Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks using hybrid SAPSO algorithm
- 1. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020, pp. 6153~6163 ISSN: 2088-8708, DOI: 10.11591/ijece.v10i6.pp6153-6163 6153 Journal homepage: http://ijece.iaescore.com/index.php/IJECE Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks using hybrid SAPSO algorithm Mohammed Hamouda Ali, Mohammed Mehanna, Elsaied Othman Department of Electrical Engineering, AL-Azhar University, Egypt Article Info ABSTRACT Article history: Received Apr 10, 2020 Revised May 28, 2020 Accepted Jun 10, 2020 The impact of the renewable distributed generations (RDGs), such as photovoltaic (PV) and wind turbine (WT) systems can be positive or negative on the system, based on the location and size of the DG. So, the correct location and size of DG in the distribution network remain an obstacle to achieving their full possible benefits. Therefore, the future distribution networks with the high penetration of DG power must be planned and operated to improve their efficiency. Thus, this paper presents a new methodology for integrated of renewable energy-based DG units with electrical distribution network. Since the main objective of the proposed methodology is to reduce the power losses and improve the voltage profile of the radial distribution system (RDS). In this regard, the optimization problem was formulated using loss sensitivity factor (LSF), simulated annealing (SA), particle swarm optimization (PSO) and a combination of loss sensitivity index (LSI) with SA and PSO (LSISA, LSIPSO) respectively. This paper contributes a new methodology SAPSO, which prevents the defects of SA and PSO. Optimal placement and sizing of renewable energy-based DG tested on 33-bus system. The results demonstrate the reliability and robustness of the proposed SAPSO algorithm to find the near-optimal position and size of the DG units to mitigate the power losses and improve the radial distribution system's voltage profile. Keywords: Distributed generation Distribution network Hybrid algorithm Load flow Loss sensitivity factor Optimal siting and sizing Particle swarm optimization Simulated annealing Copyright © 2020 Institute of Advanced Engineering and Science. All rights reserved. Corresponding Author: Mohammed Hamouda Ali, Department of Electrical Engineering, AL-Azhar University, P.O. Box 11751, El Nasr St, Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt. Email: [email protected] 1. INTRODUCTION The distribution network (DN) aims to provide higher demand rates for consumers. It is a very critical part of the power grid and is also the key cause of electrical losses in the network because of low reactance to resistance ratios. As a result of the constant growth in demand loads, the line currents will increase, which leads to an increase in the line losses and the voltage deviation. The RDS is the most common due to lower installation cost, easier power flow and voltage control than other types of distribution systems. Current distribution infrastructure constraints and increased interest in green technology utilization have culminated in the use of distributed generation (DG). There is other terminology and meanings used to describe DG, and this produces various viewpoints [1]: The Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) classifies DG as generation from a few kilowatts up to 50 MW. International energy agency (IEA) identifies DG as generating plant supplying a customer on-site or supporting to a distribution network connected to the grid. The International Conference on large High Voltage Electric Systems (CIGRE) classifies DG as smaller than 50-100 MW.
- 2. ISSN: 2088-8708 Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163 6154 DG can be defined as small-scale power generation to reduce customer demand near to load center. Distributed generation may come from several technologies and sources. The principal explanations for DG's growing use can be outlined as below [2]: Highly efficient modern technology. Cost of Transmission and Distribution systems can be reduced because of the DG units are near to consumers. Its positions can be located better due to small capacity. The installation period of the DG plants is shorter, and the investment risk isn't very high. Simplicity of the energy management by tracking the loads due to its small capacity. Provides a flexible way to select a wide variety of costing and reliable combinations. DG technologies are broadly categorized into two types: renewable technologies (PV, WT) and non-renewable technologies (fuel cells). It is important to determine the optimal location and size of DGs to achieve the desired performance, grid reinforcement, minimizing power loss and on-peak operating costs, improve the voltage profile and loading factors, reprieve or canceling the system upgrades, improving the system security, increasing reliability and efficiency, and improving the power quality of the electrical grid. Different approaches have been suggested for determining the optimal site and size of DGs in the DN. Gandomkar et al., provided a new approach based on a combination of genetic algorithm (GA) and SA algorithms for optimal allocation of DGs in distribution networks to improve the optimization goal [3]. Sutthibun and Bhasaputra applied SA for optimal location of DG on the IEEE 30 bus test system [4]. Kefayat et al., presented a hybrid of ant colony optimization and artificial bee colony optimization for optimal siting and sizing of DG [5]. Alinezhad et al., proposed three algorithms, PSO, GSA and GA for optimal location of DG in distribution system [6]. Jordehi proposed various approaches for determination the best sitting and sizing of DGs in electric power systems [7]. Prakash and Khatod presented a review for minimizing the system losses, improving the voltage profile, enhancing the system reliability, stability and loadability by optimal sizing and siting techniques for DG [8]. Vijay et al., applying bat motivated optimization algorithm (BMOA) for optimal placement and sizing of distributed power sources to reduce the active power loss in 33-bus test system [9]. Singh and Sharma, illustrated a review on DG planning in the distribution system performances such as real and reactive power loss, power system loadability, stability, reliability, security, available power transfer capacity [10]. Banhthasit et al., suggest an optimal generation scheduling method for integrated of renewable energy-based DGs and energy storage systems with electrical power system [11]. UshaReddy et al., proposed LSF & DE to determine the optimal size and location of capacitors for minimizing the power losses and improving the voltage profile in RDN [12]. Lin et al., presented a hybrid approach of analytical method (LSF) for sizing DGs and meta-heuristic method (PSO) for sitting DGs based on optimal reactive power dispatch for decreasing the real power loss [13]. EL-Sayed, determine the optimal location, size and numbers of DGs to reduce power loss and improve voltage profile [14]. M. H. Moradi and M. Abedini, presented a hybrid approach of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for optimal DG location and sizing in distribution system [15]. Jithendranath et al., illustrated a combination approach based on PSO and GSA to solve the optimal reactive power dispatch problem in power system [16]. Verma and Lakhwani, present strong rules discovered in databases using hybrid algorithm of GA and PSO [17]. In this paper, LSI, SA, PSO, LSISA, LSIPSO and SAPSO optimization algorithms are used for positioning and sizing of DGs. These algorithms have been tested on IEEE 33-bus radial distribution system. 2. PROBLEM FORMULATION The higher losses, higher voltage drop and thermal limitation are very most significant problem in the distribution system. So, intensive attention to the DGs technology has become a vital issue that must be taken into consideration for its impact on the distribution system. To solve this problem, it became necessary to determine the optimal location and size of DGs as it represented the main problem under network restrictions including load flow in order to increase the overall efficiency of system performance. 2.1. Load Flow It is an important tool for power system planning, operation, optimization and control to ensure stability, reliability and economy for the electrical system. Traditional methods for load flow analysis such as Newton Raphson (NR), Gauss Seidel (GS) may be unsuitable for the distribution network and diverge due to [18]: Radial or weakly mesh network. High R/X ratio. Unbalanced operation. Distributed generation.
