Ad
Module -1.pptx on cloud computing and analyt
- 2. MODULE – 1 Introduction to Cloud services 2
- 3. • Course Handout Discussion • Introduction to cloud services • Evolution of cloud computing • Computing Platforms and Technologies • Cloud Computing Architecture • IaaS, PaaS, SaaS • Types of Clouds • Cloud Computing Environments 3 Contents
- 8. Computing • Computing is being transformed into a model consisting of services that are commoditized and delivered in a manner similar to utilities such as water, electricity, gas, and telephony.
- 9. • Cloud computing - turn the vision of “computing utilities "in to a reality. • computer utilities’ - like electric and telephone utilities - will service individual homes and offices across the country
- 10. Example of cloud computation • Users (consumers) need to pay providers only when they access the computing services. • consumers - no longer need to invest heavily - encounter difficulties in building and maintaining complex IT infrastructure.
- 11. Cloud Computing • Users access services based on their requirements without regard to where the services are hosted. • This model has been referred to as utility computing or, (since 2007), as cloud computing.
- 12. Cloud computing • Cloud computing allows - renting infrastructure, - runtime environments-IDE - and services on a pay- per-use basis. • This principle provides-several practical applications and then gives different images of cloud computing to different people.
- 13. Cloud computing One of the most diffuse views of cloud computing can be summarized as follows: I don’t care where my servers are, who manages them, where my documents are stored, or where my applications are hosted. I just want them always available and access them from any device connected through Internet. And I am willing to pay for this service for as a long as I need it. The concept expressed above has strong similarities to the way we use other services, such as water and electricity.
- 14. cloud computing cloud computing turns IT services into utilities. a delivery model is made possible by the effective composition of several technologies Web 2.0 technologies plays a central role in making cloud computing an attractive opportunity for building computing systems.
- 15. • Service orientation allows cloud computing - to deliver its capabilities with familiar abstractions. • virtualization allows cloud computing - provides the necessary degree of customization, - control, and flexibility for building production and enterprise systems.
- 16. Cloud computing at a glance
- 17. Massive transformation – from networks to cloud • Computing services readily available on demand, just as other utility services • Pay providers only when you access the computing services • Consumers no longer need to invest heavily - building and maintaining complex IT infrastructure
- 18. What is cloud computing? • Paradigm for the dynamic provisioning of computing services • supported by state-of-the-art data centers • employing virtualization technologies for consolidation and effective utilization of resources • Cloud computing allows renting infrastructure, runtime environments, and services on a pay-per-use basis
- 19. Cloud – one point of view • I don’t care where my servers are, who manages them, where my documents are stored, where my applications are hosted • I just want them • always available and access them from any device connected through Internet • And I am willing to pay for this service for as a long as I need it
- 20. Cloud – Composition of several technologies Web 2.0 technologies - transformed the Internet into a rich application and service delivery platform Service orientation - to deliver its capabilities with familiar abstractions Virtualization - necessary degree of customization, control, and flexibility for building production and enterprise systems
- 21. Why is cloud popular? 1. Flexibility: If businesses bandwidth requirements or running costs tend to fluctuate, using cloud services makes perfect sense. Cloud computing offers various pre-built platforms and services and also allows you to develop customized solutions as per your specific needs. It enables you to upgrade your services in line with your needs. Anytime you can scale up and scale down your cloud capacity depending on your requirement. There is no need to pay extra money for the services you are not using on the cloud. 2. Ensures Security: While working on a project if your laptop or hard drive get lost then it can cost a billion dollar of businesses and you can’t imagine the loss if it goes in the Well, keeping your data locally on a computer is always a risk and big issue for companies and individuals. The cost of losing your sensitive or private data is bigger than the loss of your kit or physical equipment. Cloud computing solves this problem and provides top-notch data security. If you lose your mobile device or laptop or if your computer system is attacked by viruses and worms you can still access everything you have on the cloud using another machine or device. You can also wipe data from lost laptops remotely so it doesn’t get into the wrong hands. 3. Maintains Productivity: Cloud computing allows team members to work on the same document in real-time. It becomes convenient and easier for team members to edit, share, and access the document or data anytime and from anywhere. There is no need to spend time updating, filling, and printing documents. Cloud services provide a better workflow and file sharing apps that help team members to make updates in real-time and give them full visibility of their collaborations. It requires less energy and effort that eventually maintains the productivity of the business. In nutshell, the technology eliminates the need for a back-and-forth exchange of documents.
