Meetup Big Data User Group Dresden: Gradoop - Scalable Graph Analytics with Apache Flink
- 1. GRADOOP: Scalable Graph Analytics with Apache Flink Martin Junghanns Leipzig University Big Data User Group Dresden / Graph Databases Sachsen December 2015
- 2. About the speaker and the team André, PhD StudentMartin, PhD Student Kevin, M.Sc. StudentNiklas, M.Sc. Student Prof. Dr. Erhard Rahm Database Chair
- 3. Outline Motivation Gradoop Architecture Extended Property Graph Model (EPGM) Apache Flink EPGM on Apache Flink Business Intelligence Use Case Tooling Current State & Future Work
- 4. Motivation
- 5. 𝑮𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 = (𝑽𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒, 𝑬𝑑𝑑𝑑𝑑) “Graphs are everywhere”
- 6. 𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺 = (𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔, 𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹) “Graphs are everywhere” Alice Bob Eve Dave Carol Mallory Peggy
- 7. 𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺 = (𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔, 𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹) “Graphs are everywhere” Alice Bob Eve Dave Carol Mallory Peggy
- 8. 𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺 = (𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔, 𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹) “Graphs are everywhere” Alice Bob Eve Dave Carol Mallory Peggy
- 9. 𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺 = (𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔, 𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹) “Graphs are everywhere” Alice Bob Eve Dave Carol Mallory Peggy
- 10. 𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺 = (𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔, 𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹) “Graphs are everywhere” Alice Bob Eve Dave Carol Mallory Peggy Trent
- 11. 𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺 = (𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔𝐔, 𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹) “Graphs are everywhere” Alice Bob Eve Dave Carol Mallory Peggy Trent
- 12. 𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺𝐺 = (𝐂𝐂𝐂𝐂𝐂𝐂, 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶) “Graphs are everywhere” Leipzig pop: 544K Dresden pop: 536K Berlin pop: 3.5M Hamburg pop: 1.7M Munich pop: 1.4M Chemnitz pop: 243K Nuremberg pop: 500K Cologne pop: 1M
- 13. World Wide Web ca. 1 billion websites “Graphs are large” Facebook ca. 1.49 billion active users ca. 340 friends per user
- 14. End-to-End Graph Analytics Data Integration Graph Analytics Representation Integrate data from one or more sources into a dedicated graph storage with common graph data model Definition of analytical workflows from operator algebra Result representation in a meaningful way
- 15. Graph Data Management Graph Database Systems Neo4j, OrientDB Graph Processing Systems Pregel, Giraph Distributed Workflow Systems Flink Gelly, Spark GraphX Data Model Rich Graph Models Generic Graph Models Generic Graph Models Focus Local ACID Operations Global Graph Operations Global Data and Graph Operations Query Language Yes No No Persistency Yes No No Scalability Vertical Horizontal Horizontal Workflows No No Yes Data Integration No No No Graph Analytics No Yes Yes Representation Yes No No
- 16. What‘s missing? An end-to-end framework and research platform for efficient, distributed and domain independent graph data management and analytics.
