Parallel architecture &programming
Download as PPTX, PDF3 likes1,502 views
This document discusses parallel architecture and parallel programming. It begins with an introduction to von Neumann architecture and serial computation. Then it defines parallel architecture, outlines its benefits, and describes classifications of parallel processors including multiprocessor architectures. It also discusses parallel programming models, how to design parallel programs, and examples of parallel algorithms. Specific topics covered include shared memory and distributed memory architectures, message passing and data parallel programming models, domain and functional decomposition techniques, and a case study on developing parallel web applications using Java threads and mobile agents.
1 of 33
Downloaded 72 times



























Ad
Recommended
Distributed & parallel system



Distributed & parallel systemManish Singh The document defines distributed and parallel systems. A distributed system consists of independent computers that communicate over a network to collaborate on tasks. It has features like no common clock and increased reliability. Examples include telephone networks and the internet. Advantages are information sharing and scalability, while disadvantages include difficulty developing software and security issues. A parallel system uses multiple processors with shared memory to solve problems. Examples are supercomputers and server clusters. Advantages are concurrency and saving time, while the main disadvantage is lack of scalability between memory and CPUs.
Distributed system



Distributed systemSyed Zaid Irshad DSM system
Shared memory
On chip memory
Bus based multiprocessor
Working through cache
Write through cache
Write once protocol
Ring based multiprocessor
Protocol used
Similarities and differences b\w ring based and bus based
File allocation methods (1)



File allocation methods (1)Dr. Jasmine Beulah Gnanadurai The document discusses various file allocation methods and disk scheduling algorithms. There are three main file allocation methods - contiguous allocation, linked allocation, and indexed allocation. Contiguous allocation suffers from fragmentation but allows fast sequential access. Linked allocation does not have external fragmentation but is slower. Indexed allocation supports direct access but has higher overhead. For disk scheduling, algorithms like FCFS, SSTF, SCAN, CSCAN, and LOOK are described. SSTF provides lowest seek time while SCAN and CSCAN have higher throughput but longer wait times.
Parallel and Distributed Computing chapter 1



Parallel and Distributed Computing chapter 1AbdullahMunir32 Parallel and distributed computing systems use multiple computers simultaneously to solve large computational problems faster than a single computer. Parallel computing involves breaking a problem into parts that can be solved concurrently on different processors, while distributed computing uses multiple independent computers that coordinate via message passing to appear as a single system. These approaches improve scalability, allow problems too large for one computer to be solved, and provide high throughput to handle many users concurrently.
Introduction to Parallel and Distributed Computing



Introduction to Parallel and Distributed ComputingSayed Chhattan Shah Introduction
Parallel Computer Memory Architectures
Parallel Programming Models
Design Parallel Programs
Distributed Systems
Parallel computing persentation



Parallel computing persentationVIKAS SINGH BHADOURIA Parallel computing is computing architecture paradigm ., in which processing required to solve a problem is done in more than one processor parallel way.
1.prallelism



1.prallelismMahesh Kumar Attri The document discusses parallelism and techniques to improve computer performance through parallel execution. It describes instruction level parallelism (ILP) where multiple instructions can be executed simultaneously through techniques like pipelining and superscalar processing. It also discusses processor level parallelism using multiple processors or processor cores to concurrently execute different tasks or threads.
Parallel programming model, language and compiler in ACA.



Parallel programming model, language and compiler in ACA.MITS Gwalior This document discusses parallel programming models and their key aspects. It describes five common parallel programming models: shared-variable, message-passing, data parallel, object-oriented, and functional/logic. The main types of inter-process communication are shared variables and message passing. Synchronous and asynchronous message passing are introduced. The document also covers language features that enable parallel programming such as optimization, availability, synchronization/communication, control of parallelism, data parallelism, and process management.
Lecture 4 principles of parallel algorithm design updated



Lecture 4 principles of parallel algorithm design updatedVajira Thambawita The main principles of parallel algorithm design are discussed here. For more information: visit, https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials
distributed shared memory



distributed shared memoryAshish Kumar Distributed shared memory (DSM) provides processes with a shared address space across distributed memory systems. DSM exists only virtually through primitives like read and write operations. It gives the illusion of physically shared memory while allowing loosely coupled distributed systems to share memory. DSM refers to applying this shared memory paradigm using distributed memory systems connected by a communication network. Each node has CPUs, memory, and blocks of shared memory can be cached locally but migrated on demand between nodes to maintain consistency.
Operating system paging and segmentation