- 22. Why is cloud popular? 4. Cost Savings and No Maintenance: Companies spend a lot of money on purchasing hardware, buying software licenses, maintaining, updating, distributing, and shredding paper copies. When you use cloud services it cuts out all these expenses. It eliminates the cost and complexity of owning and operating computers and networks. As we have mentioned that cloud services cost is customizable and you only pay as you go. You pay for the services you are usin on the cloud also you don’t have to worry about maintaining your system. Cloud service providers take care of your information rolling out regular software updates – including security updates. Instead of buying the capital alone and bearing all the costs, this is much easier and convenient for organizations. 5. Work From Anywhere: It doesn’t matter where you are sitting in the world, cloud service allows you to access the data anywhere, anytime. You don’t need to carry your USB or laptop in different places, you just need the internet connection to get access to your data on the cloud. Some cloud services also offer mobile apps, so you are not restricted to use any specific device. This gives more flexibility and convenience to the employees along with running the business operations smoothly.
- 23. Vision of Cloud • Anyone with a credit card can provision virtual hardware, runtime environments, and services • Used as needed, with no up-front commitments • The entire stack of a computing system is transformed into a collection of utilities • composed together to deploy systems in hours and with virtually no maintenance costs
- 24. Vision of Cloud
- 25. Future – Global cloud marketplace Give your needs – automation of discovery process and integration of the cloud services Service providers – increase their revenue Reduces the barriers between service consumers and providers Standards Optimize datacenter facilities – greener computing
- 26. Defining a Cloud
- 27. Defining a Cloud • Refers to both the applications delivered as services over the Internet and the hardware and system software in the datacenters that provide those services. • A model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
- 28. Criteria for a cloud service The service is accessible via a Web browser (nonproprietary) or a Web services application programming interface (API) Zero capital expenditure is necessary to get started You pay only for what you use as you use it
- 29. Definition (Buyya – utility-oriented) • A cloud is a type of parallel and distributed system • consisting of a collection of interconnected and virtualized computers • that are dynamically provisioned • and presented as one or more unified computing resources • based on service-level agreements • established through negotiation between the service provider and consumers
- 30. What do we get from Cloud? Large enterprises can offload some of their activities Small enterprises / start- ups translate their ideas into business results more quickly, without excessive up-front costs System developers can concentrate on the business logic rather than dealing with the complexity of infrastructure management and scalability End users can have their documents accessible from everywhere and any device IT Services on Demand
- 31. A bird’s-eye view of cloud computing
- 33. 5 Core Technologies Distributed systems Virtualization Web 2.0 Service oriented computing Utility-oriented computing
- 34. 1. Distributed systems • A distributed system is a collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single coherent system.
- 35. Evolution of Distributed Computing
- 37. Mainframes • Smaller than a super computer • Large computational facilities leveraging multiple processing units • Powerful, highly reliable computers specialized for large data movement and massive input/output (I/O) operations. USE: • online transactions • enterprise resource planning • huge data processing
- 38. Mainframes – good and bad Good Scalability Good memory storage Highly reliable Transparent fault tolerance No interruption while replacing faulty components Can run multiple OS • High cost • Difficult installation • Huge physical size • Environmental issues
- 39. Cluster Computing • Early 1980s • Low-cost alternative to mainframes and supercomputers • Increased availability of cheap commodity machines • Connected by a high-bandwidth network and controlled by specific software tools that manage them as a single system • 1980s - clusters - standard technology for parallel and high- performance computing • Could run programs which once required mainframes
- 40. Cluster Computing • Collection of tightly or loosely connected computers (nodes) that work together so that they act as a single entity (transparency) • solve complicated problems • faster computational speed • enhanced data integrity • expandability
- 41. Grid Computing • Early 1990s • Analogy to the power grid – consume resources • Aggregate geographically dispersed clusters • By means of Internet connections • These clusters belonged to different organizations • Arrangements were made among them to share the computational power • Different from a “large cluster” Computing grid - dynamic aggregation of heterogeneous computing nodes, and its scale was nationwide or even worldwide
- 42. Why Grid Computing ? (a) clusters became quite common resources (b) they were often underutilized (c) new problems were requiring computational power that went beyond the capability of single clusters (d) the improvements in networking and the Internet made possible long-distance, high-bandwidth connectivity
- 45. 2. Virtualization • Allows creation of different computing environments • These environments are called virtual because they simulate the interface that is expected by a guest • e.g. Hardware virtualization • Enables cloud computing solutions to deliver virtual servers on demand, such as Amazon EC2, RightScale, VMware vCloud
- 46. 2. Virtualization (Contd.) • Definition • Collection of solutions allowing the abstraction of some of the fundamental elements for computing • Hardware, runtime environments, storage, and networking
- 47. 3. Web 2.0 • Refers to websites that have user- generated content, ease of use, participatory culture and interoperability for end users • A collection of standards and technologies such as XML, Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (AJAX), Web Services, and others • brings interactivity and flexibility into Web pages • providing enhanced user experience
- 49. 5. Utility-oriented computing • is a service provisioning model • providing computing as a utility like natural gas, water, power, and telephone connection • computing resources are provided to the customer based on specific demand • Examples of such IT services are computing power, storage or applications.
