Ad
MongoDB Evenings Chicago - Find Your Way in MongoDB 3.2: Compass and Beyond
- 1. Finding Your Way in MongoDB 3.2: Compass and Beyond Jason Swartzbaugh Solution Architect [email protected]
- 2. Themes Broader use case portfolio. Pluggable storage engine strategy enables us to rapidly cover more use cases with a single database. Mission-critical apps. MongoDB delivers major advances in the critical areas of governance, high availability, and disaster recovery. New tools for new users. Now MongoDB is an integral part of the tooling and workflows of Data Analysts, DBAs, and Operations teams.
- 3. Storage Engines Broaden Use Cases
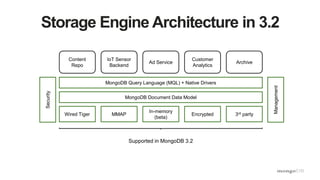
- 4. Storage Engine Architecture in 3.2 Content Repo IoT Sensor Backend Ad Service Customer Analytics Archive MongoDB Query Language (MQL) + Native Drivers MongoDB Document Data Model Wired Tiger MMAP Supported in MongoDB 3.2 Management Security In-memory (beta) Encrypted 3rd party
- 5. WiredTiger is the New Default WiredTiger – widely deployed with 3.0 – is now the default storage engine for MongoDB. • Best general purpose storage engine • 7-10x better write throughput • Up to 80% compression
- 6. Encrypted Storage Engine Encrypted storage engine for end-to-end encryption of sensitive data in regulated industries • Reduces the management and performance overhead of external encryption mechanisms • AES-256 Encryption, FIPS 140-2 option available • Key management: Local key management via keyfile or integration with 3rd party key management appliance via KMIP • Offered as an option for WiredTiger storage engine
- 7. In-Memory Storage Engine (Beta) Handle ultra-high throughput with low latency and high availability • Delivers the extreme throughput and predictable latency required by the most demanding apps in Adtech, finance, and more. • Achieve data durability with replica set members running disk-backed storage engine • Available for beta testing now and is expected for GA in 2016
- 8. One Deployment With Multiple Storage Engines
- 9. Built for Mission Critical Deployments
- 10. Data Governance with Document Validation Implement data governance without sacrificing agility that comes from dynamic schema • Enforce data quality across multiple teams and applications • Use familiar MongoDB expressions to control document structure • Validation is optional and can be as simple as a single field, all the way to every field, including existence, data types, and regular expressions
- 11. Document Validation Example The example on the left adds a rule to the contacts collection that validates: • The year of birth is no later than 1994 • The document contains a phone number and / or an email address • When present, the phone number and email addresses are strings
- 12. Enhancements for your mission-critical apps More improvements in 3.2 that optimize the database for your mission-critical applications • Meet stringent SLAs with fast-failover algorithm – Under 2 seconds to detect and recover from replica set primary failure • Simplified management of sharded clusters allow you to easily scale to many data centers – Config servers are now deployed as replica sets; up to 50 members
- 13. Tools for UsersAcross Your Organization
- 14. For Business Analysts & Data Scientists MongoDB 3.2 allows business analysts and data scientists to support the business with new insights from untapped data sources • MongoDB Connector for BI • Dynamic Lookup • New Aggregation Operators & Improved Text Search
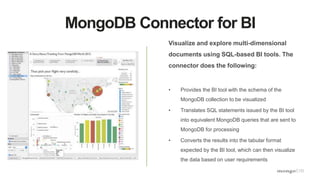
- 15. MongoDB Connector for BI Visualize and explore multi-dimensional documents using SQL-based BI tools. The connector does the following: • Provides the BI tool with the schema of the MongoDB collection to be visualized • Translates SQL statements issued by the BI tool into equivalent MongoDB queries that are sent to MongoDB for processing • Converts the results into the tabular format expected by the BI tool, which can then visualize the data based on user requirements
- 16. Dynamic Lookup Combine data from multiple collections with left outer joins for richer analytics & more flexibility in data modeling • Blend data from multiple sources for analysis • Higher performance analytics with less application- side code and less effort from your developers • Executed via the new $lookup operator, a stage in the MongoDB Aggregation Framework pipeline
- 17. Improved In-Database Analytics & Search New Aggregation operators extend options for performing analytics and ensure that answers are delivered quickly and simply with lower developer complexity • Array operators: $slice, $arrayElemAt, $concatArrays, $filter, $min, $max, $avg, $sum, and more • New mathematical operators: $stdDevSamp, $stdDevPop, $sqrt, $abs, $trunc, $ceil, $floor, $log, $pow, $exp, and more • Case sensitive text search and support for additional languages such as Arabic, Farsi, Chinese, and more
- 18. For Operations Teams MongoDB 3.2 simplifies and enhances MongoDB’s management platforms. Ops teams can be 10-20x more productive using Ops and Cloud Manager to run MongoDB. • Start from a global view of infrastructure: Integrations with Application Performance Monitoring platforms • Drill down: Visual query performance diagnostics, index recommendations • Then, deploy: Automated index builds • Refine: Partial indexes improve resource utilization
- 19. Integrations with APM Platforms Easily incorporate MongoDB performance metrics into your existing APM dashboards for global oversight of your entire IT stack • MongoDB drivers enhanced with new API that exposed query performance metrics to APM tools • In addition, Ops and Cloud Manager can complement this functionality with rich database monitoring.