- 17. Gradoop Architecture & Data Model
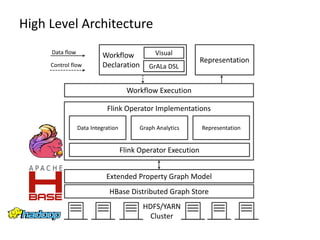
- 18. High Level Architecture HDFS/YARN Cluster HBase Distributed Graph Store Extended Property Graph Model Flink Operator Implementations Data Integration Flink Operator Execution Workflow Declaration Visual GrALa DSL Representation Data flow Control flow Graph Analytics Representation Workflow Execution
- 19. [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 Extended Property Graph Model [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013
- 20. [2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 Extended Property Graph Model [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013
- 21. Graph Operators and Algorithms Operators Unary Binary GraphCollectionLogicalGraph Algorithms Aggregation Pattern Matching Projection Summarization Equality Call * Combination Overlap Exclusion Equality Union Intersection Difference Gelly Library BTG Extraction Label Propagation Graph Forecasting Frequent Subgraphs Top Selection Distinct Sort Apply * Reduce * Call * * auxiliary
- 22. Graph Operators and Algorithms Operators Unary Binary GraphCollectionLogicalGraph Algorithms Aggregation Pattern Matching Projection Summarization Equality Call * Combination Overlap Exclusion Equality Union Intersection Difference Gelly Library BTG Extraction Label Propagation Graph Forecasting Frequent Subgraphs Top Selection Distinct Sort Apply * Reduce * Call * * auxiliary
- 23. Combination 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) [2] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 DB
- 24. [0] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013
- 25. Graph Operators and Algorithms Operators Unary Binary GraphCollectionLogicalGraph Algorithms Aggregation Pattern Matching Projection Summarization Equality Call * Combination Overlap Exclusion Equality Union Intersection Difference Gelly Library BTG Extraction Label Propagation Graph Forecasting Frequent Subgraphs Top Selection Distinct Sort Apply * Reduce * Call * * auxiliary
- 26. [0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination + Summarization [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) 2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”} 3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL} 4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|) 5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|) 6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc, edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc)
- 27. [0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination + Summarization [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) 2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”} 3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL} 4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|) 5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|) 6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc, edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc) [5] [11] Person city : Leipzig count : 2 [12] Person city : Dresden count : 3 [13] Person city : Berlin count : 1 24 25 26 27 28 knows count : 3 knows count : 1 knows count : 2 knows count : 2 knows count : 2
- 28. [0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination + Summarization + Aggregation [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) 2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”} 3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL} 4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|) 5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|) 6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc, edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc) 7: aggFunc = (Graph g => |g.E|) 8: aggGraph = sumGraph.aggregate(“edgeCount”, aggFunc) [5] [11] Person city : Leipzig count : 2 [12] Person city : Dresden count : 3 [13] Person city : Berlin count : 1 24 25 26 27 28 knows count : 3 knows count : 1 knows count : 2 knows count : 2 knows count : 2
- 29. [0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination + Summarization + Aggregation [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) 2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”} 3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL} 4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|) 5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|) 6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc, edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc) 7: aggFunc = (Graph g => |g.E|) 8: aggGraph = sumGraph.aggregate(“edgeCount”, aggFunc) [5] edgeCount : 5 [11] Person city : Leipzig count : 2 [12] Person city : Dresden count : 3 [13] Person city : Berlin count : 1 24 25 26 27 28 knows count : 3 knows count : 1 knows count : 2 knows count : 2 knows count : 2
