osi.ppt
- 1. OSI Model MIS 416 – Module II Spring 2002 Networking and Computer Security
- 2. • The OSI reference model • Services in the OSI model Topics
- 3. • OSI Reference Model - internationally standardised network architecture. • OSI = Open Systems Interconnection: deals with open systems, i.e. systems open for communications with other systems. • Specified in ISO 7498. • Model has 7 layers. OSI Reference Model
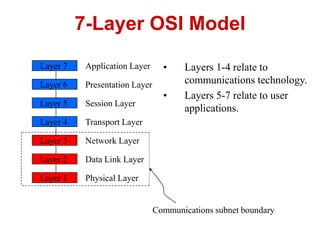
- 4. • Layers 1-4 relate to communications technology. • Layers 5-7 relate to user applications. 7-Layer OSI Model Layer 7 Layer 6 Layer 5 Layer 4 Layer 3 Layer 2 Layer 1 Application Layer Presentation Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Network Layer Data Link Layer Physical Layer Communications subnet boundary
- 5. • Level at which applications access network services. – Represents services that directly support software applications for file transfers, database access, and electronic mail etc. Layer 7: Application Layer
- 6. • Related to representation of transmitted data – Translates different data representations from the Application layer into uniform standard format • Providing services for secure efficient data transmission – e.g. data encryption, and data compression. Layer 6: Presentation Layer
- 7. • Allows two applications on different computers to establish, use, and end a session. – e.g. file transfer, remote login • Establishes dialog control – Regulates which side transmits, plus when and how long it transmits. • Performs token management and synchronization. Layer 5: Session Layer
- 8. • Manages transmission packets – Repackages long messages when necessary into small packets for transmission – Reassembles packets in correct order to get the original message. • Handles error recognition and recovery. – Transport layer at receiving acknowledges packet delivery. – Resends missing packets Layer 4: Transport Layer
- 9. • Manages addressing/routing of data within the subnet – Addresses messages and translates logical addresses and names into physical addresses. – Determines the route from the source to the destination computer – Manages traffic problems, such as switching, routing, and controlling the congestion of data packets. • Routing can be: – Based on static tables – determined at start of each session – Individually determined for each packet, reflecting the current network load. Layer 3: Network Layer
- 10. Packages raw bits from the Physical layer into frames (logical, structured packets for data). Provides reliable transmission of frames It waits for an acknowledgment from the receiving computer. Retransmits frames for which acknowledgement not received Layer 2: Data Link Layer
- 11. • Transmits bits from one computer to another • Regulates the transmission of a stream of bits over a physical medium. • Defines how the cable is attached to the network adapter and what transmission technique is used to send data over the cable. Deals with issues like – The definition of 0 and 1, e.g. how many volts represents a 1, and how long a bit lasts? – Whether the channel is simplex or duplex? – How many pins a connector has, and what the function of each pin is? Layer 1: Physical Layer
- 12. • Explicit Presentation and session layers missing in Internet Protocols • Data Link and Network Layers redesigned Internet Protocols vs OSI Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Application TCP IP Network Interface Hardware
- 13. • In OSI model, each layer provide services to layer above, and ‘consumes’ services provided by layer below. • Active elements in a layer called entities. • Entities in same layer in different machines called peer entities. Services in the OSI Model
- 14. • Layer N provides service to layer N+1 Layering Principles (N+1) Entity Service User (N) Entity Service Provider (N+1) Entity Service User (N) Entity Service Provider Layer N Service Access Point (SAP) Layer N protocol N+1 PDU Layer N+1 protocol SDU PDU - Protocol Data Unit SDU - Service Data Unit N PDU N PDU
- 15. • Layers can offer connection-oriented or connectionless services. • Connection-oriented like telephone system. • Connectionless like postal system. • Each service has an associated Quality-of- service (e.g. reliable or unreliable). Connections
- 16. • Reliable services never lose/corrupt data. • Reliable service costs more. • Typical application for reliable service is file transfer. • Typical application not needing reliable service is voice traffic. • Not all applications need connections. Reliability
- 17. • Service = set of primitives provided by one layer to layer above. • Service defines what layer can do (but not how it does it). • Protocol = set of rules governing data communication between peer entities, i.e. format and meaning of frames/packets. • Service/protocol decoupling very important. Topics