- 20. Query Perf. Visualizations & Optimization Fast and simple query optimization with the new Visual Query Profiler • Query and write latency are consolidated and displayed visually; your ops teams can easily identify slower queries and latency spikes • Visual query profiler analyzes the data it displays and provides recommendations for new indexes that can be created to improve query performance • Ops Manager and Cloud Manager can automate the rollout of new indexes, reducing risk and your team’s operational overhead
- 21. Refine with Partial Indexes Balance delivering good query performance while consuming fewer system resources • Specify a filtering expression during index creation to instruct MongoDB to only include documents that meet your desired conditions • The example to the left creates an index that only indexes the transaction documents with a modified date since Jan 1, 2014 db.transactions.createIndex( {modifiedDate: -1}, {partialFilterExpression: {modifiedDate: {$gt: Date("2014-01-01T00:00:00.000Z")} } } )
- 22. For Database Administrators MongoDB 3.2 helps users in your organization understand the data in your database • MongoDB Compass – For DBAs responsible for maintaining the database in production – No knowledge of the MongoDB query language required
- 23. MongoDB Compass For fast schema discovery and visual construction of ad-hoc queries • Visualize schema – Frequency of fields – Frequency of types – Determine validator rules • View Documents • Graphically build queries • Authenticated access
- 24. MongoDB Enterprise Advanced The best way to run MongoDB in your data center. Automated. Supported. Secured. What’s included? Enterprise-Grade Support Encrypted & In-Memory Storage Engines MongoDB Compass BI Connector Ops Manager or Cloud Manager Premium Advanced Security Commercial License Platform Certification On-Demand Training
Editor's Notes
- #3: How many of you have already upgraded to MongoDB version 3.2? There are 3 basic themes for the 3.2 release each of which we will discuss in detail: Broadening our use case portfolio Better support for Mission Critical-apps And, New tools for new users
- #5: MongoDB 3.0 introduced a new flexible storage engine architecture. This makes it fast and easy to build new pluggable storage engines to extend the database with new capabilities and address specific workload requirements. MongoDB 3.2 adds 2 new options to the mix: An Encrypted storage engine to protect highly sensitive data, without the performance or management overhead of separate filesystem encryption. And an In-memory storage engine that delivers extreme performance and predictable latency.
- #6: The WiredTiger storage engine was first made available as an option with MongoDB 3.0. How many of you have moved to the WiredTiger storage engine? With the 3.2 version of MongoDB, WiredTiger as its default storage engine. Fresh download would start up with WiredTiger as the storage engine When compared to the original MMAP storage engine used in earlier MongoDB releases, write performance has improved by 7 to 10 times, and storage overhead has reduced by up to 80%. These improvements were made possible due to WiredTiger’s more granular concurrency control and native compression.
- #7: With the introduction of the Encrypted storage engine, MongoDB now provides end-to-end encryption. Because the storage engine natively encrypts the database files on disk, the management and performance overhead of other external encryption mechanisms is reduced. We use 256-bit encryption, and data is encrypted using an algorithm that takes a random encryption key as input and generates ciphertext that can only be read if decrypted with the decryption key. This encryption/decryption process is completely transparent to the application, and the storage engine encrypts each database with a separate key. MongoDB supports two key management options: Local key management via a key file OR Integration with the 3rd party key management appliance using the KMIP protocol.