- 3. Int J Elec & Comp Eng ISSN: 2088-8708 Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks… (Mohammed Hamouda) 6155 Backward/Forward Sweep (BFS) algorithm is preferred for correct planning due to: The ill-state nature of RDS. Accurate results of power flow depend on convergence, implementation time and iterations number. This approach is implemented in two steps: the backward and forward sweep using the load and line data. In the backward sweep, voltages and currents are calculated using KVL and KCL starting from the farthest node. In forward sweep, the downstream voltage is calculated starting from the source node. The steps of BFS algorithm are mentioned below: Initialize the injected current (𝐼𝑖 = 0) Initialize all buses voltage (𝑉𝑖= 1pu) Calculate the node current (𝐼𝑖 = 𝑆𝑖 ∗ 𝑉𝑖 ∗) Calculate the line current (backward sweep) 𝐼(𝑖,𝑖+1) = 𝐼𝑖+1 + ∑(𝑏𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠′ 𝑠 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑎𝑡 𝑛𝑜𝑑𝑒 𝑖 + 1) Update the buses voltage (𝑉𝑖 = 𝑉𝑖+1 + (𝑍(𝑖,𝑖+1) ∗ 𝐼(𝑖,𝑖+1))) Until stopping criterion. 2.2. Objective function (OF) The main objective problem is to reduce the total power losses and boost the system's voltage profile through determine the optimal capacity and positioning of the DGs using the various proposed methods. 𝑂𝐹 = 𝑚𝑖𝑛(𝑃𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠) = 𝑚𝑖𝑛 ∑ 𝐺 𝑘(𝑉𝑖 2 + 𝑉𝑗 2 − 2𝑉𝑖 𝑉𝑗 cos(𝛿𝑖 − 𝛿𝑗))𝑁𝐿 𝑘=1 (1) 2.3. System constrains There are two types of constraints which control the minimization of objective function: Equality constraints: These constraints formulated the active and reactive power balance by power flow equations. 𝑃𝐺𝑖 − 𝑃𝐷𝑖 − 𝑃𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠 = 0 (2) 𝑄 𝐺𝑖 − 𝑄 𝐷𝑖 − 𝑄𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠 = 0 (3) Inequality constraints: These constraints determine the technical operation limits of power system. Bus voltage 𝑉𝑖 𝑚𝑖𝑛 ≤ 𝑉𝑖 ≤ 𝑉𝑖 𝑚𝑎𝑥 (4) DG capacity 𝑃𝐷𝐺 𝑚𝑖𝑛 ≤ 𝑃𝐷𝐺 ≤ 𝑃𝐷𝐺 𝑚𝑎𝑥 , 𝑄 𝐷𝐺 𝑚𝑖𝑛 ≤ 𝑄 𝐷𝐺 ≤ 𝑄 𝐷𝐺 𝑚𝑎𝑥 (5) DG location 2 ≤ 𝐷𝐺 𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 ≤ 𝑁𝑏𝑢𝑠 (6) 3. METHODOLOGIES DG’s problem is evaluating the optimal size and location to optimize the required objective function. Major methodological techniques for sizing and sitting of DGs are summarized as below [19]: Analytical technique. Conventional technique. Meta-heuristic optimization technique. Hybrid technique. Artificial intelligence technique.
- 4. ISSN: 2088-8708 Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163 6156 4. MATHEMATICLE MODEL OF OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES 4.1. Loss sensitivity factor (LSF) LSF is helpful to obtain the critical buses in the network. It can estimate which bus will have the greatest loss reduction when a DG is placed. The search space of the optimization problem is reduced due to the estimation of these candidate buses [12, 20, 21]. Figure 1 illustrates a distribution line " 𝑘 " with an impedance 𝑅 𝑘 + 𝑗𝑋 𝑘 and a load of 𝑃𝑖𝑗 + 𝑗𝑄𝑖𝑗 connected between ‘𝑖’ and ‘𝑗’ buses. Figure 1. A radial distribution feeder The real power loss (𝐼2 𝑅) at each node in radial distribution network (RDN) can be calculated as: 𝑃𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠(𝑗) = (𝑃 𝑒𝑓𝑓 2 (𝑗)+𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓 2 (𝑗)) (𝑉(𝑗)) 2 ∗ 𝑅(𝑘) (7) Also, the reactive power loss (𝐼2 𝑋) at each node in RDN can be given as: 𝑄𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠(𝑗) = (𝑃 𝑒𝑓𝑓 2 (𝑗)+𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓 2 (𝑗)) (𝑉(𝑗)) 2 ∗ 𝑋(𝑘) (8) where: 𝑃𝑒𝑓𝑓(𝑗) = Total real power supplied beyond the bus "𝑗". 𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓(𝑗) = Total reactive power supplied beyond the bus "𝑗". Now, the LSF can be expressed as: 𝜕𝑃 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝜕𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓 = 2∗𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓(𝑗)∗𝑅(𝑘) (𝑉(𝑗)) 2 (9) 𝜕𝑄 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝜕𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓 = 2∗𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓(𝑗)∗𝑋(𝑘) (𝑉(𝑗)) 2 (10) The steps of LSF to find the selected bus for DG placement can be summarized as below: LSF has been calculated as given in (9) from the base case load flow. The values of LSF have been sorted descending and its bus index in bus positions “bpos (i)”, which determine the sequence for mitigation. Voltage sensitivity factors (VSF) are calculated as given in (11) by considering the minimum voltage magnitude is 0.95 pu as below: 𝑉𝑆𝐹(𝑖) = 𝑉(𝑖) 0.95 (11) where 𝑉(𝑖) is the bus voltage. The values of 𝑉𝑆𝐹 which less than 1.01 can be sorted ascending and its bus index in the candidate buses “bcan(i)”. The selected bus for DG placement can be determined by comparing the bus positions and the candidate buses and choosing the first common bus.
- 5. Int J Elec & Comp Eng ISSN: 2088-8708 Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks… (Mohammed Hamouda) 6157 4.2. Simulated annealing (SA) SA is a simple form local search algorithm (a descent algorithm), which preferred when problem size is large. It is a meta-heuristic technique that has been used extensively to solve a complicated optimization problem. The word annealing refers to the cooling process after heating of the material to become homogeneous and more harden [14]. The concept of solution based on cool down the possible state of a thermo dynamic system from the preliminary high temperature. The objective function or cost of a solution is corresponding to the energy of the physical state. All solutions of the optimization problem are accepted at high temperature, but at low temperature only the minimal cost solutions are accepted. Although simplicity and quick execution of SA algorithm, the drawback of this approach is that the local minimum found may be far from the global minimum [3]. To avoid this defect, it is necessary to increase the number of iterations combined with an increased number of searches at each iteration. The initial solution of SA is random then new ones are proposed through local changes and accepted depend on the controlled probability. The major steps of SA algorithm can be summarized as following: Select an initial solution 𝑋0𝑖 ∈ 𝑆 (search space). Select an initial temperature 𝑇 𝑚𝑎𝑥. Set temperature change counter n = 0. Set a repetition counter k (number of iterations at each T). Generate a new solution 𝑋𝑖 ∈ 𝑆. Calculate ∆= 𝑓(𝑋𝑖 ) − 𝑓(𝑋0𝑖 ). If ∆< 0, 𝑋0𝑖 = 𝑋𝑖 . Else if random (0,1) < exp(- ∆/T). Then, 𝑋0𝑖 = 𝑋𝑖 . k = k + 1 n = n + 1 Until stopping criterion. 4.3. Particle swarm optimization (PSO) This algorithm is depending on the perception of nature and swarming seen in birds or fish. PSO is used when the optimization problems have several solutions. In this algorithm the particles move in a bounded search space to find the overall best velocity and position depend on social experience of the swarm [22-26]. The value of the agent’s velocity and its position of the swarm is updated as shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. Particle movement in PSO algorithm 𝑣𝑖𝑗 𝑘+1 = 𝑤𝑣𝑖𝑗 𝑘 + 𝑐1 𝑟1(𝑝 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡,𝑖 𝑘 − 𝑥𝑖𝑗 𝑘 ) + 𝑐2 𝑟2(𝑔 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑘 − 𝑥𝑖𝑗 𝑘 ) (12) 𝑥𝑖𝑗 𝑘+1 = 𝑥𝑖𝑗 𝑘 + 𝑣𝑖𝑗 𝑘+1 (13) Where: 𝑖 is the number of particles, 𝑗 is the dimension of problem, 𝑣 & 𝑥 are the velocity of particle and its position respectively, 𝑝 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡 & 𝑔 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡 are the personal and global best respectively, 𝑤 is weighting or learning factor, 𝑐1 & 𝑐2 are accelerating factors and 𝑟1 & 𝑟2 are random numbers in the range of (0,1). The new solution in PSO depends on its initial solution, so it may be can’t succeed to reach the optimal solution. The steps of PSO algorithm are presented below: Initialization randomly of velocity and position for N particles (𝑥𝑖𝑗 & 𝑣𝑖𝑗).