Operating system paging and segmentationhamza haseeb This document discusses paging and segmentation in operating systems. Paging divides memory into fixed-size pages for faster data access and allows physical addresses to be non-contiguous. It has advantages like no external fragmentation but disadvantages like internal fragmentation and consuming memory for page tables. Segmentation divides memory into segments of varying lengths and permissions for memory protection. It has advantages like no internal fragmentation and less memory used for segment tables, while lending itself to data sharing and protection but has the disadvantage of a more costly memory management algorithm.
Parallel computing



Parallel computingvirend111 Parallel computing is the simultaneous use of multiple compute resources to solve a computational problem faster. It allows for larger problems to be solved and provides cost savings over serial computing. There are different models of parallelism including data parallelism and task parallelism. Flynn's taxonomy categorizes computer architectures as SISD, SIMD, MISD and MIMD based on how instructions and data are handled. Shared memory and distributed memory are two common architectures that differ in scalability and communication handling. Programming models include shared memory, message passing and data parallel approaches. Design considerations for parallel programs include partitioning work, communication between processes, and synchronization.
Parallel computing and its applications



Parallel computing and its applicationsBurhan Ahmed Parallel computing is a type of computing architecture in which several processors execute or process an application or computation simultaneously. Parallel computing helps in performing large computations by dividing the workload between more than one processor, all of which work through the computation at the same time. Most supercomputers employ parallel computing principles to operate. Parallel computing is also known as parallel processing.
↓↓↓↓ Read More:
Watch my videos on snack here: --> --> http://sck.io/x-B1f0Iy
@ Kindly Follow my Instagram Page to discuss about your mental health problems-
-----> https://instagram.com/mentality_streak?utm_medium=copy_link
@ Appreciate my work:
-----> behance.net/burhanahmed1
Thank-you !
Distributed Operating System_1



Distributed Operating System_1Dr Sandeep Kumar Poonia INTRODUCTIONTO OPERATING SYSTEM
What is an Operating System?
Mainframe Systems
Desktop Systems
Multiprocessor Systems
Distributed Systems
Clustered System
Real -Time Systems
Handheld Systems
Computing Environments
Centralized shared memory architectures



Centralized shared memory architecturesGokuldhev mony This document discusses centralized shared-memory architectures and cache coherence protocols. It begins by explaining how multiple processors can share memory through a shared bus and cached data. It then discusses the cache coherence problem that arises when caches contain replicated data. Write invalidate is introduced as the most common coherence protocol, where a write invalidates other caches' copies of the block. The implementation of write invalidate protocols with snooping and directory approaches is covered, focusing on supporting write-back caches through tracking shared state and bus snooping.
Cache coherence



Cache coherenceEmployee The document discusses cache coherence in multiprocessor systems. It describes the cache coherence problem that can arise when multiple processors have caches and can access shared memory. It then summarizes two primary hardware solutions: directory protocols which maintain information about which caches hold which memory lines; and snoopy cache protocols where cache controllers monitor bus traffic to maintain coherence without a directory. Finally it mentions a software-based solution relying on compiler analysis and operating system support.
advanced computer architesture-conditions of parallelism



advanced computer architesture-conditions of parallelismPankaj Kumar Jain This PPT contains Data and Resource Dependencies,Control Dependence,Resource Dependence,Bernstein’s Conditions ,Hardware And Software Parallelism,Types of Software Parallelism
Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computing



Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computingVajira Thambawita This gives you an introduction to parallel and distributed computing. More details: https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials
Lecture 11 - distributed database



Lecture 11 - distributed databaseHoneySah This document discusses concepts related to distributed database management systems (DDBMS). It defines a distributed database as a logically interrelated collection of shared data distributed over a computer network. A DDBMS manages the distributed database and makes the distribution transparent to users. The document covers distributed database design topics like fragmentation, allocation, and replication of data across multiple sites. It also discusses various types of transparency that a DDBMS provides, such as distribution, transaction, and performance transparency.
Multiprocessor