- #8: Most people understand the advantages of in-memory computing. Data can be accessed in RAM nearly 100,000 times faster than retrieving it from disk, and writes do not need to be persisted to disk. Because of this fast access and the fact that the data never needs to be persisted to disk, the in-memory storage engine delivers the highest possible performance for the most demanding applications. Data durability and persistence can be achieved by using secondary replica set members with disk-based storage. The in-memory storage engine is available for beta testing now and is expect to be General Availability this year (2016).
- #9: In this ecommerce example, we are using a mix of storage engines. User data is managed by the In-Memory engine to provide the throughput and low latency needed for great customer experience, while the product catalog’s data gets provisioned to another MongoDB replica set configured with the disk-based WiredTiger storage engine. You’ll also notice that in the user data replica set example that although the primary is using the in-memory storage engine, the secondaries are using the WiredTiger storage engine with disk-based storage. So even though no data gets persisted to disk on the primary, the secondaries provide additional data protection by persisting the data to disk. Our flexible storage architecture means there is no need to use different in-memory and disk-based databases to support the e-commerce application. It’s the same Mongo database for both replica sets, it’s just a different storage engine that happens to be the best suited for the use case.
- #11: We all know that one of the major benefits of MongoDB is it’s dynamic and flexible schema, but it is also important to be able to implement controls to maintain data quality. To address this, MongoDB no offers document validation within the database so that data validation doesn’t need to take place within the application. Validation checks can be done on document structure, data types, data ranges, and the presence of mandatory fields. Validations can be set to reject documents that violate the validation rule OR warn and log the violation but allow the invalid document to be inserted or updated
- #12: Just to show you an example of how to add a validation, here we are adding a rule to the “CONTACTS” collection. For any newly inserted or updated documents, this rule will check that the year of birth is less than or equal to 1994, that it contains a phone number AND/OR an email address, and that when the phone number or email address fields are present, that they are a string data type.
- #13: MongoDB 3.2 also introduced an enhanced replication protocol available that delivers faster recovery in the event of a primary failure. The enhanced protocol reduces the length of time for failover by optimizing the algorithm to detect replica set primary failures and elect a new primary. Failover time is dependent on several factors including network latency. For those of you with sharded clusters, another enhancement with MongoDB 3.2 is that config servers can now be deployed as replica sets. Prior to 3.2, the config servers were implemented as 3 AND ONLY 3 special-purpose servers with their own write protocols, coordinators, and consistency checking.
- #15: We’ve added new capabilities targeted for use by business analysts and data scientists
- #16: SQL-based BI tools expect to connect to a data source with a fixed schema presenting tabular data. This can be a challenge when working with MongoDB’s dynamic schema and rich documents. To allow SQL-based BI tools to query MongoDB as a data source, we have developed the BI Connector. Now, business analysts can use BI visualization tools like Tableau, Qlik, Business Objects, and Cognos. The BI Connector performs 3 functions: First, it provides the BI tool with the schema of the MongoDB collection. The schema output generated by the BI Connector can be reviewed to ensure that data types, sub-documents and arrays are represented correctly. Second, it translates SQL statements issued by the BI tool into the equivalent MongoDB queries that are then sent to MongoDB for processing. And lastly, it converts the returned results into the tabular format expected by the BI tool, which can then visualize the data based on the user requirements.
- #17: We’ve also added the ability to combine data from multiple collections by implementing left outer joins via the $lookup operator. The $lookup operator can be included as a stage in the MongoDB aggregation framework and gives you more flexibility in data modeling. It allows richer analytics to be run in the database with higher performance and less application-side code.
- #18: MongoDB 3.2 also expands the options for running analytics on the operational database. We already know that MongoDB has a very flexible schema, and we can store arrays as well as simple values. Being able to manipulate and filter these arrays during aggregation is really important. New operators have been added to allow for more flexibility when dealing with arrays. We’ve also added new mathematical operators such as truncate, ceiling, floor, absolute, and standard deviation. These operators allow you to move code out of the client tier directly into the database resulting in higher performance and less developer complexity. And for text searches, we have increased the set of use cases by adding support for case-sensitive searches, as well as, additional languages.