- 6. ISSN: 2088-8708 Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163 6158 Set 𝑝 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡,𝑖 = 𝑥𝑖𝑗. Calculate 𝑔 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡 through iterative evaluation of fitness function. Update each particle’s velocity and position. Run the load flow to obtain the cost function. Update 𝑝 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡,𝑖 & 𝑔 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡 according to the fitness value. Until stopping criterion. 4.4. Hybrid algorithms This paper presented two methodologies for hybrid algorithms: a. To reduce the complexity of computational, search space, the dimension of the optimization problem and increase the accuracy, a combination of analytical technique (LSF) and heuristic algorithms (SA, PSO) is used in two steps for solving the problem. The first step to determine the optimal location by using LSF and SA or PSO in second step for optimal size as demonstrated in Figure 3. Figure 3. LSISA & LSIPSO algorithms b. To avoid the drawback of heuristic algorithm ( SA & PSO), this paper suggested a new approach as presented in Figure 4, its concept based on combination of SA and PSO by two strategies: The first strategy is avoiding the defect of SA, which is updating the solution randomly until stopping criterion by a systematic approach to reach the optimal solution without falling into the problem of local minima. This methodology for systematic updating can be achieved by using the same manner in PSO.
- 7. Int J Elec & Comp Eng ISSN: 2088-8708 Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks… (Mohammed Hamouda) 6159 The second strategy is avoiding the defect of PSO, which is the falling into local optimum due to lower convergence precision. Therefore, an improved algorithm is proposed, which makes up for the deficiency of PSO by a stochastic approach using SA. At the high temperature the suggested strategy doesn't affect, but with decreasing temperature it can converge to the global optimal value based on controlled probability which help to escape from the local minima. (a) (b) Figure 4. SAPSO algorithm (a) First strategy SAPSO1, (b) Second strategy SAPSO2
- 8. ISSN: 2088-8708 Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163 6160 5. TEST SYSTEM The IEEE 33 bus distribution system [27] is used for testing the proposed algorithms. A single line diagram is illustrated in Figure 5, which has the total real power 3720 kw and reactive power 2300 kvar. The proposed methodologies are carried out by Matlab 2019 software using intel ® Core ™ i7-8550U CPU @ 1.80GHz 1.99 GHz, 16.0 GB RAM, 64-bit Operating System, x64-based processor. Figure 5. IEEE-33 bus test system 6. RESULTS In LSF, as shown in Figure 6, bus 6 was chosen for DG placement based on the results in Table 1, which sets the candidate bus priority. Since it was a junction node of several branches, so voltage profile improvement was better in this case. Figure 7 shows the voltage profile before and after DG installation. Bus 18 is the farthest end from the supply node, so its voltage in the base scenario (without DG) is the lowest and its value is 0.90421 pu (unaccepted). Buses 6 to 18 and buses 26 to 33 have voltage lower than 0.95 pu without DG unit, while after adding DG a significant improvement of voltage profile within limits (accepted). Table 2, shows the most proper location and capacity of DG and corresponding the total losses for each scenario. Also, it is clear the minimum voltage bus and its value. This indicates that the proposed algorithms predict the optimal position and size for DGs with high efficiency and accuracy. To prove the effectiveness of the novel algorithm SAPSO, the results achieved by this technique have been compared with those obtained by the other algorithms. By comparison, it demonstrated the ability of SAPSO2 to reduce system losses to the lowest possible value 67.8113 kw and increasing the voltage profile to the highest value 0.95896 pu (within accepted limit) simultaneously. In addition, the DG's capacity is the lowest, which means that the minimum cost is achieved. The optimization process to reach the optimal solution for the constrained objective function can be implemented iteratively. Firstly, initialize the solution randomly then the solution updated iterative till it is reached to global optimal minimum real power loss is obtained, which around 67.8113 kw. Figure 8 illustrates the fitness function convergence for all algorithms. SAPSO algorithm have demonstrated the superiority through discovery the optimal solution to achieve global minimum fitness. Figure 8 shows the novelty of the SAPSO algorithm, which converges quickly before the other algorithms to achieve the optimal fitness function. Where SAPSO1, SAPSO2, LSIPSO, LSISA, PSO and SA reach after 10 iterations, 18 iterations, 33 iterations, 63 iterations, 40 iterations and 60 iterations, respectively. Figure 6. Loss sensitivity index Figure 7. Voltage profile for IEEE-33 bus test system
- 9. Int J Elec & Comp Eng ISSN: 2088-8708 Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks… (Mohammed Hamouda) 6161 Table 1. LSF and VSF in IEEE-33bus test system Bus Number LSF VSF Bus Number LSF VSF Bus Number LSF VSF 6 0.02327 0.99992 31 0.00605 0.96668 26 0.00259 0.99791 8 0.02134 0.98496 30 0.00461 0.97106 15 0.00239 0.95953 28 0.01211 0.98331 27 0.00341 0.99525 16 0.00236 0.95809 9 0.01004 0.97837 14 0.00316 0.96100 11 0.00159 0.97137 13 0.00984 0.96338 17 0.00292 0.95597 32 0.00124 0.96572 10 0.00935 0.97228 12 0.00281 0.96979 18 0.00099 0.95534 29 0.00866 0.97475 7 0.00280 0.99628 33 0.00030 0.96542 Table 2. The performance analysis of proposed algorithms in IEEE-33bus test system Scenarios Power losses (kw) Loss Reduction Min Voltage (pu) & Bus Number DG Location DG Size P (kw) & Q (kvar) Base Case 210.0794 - 0.90421 18 - - - SA 70.1894 66.6% 0.95904 18 6 2935.6 1554.8 PSO 67.8228 67.7% 0.95862 18 6 2528.3 1747.9 LSI-SA 67.8118 67.7% 0.96041 18 6 2556.7 1750.0 LSI-PSO 67.8113 67.7% 0.96010 18 6 2658.8 1619.6 SA-PSO1 67.8123 67.7% 0.95872 18 6 2557.7 1748.4 SA-PSO2 67.8113 67.7% 0.95896 18 6 2511.9 1530.5 Figure 8. Convergence characteristic of proposed algorithms
- 10. ISSN: 2088-8708 Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163 6162 7. CONCLUSION Due to ill-conditioned nature of RDNs, losses minimization and voltage profile enhancement have been of great concern. The integration of optimal placement and sizing of RDGs in RDS minimized the system losses and enhanced the voltage profile. The voltage profile improvement can be achieved within the network constraints, since the DGs is located closely at loads and can be partially supplied a real and reactive power to the loads. It can be concluded that, the optimal DG placement and sizing gives orientation for the economic planning and operation of power system in the modern integrated grid. This paper investigates the typical analytical, heuristic and hybrid integrating scheme to calculate the optimal placement and capacity of DGs. In this paper, SA and PSO among heuristic techniques have been performed to solve the DGs problem. A new powerful evaluation algorithm LSISA and LSIPSO have been presented in this research. LSI is an efficient integrated method with SA and PSO algorithms for determining the optimal location and reduced the time simulation to reach the optimal solution through the most voltage sensitivity bus (the least VSF value) and power losses (the highest LSF value). The sensitivity factors reduced the search space and the dimension of the optimization problem by estimating the selected bus for DG sitting. LSI accuracy has been verified by the other proposed algorithms for finding the optimal solution. A novel approach principle is proposed based on SA and PSO algorithms in one hybrid algorithm called SAPSO algorithm. The novelty of this algorithm based on two strategies: the first strategy is avoiding randomly generation and updating the solution in SA by using the same manner in PSO. The second strategy is avoiding the local minima problem in PSO because its particles may be failed to converge depend on its initial value, so it is integrated with SA in order to benefit from the probability rate to accept or discard the solution and escape from the local minimum. The BFS algorithm is used for power flow calculations. The proposed algorithms have been tested on IEEE 