MultiprocessorKamal Acharya This document discusses multiprocessor systems, including their interconnection structures, interprocessor arbitration, communication and synchronization, and cache coherence. Multiprocessor systems connect two or more CPUs with shared memory and I/O to improve reliability and enable parallel processing. They use various interconnection structures like buses, switches, and hypercubes. Arbitration logic manages shared resources and bus access. Synchronization ensures orderly access to shared data through techniques like semaphores. Cache coherence protocols ensure data consistency across processor caches and main memory.
Multiprocessor system 



Multiprocessor system Mr. Vikram Singh Slathia Multiprocessor system is an interconnection of two or more CPUs with memory and input-output equipment
The components that forms multiprocessor are CPUs IOPs connected to input –output devices , and memory unit that may be partitioned into a number of separate modules.
Multiprocessor are classified as multiple instruction stream, multiple data stream (MIMD) system.
Parallel sorting Algorithms



Parallel sorting AlgorithmsGARIMA SHAKYA These slides are about parallel sorting algorithms. In which four types of sorting algorithms are discussed with the comparison between their sequential and parallel ways. The four algorithms which are included are: Bubble sort, merge sort, Bitonic sort and Shear sort.
Distributed shared memory ch 5



Distributed shared memory ch 5Alagappa Government Arts College, Karaikudi The document discusses distributed shared memory (DSM) which provides a shared memory abstraction for loosely coupled distributed systems. DSM allows processes on different nodes in a distributed system to access shared memory as if it were a single logical memory. It implements this shared memory space through caching blocks of data in local memories and migrating blocks between nodes when needed to service memory requests. Key aspects of DSM systems covered include memory coherence protocols to ensure data consistency and techniques for managing caching and data migration between distributed nodes.
parallel programming models



parallel programming modelsSwetha S Parallel programming model is a set of program abstraction for filtering parallel activities from the application to the underlying parallel hardware.
Disk structure



Disk structuresangrampatil81 The document discusses secondary storage and magnetic disk structure. It provides details on:
- Secondary storage devices like disks, tapes, and drives have non-volatile memory and are slower but cheaper than primary storage like RAM.
- Magnetic disks are divided into platters, tracks, cylinders, and sectors. Read/write heads access data locations specified by head, sector, cylinder addresses.
- Various disk scheduling algorithms like FCFS, SSTF, SCAN, C-SCAN, and LOOK are described which improve disk bandwidth and access time by processing requests in different orders.
Cache memory 



Cache memory Zalal Udeen Cache memory is a type of fast RAM that a computer processor can access more quickly than regular RAM. It stores recently accessed data from main memory to allow for faster future access if the same data is needed again. Cache memory is organized into levels based on proximity and speed of access to the processor, with L1 cache being fastest as it is located directly on the CPU chip, and L2 cache and main memory being progressively slower as they are located further away. Modern processors integrate both L1 and L2 cache onto the CPU package to improve performance by reducing access time.
Query trees



Query treesShefa Idrees Hey friends, here is my "query tree" assignment. :-) I have searched a lot to get this master piece :p and I can guarantee you that this one gonna help you In Sha ALLAH more than any else document on the subject. Have a good day :-)
virtual memory management in multi processor mach os



virtual memory management in multi processor mach osAJAY KHARAT Virtual memory management in multi-processor Mach OS allows processes to access more memory than is physically installed by using virtual addresses. The Mach kernel provides basic services like tasks, threads, messages, and ports to enable parallel and distributed applications. Tasks have their own virtual address spaces that are divided into pages which are allocated to physical frames. The virtual memory system provides protection at the page level by using protection codes in page table entries to control read, write, and execute permissions.
Parallel Computing Application



Parallel Computing Applicationhanis salwan This research article proposes accelerating a geodesic ray-tracing algorithm for fiber tracking in brain imaging using parallel programming on a GPU. Fiber tracking uses diffusion MRI to noninvasively examine brain fiber structures at a microscopic level. While geodesic ray-tracing is robust, it is computationally expensive to reliably find all fibers between seed points and target regions. The authors implemented a highly parallel version of the algorithm using NVIDIA's CUDA platform on a GPU. This provided a significant reduction in running time of up to 40x compared to a multithreaded CPU implementation, greatly increasing the applicability of the algorithm.
Parallel Computing 