- 30. Graph Operators and Algorithms Operators Unary Binary GraphCollectionLogicalGraph Algorithms Aggregation Pattern Matching Projection Summarization Equality Call * Combination Overlap Exclusion Equality Union Intersection Difference Gelly Library BTG Extraction Label Propagation Graph Forecasting Frequent Subgraphs Top Selection Distinct Sort Apply * Reduce * Call * * auxiliary
- 31. Selection 1: resultColl = db.G[0,1,2].select((Graph g => g[“vertexCount”] > 3)) [2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 DB
- 32. Selection 1: resultColl = db.G[0,1,2].select((Graph g => g[“vertexCount”] > 3)) [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 DB [2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4 [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 0 1 2 3 4 5 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014
- 33. Graph Operators and Algorithms Operators Unary Binary GraphCollectionLogicalGraph Algorithms Aggregation Pattern Matching Projection Summarization Equality Call * Combination Overlap Exclusion Equality Union Intersection Difference Gelly Library BTG Extraction Label Propagation Graph Forecasting Frequent Subgraphs Top Selection Distinct Sort Apply * Reduce * Call * * auxiliary
- 34. Apache Flink
- 35. Apache Flink http://www.slideshare.net/robertmetzger1/apache-flink-meetup-munich-november-2015-flink-overview-architecture-integrations-and-use-case „Streaming Dataflow Engine that provides • data distribution, • communication, • and fault tolerance for distributed computations over data streams.“ HDFS LocalFS HBase JDBC Kafka RabbitMQ Flume (Neo4j) EmbeddedTezYarnClusterLocal Streaming Dataflow Runtime DataSet DataStream HadoopMR Table Gelly ML Table Zeppelin Cascading MRQL Dataflow Storm(wip) Dataflow(wip) SAMOA
- 36. Apache Flink – DataSet API DataSet := Distributed Collection of Data Transformation := Operation applied on DataSet Flink Program := Composition of Transformations DataSet DataSet DataSet Transformation Transformation DataSet DataSet Transformation DataSet Flink Program
- 37. Apache Flink – DataSet Transformations aggregate coGroup cross distinct filter first-N flatMap groupBy join leftOuterJoin rightOuterJoin fullOuterJoin map mapPartition reduce reduceGroup union iterate iterateDelta
- 38. The „Hello World“ of Big Data – Word Count 1: ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); 2: 3: DataSet<String> text = env.fromElements( // or env.readTextFile(„hdfs://…“) 4: „He who controls the past controls the future.“, 5: „He who controls the present controls the past.“); 6: 7: DataSet<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordCounts = text 8: .flatMap(new LineSplitter()) // splits the line and outputs (word, 1) tuples 9: .groupBy(0) 10: .sum(1); 11: 12: wordCounts.print(); // trigger execution flatMap „He who controls the past controls the future.“ „He who controls the present controls the past.“ (He,1) (who,1) (controls,1) (the,1) (past,1) // ... groupBy(0) [(He,1),(He,1)] [(who,1),(who,1)] [(future,1)] [(past,1),(past,1)] [(present,1)] // ... sum(1) (He,2) (who,2) (future,1) (past,2) (present,1) // ...
- 39. EPGM on Apache Flink
- 40. EPGM in Apache Flink – User facing API LogicalGraph fromCollections(…) : LogicalGraph fromDataSets(…) : LogicalGraph fromGellyGraph(…) : LogicalGraph getGraphHead() : DataSet<EPGMGraphHead> toGellyGraph() : Graph combine(…) : LogicalGraph intersect(…) : LogicalGraph summarize(…) : LogicalGraph match(…) : GraphCollection // ... GraphCollection fromCollections(…) : GraphCollection fromDataSets(…) : GraphCollection getGraphHeads() : DataSet<EPGMGraphHead> getGraph(…) : LogicalGraph getGraphs(…) : GraphCollection select(…) : GraphCollection union(…) : GraphCollection distinct(…) : GraphCollection sortBy(…) : GraphCollection // ... GraphBase getVertices() : DataSet<EPGMVertex> getEdges() : DataSet<EPGMEdge> // ... graphHeads : DataSet<EPGMGraphHead> vertices : DataSet<EPGMVertex> edges : DataSet<EPGMEdge> EPGMDatabase fromCollections(…) : EPGMDatabase fromJSONFile(…) : EPGMDatabase fromHBase(…) : EPGMDatabase writeAsJSON(…) : void writeToHBase(…) : void getDatabaseGraph() : LogicalGraph // ...
