Object Oriented Programming (OOP) using C++ - Lecture 4
- 1. Object Oriented Programming using C++ By Mohamed Gamal © Mohamed Gamal 2024
- 2. The topics of today’s lecture: Agenda
- 4. #include <iostream> #include <cstring> //for strcpy(), etc using namespace std; class String { private: char *str; //pointer to string public: String(char *s) //constructor, one arg { int length = strlen(s); //length of string argument str = new char[length + 1]; //get memory strcpy(str, s); //copy argument to it } ~String() //destructor { cout << "Deleting str.n"; delete[] str; //release memory } void display() //display the String { cout << str << endl; } }; int main() { String s1 = "Who knows nothing doubts nothing."; cout << "s1 = "; //display string s1.display(); return 0; } A String class using new and delete
- 5. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Distance { private: int feet; float inches; public: void getdist() { cout << "nEnter feet: "; cin >> feet; cout << "Enter inches: "; cin >> inches; } void showdist() { cout << feet << "' - " << inches << '"'; } }; int main() { Distance dist; //define a named Distance object dist.getdist(); //access object members dist.showdist(); // with dot operator Distance* distptr; //pointer to Distance distptr = new Distance; //points to new Distance object distptr->getdist(); //access object members distptr->showdist(); // with -> operator return 0; } Pointer to objects // ok but inelegant (*distptr).getdist(); // create Distance object (access with dot) Distance& dist = *(new Distance);
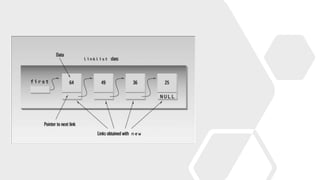
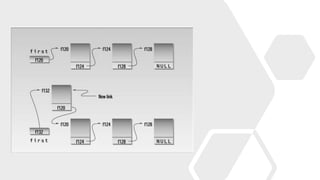
- 7. #include <iostream> using namespace std; struct link //one element of list { int data; //data item link *next; //pointer to next link }; class linklist //a list of links { private: link *first; //pointer to first link public: linklist() //no-argument constructor { first = NULL; //no first link } void additem(int d); //add data item (one link) void display(); //display all links }; void linklist::additem(int d) //add data item { link *newlink = new link; //make a new link newlink -> data = d; //give it data newlink -> next = first; //it points to next link first = newlink; //now first points to this } void linklist::display() //display all links { link *current = first; //set ptr to first link while (current != NULL) //quit on last link { cout << current -> data << endl; //print data current = current -> next; //move to next link } } int main() { linklist li; //make linked list //add four items to list li.additem(25); li.additem(36); li.additem(49); li.additem(64); li.display(); //display entire list return 0; } Linked List
- 10. Virtual Functions – Virtual means existing in appearance but not in reality. – When virtual functions are used, a program that appears to be calling a function of one class may in reality be calling a function of a different class. – Polymorphism means different forms.
- 11. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base //base class { public: void show() { cout << "Base Class.n"; } }; class Derv1 : public Base //derived class 1 { public: void show() { cout << "Derv1 Classn"; } }; class Derv2 : public Base //derived class 2 { public: void show() { cout << "Derv2 Classn"; } }; int main() { Derv1 dv1; //object of derived class 1 Derv2 dv2; //object of derived class 2 Base *ptr; //pointer to base class ptr = &dv1; //put address of dv1 in pointer ptr -> show(); //execute show() ptr = &dv2; //put address of dv2 in pointer ptr -> show(); //execute show() return 0; } Example 1 Normal Member Functions Accessed with Pointers
- 13. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base //base class { public: //virtual function virtual void show() { cout << "Base Classn"; } }; class Derv1 : public Base //derived class 1 { public: void show() { cout << "Derv1 Classn"; } }; class Derv2 : public Base //derived class 2 { public: void show() { cout << "Derv2 Classn"; } }; int main() { Derv1 dv1; //object of derived class 1 Derv2 dv2; //object of derived class 2 Base *ptr; //pointer to base class ptr = &dv1; //put address of dv1 in pointer ptr -> show(); //execute show() ptr = &dv2; //put address of dv2 in pointer ptr -> show(); //execute show() return 0; } Example 2 Virtual Member Functions Accessed with Pointers The same function call ptr -> show(); executes different functions, depending on the contents of ptr.
- 14. Late/Dynamic Binding – Which version of show() does the compiler call? – In fact the compiler doesn’t know what to do, so it arranges for the decision to be deferred until the program is running. – At runtime, when it is known what class is pointed to by ptr, the appropriate version of draw will be called. This is called late binding or dynamic binding. – Choosing functions in the normal way, during compilation, is called early binding or static binding. – < – Late binding requires some overhead but provides increased power and flexibility.