Parallel Computing Mr. Vikram Singh Slathia This document discusses parallel computing. It begins by defining parallel processing as using simultaneous data processing tasks to save time and/or money and solve larger problems. It then discusses how parallel computing uses multiple compute resources simultaneously to solve computational problems. Some examples of parallel phenomena in nature and technology are provided. The document outlines several areas where parallel computing is applied, including physics, bioscience, and computer science. It discusses the benefits of parallel computing in saving time and money and solving larger problems too large for a single computer. Finally, it briefly mentions ways to classify parallel computers and some basic requirements for achieving parallel execution.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Lecture 4 principles of parallel algorithm design updated



Lecture 4 principles of parallel algorithm design updatedVajira Thambawita The main principles of parallel algorithm design are discussed here. For more information: visit, https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials
distributed shared memory



distributed shared memoryAshish Kumar Distributed shared memory (DSM) provides processes with a shared address space across distributed memory systems. DSM exists only virtually through primitives like read and write operations. It gives the illusion of physically shared memory while allowing loosely coupled distributed systems to share memory. DSM refers to applying this shared memory paradigm using distributed memory systems connected by a communication network. Each node has CPUs, memory, and blocks of shared memory can be cached locally but migrated on demand between nodes to maintain consistency.
Operating system paging and segmentation



Operating system paging and segmentationhamza haseeb This document discusses paging and segmentation in operating systems. Paging divides memory into fixed-size pages for faster data access and allows physical addresses to be non-contiguous. It has advantages like no external fragmentation but disadvantages like internal fragmentation and consuming memory for page tables. Segmentation divides memory into segments of varying lengths and permissions for memory protection. It has advantages like no internal fragmentation and less memory used for segment tables, while lending itself to data sharing and protection but has the disadvantage of a more costly memory management algorithm.
Parallel computing



Parallel computingvirend111 Parallel computing is the simultaneous use of multiple compute resources to solve a computational problem faster. It allows for larger problems to be solved and provides cost savings over serial computing. There are different models of parallelism including data parallelism and task parallelism. Flynn's taxonomy categorizes computer architectures as SISD, SIMD, MISD and MIMD based on how instructions and data are handled. Shared memory and distributed memory are two common architectures that differ in scalability and communication handling. Programming models include shared memory, message passing and data parallel approaches. Design considerations for parallel programs include partitioning work, communication between processes, and synchronization.
Parallel computing and its applications



Parallel computing and its applicationsBurhan Ahmed Parallel computing is a type of computing architecture in which several processors execute or process an application or computation simultaneously. Parallel computing helps in performing large computations by dividing the workload between more than one processor, all of which work through the computation at the same time. Most supercomputers employ parallel computing principles to operate. Parallel computing is also known as parallel processing.
↓↓↓↓ Read More:
Watch my videos on snack here: --> --> http://sck.io/x-B1f0Iy
@ Kindly Follow my Instagram Page to discuss about your mental health problems-
-----> https://instagram.com/mentality_streak?utm_medium=copy_link
@ Appreciate my work:
-----> behance.net/burhanahmed1
Thank-you !
Distributed Operating System_1



Distributed Operating System_1Dr Sandeep Kumar Poonia INTRODUCTIONTO OPERATING SYSTEM
What is an Operating System?
Mainframe Systems
Desktop Systems
Multiprocessor Systems
Distributed Systems
Clustered System
Real -Time Systems
Handheld Systems
Computing Environments
Centralized shared memory architectures



Centralized shared memory architecturesGokuldhev mony This document discusses centralized shared-memory architectures and cache coherence protocols. It begins by explaining how multiple processors can share memory through a shared bus and cached data. It then discusses the cache coherence problem that arises when caches contain replicated data. Write invalidate is introduced as the most common coherence protocol, where a write invalidates other caches' copies of the block. The implementation of write invalidate protocols with snooping and directory approaches is covered, focusing on supporting write-back caches through tracking shared state and bus snooping.
Cache coherence