- 50. Cloud Computing SERVICE Reference Model Runtime Environment for Applications Development and Data Processing Platforms Examples: Windows Azure, Hadoop, Google AppEngine, Aneka Platform as a Service Virtualized Servers Storage and Networking Examples: Amazon EC2, S3, Rightscale, vCloud S3: Amazon Simple Storage Service Infrastructure as a Service End user applications Scientific applications Office automation, Photo editing, CRM, and Social Networking Examples: Google Documents, Facebook, Flickr, Salesforce Software as a Service Web 3.0 Interfaces
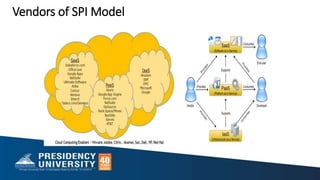
- 51. Vendors of SPI Model
- 52. Basic Structure of Cloud Computing
- 54. Concept of a “Service” in Cloud Computing In the Cloud scenario, the provider Organization (Microsoft, Oracle, Amazon, Google) offers the following commodities as services: 1. Infrastructure (Hardware) -> Storage, Servers, Networking components 2. Platform to run applications -> Runtimes (JRE, CLR), Operating Systems (Windows, Linux), Databases (MySQL, Oracle) 3. Applications -> Gmail, Facebook, CRM, etc. All these services are offered through Web APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) Ex: Office 365 suite of applications, Google Drive suite of applications
- 55. Types of Services available in cloud computing • IaaS --- Infrastructure as a Service --- server, memory, CPU processor, storage space, network components, disk space, hard disk • PaaS---Platform as a Service --- Provides run time environment for developers – visual studio, IDE, WORD , OPERATING SYSTEM, VMWARE • SaaS – Software as a Service- ALL TYPE OF APPLICATION – FACEBOOK, GMAIL. Google drive, google document,etc • Stack of cloud computing --- arrangement of services • SaaS • PaaS • IaaS
- 56. IaaS • IaaS allows the cloud provider to freely locate the infrastructure over the Internet in a cost-effective manner. Some of the key benefits of IaaS are listed below: • Full control of the computing resources through administrative access to VMs. • Flexible and efficient renting of computer hardware. • Portability, interoperability with legacy applications Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 56
- 57. Characteristics of IaaS - Virtual machines with pre-installed software. - Virtual machines with pre-installed operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and Solaris. - On-demand availability of resources. - Allows to store copies of particular data at different locations. - The computing resources can be easily scaled up and down. Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 57
- 58. IaaS- Advantages and Disadvantages • Advantages of IaaS: Cost Saving, On-demand scalability, Have the Flexibility You Need, Focus on business growth, • Disadvantages of IaaS: Security, Lack of flexibility, Over Dependency,Compatibility with legacy security vulnerabilities, Virtual Machine sprawl
- 59. PaaS • Platform-as-a-Service offers the runtime environment for applications. • It also offers development and deployment tools required to develop applications. • PaaS has a feature of point-and-click tools that enables non- developers to create web applications. • Developer may log on to these websites and use the built-in API to create web-based applications. Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 59
- 60. Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 60
- 61. PaaS- Advantages Time Savings: No need to spend time setting up/maintaining the core stack. Speed to Market: Speed up the creation of apps. Increase Security: PaaS providers invest heavily in security technology and expertise. More current system software
- 62. PaaS- Disadvantages Security: All the data of applications are stored inside the provider's cloud database. Control: Users lack some control over a PaaS solution. Reliability: PaaS solutions often face reliability concerns. Lack of portability among PaaS clouds
- 63. SaaS • Software-as–a-Service (SaaS) model allows to provide software application as a service to the end users. It refers to a software that is deployed on a host service and is accessible via Internet. There are several SaaS applications listed below: • Billing and invoicing system • Customer Relationship Management (CRM) applications • Help desk applications • Human Resource (HR) solutions Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 63
- 64. SaaS- Advantages Operational Management: No installation, equipment updates or traditional licensing management. Cost-Effective: There are no upfront hardware costs and flexible payment methods such as pay-as-you-go models. Scalability: Easily scale a solution to accommodate changing needs. Data Storage: Data is routinely saved in the cloud. Modest software tools
- 65. SaaS- Disadvantages • Disadvantages of SaaS: Loss of Control: The vendor manages everything, making you dependent upon the vendor's capabilities. Limited Customization: Most SaaS applications offer little in the way of customization from the vendor. Slower Speed: SaaS solutions can have more latency than client/server apps.