- 15. Abstract Classes and Pure Virtual Functions – When we will never want to instantiate objects of a base class, we call it an abstract class. – Such a class exists only to act as a parent of derived classes that will be used to instantiate objects. – It may also provide an interface for the class hierarchy. – How can we can mark a class as abstract? By placing at least one pure virtual function in the base class. – A pure virtual function is one with the expression =0 added to the declaration.
- 16. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base //base class { public: virtual void show() = 0; //pure virtual function }; class Derv1 : public Base //derived class 1 { public: void show() { cout << "Derv1 Classn"; } }; class Derv2 : public Base //derived class 2 { public: void show() { cout << "Derv2 Classn"; } }; int main() { // Base bad; //can’t make object from abstract class Derv1 dv1; //object of derived class 1 Derv2 dv2; //object of derived class 2 Base *ptr; //pointer to base class ptr = &dv1; //put address of dv1 in pointer ptr-> show(); //execute show() ptr = &dv2; //put address of dv2 in pointer ptr -> show(); //execute show() return 0; } Example 1 Pure Virtual Function Abstract Class =0 expression
- 17. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class person //person class { protected: char name[40]; public: void getName() { cout << " Enter name: "; cin >> name; } void putName() { cout << "Name: " << name << endl; } virtual void getData() = 0; //pure virtual func virtual bool isOutstanding() = 0; //pure virtual func }; class student : public person //student class { private: float gpa; //grade point average public: void getData() //get student data from user { person::getName(); cout << " Enter student's GPA: "; cin >> gpa; } bool isOutstanding() { return (gpa > 3.5) ? true : false; } }; class professor : public person //professor class { private: int numPubs; //number of papers published public: void getData() //get professor data from user { person::getName(); cout << " Enter number of professor's publications: "; cin >> numPubs; } bool isOutstanding() { return (numPubs > 100) ? true : false; } }; int main() { person *persPtr[100]; //array of pointers to persons int n = 0; //number of persons on list char choice; do { cout << "Enter student or professor (s/p): "; cin >> choice; if (choice == 's') //put new student persPtr[n] = new student; // in array else //put new professor persPtr[n] = new professor; // in array persPtr[n++] -> getData(); //get data for person cout << " Enter another (y/n)? "; //do another person? cin >> choice; } while (choice == 'y'); //cycle until not ‘y’ //print names of all persons, and say if outstanding for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { persPtr[j] -> putName(); if (persPtr[j] -> isOutstanding()) cout << " This person is outstanding!n"; } return 0; } Example 2 Pure Virtual Function Abstract Class =0 expression
- 19. Friend Function – A friend function is a function which operates on private data from objects of two different classes. – The function will take objects of the two classes as arguments and operate on their private data.
- 20. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class beta; //needed for frifunc declaration class alpha { private: int data; public: alpha() : data(3) { } friend int frifunc(alpha, beta); //friend function }; class beta { private: int data; public: beta() : data(7) { } friend int frifunc(alpha, beta); //friend function }; int frifunc(alpha a, beta b) //function definition { return (a.data + b.data); } int main() { alpha aa; beta bb; cout << frifunc(aa, bb) << endl; //call the function return 0; } Example 1 Friend Function
- 21. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Distance //English Distance class { private: int feet; float inches; public: Distance() : feet(0), inches(0.0) { } Distance(float fltfeet) //convert float to Distance { feet = static_cast<int>(fltfeet); //feet is integer part inches = 12 * (fltfeet - feet); //inches is what's left } Distance(int ft, float in) //constructor (two args) { feet = ft; inches = in; } void showdist() //display distance { cout << feet << "' - " << inches << '“’; } Distance operator + (Distance); }; //add this distance to d2 Distance Distance::operator + (Distance d2) //return the sum { int f = feet + d2.feet; //add the feet float i = inches + d2.inches; //add the inches if (i >= 12.0) //if total exceeds 12.0 { i -= 12.0; f++; } return Distance(f, i); //return new Distance with sum } int main() { Distance d1 = 2.5; //constructor converts Distance d2 = 1.25; //float feet to Distance Distance d3; cout << "nd1 = "; d1.showdist(); cout << "nd2 = "; d2.showdist(); d3 = d1 + 10.0; //distance + float: OK (Distance(float fltfeet) ctor) cout << "nd3 = "; d3.showdist(); // d3 = 10.0 + d1; //float + Distance: ERROR // cout << "nd3 = "; d3.showdist(); return 0; } Example 2 Without Friend Function