33 bus system. The results proved the proposed algorithms have the capability to provide the optimal solution for the problem optimization. Furthermore, the results show the efficiency of these approaches for the voltage sag mitigation within limits and power loss reduction. Although the distinguished performance of all techniques in terms of solution and convergence performance, SAPSO algorithm have proved the superiority through finding the optimal solution rapidly, economically and accurately which allowing its application in the large-scale distribution systems. Finally, some recommendation to consider in the future work in this field: (a) the power factor while sizing DGs; (b) the reliability indices as an objective function combined with the mentioned objective function to have a reliable and secure distribution systems. REFERENCES [1] T. Ackermann, G. Andersson, and L. Söder, "Distributed generation: A definition," Electric Power Systems Research, vol. 57, pp. 195-204, 2001. [2] G. Celli, F. Pilo, “Optimal distributed generation allocation in MV distribution networks,” 22nd International Conference IEEE Power Engineering Society, pp. 81-86, 2001. [3] Gandomkar M, Vakilian M, Ehsan M., "A combination of genetic algorithm and simulated annealing for optimal DG allocation in distribution networks," Proceeding of IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, 645-648, 2005. [4] T. Sutthibun and P. Bhasaputra, "Multi-Objective Optimal Distributed Generation Placement Using Simulated Anneal-ing," International Conference Electrical Engineering/Electronics Computer Tele-communications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), 2010. [5] M. Kefayat, A. Lashkar Ara and S. A. Nabavi Niaki, "A hybrid of ant colony optimization and artificial bee colony algorithm for probabilistic optimal placement and sizing of distributed energy resources," Energy Conversion and Management, vol. 92, pp. 149-161, 2015. [6] Alinezhad, P., Bakhoda, O. Z., and Menhaj, M. B. "Optimal DG placement and capacity allocation using intelligent algorithms," 4th Iranian Joint Congress on Fuzzy and Intelligent Systems (CFIS), pp. 1-8, 2015. [7] A. R. Jordehi, "Allocation of distributed generation units in electric power systems: A review," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 56, pp. 893-905, 2016. [8] P. Prakash and D. K. Khatod, "Optimal sizing and siting techniques for distributed generation in distribution systems: A review," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 57, pp. 111-130, 2016. [9] Vijay R, Jeeva M, Ravichandran C. S, "Optimal Location of Distributed Energy Resources in Microgrid for Power Loss Minimization Using Bat Inspired Algorithm," SSRG International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering, pp. 101-106, 2016. [10] B. Singh and J. Sharma, "A review on distributed generation planning," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 76, pp. 529-544, 2017. [11] B. Banhthasit, C. Jamroen, and S. Dechanupaprittha, "Optimal Generation Scheduling of Power System for Maximum Renewable Energy Harvesting and Power Losses Minimization," International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE), vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 1954-1966, 2018.
- 11. Int J Elec & Comp Eng ISSN: 2088-8708 Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks… (Mohammed Hamouda) 6163 [12] V. Usha Reddy, Dr.T.Gowri Manohar, P. Dinakara Prasad Reddy, “Capacitor Placement for loss reduction in radial distribution networks:A two stage approach,” Journal of electrical engineering, vol. 12, 2012. [13] K. M. Lin, P. L. Swe, and K. Z. Oo, "Optimal Distributed Generator Sizing and Placement by Analytical Method and PSO Algorithm Considering Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch," World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering, vol. 13, no. 1, 2019. [14] S. K. EL-Sayed, "Optimal Location and Sizing of Distributed Generation for Minimizing Power Loss Using Simulated Annealing Algorithm," Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 104-110, 2017. [15] M. H. Moradi and M. Abedini, "A Combination of Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization for Optimal DG location and Sizing in Distribution System," Electrical Power and Energy System, vol. 34, pp. 66-74, 2012. [16] J. V. U. Jithendranath, A. S. V. U. Babu, and G. D. V. U. Sukumar, "Hybrid PSOGSA Method of Solving ORPD Problem with Voltage Stability Constraint," Indones. J. Electr. Eng., vol. 12, no. 8, pp. 5807-5813 2014. [17] M. Verma and R. Lakhwani, "Association Rule Generation by Hybrid Algorithm based on Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithm," International Journal of Science, Engineering and Computer Technology, vol. 5, no. 12, pp. 423-426, 2015. [18] M. T. Hagh, T. Ahamadzadeh, K. M. Muttaqi, and D. Sutanto, "Load flow analysis of radial and weakly meshed distribution systems including distributed generations,” Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference, 2014. [19] K. Sampangi Sambaiah, "A Review on Optimal Allocation and Sizing Techniques for DG in Distribution Systems," International Journal Of Renewable Energy Research, vol. 8, no. 3, 2018. [20] Chin Chia Seet, Jagadeesh Pasupuleti, M. Reyasudin Basir Khan, "Optimal Placement and Sizing of Distributed Generation in Distribution System using Analytical Method," International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE), vol. 8, no. 4, 2019. [21] K. Cabana, J. Candelo, R. Castillo and E. De-la-Hoz-Franco, "Voltage sensitivity analysis to determine the optimal integration of distributed generation in distribution systems," International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 55-65 2019. [22] A. N. Hussain, and A. A. Ismail, "Operation cost reduction in unit commitment problem using improved quantum binary PSO algorithm," International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 1149-1155, 2020. [23] A. B. Kunya, et al., "Distribution Network Reconfiguration for Loss Reduction and Voltage Profile Improvement using B-PSO ", ICAT’16 International Conference on Advanced Technology and Sciences, vol. 3, 2016. [24] Sahib, T. J., Ghani, M. R. A., Jano, Z., “Optimum allocation of distributed generation using PSO: IEEE test case studies evaluation," Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res, vol. 12, no. 11, pp. 2900-2906, 2017. [25] Y. Merzoug, et al., “Optimal placement of wind turbine in a radial distribution network using PSO method,” International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive System, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 1074-1081, 2020. [26] Y. Merzoug, B. Abdelkrim and B. Larbi, "Distribution network reconfiguration for loss reduction using PSO method,” International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 5009-5015, 2020. [27] Zhang, S., Cheng, H., Li, K., Tai, N., Wang, D., and Li, F. "Multi-objective distributed generation planning in distribution network considering correlations among uncertainties,” Applied Energy, vol. 226, pp. 743-755, 2018. BIOGRAPHIES OF AUTHORS Mohammed Hamouda Ali received the B.Sc. (2011) & M.Sc. (2016) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Al-Azhar University. Currently he is Teaching Assistant in the Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Egypt. His research interests are in power electronics, power system planning, optimization, operation, power system control, power quality, reliability and renewable energy technology. Mohammed Mehanna received the B.Sc. (1995) & M.Sc. (2002) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Al-Azhar University. He received his PhD in Al-Azhar University, Egypt (2007). Currently he is a professor, Agent of Faculty of Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Egypt. His research interests are in power system planning, operation, power system control, optimization theory, power quality and renewable energy. Elsaied Othman received the B.Sc. (1972) & M.Sc. (1980) degrees in Electrical Engineering from Al-Azhar University. He received his PhD in Al-Azhar University, Egypt (1983). Currently he is a professor, Head of Physics & Mathematics Department, Faculty of Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Egypt. His research interests are in power system operation, power system control, optimization theory, power quality, reliability, power system security and renewable.
