Objective structured practical question
- 1. Objective Structured Practical Question (OSPE) Subject: Ophthalmology According to the course curriculum of Bangladesh College of Physician & Surgeon (BCPS)
- 2. AUTHOR: Dr Md Anisur Rahman Anjum. MBBS (Dhaka Medical College). DO (Dhaka University) FCPS (EYE) Associate Professor National Institute of Ophthalmology Dhaka, Bangladesh. Chamber: Mojibunnessa Eye Hospital House: 18 Road: 6. Dhanmondi, Dhaka, 1205. Bangladesh. Email: [email protected] Cell: 01711-832397 7/15/2014 [email protected]
- 3. OSPE:1
- 4. Q:1(a) • 1) What does the picture show? • 2) What is the most likely underlying medical condition?
- 5. Answer:1(a) • 1) This is the right fundal FFA taken at the venous phase. There are multiple areas of circular dots with both hypo and hyperfluorescein. • 2) This most likely underlying condition is diabetic maculopathy which has been treated with photocoagulation.
- 6. Q:1(b) 1) What is the name of this investigation? 2) What does this picture show? 3) What is your diagnosis?
- 7. Answer: 1(b) 1) This is the Fluorescence angiography of the right fundus taken at the venous phase. 2) There are multiple spots of fluorescence (dot & blot haemorrhage). 3) The patient has background diabetic retinopathy.
- 8. 3 Q: (1C) 1) What phase is this frame of fluorescein angiography? 2) What does the picture show? & 3) What is the diagnosis?
- 9. Answer(1c) • 1) The late phase. • 2) Area of hyperfluorescence with pooling. The area with the most intense hyperfluorescence has a smoke stack appearance. The diagnosis is CSCR.
- 10. OSPE:2
- 12. Q:2 • The picture and fluorescein angiography are taken from a patient complaining of distorted right vision. • a. What phase is the fluorescein angiography? • b. What is the diagnosis? • c. What underlying medical condition may be present in this patient?
- 13. ANSWER:2 Venous phase Macroaneurysm. The colour picture shows circinate exudates surrounding an area of haemorrhage. FA shows local dilatation of the superior retinal artery corresponding to the area of haemorrhage. The feature is that of Macroaneurysm. Hypertension..
- 14. OSPE:3
- 15. Q:3 Answer the following questions with reference to the fluorescein angiography. 1) What abnormality is seen in the above picture? 2) Suggest two possible causes
- 16. Answer:3 1) Optic disc swelling. (The fluorescence which is taken at venous phase shows hyper fluorescence of the optic disc) 2) i. Raised intracranial pressure ii. Acute AION.
- 17. OSPE:4
- 18. Q:4 1) What imaging is shown? 2) What does it show? 3) Name two ocular signs which may be present?
- 19. Answer:4 1) A transverse CT scan of the brain. 2) The CT scan shows hydrocephalus. 3) 6 th nerve palsy & papillodema.
- 20. OSPE:5
- 21. This 70 year-old man suffered from progressive left exophthalmos. His CT scan is shown as 1) What does the CT scan show? 2) What is the most likely diagnosis? 3) What are the advantages of CT scan over MRI in orbital imaging? Q:5
- 22. 1) Hyperostosis of the left lateral portion of the sphenoid with left proptosis. 2) Sphenoid wing meningioma. 3) Better bony definition than MRI especially in detecting orbital fractures and bony metastasis Detecting metallic foreign body within the orbit or globe (contraindicated in MRI) Shorter running time than MRI Less expensive than MRI Answer:5
- 23. OSPE:6
- 24. This 70 year-old man suffered from progressive left exophthalmos. His CT scan is shown as below • a. What does the CT scan show? =2 • b. What is the most likely diagnosis? =2 • c. What are the advantages of CT scan over MRI in orbital imaging? Mention 3 points =6 Q:6
- 25. Answer:6 • a. Hyperostosis of the left lateral portion of the sphenoid with left proptosis. • b. Sphenoid wing meningioma. • c. • Better bony definition than MRI especially in detecting orbital fractures and bony metastasis • Detecting metallic foreign body within the orbit or globe (contraindicated in MRI) • Shorter running time than MRI • Less expensive than MRI
- 26. OSPE:7
- 28. Answer:7 a. Coronal section. b. Enlargement of the muscles in the right eyes especially the inferior rectus. c. Right thyroid eye disease. d. Any of the following abnormalities may occur: i. lid lag ii. restricted eye movement in all directions especially up gaze
- 29. OSPE:8
- 30. This is the CT scan of a 65 year-old woman with unilateral (R/E) proptosis • a. What orientation is this CT scan? • b. What abnormalities are shown? • c. What is the most likely diagnosis? • d. What abnormalities may occur when testing her ocular movement?
- 31. Answer:8 • a. Coronal section. • b. Enlargement of the muscles in the right eyes especially the inferior rectus. • c. Right thyroid eye disease. • d. Any of the following abnormalities may occur: • lid lag • restricted eye movement in all directions especially up gaze
- 32. OSPE:9
- 33. Q:9 • This one year baby was referred to the eye clinic because of suspected failure of visual development. Following fundoscopy an urgent CT scan was ordered.
- 34. Q:9 • a. What does the CT scan show? =2.5 • b. What is the most likely diagnosis? =2.5 • c. Write 3 factors will determine the prognosis of this patient? =3 • d. What is the chance of his offspring getting the same condition? =2
- 35. Answer:9 a) The CT scan shows bilateral solid masses within the globes with the density of the bone i.e. calcification. b) Retinoblastoma c) i. Optic nerve involvement = 1 ii. Tumour size and location = 1 iii. Tumour differentiation = 1 iv. Age of the patient = 0.5 v. Secondary tumour = 0.5 d) 40%
- 36. OSPE:10
- 37. Q:10 Suppose you are working in a primary eye care hospital at upo jilla level. A boy of 7 years old came to you with penetrating corneal injury & iris prolapse. Q=1 Before referring the boy at tertiary eye care centre, give him 2 treatment. If you are working at tertiary eye care centre, you will manage the patient by repairing of cornea under G/A.