- 66. Cloud Deployment Models • Public Cloud • Private Cloud • Community Cloud • Hybrid cloud Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 66
- 67. Public Cloud Public cloud is open to all to store and access information via the Internet using the pay-per-usage method. In public cloud, computing resources are managed and operated by the Cloud Service Provider (CSP). Example: Amazon elastic compute cloud (EC2), IBM SmartCloud Enterprise, Microsoft, Google App Engine, Windows Azure Services Platform. Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 67
- 68. Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 68
- 69. Advantages: - Public cloud is owned at a lower cost than the private and hybrid cloud. - maintained by the cloud service provider, so do not need to worry about the maintenance. - location independent because its services are delivered through the internet. - highly scalable as per the requirement of computing resources. - accessible by the general public, so there is no limit to the number of users. Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 69
- 70. Disadvantages: - Public Cloud is less secure because resources are shared publicly. - Performance depends upon the high-speed internet network link to the cloud provider. - The Client has no control of data. Mr. R C Ravindranath, Asst. Prof, SOE-CSE 70
- 71. Private Cloud - Private cloud is also known as an internal cloud or corporate cloud. It is used by organizations to build and manage their own data centers internally or by the third party. - It can be deployed using Opensource tools such as Openstack and Eucalyptus.
- 72. Advantages • Private cloud provides a high level of security and privacy to the users. • better performance with improved speed and space capacity. • allows the IT team to quickly allocate and deliver on-demand IT resources. • The organization has full control over the cloud because it is managed by the organization itself. So, there is no need for the organization to depends on anybody. • It is suitable for organizations that require a separate cloud for their personal use and data security is the first priority. 72
- 73. Disadvantages • Skilled people are required to manage and operate cloud services. • Private cloud is accessible within the organization, so the area of operations is limited. • Private cloud is not suitable for organizations that have a high user base, and organizations that do not have the prebuilt infrastructure, sufficient manpower to maintain and manage the cloud 73
- 74. Cloud Deployment Models – Contd. 3. Hybrid Clouds= public + private • Whenever private cloud resources are unable to meet users’ quality-of- service requirements, hybrid computing systems, partially composed of public cloud resources and privately owned infrastructures, are created to serve the organization’s needs
- 75. Advantages • Hybrid cloud is suitable for organizations that require more security than the public cloud. • Hybrid cloud helps you to deliver new products and services more quickly. • Hybrid cloud provides an excellent way to reduce the risk. • Hybrid cloud offers flexible resources because of the public cloud and secure resources because of the private cloud. 75
- 76. Disadvantages • In Hybrid Cloud, security feature is not as good as the private cloud. • Managing a hybrid cloud is complex because it is difficult to manage more than one type of deployment model. • In the hybrid cloud, the reliability of the services depends on cloud service providers. 76
- 77. Community Cloud • Community cloud allows systems and services to be accessible by a group of several organizations to share the information between the organization and a specific community. • It is owned, managed, and operated by one or more organizations in the community, a third party, or a combination of them. • e.g.- Healthcare community cloud 77
- 78. Advantages • Community cloud is cost-effective because the whole cloud is being shared by several organizations or communities. • Community cloud is suitable for organizations that want to have a collaborative cloud with more security features than the public cloud. • It provides better security than the public cloud. • It provides collaborative and distributive environment. • Community cloud allows us to share cloud resources, infrastructure, and other capabilities among various organizations. 78
- 79. Disadvantages • Community cloud is not a good choice for every organization. • Security features are not as good as the private cloud. • It is not suitable if there is no collaboration. • The fixed amount of data storage and bandwidth is shared among all community members. 79
- 80. Major deployment models for cloud computing
- 81. Characteristics and benefits of Cloud • No up-front commitments • On-demand access • Nice pricing • Simplified application acceleration and scalability • Efficient resource allocation • Energy efficiency • Seamless creation and use of third-party services
- 82. Cloud computing - challenges • Technical • Security • Legal