![International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE)
Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020, pp. 6153~6163
ISSN: 2088-8708, DOI: 10.11591/ijece.v10i6.pp6153-6163 6153
Journal homepage: http://ijece.iaescore.com/index.php/IJECE
Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks
using hybrid SAPSO algorithm
Mohammed Hamouda Ali, Mohammed Mehanna, Elsaied Othman
Department of Electrical Engineering, AL-Azhar University, Egypt
Article Info ABSTRACT
Article history:
Received Apr 10, 2020
Revised May 28, 2020
Accepted Jun 10, 2020
The impact of the renewable distributed generations (RDGs), such as
photovoltaic (PV) and wind turbine (WT) systems can be positive or negative
on the system, based on the location and size of the DG. So, the correct
location and size of DG in the distribution network remain an obstacle to
achieving their full possible benefits. Therefore, the future distribution
networks with the high penetration of DG power must be planned and
operated to improve their efficiency. Thus, this paper presents a new
methodology for integrated of renewable energy-based DG units with
electrical distribution network. Since the main objective of the proposed
methodology is to reduce the power losses and improve the voltage profile of
the radial distribution system (RDS). In this regard, the optimization problem
was formulated using loss sensitivity factor (LSF), simulated annealing (SA),
particle swarm optimization (PSO) and a combination of loss sensitivity
index (LSI) with SA and PSO (LSISA, LSIPSO) respectively. This paper
contributes a new methodology SAPSO, which prevents the defects of SA
and PSO. Optimal placement and sizing of renewable energy-based DG
tested on 33-bus system. The results demonstrate the reliability and
robustness of the proposed SAPSO algorithm to find the near-optimal
position and size of the DG units to mitigate the power losses and improve
the radial distribution system's voltage profile.
Keywords:
Distributed generation
Distribution network
Hybrid algorithm
Load flow
Loss sensitivity factor
Optimal siting and sizing
Particle swarm optimization
Simulated annealing
Copyright © 2020 Institute of Advanced Engineering and Science.
All rights reserved.
Corresponding Author:
Mohammed Hamouda Ali,
Department of Electrical Engineering,
AL-Azhar University,
P.O. Box 11751, El Nasr St, Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt.
Email: Eng_MohammedHamouda@azhar.edu.eg
1. INTRODUCTION
The distribution network (DN) aims to provide higher demand rates for consumers. It is a very
critical part of the power grid and is also the key cause of electrical losses in the network because of low
reactance to resistance ratios. As a result of the constant growth in demand loads, the line currents will
increase, which leads to an increase in the line losses and the voltage deviation. The RDS is the most
common due to lower installation cost, easier power flow and voltage control than other types of distribution
systems. Current distribution infrastructure constraints and increased interest in green technology utilization
have culminated in the use of distributed generation (DG). There is other terminology and meanings used to
describe DG, and this produces various viewpoints [1]:
The Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) classifies DG as generation from a few kilowatts up to
50 MW.
International energy agency (IEA) identifies DG as generating plant supplying a customer on-site or
supporting to a distribution network connected to the grid.
The International Conference on large High Voltage Electric Systems (CIGRE) classifies DG as smaller
than 50-100 MW.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/052284210jun28may10apry-201223015727/85/Optimal-planning-of-RDGs-in-electrical-distribution-networks-using-hybrid-SAPSO-algorithm-1-320.jpg)
![ ISSN: 2088-8708
Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163
6154
DG can be defined as small-scale power generation to reduce customer demand near to load center.
Distributed generation may come from several technologies and sources. The principal explanations for DG's
growing use can be outlined as below [2]:
Highly efficient modern technology.
Cost of Transmission and Distribution systems can be reduced because of the DG units are near to
consumers.
Its positions can be located better due to small capacity.
The installation period of the DG plants is shorter, and the investment risk isn't very high.
Simplicity of the energy management by tracking the loads due to its small capacity.
Provides a flexible way to select a wide variety of costing and reliable combinations.
DG technologies are broadly categorized into two types: renewable technologies (PV, WT) and
non-renewable technologies (fuel cells). It is important to determine the optimal location and size of DGs to
achieve the desired performance, grid reinforcement, minimizing power loss and on-peak operating costs,
improve the voltage profile and loading factors, reprieve or canceling the system upgrades, improving
the system security, increasing reliability and efficiency, and improving the power quality of the electrical
grid. Different approaches have been suggested for determining the optimal site and size of DGs in the DN.
Gandomkar et al., provided a new approach based on a combination of genetic algorithm (GA) and
SA algorithms for optimal allocation of DGs in distribution networks to improve the optimization goal [3].
Sutthibun and Bhasaputra applied SA for optimal location of DG on the IEEE 30 bus test system [4].
Kefayat et al., presented a hybrid of ant colony optimization and artificial bee colony optimization for
optimal siting and sizing of DG [5]. Alinezhad et al., proposed three algorithms, PSO, GSA and GA for
optimal location of DG in distribution system [6]. Jordehi proposed various approaches for determination
the best sitting and sizing of DGs in electric power systems [7]. Prakash and Khatod presented a review for
minimizing the system losses, improving the voltage profile, enhancing the system reliability, stability and
loadability by optimal sizing and siting techniques for DG [8]. Vijay et al., applying bat motivated
optimization algorithm (BMOA) for optimal placement and sizing of distributed power sources to reduce
the active power loss in 33-bus test system [9]. Singh and Sharma, illustrated a review on DG planning in
the distribution system performances such as real and reactive power loss, power system loadability, stability,
reliability, security, available power transfer capacity [10]. Banhthasit et al., suggest an optimal generation
scheduling method for integrated of renewable energy-based DGs and energy storage systems with electrical
power system [11]. UshaReddy et al., proposed LSF & DE to determine the optimal size and location of
capacitors for minimizing the power losses and improving the voltage profile in RDN [12]. Lin et al.,
presented a hybrid approach of analytical method (LSF) for sizing DGs and meta-heuristic method (PSO) for
sitting DGs based on optimal reactive power dispatch for decreasing the real power loss [13]. EL-Sayed,
determine the optimal location, size and numbers of DGs to reduce power loss and improve voltage
profile [14]. M. H. Moradi and M. Abedini, presented a hybrid approach of genetic algorithm and particle
swarm optimization for optimal DG location and sizing in distribution system [15]. Jithendranath et al.,
illustrated a combination approach based on PSO and GSA to solve the optimal reactive power dispatch
problem in power system [16]. Verma and Lakhwani, present strong rules discovered in databases using
hybrid algorithm of GA and PSO [17]. In this paper, LSI, SA, PSO, LSISA, LSIPSO and SAPSO
optimization algorithms are used for positioning and sizing of DGs. These algorithms have been tested on
IEEE 33-bus radial distribution system.
2. PROBLEM FORMULATION
The higher losses, higher voltage drop and thermal limitation are very most significant problem in
the distribution system. So, intensive attention to the DGs technology has become a vital issue that must be
taken into consideration for its impact on the distribution system. To solve this problem, it became necessary
to determine the optimal location and size of DGs as it represented the main problem under network
restrictions including load flow in order to increase the overall efficiency of system performance.
2.1. Load Flow
It is an important tool for power system planning, operation, optimization and control to ensure
stability, reliability and economy for the electrical system. Traditional methods for load flow analysis such as
Newton Raphson (NR), Gauss Seidel (GS) may be unsuitable for the distribution network and diverge due to [18]:
Radial or weakly mesh network.
High R/X ratio.
Unbalanced operation.
Distributed generation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/052284210jun28may10apry-201223015727/85/Optimal-planning-of-RDGs-in-electrical-distribution-networks-using-hybrid-SAPSO-algorithm-2-320.jpg)
![Int J Elec & Comp Eng ISSN: 2088-8708
Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks… (Mohammed Hamouda)
6155
Backward/Forward Sweep (BFS) algorithm is preferred for correct planning due to:
The ill-state nature of RDS.
Accurate results of power flow depend on convergence, implementation time and iterations number.