- 38. Q:10 • Q 2. What minimum instruments are required to repair.=4 • Q 3. What will be your instruction to anesthetist.=1 • Q 4. How you will decide to reposition of the iris. Mention 2 points=3
- 39. Answer:10 ANS=1. Light Pad & bandage of the eye (no drop or ointment inside the eye). Systemic analgesic & antibiotics. ANS=2. Eye speculum. Barraquer needle holder Corneal forceps/St Martin 2 tying forceps
- 40. Ans:10 ANS=3. Please caring about raised IOP (avoid Suxamethonium) ANS=4 If iris is viable then it will reposited. If there is a fibrinious coating over the iris then it is sterile and can be reposited.
- 41. OSPE:11
- 43. Answer CHECKLIST A. Greetings--------------------0.5 B. explanation of procedure: i. Inj. Na Fluoride--------1.0 ii. Taking of picture----- 1.0 C. Prerequisite: i. Dilated pupil---------1.0 ii. Renal function test—1.0 iii. Any hypersensitivity of Fluoride—1.0
- 44. Answer D. Possible side effects: i. Nausea/vomiting---1.0 ii. Yellow urine---------1.0 iii. Anaphylaxis /syncope—1.0 E. Talk about cost----------1.0 i. Thanks & Feedback----0.5 ii. Total-----------------------10
- 45. OSPE:11
- 46. A 50 years old lady came to you for routine eye examination. Incidentally, it was diagnosed as a case of POAG. How will you counseling the lady?
- 47. Check list for observer Done Not done Greetings Give idea of POAG Rx Medical Rx Surgical Complications of surgery Fate if untreated Follow up after surgery Advice Thanks
- 48. Assessor for marking Done Not done Greetings 0.50 Give idea of POAG 2.50 Rx Medical 1.50 Rx Surgical 1.50 Complications of surgery 1.00 Fate if untreated 1.50 Follow up after surgery 1,00 Thanks 0.50
- 49. OSPE: 12
- 50. • A young patient comes to you with the complains of uniocular sudden loss of vision. How will you examine the patient with given instruments- (pen torch. Snellen chart. Ishihara chart. Ophthalmoscope.)
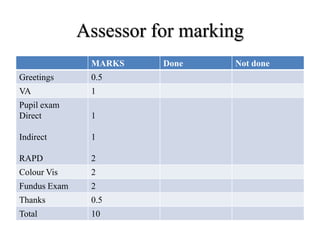
- 51. Check list for the observer MARKS Done Not done Greetings VA Pupil exam : Direct Indirect RAPD Colour Vision Fundus Exam
- 52. Assessor for marking MARKS Done Not done Greetings 0.5 VA 1 Pupil exam Direct Indirect RAPD 1 1 2 Colour Vis 2 Fundus Exam 2 Thanks 0.5 Total 10
- 53. OSPE:13
- 54. Question Examine the simulating patient of Keratoconus with the supplied instruments(pen torch, ophthalmoscope, retinoscope) and mention 1) 2 signs with pen torch. 2) 1 sign with ophthalmoscope. 3) 1 sign with retinoscope.
- 55. Answer i. Greetings-& permission---- 1.0 ii. Rizuti reflex by torch ----1.0. iii. Munsen sign by torch-----1.0. iv. Oil drop reflex by ophthalmoscope—1.5. v. Scissors reflex by retinoscope----1.5
- 56. Answer Or if slit lamp is given then I. -Greetings----------------0.25 II. -Positioning of patient-----0.25 III. -Positioning of slit lamp---0.5 IV. -Munsen sign( by looking down & holding the upper lids)-------1.0 V. Diffuse illumination( see hydropic scar & volks striae)-1.0 VI. -Oblique illumination(corneal thining/ steepening)-1.0 VII.-Fleischer ring (using cobalt blue filter)---1.0
- 57. OSPE:14
- 58. Usually BCC form a nodule in the eyelid but here in the picture does not make a nodule and grows within the eyelid, it induce pulling of the eyelid. Q:1. What is the name of this variant? Q:2 Why this is more difficult to treat? Q:3. Write one D/D. Q:4. Which is the most common site in the eye? Q:5. In which location of the eye it has the worst prognosis? Q:6 Which will you prefer? Excisional biopsy or incisional biopsy and why?
- 59. Answer 1) Sclerosing BCC or Morpheaform variant. = 2 2) Much more difficult to treat because its edges are harder to define. = 2 3) Chronic blepharitis. = 1 4) Lower eyelid.= 1 5) Medial canthus. = 1 6) Excisional biopsy. Because tumours that recur following incomplete treatment tend to be more aggressive. = 1 + 2 = 3
- 60. OSPE:15
- 61. This is the picture of a 50 year old man who came to you with the painless diffuse violet nodule in the left lower lid. On previous medical report you have noted that he is suffering from AIDS.
- 62. Question 1) What is the diagnosis of the nodule? 2) What type of tumour is this? 3) What is the causative organism? 4) In this condition, what will be the CD+4 cell count?
- 63. 1) Kaposi sarcoma. 2) This is a malignant vascular tumour 3) caused by Human Herpes Virus 8 (HHV-8)4. 4) Below 500
- 64. THANK’S A LOT FOR YOUR PATIENCE HEARING