MCT -5G Architecture , Testing and Development and Security Issues, MIMO
- 2. Syllabus UNIT-1 Basics of Mobile Computing UNIT-2 5G Basics and Core Architecture UNIT-3 5G Technology Enablers UNIT-4 5G Network Testing & Deployment UNIT-5 Security Issues and Design thinking in 5G
- 3. • The rapidly expanding technology of cellular communication, wireless LANs, and satellite services will make information accessible anywhere and at any time. Regardless of size, most mobile computers will be equipped with a wireless connection to the fixed part of the network, and, perhaps, to other mobile computers. • The resulting computing environment, which is often referred to as mobile or nomadic computing Mobile Computing is an umbrella term used to describe technologies that enable people to access network services anyplace, anytime, and anywhere
- 4. • Mobile communication • Mobile hardware • Mobile software Mobile communication Mobile hardware Mobile software
- 5. 1. Portability - The Ability to move a device within a learning environment or to different environments with ease. 2. Social Interactivity - The ability to share data and collaboration between users. 3. Connectivity - The ability to be digitally connected for the purpose of communication of data in any environment. 4. Individuality - The ability to use the technology to provide scaffolding on difficult activities and lesson customization for individual learners. Advantage of Mobile Computing 1. Location flexibility 2. Saves time 3. Enhanced Productivity 4. Entertainment 5. Ease of Research 6. Cloud Computing 7. Social Engagement Disadvantage of Mobile Computing 1. Security 2. Distractions 3. power consumption 4. quality of connectivity 5. Cost 6. Screen Size
- 6. Term Definition Communication Communication refers to exchange of information. A communication system enables electronic transmission and receiving of information over short and long distances. Cellular Networks Cellular networks enable short and long range connectivity to devices on the move. Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves refers to waves created due to oscillation of electric and magnetic waves. These are formed when an electric field comes in contact with a magnetic field. Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to propagate. They can travel through vacuum, air, and solids. Examples of EM waves are Radio Waves, Infrared Waves, X-rays, etc. Spectrum Spectrum is a range of radio frequencies used for communication purposes. There are 3 categories of spectrum: low, mid, high frequency. Low (< 3GHz) is for long distances, low speed, High (> 24GHz) is for short distances, high speed and mid (3-24 GHz) is a mix of coverage and speed. Spectrum is assigned by a regulatory agency for use by a given group or organization Bandwidth Bandwidth is the volume of information that can be sent over a communication channel in a unit second. For example, 1M bits per seconds. Channel Channel refers to the medium used to transmit and receive messages. The communication channel is either wire, fiber, air.
- 7. Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) Ethernet is a wired based approach to interconnect networks and computing systems. Primarily used for creating small and medium size local area networks (LAN). IEEE 802.3 defines standards for Ethernet protocols Beamforming Beamforming is a technique by which an array of antennas can be steered to transmit radio signals in a specific direction. Rather than simply broadcasting energy/signals in all directions, the antenna arrays that use beamforming, determine the direction of interest and send/receive a stronger beam of signals in that specific direction. Wired Wired communication refers to transmission and receiving of information using a wired based technology. Examples - TV cables, Telephone, Fiber Optics links, Ethernet cable. Wireless Wireless communications allows devices to be inter-connected without using any physical media. Wireless allows devices to be connected and at the sametime roam or move around enabling mobility. Examples- Satellite communication, Cellular Networks, WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, WiFi (IEEE 802.11) WiFi provides wireless connectivity to network and computing systems using unlicensed wireless spectrum. Predominantly used for enabling W-LAN (called Wireless local area network) connectivity for Mobile, Laptops, Smart Devices and so on. IEEE 802.11 defines standards for WiFi protocols WiMAX (IEEE 802.16) WiMAX is a wireless communication standard for a large area of coverage for creating wireless metropolitan area networks (MAN). For example, WiFi range is around 100 feet, while WiMAX can cover up to 30-50 kilometers.