This approach is implemented in two steps: the backward and forward sweep using the load and line
data. In the backward sweep, voltages and currents are calculated using KVL and KCL starting from
the farthest node. In forward sweep, the downstream voltage is calculated starting from the source node.
The steps of BFS algorithm are mentioned below:
Initialize the injected current (𝐼𝑖 = 0)
Initialize all buses voltage (𝑉𝑖= 1pu)
Calculate the node current (𝐼𝑖 =
𝑆𝑖
∗
𝑉𝑖
∗)
Calculate the line current (backward sweep)
𝐼(𝑖,𝑖+1) = 𝐼𝑖+1 + ∑(𝑏𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠′
𝑠 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑎𝑡 𝑛𝑜𝑑𝑒 𝑖 + 1)
Update the buses voltage (𝑉𝑖 = 𝑉𝑖+1 + (𝑍(𝑖,𝑖+1) ∗ 𝐼(𝑖,𝑖+1)))
Until stopping criterion.
2.2. Objective function (OF)
The main objective problem is to reduce the total power losses and boost the system's voltage profile
through determine the optimal capacity and positioning of the DGs using the various proposed methods.
𝑂𝐹 = 𝑚𝑖𝑛(𝑃𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠) = 𝑚𝑖𝑛 ∑ 𝐺 𝑘(𝑉𝑖
2
+ 𝑉𝑗
2
− 2𝑉𝑖 𝑉𝑗 cos(𝛿𝑖 − 𝛿𝑗))𝑁𝐿
𝑘=1 (1)
2.3. System constrains
There are two types of constraints which control the minimization of objective function:
Equality constraints: These constraints formulated the active and reactive power balance by power flow
equations.
𝑃𝐺𝑖 − 𝑃𝐷𝑖 − 𝑃𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠 = 0 (2)
𝑄 𝐺𝑖 − 𝑄 𝐷𝑖 − 𝑄𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠 = 0 (3)
Inequality constraints: These constraints determine the technical operation limits of power system.
Bus voltage
𝑉𝑖
𝑚𝑖𝑛
≤ 𝑉𝑖 ≤ 𝑉𝑖
𝑚𝑎𝑥
(4)
DG capacity
𝑃𝐷𝐺
𝑚𝑖𝑛
≤ 𝑃𝐷𝐺 ≤ 𝑃𝐷𝐺
𝑚𝑎𝑥
, 𝑄 𝐷𝐺
𝑚𝑖𝑛
≤ 𝑄 𝐷𝐺 ≤ 𝑄 𝐷𝐺
𝑚𝑎𝑥
(5)
DG location
2 ≤ 𝐷𝐺 𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 ≤ 𝑁𝑏𝑢𝑠 (6)
3. METHODOLOGIES
DG’s problem is evaluating the optimal size and location to optimize the required objective
function. Major methodological techniques for sizing and sitting of DGs are summarized as below [19]:
Analytical technique.
Conventional technique.
Meta-heuristic optimization technique.
Hybrid technique.
Artificial intelligence technique.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/052284210jun28may10apry-201223015727/85/Optimal-planning-of-RDGs-in-electrical-distribution-networks-using-hybrid-SAPSO-algorithm-3-320.jpg)
![ ISSN: 2088-8708
Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163
6156
4. MATHEMATICLE MODEL OF OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES
4.1. Loss sensitivity factor (LSF)
LSF is helpful to obtain the critical buses in the network. It can estimate which bus will have
the greatest loss reduction when a DG is placed. The search space of the optimization problem is reduced due
to the estimation of these candidate buses [12, 20, 21]. Figure 1 illustrates a distribution line " 𝑘 " with an
impedance 𝑅 𝑘 + 𝑗𝑋 𝑘 and a load of 𝑃𝑖𝑗 + 𝑗𝑄𝑖𝑗 connected between ‘𝑖’ and ‘𝑗’ buses.
Figure 1. A radial distribution feeder
The real power loss (𝐼2
𝑅) at each node in radial distribution network (RDN) can be calculated as:
𝑃𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠(𝑗) =
(𝑃 𝑒𝑓𝑓
2 (𝑗)+𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓
2 (𝑗))
(𝑉(𝑗))
2 ∗ 𝑅(𝑘) (7)
Also, the reactive power loss (𝐼2
𝑋) at each node in RDN can be given as:
𝑄𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠(𝑗) =
(𝑃 𝑒𝑓𝑓
2 (𝑗)+𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓
2 (𝑗))
(𝑉(𝑗))
2 ∗ 𝑋(𝑘) (8)
where:
𝑃𝑒𝑓𝑓(𝑗) = Total real power supplied beyond the bus "𝑗".
𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓(𝑗) = Total reactive power supplied beyond the bus "𝑗".
Now, the LSF can be expressed as:
𝜕𝑃 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠
𝜕𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓
=
2∗𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓(𝑗)∗𝑅(𝑘)
(𝑉(𝑗))
2 (9)
𝜕𝑄 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠
𝜕𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓
=
2∗𝑄 𝑒𝑓𝑓(𝑗)∗𝑋(𝑘)
(𝑉(𝑗))
2 (10)
The steps of LSF to find the selected bus for DG placement can be summarized as below:
LSF has been calculated as given in (9) from the base case load flow. The values of LSF have been
sorted descending and its bus index in bus positions “bpos (i)”, which determine the sequence for mitigation.
Voltage sensitivity factors (VSF) are calculated as given in (11) by considering the minimum voltage
magnitude is 0.95 pu as below:
𝑉𝑆𝐹(𝑖) =
𝑉(𝑖)
0.95
(11)
where 𝑉(𝑖) is the bus voltage. The values of 𝑉𝑆𝐹 which less than 1.01 can be sorted ascending and its bus
index in the candidate buses “bcan(i)”. The selected bus for DG placement can be determined by comparing
the bus positions and the candidate buses and choosing the first common bus.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/052284210jun28may10apry-201223015727/85/Optimal-planning-of-RDGs-in-electrical-distribution-networks-using-hybrid-SAPSO-algorithm-4-320.jpg)
![Int J Elec & Comp Eng ISSN: 2088-8708
Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks… (Mohammed Hamouda)
6157
4.2. Simulated annealing (SA)
SA is a simple form local search algorithm (a descent algorithm), which preferred when problem
size is large. It is a meta-heuristic technique that has been used extensively to solve a complicated
optimization problem. The word annealing refers to the cooling process after heating of the material to
become homogeneous and more harden [14]. The concept of solution based on cool down the possible state
of a thermo dynamic system from the preliminary high temperature. The objective function or cost of
a solution is corresponding to the energy of the physical state. All solutions of the optimization problem are
accepted at high temperature, but at low temperature only the minimal cost solutions are accepted. Although
simplicity and quick execution of SA algorithm, the drawback of this approach is that the local minimum
found may be far from the global minimum [3]. To avoid this defect, it is necessary to increase the number of
iterations combined with an increased number of searches at each iteration. The initial solution of SA is
random then new ones are proposed through local changes and accepted depend on the controlled probability.
The major steps of SA algorithm can be summarized as following:
Select an initial solution 𝑋0𝑖 ∈ 𝑆 (search space).
Select an initial temperature 𝑇 𝑚𝑎𝑥.
Set temperature change counter n = 0.
Set a repetition counter k (number of iterations at each T).
Generate a new solution 𝑋𝑖 ∈ 𝑆.
Calculate ∆= 𝑓(𝑋𝑖 ) − 𝑓(𝑋0𝑖 ).
If ∆< 0, 𝑋0𝑖 = 𝑋𝑖 .
Else if random (0,1) < exp(- ∆/T).
Then, 𝑋0𝑖 = 𝑋𝑖 .
k = k + 1
n = n + 1
Until stopping criterion.