- 41. EPGM in Apache Flink – DataSets Id Label Properties Graphs Id Label Properties SourceId TargetId Graphs EPGMGraphHead EPGMVertex EPGMEdge Id Label Properties POJO POJO POJO DataSet<EPGMGraphHead> DataSet<EPGMVertex> DataSet<EPGMEdge> Id Label Properties Graphs EPGMVertex GradoopId := UUID 128-bit String PropertyList := List<Property> Property := (String, PropertyValue) PropertyValue := byte[] GradoopIdSet := Set<GradoopId> (55421132-f45b-40f0-8f6a-50ea13dbf2ea:Person{gender=f,city=Leipzig,name=Alice,age=20} @ [c2c0f288-9f27-4e55-b1c6-7a35e0eabe36, 77b710f9-07c2-49ab-b4bf-51e1a3138822])
- 42. EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion // input: firstGraph (G[0]), secondGraph (G[2]) 1: DataSet<GradoopId> graphId = secondGraph.getGraphHead() 2: .map(new Id<G>()); 3: 4: DataSet<V> newVertices = firstGraph.getVertices() 5: .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<V>()) 6: .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID); 7: 8: DataSet<E> newEdges = firstGraph.getEdges() 9: .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<E>()) 10: .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID) 11: .join(newVertices) 12: .where(new SourceId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>()) 13: .with(new LeftSide<E, V>()) 14: .join(newVertices) 15: .where(new TargetId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>()) 16: .with(new LeftSide<E, V>()); db.G[0].exclude(db.G[2]) [2] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4 [0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013
- 43. EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion Id Label Properties 2 Community interest: Graphs vertexCount: 4 graphId = secondGraph.getGraphHead() Id 2 newVertices = firstGraph.getVertices() Id Label Properties Graphs 5 Person name: Alice gender: f … [0, 2] 6 Person name: Bob gender: m … [0, 2] 9 Person name: Eve gender: f … [0] Id Label Properties Graphs 9 Person name: Eve gender: f … [0] .map(new Id<G>()); .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<V>()) .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID);
- 44. EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion newEdges = firstGraph.getEdges() Id Label SourceId TargetId Properties Graphs 0 knows 5 6 since: 2014 [0, 2] 1 knows 6 5 since: 2014 [0, 2] 6 knows 9 5 since: 2013 [0] 7 knows 9 6 since: 2015 [0] Id Label SourceId TargetId Properties Graphs 6 knows 9 5 since: 2013 [0] 7 knows 9 6 since: 2015 [0] Id Label SourceId TargetId … Id Label … 6 knows 9 5 … 9 Person … 7 knows 9 6 … 9 Person … Id Label SourceId TargetId … 6 knows 9 5 … 7 knows 9 6 … Id Label SourceId TargetId … Id Label … Id Label SourceId TargetId ….with(new LeftSide<E, V>()); .join(newVertices) .where(new TargetId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>()) .with(new LeftSide<E, V>()) .join(newVertices) .where(new SourceId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>()) .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<E>()) .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID)
- 45. Use Case: Graph Business Intelligence
- 46. Use Case: Graph Business Intelligence Business intelligence usually based on relational data warehouses Enterprise data is integrated within dimensional schema Analysis limited to predefined relationships No support for relationship-oriented data mining Graph-based approach Integrate data sources within an instance graph by preserving original relationships between data objects (transactional and master data) Determine subgraphs (business transaction graphs) related to business activities Analyze subgraphs or entire graphs with aggregation queries, mining relationship patterns, etc. Facts Dim 1 Dim 2 Dim 3
