Multithreaded_Programming_in_Python.pdf
- 2. Introduction: • Multitasking is a process of executing multiple tasks simultaneously, we use multitasking to utilize the CPU. • Multitasking can be achieved by two ways or classified into two types – Process-Based Multitasking(Multiprocessing) – Thread-Based Multitasking(Multithreading) • Process-Based Multitasking(Multiprocessing): Executing multiple tasks simultaneously, where each task is separate independent process (or) program is called as process based multitasking. Example: – Typing a python program in notepad – Listening audio songs – Download a file from internet • The above three tasks are performed simultaneously in a system, but there is no dependence between one task and another task. • Process based multitasking is best suitable at “Operating System” level not at programming level.
- 3. • Thread-Based Multitasking(Multithreading): Executing multiple tasks simultaneously, where each task is separate independent part of process (or) program is called as thread based multitasking. • The each independent part is called as thread. The thread based multitasking is best suitable at programming level. Example: Let a program has 10k line of code, where last 5k lines of code doesn’t depend on first 5k lines of code, then both are the execution simultaneously. So takes less time to complete the execution. Note: Any type of multitasking is used to reduce response time of system and Improves performance.
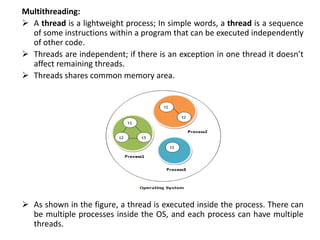
- 4. Multithreading: A thread is a lightweight process; In simple words, a thread is a sequence of some instructions within a program that can be executed independently of other code. Threads are independent; if there is an exception in one thread it doesn’t affect remaining threads. Threads shares common memory area. As shown in the figure, a thread is executed inside the process. There can be multiple processes inside the OS, and each process can have multiple threads.
- 5. Definition: Multithreading is a process of executing multiple threads simultaneously. Multithreading allows you to break down an application into multiple sub-tasks and run these tasks simultaneously. • In other words, the ability of a process to execute multiple threads parallelly is called multithreading. Ideally, multithreading can significantly improve the performance of any program. • Multiprocessing and Multithreading both are used to achieve multitasking, but we use multithreading than multiprocessing because threads shares a common memory area and context-switching between threads takes less time than process. Advantages: • Multithreading can significantly improve the speed of computation on multiprocessor • Multithreading allows a program to remain responsive while one thread waits for input, and another runs a GUI at the same time. Disadvantages: • It raises the possibility of deadlocks. • It may cause starvation when a thread doesn’t get regular access to shared resources.
- 6. Global Interpreter Lock (GIL): • Execution of Python code is controlled by the Python Virtual Machine. • Python was designed in such a way that only one thread may be executing in Python Virtual Machine. similar to how multiple processes in a system share a single CPU. • Many programs may be in memory, but only one is live on the CPU at any given moment. • Likewise, although multiple threads may be "running" within the Python interpreter, only one thread is being executed by the interpreter at any given time. • Access to the Python Virtual Machine is controlled by the global interpreter lock (GIL). This lock is what ensures that exactly one thread is running.
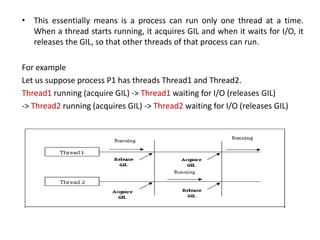
- 7. • This essentially means is a process can run only one thread at a time. When a thread starts running, it acquires GIL and when it waits for I/O, it releases the GIL, so that other threads of that process can run. For example Let us suppose process P1 has threads Thread1 and Thread2. Thread1 running (acquire GIL) -> Thread1 waiting for I/O (releases GIL) -> Thread2 running (acquires GIL) -> Thread2 waiting for I/O (releases GIL)
- 8. Multithreading Modules: Python offers two modules to implement threads in programs. – thread module and – threading module. Thread Module(_thread): • This module provides low-level primitives for working with multiple threads . • The <_thread> module supports one method to create thread. That is thread.start_new_thread(function, args) • This method starts a new thread and returns its identifier. It’ll invoke the function specified as the “function” parameter with the passed list of arguments. When the <function> returns, the thread would silently exit. • Here, args is a tuple of arguments; use an empty tuple to call <function> without any arguments.
- 9. Note: Python 2.x used to have the <thread> module. But it got deprecated in Python 3.x and renamed to <_thread> module for backward compatibility. Example: from _thread import start_new_thread from time import sleep def disp(n): for i in range(5): print(n) start_new_thread(disp, ("hai", )) start_new_thread(disp, ("hello", )) sleep(2) print("threads are executed...") Output: >>>python multithr1.py hai hello hai hai hai hai hello hello hello hello threads are executed...
- 10. Threading Module: • The threading module provides more features and good support for threads than thread module. • This Module provides Thread class, and this Thread class provide following methods • start() − The start() method starts a thread by calling the run method. • join([time]) − The join() waits for threads to terminate. • isAlive() − The isAlive() method checks whether a thread is still executing. • getName() − The getName() method returns the name of a thread. • setName() − The setName() method sets the name of a thread.
- 11. Creating Thread Using Threading Module • To implement a new thread using the threading module, use following code snippet Syntax: threading.Thread (target=None, name=None, args=()) This method has following arguments. Those are: • target is the callable function to be invoked by the run() method. Defaults to None, meaning nothing is called. • name is the thread name. By default, a unique name is constructed of the form “Thread-N” where N is a small decimal number. • args is the argument tuple for the function invocation. Defaults to ().
- 12. Example: import threading #function display def display(msg): for i in range(5): print(msg) # creating thread t1 = threading.Thread(target=display, args=("Thread1",)) t2 = threading.Thread(target=display, args=("Thread2",)) # starting thread 1 t1.start() # starting thread 2 t2.start() # wait until thread 1 is completely executed t1.join() # wait until thread 2 is completely executed t2.join() # both threads completely executed print("Done!") Output: >>>python multithr.py Thread1 Thread1 Thread2 Thread1 Thread1 Thread2 Thread1 Thread2 Thread2 Thread2 Done!
- 13. Let us try to understand the above code: • To import the threading module, we do: import threading • To create a new thread, we create an object of Thread class. It takes following arguments: target: the function to be executed by thread args: the arguments to be passed to the target function • In above example, we created 2 threads with different target functions: t1 = threading.Thread(target=display, args=(“Thread1”,)) t2 = threading.Thread(target=display, args=(“Thread2”,)) • To start a thread, we use start method of Thread class. t1.start() t2.start() • Once the threads start, the current program also keeps on executing. In order to stop execution of current program until a thread is complete, we use join method. t1.join() t2.join() • As a result, the current program will first wait for the completion of t1 and then t2. Once, they are finished, the remaining statements of current program are executed.







![Threading Module:
• The threading module provides more features and good support for
threads than thread module.
• This Module provides Thread class, and this Thread class provide following
methods
• start() − The start() method starts a thread by calling the run method.
• join([time]) − The join() waits for threads to terminate.
• isAlive() − The isAlive() method checks whether a thread is still executing.
• getName() − The getName() method returns the name of a thread.
• setName() − The setName() method sets the name of a thread.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreadedprogramminginpython-221123080829-91b1bf0a/85/Multithreaded_Programming_in_Python-pdf-10-320.jpg)


