CHAPTER 4 69
- 70. Doubly Linked Lists typedef struct node *node_pointer; typedef struct node { node_pointer llink; ptr element item; = ptr->rlink->llink node_pointer rlink; = ptr->llink->rlink } head node llink item rlink CHAPTER 4 70
- 71. ptr *Figure 4.24:Empty doubly linked circular list with head node (p.180) CHAPTER 4 71
- 72. node node newnode *Figure 4.25: Insertion into an empty doubly linked circular list (p.181) CHAPTER 4 72
- 73. Insert void dinsert(node_pointer node, node_pointer newnode) { (1) newnode->llink = node; (2) newnode->rlink = node->rlink; (3) node->rlink->llink = newnode; (4) node->rlink = newnode; } head node llink item rlink (1) (3) (2) (4) CHAPTER 4 73
- 74. Delete void ddelete(node_pointer node, node_pointer deleted) { if (node==deleted) printf(“Deletion of head node not permitted.n”); else { (1) deleted->llink->rlink= deleted->rlink; (2) deleted->rlink->llink= deleted->llink; free(deleted); } } head node (1) llink item rlink (2) CHAPTER 4 74









![Example 4.1: create a linked list of words
Declaration
typedef struct list_node, *list_pointer;
typedef struct list_node {
char data [4];
list_pointer link;
};
Creation
list_pointer ptr =NULL;
Testing
#define IS_EMPTY(ptr) (!(ptr))
Allocation
ptr=(list_pointer) malloc (sizeof(list_node));
CHAPTER 4 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-9-320.jpg)









![Represent n stacks
#define MAX_STACKS 10 /* maximum number of
stacks */
typedef struct {
int key;
/* other fields */
} element;
typedef struct stack *stack_pointer;
typedef struct stack {
element item;
stack_pointer link;
};
stack_pointer top[MAX_STACKS];
CHAPTER 4 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-19-320.jpg)
![Represent n queues
#define MAX_QUEUES 10 /* maximum number of
queues */
typedef struct queue *queue_pointer;
typedef struct queue {
element item;
queue_pointer link;
};
queue_pointer front[MAX_QUEUE],
rear[MAX_QUEUES];
CHAPTER 4 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-20-320.jpg)






























![First Refinement
#include <stdio.h>
#include <alloc.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 24
#define IS_FULL(ptr) (!(ptr))
#define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1
void equivalence()
{
initialize seq to NULL and out to TRUE
while (there are more pairs) {
read the next pair, <i,j>;
put j on the seq[i] list;
put i on the seq[j] list;
}
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
if (out[i]) { direct equivalence
out[i]= FALSE;
output this equivalence class;
}
} Compute indirect equivalence
using transitivity
CHAPTER 4 52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-52-320.jpg)
![Lists After Pairs are input
[0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11]
0≡4
seq
3≡1
6 ≡ 10
8≡9 11 3 11 5 7 3 8 4 6 8 6 0
7≡4 NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL
6≡8
3≡5
2 ≡ 11 4 1 0 10 9 2
11 ≡ 0 NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL
typedef struct node *node_pointer ;
typedef struct node {
int data;
node_pointer link;
}; CHAPTER 4 53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-53-320.jpg)
![Final Version for
Finding Equivalence Classes
void main(void)
{
short int out[MAX_SIZE];
node_pointer seq[MAX_SIZE];
node_pointer x, y, top;
int i, j, n;
printf(“Enter the size (<= %d) “, MAX_SIZE);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
out[i]= TRUE; seq[i]= NULL;
}
printf(“Enter a pair of numbers (-1 -1 to quit): “);
scanf(“%d%d”, &i, &j);
Phase 1: input the equivalence pairs:
CHAPTER 4 54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-54-320.jpg)
![while (i>=0) {
x = (node_pointer) malloc(sizeof(node));
if (IS_FULL(x))
fprintf(stderr, “memory is fulln”);
exit(1);
} Insert x to the top of lists seq[i]
x->data= j; x->link= seq[i]; seq[i]= x;
if (IS_FULL(x))
fprintf(stderr, “memory is fulln”);
exit(1);
} Insert x to the top of lists seq[j]
x->data= i; x->link= seq[j]; seq[j]= x;
printf(“Enter a pair of numbers (-1 -1 to
quit): “);
scanf(“%d%d”, &i, &j);
}
CHAPTER 4 55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-55-320.jpg)
![Phase 2: output the equivalence classes
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
if (out[i]) {
printf(“nNew class: %5d”, i);
out[i]= FALSE;
x = seq[i]; top = NULL;
for (;;) {
while (x) {
j = x->data;
if (out[j]) {
printf(“%5d”, j); push
out[j] = FALSE;
y = x->link; x->link = top;
top = x; x = y;
}
else x = x->link;
}
if (!top) break; pop
x = seq[top->data]; top = top->link;
}
}
}
CHAPTER 4 56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-56-320.jpg)




![union {
matrix_pointer next;
entry_node entry;
} u;
};
matrix_pointer hdnode[MAX_SIZE];
CHAPTER 4 61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-61-320.jpg)
![[0] [1] [2]
[0] 4 4 4
[1] 0 2 11
[2] 1 0 12
[3] 2 1 -4
[4] 3 3 -15
*Figure 4.22: Sample input for sparse matrix (p.174)
CHAPTER 4 62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-62-320.jpg)

![scanf(“%d%d%d”, &num_rows, &num_cols,
&num_terms);
num_heads =
(num_cols>num_rows)? num_cols : num_rows;
/* set up head node for the list of head
nodes */
node = new_node(); node->tag = entry;
node->u.entry.row = num_rows;
node->u.entry.col = num_cols;
if (!num_heads) node->right = node;
else { /* initialize the head nodes */
for (i=0; i<num_heads; i++) {
term= new_node();
hdnode[i] = temp;
hdnode[i]->tag = head; O(max(n,m))
hdnode[i]->right = temp;
hdnode[i]->u.next = temp;
}
CHAPTER 4 64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-64-320.jpg)
![current_row= 0; last= hdnode[0];
for (i=0; i<num_terms; i++) {
printf(“Enter row, column and value:”);
scanf(“%d%d%d”, &row, &col, &value);
if (row>current_row) {
last->right= hdnode[current_row];
current_row= row; last=hdnode[row];
} ...
temp = new_node();
temp->tag=entry; temp->u.entry.row=row;
temp->u.entry.col = col;
temp->u.entry.value = value;
last->right = temp;/*link to row list */
last= temp;
/* link to column list */
hdnode[col]->u.next->down = temp;
hdnode[col]=>u.next = temp;
}
利用 next field 存放 column 的 last node
CHAPTER 4 65](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-65-320.jpg)
![/*close last row */
last->right = hdnode[current_row];
/* close all column lists */
for (i=0; i<num_cols; i++)
hdnode[i]->u.next->down = hdnode[i];
/* link all head nodes together */
for (i=0; i<num_heads-1; i++)
hdnode[i]->u.next = hdnode[i+1];
hdnode[num_heads-1]->u.next= node;
node->right = hdnode[0];
}
return node;
}
O(max{#_rows, #_cols}+#_terms)
CHAPTER 4 66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lists-130409104733-phpapp01/85/Lists-66-320.jpg)