- 47. Prerequisites: Data Integration metadata Data SourcesEnterprise Service Bus Unified Metadata Graph Domain expert (1) Metadata aquisition (2) Graph integration Integrated Instance Graph data Business Transaction Graphs (3) Subgraph Detection
- 48. Business Transaction Graphs CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills processedBy
- 49. Business Transaction Graphs CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills
- 50. Business Transaction Graphs CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills
- 51. Business Transaction Graphs CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills
- 52. Business Transaction Graphs CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills
- 53. Business Transaction Graphs CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills
- 54. BTG 1 (1) BTG Extraction BTG 2 BTG 3 BTG 4 BTG 5 BTG n …
- 55. (1) BTG Extraction // generate base collection btgs = iig.callForCollection( :BusinessTransactionGraphs , {} )
- 56. (2) Profit Aggregation CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills
- 57. (2) Profit Aggregation // generate base collection btgs = iig.callForCollection( :BusinessTransactionGraphs , {} ) // define profit aggregate function aggFunc = ( Graph g => g.V.values(“Revenue").sum() - g.V.values(“Expense").sum() )
- 58. (2) Profit Aggregation BTG 1 BTG 2 BTG 3 BTG 4 BTG 5 BTG n … ∑ Revenue ∑ Expenses Net Profit 5,000 -3,000 2,000 9,000 -3,000 6,000 2,000 -1,500 500 5,000 -7,000 -2,000 10,000 -15,000 -5,000 … … … 8,000 -4,000 4,000
- 59. (2) Profit Aggregation // generate base collection btgs = iig.callForCollection( :BusinessTransactionGraphs , {} ) // define profit aggregate function aggFunc = ( Graph g => g.V.values(“Revenue").sum() - g.V.values(“Expense").sum() ) // apply aggregate function and store result at new property btgs = btgs.apply( Graph g => g.aggregate( “Profit“ , aggFunc ) )
- 60. (3) BTG Clustering BTG 1 BTG 2 BTG 3 BTG 4 BTG 5 BTG n … ∑ Revenue ∑ Expenses Net Profit 5,000 -3,000 2,000 9,000 -3,000 6,000 2,000 -1,500 500 5,000 -7,000 -2,000 10,000 -15,000 -5,000 … … … 8,000 -4,000 4,000
- 61. (3) BTG Clustering // select profit and loss clusters profitBtgs = btgs.select( Graph g => g[“Profit”] >= 0 ) lossBtgs = btgs.difference(profitBtgs)
- 62. (4) Cluster Characteristic Patterns CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills
- 63. (4) Cluster Characteristic Patterns CIT ERP Employee Name: Dave Employee Name: Alice Employee Name: Bob Employee Name: Carol Ticket Expense: 500 SalesQuotation SalesOrder PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrder SalesInvoice Revenue: 5,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 2,000 PurchaseInvoice Expense: 1,500 sentBy createdBy processedBy createdBy openedFor processedBy processedBy basedOn serves serves bills bills bills
- 64. (4) Cluster Characteristic Patterns BTG 1 BTG 2 BTG 3 BTG 4 BTG 5 BTG n … ∑ Revenue ∑ Expenses Net Profit 5,000 -3,000 2,000 9,000 -3,000 6,000 2,000 -1,500 500 5,000 -7,000 -2,000 10,000 -15,000 -5,000 … … … 8,000 -4,000 4,000 TicketAlice processedBy Bob createdBy PurchaseOrder
- 65. (4) Cluster Characteristic Patterns // select profit and loss clusters profitBtgs = btgs.select( Graph g => g[“Profit”] >= 0 ) lossBtgs = btgs.difference(profitBtgs) // apply magic profitFreqPats = profitBtgs.callForCollection( :FrequentSubgraphs , {“Threshold”:0.7} ) lossFreqPats = lossBtgs.callForCollection( :FrequentSubgraphs , {“Threshold”:0.7} ) // determine cluster characteristic patterns trivialPats = profitFreqPats.intersect(lossFreqPats) profitCharPatterns = profitFreqPats.difference(trivialPats) lossCharPatterns = lossFreqPats.difference(trivialPats)
- 66. Tooling
- 67. Graph Definition Language (Cypher for EPGM) Unit Testing graph analytical operators can be hard
- 68. Graph Definition Language (Cypher for EPGM) Unit Testing graph analytical operators can be hard Y U NO MAKE IT DECLARATIVE?