- #19: We’ve made several enhancements that are applicable to Operations teams for monitoring and managing MongoDB
- #20: Many operations teams use Application Performance Management platforms like New Relic and AppDynamics to view their entire IT infrastructure from a single “pane of glass”. We now have a new API that exposes query performance metrics to these APM tools. Also, MongoDB Cloud Manager now provides packaged integration with the New Relic platform. Nothing additional needs to be installed, you can just copy and paste a couple of keys to display the MongoDB metrics, events, and visualizations directly in New Relic.
- #21: Some of you may already be intimately familiar with the database profiler. The profiler collects fined-grained information that can be used to analyze query performance. Parsing through the profiler output, though, isn’t always the easiest thing to do. Ops Manager and Cloud Manager Premium now include a Visual Query Profiler that gives DBAs and operations teams a quick and easy way to analyze specific queries. It visually displays how query and write latency varies over time and helps make it easy to identify slow queries and latency spikes. The Visual Query Profiler also analyzes the data it collects and can make recommendations for new indexes to improve query performance.
- #22: We all know that Secondary Indexes are one of the ways that MongoDB is different from other NoSQL databases. They help provide efficient access to data, and increase read performance. BUT.....indexes do have a cost: 1) Databases writes will be slower when they need to update the index 2) Memory and storage are needed to store the index. Partial indexes are meant to balance the delivery of good query performance while using fewer systems resources. By specifying a filtering expression when creating an index – like having a date greater than January 1, 2014, only documents that meet that criteria will be included in the index.
- #23: And last but not least for you Database Administrators, we’ve also create a new schema visualization and ad-hoc query tool.
- #24: In the past, it has been difficult to explore and understand the underlying data and its structure in MongoDB because of our dynamic schema. It meant connecting to the MongoDB shell and writing queries to determine the document structure, field names, and data types. Now, we have a new graphical tool called MongoDB Compass. Compass allows users to understand the structure of the data in the database and perform ad-hoc queries without having to understand MongoDB’s query language. The tool works by sampling a subset of documents from a collection and it displays information about the schema such as frequency of fields and frequency of types. By using a sampling algorithm, it minimizes overhead and can present results to the user almost instantly. To query a collection, document elements can be selected from the user interface and the query can then be run with the push of a button. Results from the query can be viewed both graphically and as a set of JSON documents. And now, one last slide, and then I’ll help you “find your way” with an actual MongoDB Compass demonstration.
- #25: Many of you are probably using the open source community version of MongoDB, and that’s great, but MongoDB also offer an Enterprise version of our software that includes 7x24 support, a commercial license, a number of security features and capabilities like an encrypted storage engine, as well as operational management tools like Ops Manager or Cloud Manager. 7x24x365 Support with a 1 hr SLA Encrypted Storage Engine for end-to-end database encryption In memory storage engine for your ultra throughput, most demanding apps: in memory computing without sacrificing data durability MongoDB Compass – Schema and data visualization; understand the data stored in your database with no knowledge of the MongoDB query language. Ad hoc queries with a few clicks of your mouse BI Connector – Visualize and analyze the multi-structured data stored in MongoDB using SQL-based BI tools such as Tableau, Qlikview, Spotfire and more MongoDB Ops Manager – full management platform to de-risk MongoDB in production Monitor the health of your system Automate deployment, configuration, maintenance, upgrades and scaling Back up and restore to any point in time (standard network mountable filesystems supported) Visual Query profiler to identify slow-running queries Index suggestions and automated index rollouts APM integration with enhanced drivers Runs behind your firewall. Enterprise-grade, follow the sun support with a 1-hour SLA Not just break/fix support Direct access to industry best-practices Advanced Security LDAP and Kerberos to integrate with existing authentication and authorization infrastructure Auditing of all database operations for compliance Commercial license To meet the needs of organizations that have policies against using open source, AGPL software Platform Certification Tested and certified for stability and performance on Windows, Red Hat/CentOS, Ubuntu, and Amazon Linux On-Demand Training Access to our online courses at your own pace to get team members up to speed















































































![MongoDB .local San Francisco 2020: Powering the new age data demands [Infosys]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/315pminfosysfinalsfoversionvocalpart1-200120221508-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)