4.3. Particle swarm optimization (PSO)
This algorithm is depending on the perception of nature and swarming seen in birds or fish. PSO is
used when the optimization problems have several solutions. In this algorithm the particles move in a bounded
search space to find the overall best velocity and position depend on social experience of the swarm [22-26].
The value of the agent’s velocity and its position of the swarm is updated as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Particle movement in PSO algorithm
𝑣𝑖𝑗
𝑘+1
= 𝑤𝑣𝑖𝑗
𝑘
+ 𝑐1 𝑟1(𝑝 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡,𝑖
𝑘
− 𝑥𝑖𝑗
𝑘
) + 𝑐2 𝑟2(𝑔 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡
𝑘
− 𝑥𝑖𝑗
𝑘
) (12)
𝑥𝑖𝑗
𝑘+1
= 𝑥𝑖𝑗
𝑘
+ 𝑣𝑖𝑗
𝑘+1
(13)
Where: 𝑖 is the number of particles, 𝑗 is the dimension of problem, 𝑣 & 𝑥 are the velocity of particle
and its position respectively, 𝑝 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡 & 𝑔 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡 are the personal and global best respectively, 𝑤 is weighting or
learning factor, 𝑐1 & 𝑐2 are accelerating factors and 𝑟1 & 𝑟2 are random numbers in the range of (0,1).
The new solution in PSO depends on its initial solution, so it may be can’t succeed to reach the optimal
solution. The steps of PSO algorithm are presented below:
Initialization randomly of velocity and position for N particles (𝑥𝑖𝑗 & 𝑣𝑖𝑗).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/052284210jun28may10apry-201223015727/85/Optimal-planning-of-RDGs-in-electrical-distribution-networks-using-hybrid-SAPSO-algorithm-5-320.jpg)


![ ISSN: 2088-8708
Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163
6160
5. TEST SYSTEM
The IEEE 33 bus distribution system [27] is used for testing the proposed algorithms. A single line
diagram is illustrated in Figure 5, which has the total real power 3720 kw and reactive power 2300 kvar.
The proposed methodologies are carried out by Matlab 2019 software using intel ® Core ™ i7-8550U CPU
@ 1.80GHz 1.99 GHz, 16.0 GB RAM, 64-bit Operating System, x64-based processor.
Figure 5. IEEE-33 bus test system
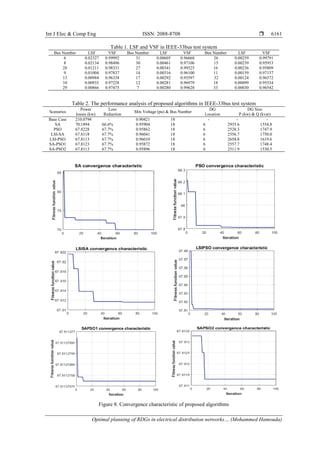
6. RESULTS
In LSF, as shown in Figure 6, bus 6 was chosen for DG placement based on the results in Table 1,
which sets the candidate bus priority. Since it was a junction node of several branches, so voltage profile
improvement was better in this case. Figure 7 shows the voltage profile before and after DG installation.
Bus 18 is the farthest end from the supply node, so its voltage in the base scenario (without DG) is the lowest
and its value is 0.90421 pu (unaccepted). Buses 6 to 18 and buses 26 to 33 have voltage lower than 0.95 pu
without DG unit, while after adding DG a significant improvement of voltage profile within limits
(accepted). Table 2, shows the most proper location and capacity of DG and corresponding the total losses
for each scenario. Also, it is clear the minimum voltage bus and its value. This indicates that the proposed
algorithms predict the optimal position and size for DGs with high efficiency and accuracy. To prove
the effectiveness of the novel algorithm SAPSO, the results achieved by this technique have been compared
with those obtained by the other algorithms. By comparison, it demonstrated the ability of SAPSO2 to reduce
system losses to the lowest possible value 67.8113 kw and increasing the voltage profile to the highest value
0.95896 pu (within accepted limit) simultaneously. In addition, the DG's capacity is the lowest, which means
that the minimum cost is achieved.
The optimization process to reach the optimal solution for the constrained objective function can be
implemented iteratively. Firstly, initialize the solution randomly then the solution updated iterative till it is
reached to global optimal minimum real power loss is obtained, which around 67.8113 kw. Figure 8
illustrates the fitness function convergence for all algorithms. SAPSO algorithm have demonstrated
the superiority through discovery the optimal solution to achieve global minimum fitness. Figure 8 shows
the novelty of the SAPSO algorithm, which converges quickly before the other algorithms to achieve
the optimal fitness function. Where SAPSO1, SAPSO2, LSIPSO, LSISA, PSO and SA reach after 10
iterations, 18 iterations, 33 iterations, 63 iterations, 40 iterations and 60 iterations, respectively.
Figure 6. Loss sensitivity index Figure 7. Voltage profile for IEEE-33 bus test system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/052284210jun28may10apry-201223015727/85/Optimal-planning-of-RDGs-in-electrical-distribution-networks-using-hybrid-SAPSO-algorithm-8-320.jpg)
![ ISSN: 2088-8708
Int J Elec & Comp Eng, Vol. 10, No. 6, December 2020 : 6153 - 6163
6162
7. CONCLUSION
Due to ill-conditioned nature of RDNs, losses minimization and voltage profile enhancement have
been of great concern. The integration of optimal placement and sizing of RDGs in RDS minimized
the system losses and enhanced the voltage profile. The voltage profile improvement can be achieved within
the network constraints, since the DGs is located closely at loads and can be partially supplied a real and
reactive power to the loads. It can be concluded that, the optimal DG placement and sizing gives orientation
for the economic planning and operation of power system in the modern integrated grid. This paper
investigates the typical analytical, heuristic and hybrid integrating scheme to calculate the optimal placement
and capacity of DGs.
In this paper, SA and PSO among heuristic techniques have been performed to solve the DGs
problem. A new powerful evaluation algorithm LSISA and LSIPSO have been presented in this research.
LSI is an efficient integrated method with SA and PSO algorithms for determining the optimal location and
reduced the time simulation to reach the optimal solution through the most voltage sensitivity bus (the least
VSF value) and power losses (the highest LSF value). The sensitivity factors reduced the search space and
the dimension of the optimization problem by estimating the selected bus for DG sitting. LSI accuracy has
been verified by the other proposed algorithms for finding the optimal solution.
A novel approach principle is proposed based on SA and PSO algorithms in one hybrid algorithm
called SAPSO algorithm. The novelty of this algorithm based on two strategies: the first strategy is avoiding
randomly generation and updating the solution in SA by using the same manner in PSO. The second strategy
is avoiding the local minima problem in PSO because its particles may be failed to converge depend on its
initial value, so it is integrated with SA in order to benefit from the probability rate to accept or discard
the solution and escape from the local minimum.
The BFS algorithm is used for power flow calculations. The proposed algorithms have been tested
on IEEE 33 bus system. The results proved the proposed algorithms have the capability to provide
the optimal solution for the problem optimization. Furthermore, the results show the efficiency of these
approaches for the voltage sag mitigation within limits and power loss reduction. Although the distinguished
performance of all techniques in terms of solution and convergence performance, SAPSO algorithm have
proved the superiority through finding the optimal solution rapidly, economically and accurately which
allowing its application in the large-scale distribution systems. Finally, some recommendation to consider in
the future work in this field: (a) the power factor while sizing DGs; (b) the reliability indices as an objective
function combined with the mentioned objective function to have a reliable and secure distribution systems.
REFERENCES
[1] T. Ackermann, G. Andersson, and L. Söder, "Distributed generation: A definition," Electric Power Systems
Research, vol. 57, pp. 195-204, 2001.
[2] G. Celli, F. Pilo, “Optimal distributed generation allocation in MV distribution networks,” 22nd International
Conference IEEE Power Engineering Society, pp. 81-86, 2001.