Cache coherenceEmployee The document discusses cache coherence in multiprocessor systems. It describes the cache coherence problem that can arise when multiple processors have caches and can access shared memory. It then summarizes two primary hardware solutions: directory protocols which maintain information about which caches hold which memory lines; and snoopy cache protocols where cache controllers monitor bus traffic to maintain coherence without a directory. Finally it mentions a software-based solution relying on compiler analysis and operating system support.
advanced computer architesture-conditions of parallelism



advanced computer architesture-conditions of parallelismPankaj Kumar Jain This PPT contains Data and Resource Dependencies,Control Dependence,Resource Dependence,Bernstein’s Conditions ,Hardware And Software Parallelism,Types of Software Parallelism
Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computing



Lecture 1 introduction to parallel and distributed computingVajira Thambawita This gives you an introduction to parallel and distributed computing. More details: https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials
Lecture 11 - distributed database



Lecture 11 - distributed databaseHoneySah This document discusses concepts related to distributed database management systems (DDBMS). It defines a distributed database as a logically interrelated collection of shared data distributed over a computer network. A DDBMS manages the distributed database and makes the distribution transparent to users. The document covers distributed database design topics like fragmentation, allocation, and replication of data across multiple sites. It also discusses various types of transparency that a DDBMS provides, such as distribution, transaction, and performance transparency.
Multiprocessor



MultiprocessorKamal Acharya This document discusses multiprocessor systems, including their interconnection structures, interprocessor arbitration, communication and synchronization, and cache coherence. Multiprocessor systems connect two or more CPUs with shared memory and I/O to improve reliability and enable parallel processing. They use various interconnection structures like buses, switches, and hypercubes. Arbitration logic manages shared resources and bus access. Synchronization ensures orderly access to shared data through techniques like semaphores. Cache coherence protocols ensure data consistency across processor caches and main memory.
Multiprocessor system 



Multiprocessor system Mr. Vikram Singh Slathia Multiprocessor system is an interconnection of two or more CPUs with memory and input-output equipment
The components that forms multiprocessor are CPUs IOPs connected to input –output devices , and memory unit that may be partitioned into a number of separate modules.
Multiprocessor are classified as multiple instruction stream, multiple data stream (MIMD) system.
Parallel sorting Algorithms



Parallel sorting AlgorithmsGARIMA SHAKYA These slides are about parallel sorting algorithms. In which four types of sorting algorithms are discussed with the comparison between their sequential and parallel ways. The four algorithms which are included are: Bubble sort, merge sort, Bitonic sort and Shear sort.
Distributed shared memory ch 5



Distributed shared memory ch 5Alagappa Government Arts College, Karaikudi The document discusses distributed shared memory (DSM) which provides a shared memory abstraction for loosely coupled distributed systems. DSM allows processes on different nodes in a distributed system to access shared memory as if it were a single logical memory. It implements this shared memory space through caching blocks of data in local memories and migrating blocks between nodes when needed to service memory requests. Key aspects of DSM systems covered include memory coherence protocols to ensure data consistency and techniques for managing caching and data migration between distributed nodes.
parallel programming models



parallel programming modelsSwetha S Parallel programming model is a set of program abstraction for filtering parallel activities from the application to the underlying parallel hardware.
Disk structure



Disk structuresangrampatil81 The document discusses secondary storage and magnetic disk structure. It provides details on:
- Secondary storage devices like disks, tapes, and drives have non-volatile memory and are slower but cheaper than primary storage like RAM.
- Magnetic disks are divided into platters, tracks, cylinders, and sectors. Read/write heads access data locations specified by head, sector, cylinder addresses.
- Various disk scheduling algorithms like FCFS, SSTF, SCAN, C-SCAN, and LOOK are described which improve disk bandwidth and access time by processing requests in different orders.
Cache memory 



Cache memory Zalal Udeen Cache memory is a type of fast RAM that a computer processor can access more quickly than regular RAM. It stores recently accessed data from main memory to allow for faster future access if the same data is needed again. Cache memory is organized into levels based on proximity and speed of access to the processor, with L1 cache being fastest as it is located directly on the CPU chip, and L2 cache and main memory being progressively slower as they are located further away. Modern processors integrate both L1 and L2 cache onto the CPU package to improve performance by reducing access time.
Query trees