- 8. A Cellular network or Mobile network is a radio network distributed over land areas called cells, each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver, known as a cell site or base station. ● Cellular network is an underlying technology for mobile phones, personal communication systems, wireless networking etc. ● Cellular networks use lower power, shorter range and more transmitters for data transmission. ● Each cellular base station is allocated a group of radio channels within a small geographic area called a cell
- 11. Cellular systems are measured by certain performance characteristics like: a) Voice quality. b) Service Quality like coverage and quality of service. c) Number of Dropped calls. d) Special features like call forwarding, call diverting, call barring. 1. Voice Quality Voice quality is very hard to judge without subjective tests for users’ opinions. In this technical area, engineers cannot decide how to build a system without knowing the voice quality that will satisfy the users. CM: For any given commercial communications system, the voice quality will be based on the following criterion MOS: As the percentage of customers choosing CM4 and CM5 increases, the cost of building the system rises. DRT (Diagnostic Rhyme Test)
- 12. 2. Service Quality Three items are required for service quality 1. Coverage: The system should serve an area as large as possible. 2. Required grade of service: For a normal start-up system, the grade of service is specified for a blocking probability of .02 for initiating calls at the busy hour. 3. Number of dropped calls: During Q calls in an hour, if a call is dropped and Q-1 calls are completed, then the call drop rate is 1/Q. This drop rate must be kept low. Special Features A system would like to provide as many special features as Call Forwarding call waiting voice stored (VSR) box automatic roaming short message service (SMS) multimedia service (MMS) Navigation services.
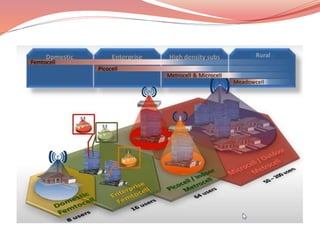
- 13. There are 2 techniques for improving cell capacity in cellular system, namely: ● Cell Splitting. ● Sectoring. Capacity Increasing Methods 1.New addition of channels 2. Frequency Barrowing Cell Splitting: It is the process of subdividing a congested cell into smaller cells(Micro Cells) Cell splitting increases capacity of cellular systems since it increases the number of times that channels are reused There are two types of cell splitting. - Permanent cell splitting - Dynamic cell splitting
- 14. Advantages: ● Improvement in Signal capacity. ● Improvement in signal to interference ratio. ● Increases frequency reuse. Disadvantages: ● Increase in number of handoffs. ● Increase in the number of antennas at each base station. Sectoring ● This is another method to increase cellular capacity and coverage by keeping cell radius unchanged. ● In this approach, capacity improvement is achieved by reducing the number of cells in a cluster and thus increasing the frequency reuse.
- 15. Reuse is the scheme in which allocation and reuse of channels throughout a coverage region is done. Each cellular base station is allocated a group of radio channels or Frequency sub-bands to be used within a small geographic area known as a cell The shape of the cell is Hexagonal. The process of selecting and allocating the frequency sub-bands for all of the cellular base stations within a system is called Frequency reuse or Frequency Planning. Salient Features of using Frequency Reuse: ● Frequency reuse improves the spectral efficiency and signal Quality (QoS). ● Frequency reuse offers a protection against interference. ● In the Frequency Reuse scheme, total bandwidth is divided into different sub-bands that are used by cells. Frequency reuse and cell splitting are two main concepts in cellular networks.
- 16. Cell Handoffs Cellular Handoffs refers to the process of transferring ongoing call or data connectivity from one Cellular station to another cell station. A B There are two types of Handoffs: 1. Hard Handoff - “break and make” 2. Soft Handoff - “make and break”
- 17. 5G cell towers are different from 4G cell towers both functionally and physically ● 4G cell towers are physically larger cells called “macrocells” as they cover a large areas.
- 19. 5G cell towers called “smallcells” are relatively smaller in size compared to 4G cell towers. These can be installed easily on street poles, building tops or buried underground.
- 22. ● Interference in data transmission. ● Coverage Gaps ● Low Bandwidth during communication. ● Regulations and spectrum. ● High delays, large delay variation. ● Vulnerable to security issues and threats, simpler to attack.
- 28. The vision of 5G is to incorporate new uses that go beyond the Mobile internet. The new use of 5G are: eMBB , URLCC and mMTC 1. Enhanced Mobile Broadband - eMBB To bring in faster, reliable and secure internet service for the next wave of consumer devices and applications. Fiber like data speeds. Use Cases: 3D video, UHD Screens, Augmented / Mixed Reality, Realtime Gaming, Metaverse
- 30. 2. Ultra-reliable low-latency communications - URLCC Many mission critical and command control systems, smart grids, connected Transport, remote surgery system that has to be super reliable with very minimum latency / delays. Use Cases: Remote Surgeries, Self-Driving Vehicles, Drone navigation
- 32. 3. Massive Machine Type communications - mMTC Connection of Massive number of IoT and Smart systems and sensors to internet and applications and controls centers running Cloud. Use Cases: Smart Cities, Industrial Automation, Smart Buildings
- 34. Typical metrics used to drive 5G technology: Peak Data Rate - Provide upto 20 Gbps User Experience - 100 - 1000 Mbps (1Gbps) data speed Area Traffic Capacity - Upto 10 Mbits per second per meters square Network Efficiency - 100 times efficient, manageable, programmable, virtualized, softwarized Connection Density - 10^6 devices / km square (10 Lakh devices / km sq) Mobility - High speed mobility and handoffs upto 500kms Latency - Less than < 1 millisec Spectrum Efficiency 3 times more efficient, better utilization and reuse of spectrum.