[3] Gandomkar M, Vakilian M, Ehsan M., "A combination of genetic algorithm and simulated annealing for optimal
DG allocation in distribution networks," Proceeding of IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer
Engineering, 645-648, 2005.
[4] T. Sutthibun and P. Bhasaputra, "Multi-Objective Optimal Distributed Generation Placement Using Simulated
Anneal-ing," International Conference Electrical Engineering/Electronics Computer Tele-communications and
Information Technology (ECTI-CON), 2010.
[5] M. Kefayat, A. Lashkar Ara and S. A. Nabavi Niaki, "A hybrid of ant colony optimization and artificial bee colony
algorithm for probabilistic optimal placement and sizing of distributed energy resources," Energy Conversion and
Management, vol. 92, pp. 149-161, 2015.
[6] Alinezhad, P., Bakhoda, O. Z., and Menhaj, M. B. "Optimal DG placement and capacity allocation using intelligent
algorithms," 4th Iranian Joint Congress on Fuzzy and Intelligent Systems (CFIS), pp. 1-8, 2015.
[7] A. R. Jordehi, "Allocation of distributed generation units in electric power systems: A review," Renewable and
Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 56, pp. 893-905, 2016.
[8] P. Prakash and D. K. Khatod, "Optimal sizing and siting techniques for distributed generation in distribution
systems: A review," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 57, pp. 111-130, 2016.
[9] Vijay R, Jeeva M, Ravichandran C. S, "Optimal Location of Distributed Energy Resources in Microgrid for Power
Loss Minimization Using Bat Inspired Algorithm," SSRG International Journal of Electronics and Communication
Engineering, pp. 101-106, 2016.
[10] B. Singh and J. Sharma, "A review on distributed generation planning," Renewable and Sustainable Energy
Reviews, vol. 76, pp. 529-544, 2017.
[11] B. Banhthasit, C. Jamroen, and S. Dechanupaprittha, "Optimal Generation Scheduling of Power System for
Maximum Renewable Energy Harvesting and Power Losses Minimization," International Journal of Electrical and
Computer Engineering (IJECE), vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 1954-1966, 2018.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/052284210jun28may10apry-201223015727/85/Optimal-planning-of-RDGs-in-electrical-distribution-networks-using-hybrid-SAPSO-algorithm-10-320.jpg)
![Int J Elec & Comp Eng ISSN: 2088-8708
Optimal planning of RDGs in electrical distribution networks… (Mohammed Hamouda)
6163
[12] V. Usha Reddy, Dr.T.Gowri Manohar, P. Dinakara Prasad Reddy, “Capacitor Placement for loss reduction in radial
distribution networks:A two stage approach,” Journal of electrical engineering, vol. 12, 2012.
[13] K. M. Lin, P. L. Swe, and K. Z. Oo, "Optimal Distributed Generator Sizing and Placement by Analytical Method
and PSO Algorithm Considering Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch," World Academy of Science, Engineering and
Technology International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering, vol. 13, no. 1, 2019.
[14] S. K. EL-Sayed, "Optimal Location and Sizing of Distributed Generation for Minimizing Power Loss Using Simulated
Annealing Algorithm," Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 104-110, 2017.
[15] M. H. Moradi and M. Abedini, "A Combination of Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization for
Optimal DG location and Sizing in Distribution System," Electrical Power and Energy System, vol. 34, pp. 66-74, 2012.
[16] J. V. U. Jithendranath, A. S. V. U. Babu, and G. D. V. U. Sukumar, "Hybrid PSOGSA Method of Solving ORPD
Problem with Voltage Stability Constraint," Indones. J. Electr. Eng., vol. 12, no. 8, pp. 5807-5813 2014.
[17] M. Verma and R. Lakhwani, "Association Rule Generation by Hybrid Algorithm based on Particle Swarm
Optimization and Genetic Algorithm," International Journal of Science, Engineering and Computer Technology,
vol. 5, no. 12, pp. 423-426, 2015.
[18] M. T. Hagh, T. Ahamadzadeh, K. M. Muttaqi, and D. Sutanto, "Load flow analysis of radial and weakly meshed
distribution systems including distributed generations,” Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference, 2014.
[19] K. Sampangi Sambaiah, "A Review on Optimal Allocation and Sizing Techniques for DG in Distribution Systems,"
International Journal Of Renewable Energy Research, vol. 8, no. 3, 2018.
[20] Chin Chia Seet, Jagadeesh Pasupuleti, M. Reyasudin Basir Khan, "Optimal Placement and Sizing of Distributed
Generation in Distribution System using Analytical Method," International Journal of Recent Technology and
Engineering (IJRTE), vol. 8, no. 4, 2019.
[21] K. Cabana, J. Candelo, R. Castillo and E. De-la-Hoz-Franco, "Voltage sensitivity analysis to determine the optimal
integration of distributed generation in distribution systems," International Journal of Electrical and Computer
Engineering, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 55-65 2019.
[22] A. N. Hussain, and A. A. Ismail, "Operation cost reduction in unit commitment problem using improved quantum binary
PSO algorithm," International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 1149-1155, 2020.
[23] A. B. Kunya, et al., "Distribution Network Reconfiguration for Loss Reduction and Voltage Profile Improvement
using B-PSO ", ICAT’16 International Conference on Advanced Technology and Sciences, vol. 3, 2016.
[24] Sahib, T. J., Ghani, M. R. A., Jano, Z., “Optimum allocation of distributed generation using PSO: IEEE test case
studies evaluation," Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res, vol. 12, no. 11, pp. 2900-2906, 2017.
[25] Y. Merzoug, et al., “Optimal placement of wind turbine in a radial distribution network using PSO method,”
International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive System, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 1074-1081, 2020.
[26] Y. Merzoug, B. Abdelkrim and B. Larbi, "Distribution network reconfiguration for loss reduction using PSO
method,” International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 5009-5015, 2020.
[27] Zhang, S., Cheng, H., Li, K., Tai, N., Wang, D., and Li, F. "Multi-objective distributed generation planning in
distribution network considering correlations among uncertainties,” Applied Energy, vol. 226, pp. 743-755, 2018.
BIOGRAPHIES OF AUTHORS
Mohammed Hamouda Ali received the B.Sc. (2011) & M.Sc. (2016) degrees in Electrical
Engineering from Al-Azhar University. Currently he is Teaching Assistant in the Department of
Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Egypt. His research interests
are in power electronics, power system planning, optimization, operation, power system control,
power quality, reliability and renewable energy technology.
Mohammed Mehanna received the B.Sc. (1995) & M.Sc. (2002) degrees in Electrical Engineering
from Al-Azhar University. He received his PhD in Al-Azhar University, Egypt (2007). Currently he
is a professor, Agent of Faculty of Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Egypt. His research interests
are in power system planning, operation, power system control, optimization theory, power quality
and renewable energy.
Elsaied Othman received the B.Sc. (1972) & M.Sc. (1980) degrees in Electrical Engineering from
Al-Azhar University. He received his PhD in Al-Azhar University, Egypt (1983). Currently he is
a professor, Head of Physics & Mathematics Department, Faculty of Engineering, Al-Azhar
University, Egypt. His research interests are in power system operation, power system control,
optimization theory, power quality, reliability, power system security and renewable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/052284210jun28may10apry-201223015727/85/Optimal-planning-of-RDGs-in-electrical-distribution-networks-using-hybrid-SAPSO-algorithm-11-320.jpg)
















![[IJET-V1I4P9] Author :Su Hlaing Win](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ijet-v1i4p9-150824171458-lva1-app6891-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)




















































![[HIFLUX] Lok Fitting&Valve Catalog 2025 (Eng)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lokfittingen-250528072439-8696f1c6-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

