Query treesShefa Idrees Hey friends, here is my "query tree" assignment. :-) I have searched a lot to get this master piece :p and I can guarantee you that this one gonna help you In Sha ALLAH more than any else document on the subject. Have a good day :-)
virtual memory management in multi processor mach os



virtual memory management in multi processor mach osAJAY KHARAT Virtual memory management in multi-processor Mach OS allows processes to access more memory than is physically installed by using virtual addresses. The Mach kernel provides basic services like tasks, threads, messages, and ports to enable parallel and distributed applications. Tasks have their own virtual address spaces that are divided into pages which are allocated to physical frames. The virtual memory system provides protection at the page level by using protection codes in page table entries to control read, write, and execute permissions.
Viewers also liked (14)
Parallel Computing Application



Parallel Computing Applicationhanis salwan This research article proposes accelerating a geodesic ray-tracing algorithm for fiber tracking in brain imaging using parallel programming on a GPU. Fiber tracking uses diffusion MRI to noninvasively examine brain fiber structures at a microscopic level. While geodesic ray-tracing is robust, it is computationally expensive to reliably find all fibers between seed points and target regions. The authors implemented a highly parallel version of the algorithm using NVIDIA's CUDA platform on a GPU. This provided a significant reduction in running time of up to 40x compared to a multithreaded CPU implementation, greatly increasing the applicability of the algorithm.
Parallel Computing 



Parallel Computing Mr. Vikram Singh Slathia This document discusses parallel computing. It begins by defining parallel processing as using simultaneous data processing tasks to save time and/or money and solve larger problems. It then discusses how parallel computing uses multiple compute resources simultaneously to solve computational problems. Some examples of parallel phenomena in nature and technology are provided. The document outlines several areas where parallel computing is applied, including physics, bioscience, and computer science. It discusses the benefits of parallel computing in saving time and money and solving larger problems too large for a single computer. Finally, it briefly mentions ways to classify parallel computers and some basic requirements for achieving parallel execution.
Extreme programming (xp) | David Tzemach



Extreme programming (xp) | David TzemachDavid Tzemach It’s simply the best presentation that explains the agile methodology of Extreme Programming!
Overview
1. What is Extreme programming?
2. Extreme programming as an agile methodology.
3. The values of Extreme programming
4. The Activities of Extreme programming
5. The 12 core practices of Extreme programming
6. The roles of Extreme programming
Enjoy :)
Parallel Computing



Parallel ComputingAmeya Waghmare Please contact me to download this pres.A comprehensive presentation on the field of Parallel Computing.It's applications are only growing exponentially day by days.A useful seminar covering basics,its classification and implementation thoroughly.
Visit www.ameyawaghmare.wordpress.com for more info
Applications of paralleL processing



Applications of paralleL processingPage Maker This document discusses various applications of parallel processing. It describes how parallel processing is used in numeric weather prediction to forecast weather by processing large amounts of observational data. It is also used in oceanography and astrophysics to study oceans and conduct particle simulations. Other applications mentioned include socioeconomic modeling, finite element analysis, artificial intelligence, seismic exploration, genetic engineering, weapon research, medical imaging, remote sensing, energy exploration, and more. The document also discusses loosely coupled and tightly coupled multiprocessors and the differences between the two approaches.
Parallel processing Concepts



Parallel processing ConceptsArmy Public School and College -Faisal This document discusses parallel processing and parallel organizations. It describes four types of parallel organizations: single instruction single data (SISD), single instruction multiple data (SIMD), multiple instruction single data (MISD), and multiple instruction multiple data (MIMD). MIMD systems are further broken down into shared memory and distributed memory architectures. Cache coherence protocols like MESI are discussed for maintaining consistency across caches in shared memory multiprocessors.
Introduction to parallel processing



Introduction to parallel processingPage Maker This presentation contains flynn's classification,difference between SIMD and MIMD some applications of parallel processing
Mobile computing