- 35. Radio refers to the technology used for signaling and communication using Radio (Electromagentic) waves. All cell phones use radio waves to connect to cellular networks. 5G introduces a new radio interface and access technology for connecting user equipment with 5G cellular networks and towers. These signals eventually get converted into digital communication and into network packets towards the internet and vice versa. 5G NR is the global standard for a unified, more capable and consistent cellular air interface. Key Features of 5G Radio are: 1. Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (M-MIMO) 2. Diverse Spectrum Ranges 3. Modulation - new Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing 4. Beaming Forming
- 38. Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) refers to antenna technology in which more than one antenna is used for transmitting and receiving communication signals at the same time. The use of MIMO improves the rate of transmission and achieves higher data rates and coverage area. A Massive MIMO is a MIMO system with a large number of antennas, such as more than 100 antennas. The excessive number of antennas allows: ● Support very high data rate communication speeds ● Connect large number of users ● Ensures reliability and efficiency of cellular communications.
- 39. Benefits of MIMO 1. Achieve high data rates with high uplink and downlink throughput 2. Reduction in communications errors 3. Help extending cell coverage area using methods like Beamforming 4. Minimizes signal fading in transmission medium. 5. High Quality of Service like signal quality, spectral efficiency Challenges of MIMO 1. Hardware complexity due to higher number of signal processing requirements. 2. Higher cost due to the high number of antenna and Radio signal processing units. 3. High power requirements due to higher communication units. 4. Higher software complexity, configuration and management of large number of antennas 5. Thermal problems due to high energy dissipation.
- 40. Diverse Spectrum Ranges - spectrum that ranges from several hundred kilohertz to millimeter wave (mmWave) to enable various use cases, cell sizes and data rates. There are two ranges defined: Frequency range 1 (FR1) is sub-6 GHz from 450 MHz to 6 GHz, which includes the LTE/4G frequency range. Frequency range 2 (FR2) is millimeter Wave (mmWave) from 24.25 GHz to 52.6 GHz. Modulation - new Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Beaming Forming - Beamforming is a technique that focuses a wireless signal towards a specific receiving device, rather than having the signal spread in all directions from a broadcast antenna, as it normally would. The resulting more direct connection is faster and more reliable than it would be without beamforming. Here’s an illustration
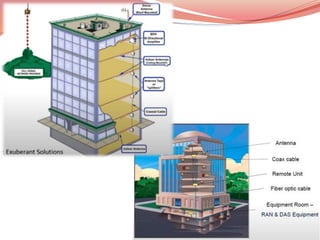
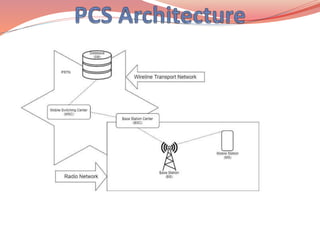
- 42. Mobile networks consists of two parts: (1) Radio Access Network (2) Packet Core Network Radio Access Network (RAN) - refers to the telecom infrastructure consisting of Radio Base Stations with large antennas that provide the basic cellular signaling and connectivity to end device or user equipment (e.g. mobile phones, cellular cameras, connected cars, so on). Core Network - refers to the data and packet switched network to provide the network path for users to access services or applications in the data network or internet. It consists of network elements such a: ● access layer switches ● aggregation routers ● identity, security and policy elements
- 45. • 5th generation mobile networks or 5th generation wireless systems ...abbreviated as 5G, are the proposed next telecommunications ...standards beyond the current 4G/IMT- Advanced standards. • initial chip design by QUALCOMM in October 2016. • It has incredible transmission speed. • 5G planning aims at higher capacity than current 4G, supporting device-to-device, ultra reliable, and massive machine communications.
- 47. 1G TECHNOLOGY • 1G refers to the first generation of wireless telephone technology, mobile telecommunications which was first introduced in1980s and completed in early 1990s. • It's Speed was up to 2.4kbps. •It allows the voice calls in 1 country. •1G network use Analog Signal. •AMPS (Advance Mobile Phone System) was first launched in USA in 1G mobile systems.
- 48. DRAWBACKS OF 1G • Poor Voice Quality • Poor Battery Life • Large Phone Size • No Security • Limited Capacity • Poor Handoff Reliability 1G Wireless System