- 69. Graph Definition Language (Cypher for EPGM) Describe expected output in unit test
- 70. Graph Definition Language (Cypher for EPGM) FlinkAsciiGraphLoader Creates LogicalGraphs and GraphCollections based on ASCII graph Based on Cypher: https://github.com/s1ck/gdl Define vertices (alice:User {name = "Alice", age = 23}) Define edges (alice)-[e1:knows {since = 2014}]->(bob) Define paths (alice)-->(bob)<--(eve)-->(carol)-->(alice) Define graphs g1:Community {title = "Graphs", memberCount = 3}[ (alice:User)-[:knows]->(bob:User) (bob)-[e:knows]->(eve:User) (eve) ]
- 71. Graph Definition Language (Cypher for EPGM)
- 72. LDBC-Flink-Import Linked Data Benchmark Council MapReduce-based data generator for social network data http://ldbcouncil.org/
- 73. LDBC-Flink-Import Makes LDBC output available in Flink DataSets https://github.com/s1ck/ldbc-flink-import 1: LDBCToFlink ldbcToFlink = new LDBCToFlink( 2: "/path/to/ldbc/output", // or "hdfs://..." 3: ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment()); 4: 5: DataSet<LDBCVertex> vertices = ldbcToFlink.getVertices(); 6: DataSet<LDBCEdge> edges = ldbcToFlink.getEdges();
- 74. Current State & Future Work
- 75. Current State 0.0.1 First Prototype (May 2015) Hadoop MapReduce and Giraph for operator implementations Too much complexity Performance loss through serialization in HDFS/HBase 0.0.2 Using Flink as execution layer (June 2015) Basic operators 0.1 Today Improved ID handling Improved property handling More operator implementations (e.g. Equality, Bool operators) Code refactoring 0.2-SNAPSHOT Graph Pattern Matching Frequent Subgraph Mining
- 76. Current State Operators Unary Binary GraphCollectionLogicalGraph Algorithms Aggregation Pattern Matching Projection Summarization Equality Call * Combination Overlap Exclusion Equality Union Intersection Difference Gelly Library BTG Extraction Label Propagation Graph Forecasting Frequent Subgraphs Top Selection Distinct Sort Apply * Reduce * Call * * auxiliary
- 77. Benchmark Preview 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1 2 4 8 16 Time [s] # Worker Summarization (Vertex and Edge Labels) 16x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2430 v2 @ 2.50GHz (12 Cores), 48 GB RAM Hadoop 2.5.2, Flink 0.9.0 slots (per node) 12 jobmanager.heap.mb 2048 taskmanager.heap.mb 40960 Foodbroker Graph (https://github.com/dbs-leipzig/foodbroker) Generates BI process data 858,624,267 Vertices, 4,406,445,007 Edges, 663GB Payload
- 78. Web UI Preview
- 79. Contributions welcome! Code Operator implementations Performance Tuning Extend HBase Storage Data! and Use Cases We are researchers, we assume ... Getting real data (especially BI data) is nearly impossible


















![[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
Extended Property Graph Model
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-19-320.jpg)
![[2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
Extended Property Graph Model
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-20-320.jpg)


![Combination
1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2])
[2] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013
DB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-23-320.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
DB
Combination
1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2])
[4]
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-24-320.jpg)

![[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
DB
Combination + Summarization
[4]
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013
1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2])
2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”}
3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL}
4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|)
5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|)
6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc,
edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-26-320.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
DB
Combination + Summarization
[4]
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013
1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2])
2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”}
3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL}
4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|)
5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|)
6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc,
edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc)
[5]
[11] Person
city : Leipzig
count : 2
[12] Person
city : Dresden
count : 3
[13] Person
city : Berlin
count : 1
24
25
26
27
28
knows
count : 3
knows
count : 1
knows
count : 2
knows
count : 2
knows