Mobile computingMayuresh Tiwari This document discusses mobile computing and computer networks. It compares wired and mobile networks, describing differences in bandwidth, resources, and connectivity. It then outlines various types of wireless networks and devices like laptops, PDAs, and cell phones. Examples of mobile computing applications are given for fields like real estate, law, and transportation. Challenges of mobile computing are addressed as well as the future potential of increased processing power and integrated circuits to improve the technology. References are provided on related research papers and websites exploring topics in mobile object databases, mobile computing issues and solutions.
Extreme programming (xp)



Extreme programming (xp)Mohamed Abdelrahman This document provides an overview of Extreme Programming (XP), an agile software development methodology. It discusses XP's history and features, which include short 2-week development cycles, pair programming, test-driven development, and frequent refactoring. The core principles of XP are also examined, such as incremental planning, small releases, simple design, and sustainable pace. Various phases of the XP process are outlined, from exploration to productionizing. Requirements are captured as scenarios and prioritized by the customer. Automated testing is a key practice in XP. Both advantages like collective code ownership and disadvantages like its unsuitability for large projects are noted.
Parallel computing



Parallel computingVinay Gupta Parallel computing involves solving computational problems simultaneously using multiple processors. It can save time and money compared to serial computing and allow larger problems to be solved. Parallel programs break problems into discrete parts that can be solved concurrently on different CPUs. Shared memory parallel computers allow all processors to access a global address space, while distributed memory systems require communication between separate processor memories. Hybrid systems combine shared and distributed memory architectures.
Parallel Algorithms Advantages and Disadvantages



Parallel Algorithms Advantages and DisadvantagesMurtadha Alsabbagh Parallel algorithms can increase throughput by using multiple processing units to perform independent tasks simultaneously. However, parallelization also introduces limitations. Amdahl's law dictates that speedup from parallelization is limited by the fraction of the algorithm that must execute sequentially. Complexity in designing, implementing, and maintaining parallel programs can outweigh performance benefits for some problems. Other challenges include data dependencies, portability across systems, scalability to larger problem and system sizes, and potential for parallel slowdown rather than speedup.
Introduction To Mobile Computing



Introduction To Mobile ComputingMadhuri Badgujar The document provides an introduction to mobile computing. It discusses how mobile computing allows transmission of data without a fixed physical link. It describes the growth of mobile voice communication and how mobile data communication has become important. It discusses existing cellular network architecture and technologies like GSM. It covers advances in technology that have enabled mobile computing. It describes the different types of device mobility and portability. It provides examples of mobile computing applications in vehicles, emergencies, business, and for information services. It also discusses the history and market for mobile communications and some open research topics in the field.
Eye gaze communication



Eye gaze communicationPRADEEP Cheekatla The document discusses the Eye Gaze system, which allows people with physical disabilities to control devices with their eyes. It describes how the system works by tracking a user's eye movements to select on-screen options. The document outlines who can benefit from the system, its various components and menus, applications, and future advancements like improved portability and tracking for limited eye control. It concludes that eye tracking interfaces can aid application control if used sensibly given the voluntary and involuntary nature of eye movements.
Mobile Computing



Mobile Computinggaurav koriya hey!!!!! everybody dats was simple ppt on mobile computing as u all aware dat d world is not stationary things are getting change technology is rocking all over so lets get into in it
and plz. dont forget to comment on my work weather u lik or not
Ad
Similar to Parallel architecture &programming (20)
Lecture 2



Lecture 2Mr SMAK This document discusses key concepts and terminologies related to parallel computing. It defines tasks, parallel tasks, serial and parallel execution. It also describes shared memory and distributed memory architectures as well as communications and synchronization between parallel tasks. Flynn's taxonomy is introduced which classifies parallel computers based on instruction and data streams as Single Instruction Single Data (SISD), Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD), Multiple Instruction Single Data (MISD), and Multiple Instruction Multiple Data (MIMD). Examples are provided for each classification.
CSA unit5.pptx



CSA unit5.pptxAbcvDef Parallel computing involves using multiple processing units simultaneously to solve computational problems. It can save time by solving large problems or providing concurrency. The basic design involves memory storing program instructions and data, and a CPU fetching instructions from memory and sequentially performing them. Flynn's taxonomy classifies computer systems based on their instruction and data streams as SISD, SIMD, MISD, or MIMD. Parallel architectures can also be classified based on their memory arrangement as shared memory or distributed memory systems.
Week # 1.pdf