- 22. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Distance { private: int feet; float inches; public: Distance() { //constructor no args feet = 0; inches = 0.0; } Distance(float fltfeet) //constructor (one arg) { //convert float to Distance feet = int(fltfeet); //feet is integer part inches = 12 * (fltfeet - feet); //inches is what's left } Distance(int ft, float in) //constructor (two args) { feet = ft; inches = in; } void showdist() { cout << feet << "' - " << inches << '“’; } friend Distance operator + (Distance, Distance); //friend }; Distance operator + (Distance d1, Distance d2) //add d1 to d2 { int f = d1.feet + d2.feet; //add the feet float i = d1.inches + d2.inches; //add the inches if (i >= 12.0) //if inches exceeds 12.0, { i -= 12.0; f++; } return Distance(f, i); //return new Distance with sum } int main() { Distance d1 = 2.5; //constructor converts Distance d2 = 1.25; //float-feet to Distance Distance d3; cout << "nd1 = "; d1.showdist(); cout << "nd2 = "; d2.showdist(); d3 = d1 + 10.0; //distance + float: OK cout << "nd3 = "; d3.showdist(); d3 = 10.0 + d1; //float + Distance: OK cout << "nd3 = "; d3.showdist(); return 0; } Example 3 Friend Function A fix for the pervious example
- 23. #include <iostream> using namespace std; //class beta; class alpha { private: int data1; public: alpha() : data1(99) { } friend class beta; //beta is a friend class //friend beta; // same (requires top definition) }; class beta { //all member functions can access private alpha data public: void func1(alpha a) { cout << "ndata1 = " << a.data1; } void func2(alpha a) { cout << "ndata1 = " << a.data1; } }; int main() { alpha a; beta b; b.func1(a); b.func2(a); return 0; } Friend Classes Example Friend Class
- 24. End of lecture 4 ThankYou!




![#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> //for strcpy(), etc
using namespace std;
class String
{
private:
char *str; //pointer to string
public:
String(char *s) //constructor, one arg
{
int length = strlen(s); //length of string argument
str = new char[length + 1]; //get memory
strcpy(str, s); //copy argument to it
}
~String() //destructor
{
cout << "Deleting str.n";
delete[] str; //release memory
}
void display() //display the String
{
cout << str << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
String s1 = "Who knows nothing doubts nothing.";
cout << "s1 = "; //display string
s1.display();
return 0;
}
A String class using
new and delete](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopusingclanguage-lecture4-240918193530-82221c81/85/Object-Oriented-Programming-OOP-using-C-Lecture-4-4-320.jpg)










![#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class person //person class
{
protected:
char name[40];
public:
void getName() {
cout << " Enter name: "; cin >> name;
}
void putName() {
cout << "Name: " << name << endl;
}
virtual void getData() = 0; //pure virtual func
virtual bool isOutstanding() = 0; //pure virtual func
};
class student : public person //student class
{
private:
float gpa; //grade point average
public:
void getData() //get student data from user
{
person::getName();
cout << " Enter student's GPA: "; cin >> gpa;
}
bool isOutstanding() {
return (gpa > 3.5) ? true : false;
}
};
class professor : public person //professor class
{
private:
int numPubs; //number of papers published
public:
void getData() //get professor data from user
{
person::getName();
cout << " Enter number of professor's publications: ";
cin >> numPubs;
}
bool isOutstanding() {
return (numPubs > 100) ? true : false;
}
};
int main()
{
person *persPtr[100]; //array of pointers to persons
int n = 0; //number of persons on list
char choice;
do {
cout << "Enter student or professor (s/p): ";
cin >> choice;
if (choice == 's') //put new student
persPtr[n] = new student; // in array
else //put new professor
persPtr[n] = new professor; // in array
persPtr[n++] -> getData(); //get data for person
cout << " Enter another (y/n)? "; //do another person?
cin >> choice;
} while (choice == 'y'); //cycle until not ‘y’
//print names of all persons, and say if outstanding
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
persPtr[j] -> putName();
if (persPtr[j] -> isOutstanding())
cout << " This person is outstanding!n";
}
return 0;
}
Example 2
Pure Virtual
Function
Abstract Class
=0 expression](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopusingclanguage-lecture4-240918193530-82221c81/85/Object-Oriented-Programming-OOP-using-C-Lecture-4-17-320.jpg)