Overview of the Health Benefits of Vitamin C by Prof Margreet Vissers
- 1. The Health Benefits of Vitamin C Prof. Margreet Vissers University of Otago, New Zealand
- 2. The Health Benefits of vitamin C Margreet Vissers Centre for Free Radical Research University of Otago, Christchurch New Zealand
- 3. The University of Otago, Dunedin, Christchurch and Wellington University of Otago, Dunedin, NZ
- 4. The Centre for Free Radical Research, Christchurch
- 5. The Good News – we are living far longer than ever
- 6. Increased lifespan comes at a price Exposure to chronic disease and loss of function How to ensure maximum healthspan? Cardiovascular disease Cancer Diabetes Cognitive decline Frailty
- 7. Increasing healthspan with diet and lifestyle choices Willett WC, Science 296, 695-698 (2002) Genetics Life- style Diet A large percentage of chronic disease is potentially reduced by diet and lifestyle changes.
- 8. J Epidemiology and Community Health, March 31, 2014 as 10.1136/jech-2013-203500 METHOD: 65,226 participants aged 35+ years in the 2001–2008 Health Surveys for England.
- 9. Multivariate-adjusted odds ratios for features of the metabolic syndrome across quintiles of fruit intake. Am J Clin Nutr 2006;84:1489–97.
- 10. The importance of study design and method for epidemiological evidence of dietary - health benefits Study design • Number and grouping of participants • Intervention or correlation? • Frequency of measures • Duration of follow-up • Participation rate • Blinding ? Method • Use of validated assessment tools • Use of validated outcome measures • Adjustments for age, race, gender?
- 11. Quirk et al. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13:175 Method: A computer-aided literature search was conducted using Medline, CINAHL, and PsycINFO, January 1965 to October 2011, and a best-evidence analysis performed. Results: Twenty-five studies from nine countries met eligibility criteria. Our best-evidence analyses found limited evidence to support an association between traditional diets (Mediterranean or Norwegian diets) and depression. We also observed a conflicting level of evidence for associations between (i) a traditional Japanese diet and depression, (ii) a “healthy” diet and depression, (iii) a Western diet and depression, and (iv) individuals with depression and the likelihood of eating a less healthy diet. Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first review to synthesize and critically analyze evidence regarding diet quality, dietary patterns and depression. Further studies are urgently required to elucidate whether a true causal association exists.
- 12. Conclusion from fruit and vegetable intake studies? (To date) Higher fruit and vegetable intake is associated with decreased risk of chronic diseases, with decreased all-cause mortality, increased lifespan and with improved health status (both mental and physical health).
- 13. Dietary Recommendations vs Reality in the Western World
- 14. Micronutrients: 13 Vitamins and 14 Minerals Essential Nutrients – Essential for Health Micronutrients have many functions in the body • Support hundreds of enzymes • Cell and tissue function • Energy production, growth and development • Heart health • Immune function • Bone health • etc Vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12, C, D, E, K Macro minerals Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium Trace minerals Chromium, Copper, Fluoride, Iodine, Manganese, Molybdenum, Selenium, Zinc
- 15. From: Mortality in Randomized Trials of Antioxidant Supplements for Primary and Secondary Prevention: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis JAMA. 2007;297(8):842-857. doi:10.1001/jama.297.8.842 What can we conclude?
- 16. From: Mortality in Randomized Trials of Antioxidant Supplements for Primary and Secondary Prevention: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis JAMA. 2007;297(8):842-857. doi:10.1001/jama.297.8.842 Included all primary and secondary prevention trials in adults randomized to receive beta carotene, vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, or selenium vs placebo or no intervention. Trials including general or healthy populations, or participants with specific diseases. Dosing regimes: All antioxidant supplements were administered orally. The dose and regimen of the antioxidant supplements were: beta carotene 1.2 to 50.0 mg , vitamin A 1333 to 200 000 IU, vitamin C 60 to 2000 mg, vitamin E 10 to 5000 IU, and selenium 20 to 200 μg daily or on alternate days for 28 days to 12 years (mean 2.7 years). In one trial antioxidants were applied in a single dose and participants were followed up for 3 months thereafter. The mean duration of follow-up in all trials was 3.3 years (range, 28 days-14.1 years).
- 17. Conclusion from dietary antioxidant supplement studies? (To date) Supplementation of the healthy population has beneficial effect on overall health status, on all-cause mortality, on susceptibility to chronic diseases. Some vitamin supplementation (Vit E, Vit A) may be harmful.
- 18. Vitamin C in plasma is inversely related to blood pressure and change in blood pressure during the previous year in young Black and White women Block et al, 2008. Nutrition Journal 7:35 Relation of Serum Ascorbic Acid to Mortality Among US Adults Simon et al, Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 2001. 3, 255–263 Plasma vitamin C levels and health outcomes Plasma and dietary vitamin C levels and risk of gastric cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC-EURGAST). Jenab et al, 2006. Carcinogenesis 27, 2250–2257 No association observed for dietary vitamin C, whereas an inverse GC risk was observed in the highest versus lowest quartile of plasma vitamin C [OR = 0.55].