- 85. What sort of applications benefit from cloud? • Dynamically scale on demand • Classes of applications 1. Web applications • Performance depends on workload generated by varying user demand • Rich, complex and interactive
- 86. What sort of applications benefit from cloud? 2. Resource-intensive applications • Data-intensive or compute-intensive applications • Resources are required to complete execution in a reasonable timeframe • But not required for a long duration • Not interactive, only batch processing • e.g. scientific applications
- 87. On-demand and dynamic scaling solution • How? (a) providing methods for renting compute power, storage, and networking (b) offering runtime environments designed for scalability and dynamic sizing (c) providing application services that mimic the behavior of desktop applications but that are completely hosted and managed on the provider side • Service orientation allows a simple and seamless integration into existing systems • Developers access such services via simple Web interfaces
- 89. How to develop cloud applications? • Leverage • Platforms • Technologies • Frameworks Amazon web services (AWS) Google AppEngine Microsoft Azure Hadoop Force.com and Salesforce.com Manjrasoft Aneka
- 90. Amazon web services (AWS) • IaaS • Platform that offers flexible, reliable, scalable, easy-to-use and, cost-effective cloud computing solutions • compute and storage-on- demand services • Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Simple Storage Service (S3)
- 91. Amazon web services (AWS) • Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) • Customizable virtual hardware • EC2 instances are deployed either by using • AWS console, which is a comprehensive Web portal for accessing AWS services • Web services API available for several programming languages • Simple Storage Service (S3) • Delivers persistent storage on demand • S3 is organized into buckets; these are containers of objects that are stored in binary form and can be enriched with attributes • Users can store objects of any size, from simple files to entire disk images, and have them accessible from everywhere
- 92. Google App Engine (GAE) • PaaS • Build highly scalable applications on a fully managed serverless platform • Large computing infrastructure of Google to dynamically scale
- 93. Google AppEngine • Services include in-memory caching, scalable data store, job queues, messaging, and cron tasks • GAE requires that applications be written in Java or Python, store data in Google Bigtable and use the Google query language. • IaaS similar to EC2 • Google provides GAE free up to a certain amount of use for the following resources: • processor storage • API calls • concurrent requests
- 94. Microsoft Azure • Provides a scalable runtime environment for Web applications and distributed applications
- 95. Microsoft Azure • Applications in Azure are organized around the concept of roles, which identify a distribution unit for applications and embody the application’s logic • Three types of role: Web role, worker role, and virtual machine role • Web role is designed to host a Web application • Worker role is a more generic container of applications and can be used to perform workload processing • Virtual machine role provides a virtual environment in which the computing stack can be fully customized, including the operating systems
- 96. Hadoop • Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework • that is suited for processing large data sets on commodity hardware • Hadoop is an integral part of the Yahoo! cloud infrastructure • Hadoop is an implementation of Map Reduce, an application programming model developed by Google • which provides two fundamental operations for data processing: map and reduce • Map - transforms and synthesizes the input data provided by the user • Reduce - aggregates the output obtained by the map operations • Hadoop provides the runtime environment • Developers need only provide the input data and specify the map and reduce functions that need to be executed
- 97. Force.com and Salesforce.com • Force.com is a cloud computing platform for developing social enterprise applications • complete set of components supporting all the activities of an enterprise • provides complete support for developing applications - design of the data layout to the definition of business rules and workflows and the definition of the user interface • The platform is the basis for SalesForce.com, a Software-as-a-Service solution for customer relationship management
- 98. Manjrasoft Aneka • Cloud application platform for rapid creation of scalable applications • Supports a collection of programming abstractions for developing applications and a distributed runtime environment that can be deployed on heterogeneous hardware (clusters, networked desktop computers, and cloud resources) • Applications are executed on the distributed service-oriented runtime environment, which can dynamically integrate additional resource on demand • Services manage most of the activities happening at runtime: scheduling, execution, accounting, billing, storage, and quality of service