count : 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-27-320.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
DB
Combination + Summarization + Aggregation
[4]
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013
1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2])
2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”}
3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL}
4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|)
5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|)
6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc,
edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc)
7: aggFunc = (Graph g => |g.E|)
8: aggGraph = sumGraph.aggregate(“edgeCount”, aggFunc)
[5]
[11] Person
city : Leipzig
count : 2
[12] Person
city : Dresden
count : 3
[13] Person
city : Berlin
count : 1
24
25
26
27
28
knows
count : 3
knows
count : 1
knows
count : 2
knows
count : 2
knows
count : 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-28-320.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
DB
Combination + Summarization + Aggregation
[4]
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013
1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2])
2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”}
3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL}
4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|)
5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|)
6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc,
edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc)
7: aggFunc = (Graph g => |g.E|)
8: aggGraph = sumGraph.aggregate(“edgeCount”, aggFunc)
[5] edgeCount : 5
[11] Person
city : Leipzig
count : 2
[12] Person
city : Dresden
count : 3
[13] Person
city : Berlin
count : 1
24
25
26
27
28
knows
count : 3
knows
count : 1
knows
count : 2
knows
count : 2
knows
count : 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-29-320.jpg)

![Selection
1: resultColl = db.G[0,1,2].select((Graph g => g[“vertexCount”] > 3))
[2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013
DB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-31-320.jpg)
![Selection
1: resultColl = db.G[0,1,2].select((Graph g => g[“vertexCount”] > 3))
[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[0] Tag
name : Databases
[1] Tag
name : Graphs
[2] Tag
name : Hadoop
[3] Forum
title : Graph Databases
[4] Forum
title : Graph Processing
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
[10] Person
name : Frank
gender : m
city : Berlin
age : 23
IP: 169.32.1.3
6 7 8 9
10
11 12 13 14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
22
23
hasInterest
hasInterest hasInterest
hasInterest
hasModeratorhasModerator
hasMember hasMember
hasMember hasMember
hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013
DB
[2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
0
1
2
3
4
5
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-32-320.jpg)





![The „Hello World“ of Big Data – Word Count
1: ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
2:
3: DataSet<String> text = env.fromElements( // or env.readTextFile(„hdfs://…“)
4: „He who controls the past controls the future.“,
5: „He who controls the present controls the past.“);
6:
7: DataSet<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordCounts = text
8: .flatMap(new LineSplitter()) // splits the line and outputs (word, 1) tuples
9: .groupBy(0)
10: .sum(1);
11:
12: wordCounts.print(); // trigger execution
flatMap
„He who controls the past controls the future.“
„He who controls the present controls the past.“
(He,1)
(who,1)
(controls,1)
(the,1)
(past,1)
// ...
groupBy(0)
[(He,1),(He,1)]
[(who,1),(who,1)]
[(future,1)]
[(past,1),(past,1)]
[(present,1)]
// ...
sum(1)
(He,2)
(who,2)
(future,1)
(past,2)
(present,1)
// ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-38-320.jpg)


![EPGM in Apache Flink – DataSets
Id Label Properties Graphs
Id Label Properties SourceId TargetId Graphs
EPGMGraphHead
EPGMVertex
EPGMEdge
Id Label Properties POJO
POJO
POJO
DataSet<EPGMGraphHead>
DataSet<EPGMVertex>
DataSet<EPGMEdge>
Id Label Properties Graphs
EPGMVertex
GradoopId := UUID
128-bit
String PropertyList := List<Property>
Property := (String, PropertyValue)
PropertyValue := byte[]
GradoopIdSet := Set<GradoopId>
(55421132-f45b-40f0-8f6a-50ea13dbf2ea:Person{gender=f,city=Leipzig,name=Alice,age=20} @ [c2c0f288-9f27-4e55-b1c6-7a35e0eabe36, 77b710f9-07c2-49ab-b4bf-51e1a3138822])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-41-320.jpg)
![EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion
// input: firstGraph (G[0]), secondGraph (G[2])
1: DataSet<GradoopId> graphId = secondGraph.getGraphHead()
2: .map(new Id<G>());
3:
4: DataSet<V> newVertices = firstGraph.getVertices()
5: .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<V>())