- 19. In the early stages, the patients do not look very sick… But in a few days develop universal lassitiude, stiffness, and feebleness of knees, difficulty breathing… Haemorrhages… the gums bleed readily then become putrid and rotten… ulcers appear, coated with blood and gore… Patients have abdominal pain, breathe with pain and labor and may die suddenly. James Lind, 1753 Vitamin C – an essential nutrient Discovery attributed to Albert Szent-Gyorgi in 1932, after a long search for the cause of scurvy
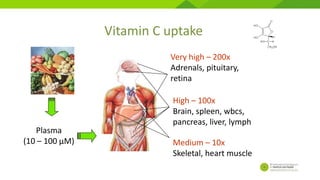
- 20. Vitamin C uptake Plasma (10 – 100 µM) High – 100x Brain, spleen, wbcs, pancreas, liver, lymph Medium – 10x Skeletal, heart muscle Very high – 200x Adrenals, pituitary, retina
- 21. Variable tissue accumulation of ascorbate - reflects functional requirement? Harrison and May (2009) Free Radic Biol Med, 46(6):719-730.
- 22. How do variable plasma vitamin C levels affect with tissue levels? Transport experiments using HT29 multicellular layers (MCL). Modelling vitamin C transport into tissue Kuiper et al 2014, Free Radical Biol Med 77:340–352
- 23. Modelling physiological plasma and tissue vitamin C levels O2 Heat map modelling Kuiper et al 2014, Free Radical Biol Med 77:340–352
- 24. How much vitamin C do we need? The RDA… EAR = estimated average requirement; RDA = recommended daily allowance; UL = upper limit
- 25. How much vitamin C do we need? The RDA… Prevention of scurvy Another health benefit Vitamin C: working on the x-axis. Levine and Eck. Am J Clin Nutr 90:1121–3 (2009)
- 26. How much vitamin C do we need? Levine et al, PNAS 93:3704-3709 (1996) Optimal levels
- 27. Vitamin C and health: What is the vitamin C status for people today? 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Frequency Plasma vitamin C (µM) Vitamin C status of 400+ normal healthy NZ adults (50 year olds), 2010
- 28. Level of Micronutrient intake insufficiency in Western Diets (data from the USA, 2011)
- 29. • A strong reducing agent, oxidised in one-electron steps. • Forms complexes with many metal ions, including Fe and Cu. • Synthesised in plants and animals - but some mammals lack the necessary enzyme, L-gulono--lactone oxidase. • Acts as a co-factor for Fe- or Cu-containing enzymes. Vitamin C: What do we know? Ascorbic acid
- 30. Primary intracellular oxidation, reduction, and degradation pathways for vitamin C Bohndiek et al 2011. J Am Chem Soc 133, 11795–11801
- 31. Antioxidant activity of vitamin C • Antioxidant activity is readily demonstrated in vitro. • Vitamin C is an excellent radical scavenger, forming the benign ascorbyl radical. • Oxidation of biological molecules (lipids, proteins, DNA) can be prevented in vitro by adding vitamin C.
- 32. Proposed antioxidant activity of vitamin C in vivo Example. Roles of ascorbic acid during synaptic activity and astrocyte-mediated recycling. Covarrubias-Pinto et al, 2015 Int J Mol Sci ;16:28194-217
- 34. British Journal of Surgery 86: 1296-1301 (1999)
- 35. Hypovitaminosis C is common in hospitalised patients Fain et al, Eur J Internal Medicine 14:419-425 (2003)
- 36. What can we conclude from in vivo evidence of vitamin C turnover? • Ascorbate turnover is accelerated in illness. • The rate of turnover is associated with disease severity and inflammatory illness. • Supplementation is associated with improved outcome for sick patients (e.g. the common cold and pneumonia). However: does oxidative damage imply antioxidant activity?