6: .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID);
7:
8: DataSet<E> newEdges = firstGraph.getEdges()
9: .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<E>())
10: .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID)
11: .join(newVertices)
12: .where(new SourceId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>())
13: .with(new LeftSide<E, V>())
14: .join(newVertices)
15: .where(new TargetId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>())
16: .with(new LeftSide<E, V>());
db.G[0].exclude(db.G[2])
[2] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4
[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3
[5] Person
name : Alice
gender : f
city : Leipzig
age : 23
[6] Person
name : Bob
gender : m
city : Leipzig
age : 30
[7] Person
name : Carol
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 30
[8] Person
name : Dave
gender : m
city : Dresden
age : 42
[9] Person
name : Eve
gender : f
city : Dresden
age : 35
speaks : en
0
1
2
3
4
5
6 7
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2013
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2014
knows
since : 2015
knows
since : 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-42-320.jpg)
![EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion
Id Label Properties
2 Community interest: Graphs vertexCount: 4
graphId =
secondGraph.getGraphHead()
Id
2
newVertices =
firstGraph.getVertices() Id Label Properties Graphs
5 Person name: Alice gender: f … [0, 2]
6 Person name: Bob gender: m … [0, 2]
9 Person name: Eve gender: f … [0]
Id Label Properties Graphs
9 Person name: Eve gender: f … [0]
.map(new Id<G>());
.filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<V>())
.withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-43-320.jpg)
![EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion
newEdges =
firstGraph.getEdges()
Id Label SourceId TargetId Properties Graphs
0 knows 5 6 since: 2014 [0, 2]
1 knows 6 5 since: 2014 [0, 2]
6 knows 9 5 since: 2013 [0]
7 knows 9 6 since: 2015 [0]
Id Label SourceId TargetId Properties Graphs
6 knows 9 5 since: 2013 [0]
7 knows 9 6 since: 2015 [0]
Id Label SourceId TargetId … Id Label …
6 knows 9 5 … 9 Person …
7 knows 9 6 … 9 Person …
Id Label SourceId TargetId …
6 knows 9 5 …
7 knows 9 6 …
Id Label SourceId TargetId … Id Label …
Id Label SourceId TargetId ….with(new LeftSide<E, V>());
.join(newVertices)
.where(new TargetId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>())
.with(new LeftSide<E, V>())
.join(newVertices)
.where(new SourceId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>())
.filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<E>())
.withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-44-320.jpg)
















![(3) BTG Clustering
// select profit and loss clusters
profitBtgs = btgs.select( Graph g => g[“Profit”] >= 0 )
lossBtgs = btgs.difference(profitBtgs)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-61-320.jpg)



![(4) Cluster Characteristic Patterns
// select profit and loss clusters
profitBtgs = btgs.select( Graph g => g[“Profit”] >= 0 )
lossBtgs = btgs.difference(profitBtgs)
// apply magic
profitFreqPats = profitBtgs.callForCollection(
:FrequentSubgraphs , {“Threshold”:0.7}
)
lossFreqPats = lossBtgs.callForCollection(
:FrequentSubgraphs , {“Threshold”:0.7}
)
// determine cluster characteristic patterns
trivialPats = profitFreqPats.intersect(lossFreqPats)
profitCharPatterns = profitFreqPats.difference(trivialPats)
lossCharPatterns = lossFreqPats.difference(trivialPats)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-65-320.jpg)




![Graph Definition Language (Cypher for EPGM)
FlinkAsciiGraphLoader
Creates LogicalGraphs and GraphCollections based on ASCII graph
Based on Cypher: https://github.com/s1ck/gdl
Define vertices
(alice:User {name = "Alice", age = 23})
Define edges
(alice)-[e1:knows {since = 2014}]->(bob)
Define paths
(alice)-->(bob)<--(eve)-->(carol)-->(alice)
Define graphs
g1:Community {title = "Graphs", memberCount = 3}[
(alice:User)-[:knows]->(bob:User)
(bob)-[e:knows]->(eve:User)
(eve)
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-70-320.jpg)






![Benchmark Preview
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1 2 4 8 16
Time [s]
# Worker
Summarization (Vertex and Edge Labels)
16x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2430 v2 @ 2.50GHz (12 Cores), 48 GB RAM
Hadoop 2.5.2, Flink 0.9.0
slots (per node) 12
jobmanager.heap.mb 2048
taskmanager.heap.mb 40960
Foodbroker Graph (https://github.com/dbs-leipzig/foodbroker)
Generates BI process data
858,624,267 Vertices, 4,406,445,007 Edges, 663GB Payload](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/85/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-77-320.jpg)