- 37. Fe and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases An extended family of enzymes found in plants and animals, with a multitude of functions. • Commonly known: Plant cell wall synthesis Collagen modification • Less commonly known: Morphine synthesis Antibiotic catabolism e.g. Penicillin C Schofield
- 38. The co-factor activity of vitamin C: 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases
- 39. The co-factor activity of Vitamin C – what’s new? Hormone synthesis Protein 3o structure HIF hydroxylases DNA & Histone demethylases EGF Asp/Asn hydroxylases Metabolic control Epigenetics Signalling Collagen hydroxylase
- 40. The co-factor activity of Vitamin C – what’s new? Tissue formation and Wound healing Mood and energyCancer, immune system, appetite Gene Function (everything) Stress responses
- 41. Vitamin C co-factor activity Mood and energy example: Vitamin C is a cofactor in the biosynthesis of carnitine. Strijbis et al 2010, IUBMB Life 62(5): 357–362
- 42. Carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are used for energy generation. Carnitine function
- 43. Week 4 Week 8 Week 4 Week 8Week 4 Week 8 Individual subject data for plasma vitamin C concentration (A) and for fat energy (B) and protein energy (C) expended during submaximal exercise in vitamin C depleted (placebo capsule daily; n = 3) and vitamin C repleted (500 mg vitamin C capsule daily; n = 5) subjects at week 4 (pre-intervention) and week 8 (post-intervention). Nutrition & Metabolism 2006, 3:35
- 44. Cell response to lack of oxygen - hypoxia Vitamin C is a cofactor for the enzymes that regulate Hypoxia-inducible factor - HIF OH OH VHL OH OH Stress responses EPO VEGF Apoptosis Hydroxylases
- 45. HIF-1 ANGIOGENESIS • Flt-1 (VEGF receptor) • Vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) • Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 • Intestinal trefoil factor • Leptin RED CELL MATURATION • Erythropoeitin • Transferrin • Ceruloplasmin • Tyrosine hydroxylase CELL GROWTH AND FATE • Insulin-like growth factor-2 • IGF-binding protein 1,2&3 • Bcl-2/EIP interacting protein 3(BNIP3) • p21 • NIP-3 GLYCOLYSIS • Adenylate kinase-3 • Aldolase A&C • Enolase 1 • Hexokinase 1 • GAPDH •Carbonic anhydrase-9 • Phosphofructokinase L&C • Pyruvate kinase • 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase • Fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase-3 • Lactate dehydrogenase MISCELLANEOUS • Cyclo-oxygenase-2 • Presinilin 1&2 • Collagen prolyl hydroxylase •VL60 • p35srj • ETS-1 • DEC 1&2 VASOMOTOR CONTROL • Endothelin-1 • Nitric oxide synthase • a-adrenergic receptor • Adrenomedullin • Heme oxygenase-1 GLUCOSE TRANSPORT • Glucose transporters 1&3
- 46. Ide et al Am J Roentgenol. 1939;42:891-899 Hypoxia and HIF-1 in biology Cancer Inflammation Hypoxia in intestinal colitis Karhausen J. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 1098–1106 (2004).
- 47. Inflammation and the Neutrophil In the circulation Movement into tissues Bacterial killing Neutrophils have high vitamin C levels, suggesting an essential function.
- 48. Vitamin C and removal of neutrophils. Regeneration of normal lung tissue homeostasis after inflammation.
- 49. Removal of dying neutrophils Mature neutrophil Neutrophil removal The same phenotype is seen in either hypoxia or with low vitamin C levels and is centered on activation of HIF-1.
- 50. Epigenetics – our growing understanding of genes and inheritance Is there a role for vitamin C?
- 51. Epigenetics and the co-factor activity of vitamin C Fe and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases • Histone demethylation Jumonji histone demethylases (JHDMs). Up to 12 known enzymes • DNA demethylation Ten-eleven translocases (Tet) – 3 known
- 52. The Tet enzymes, vitamin C and epigenetics Blaschke et al, Nature, vol 500, August 2013
- 53. Diet and the Fe-2-OGD dioxygenases Ascorbate Oxygen Fe Metabolic Intermediates
- 54. Summary • Plasma vitamin C levels are positively correlated with health and survival benefits. • Body stores and tissue saturation are dependent on adequate/optimal plasma supply. • Vitamin C is depleted by oxidative stress conditions – e.g. illness. • Intracellular vitamin C influences the activity of many Fe and Cu- containing enzymes. • Many physiological benefits of vitamin C intake reflect the co-factor activity.
- 55. CFRR Caroline Kuiper, Stef Bozonet, Anitra Carr, Juliet Pullar, Usha Pujary, Mary Morrison, Prachee Gokhalé, Amy Scott-Thomas, Rachel Wilkie, Lewis Braithwaite, Mark Hampton. McKenzie Cancer Research Group Lizzie Campbell, Gabi Dachs, Sarah Gunningham, Margaret Currie OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY Peter Sykes, John Evans UOC Arron Dyer, Ruth Owers, Katie Saunders John Pearson FUNDING: Health Research Council of NZ, Canterbury Medical Research Foundation, Zespri International, University of Otago, Tertiary Education Commission, MBIE. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS


















![Vitamin C in plasma is inversely related to blood pressure and change in blood
pressure during the previous year in young Black and White women
Block et al, 2008. Nutrition Journal 7:35
Relation of Serum Ascorbic Acid to Mortality Among US Adults
Simon et al, Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 2001. 3, 255–263
Plasma vitamin C levels and health outcomes
Plasma and dietary vitamin C levels and risk of gastric cancer in the European
Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC-EURGAST).
Jenab et al, 2006. Carcinogenesis 27, 2250–2257
No association observed for dietary vitamin C, whereas an inverse GC risk was observed in the
highest versus lowest quartile of plasma vitamin C [OR = 0.55].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160428104920/85/Overview-of-the-Health-Benefits-of-Vitamin-C-by-Prof-Margreet-Vissers-18-320.jpg)