Week # 1.pdfgiddy5 This document provides an overview of the topics that will be covered in the CS 3006 Parallel and Distributed Computing course. It introduces the course instructor, textbook, schedule, evaluation criteria, and pre-requisites. The first three lectures are also summarized, covering introduction and definitions, shared and distributed memory systems, parallel execution terms and definitions, overhead in parallel computing, speed-up and Amdahl's law, and Flynn's taxonomy of computer architectures.
Computer Architecture CSN221_Lec_37_SpecialTopics.pdf



Computer Architecture CSN221_Lec_37_SpecialTopics.pdfssuser034ce1 Computer Architecture CSN221_Lec_37_SpecialTopics.pdf
unit 4.pptx



unit 4.pptxSUBHAMSHARANRA211100 This document provides an overview of parallelism, including the need for parallelism, types of parallelism, applications of parallelism, and challenges in parallelism. It discusses instruction level parallelism and data level parallelism in software. It describes Flynn's classification of computer architectures and the categories of SISD, SIMD, MISD, and MIMD. It also covers hardware multi-threading, uni-processors vs multi-processors, multi-core processors, memory in multi-processor systems, cache coherency, and the MESI protocol.
unit 4.pptx



unit 4.pptxSUBHAMSHARANRA211100 This document provides an overview of parallelism and parallel computing architectures. It discusses the need for parallelism to improve performance and throughput. The main types of parallelism covered are instruction level parallelism, data parallelism, and task parallelism. Flynn's taxonomy is introduced for classifying computer architectures based on their instruction and data streams. Common parallel architectures like SISD, SIMD, MIMD are explained. The document also covers memory architectures for multi-processor systems including shared memory, distributed memory, and cache coherency protocols.
High performance computing



High performance computingpunjab engineering college, chandigarh This document provides an overview of high performance computing infrastructures. It discusses parallel architectures including multi-core processors and graphical processing units. It also covers cluster computing, which connects multiple computers to increase processing power, and grid computing, which shares resources across administrative domains. The key aspects covered are parallelism, memory architectures, and technologies used to implement clusters like Message Passing Interface.
Lec 2 (parallel design and programming)



Lec 2 (parallel design and programming)Sudarshan Mondal This document discusses parallel computing architectures and concepts. It begins by describing Von Neumann architecture and how parallel computers follow the same basic design but with multiple units. It then covers Flynn's taxonomy which classifies computers based on their instruction and data streams as Single Instruction Single Data (SISD), Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD), Multiple Instruction Single Data (MISD), or Multiple Instruction Multiple Data (MIMD). Each classification is defined. The document also discusses parallel terminology, synchronization, scalability, and Amdahl's law on the costs and limits of parallel programming.
VTU 6th Sem Elective CSE - Module 3 cloud computing



VTU 6th Sem Elective CSE - Module 3 cloud computingSachin Gowda The document discusses parallel and distributed computing concepts in Aneka including multiprocessing, multithreading, task-based programming, and parameter sweep applications. It describes key aspects of implementing parallel applications in Aneka such as defining tasks, managing task execution, file handling, and tools for developing parameter sweep jobs. The document also provides an overview of how workflow managers can interface with Aneka.
Concurrency Programming in Java - 01 - Introduction to Concurrency Programming



Concurrency Programming in Java - 01 - Introduction to Concurrency ProgrammingSachintha Gunasena This session discusses a basic high-level introduction to concurrency programming with Java which include:
programming basics, OOP concepts, concurrency, concurrent programming, parallel computing, concurrent vs parallel, why concurrency, real world example, terms, Moore's Law, Amdahl's Law, types of parallel computation, MIMD Variants, shared memory model, distributed memory model, client server model, scoop mechanism, scoop preview - a sequential program, in a concurrent setting - using scoop, programming then & now, sequential programming, concurrent programming,
Unit 5 Advanced Computer Architecture



Unit 5 Advanced Computer ArchitectureBalaji Vignesh This document provides an overview of hardware multithreading techniques including fine-grained, coarse-grained, and simultaneous multithreading. Fine-grained multithreading switches threads after every instruction to hide latency. Coarse-grained multithreading switches threads only after long stalls to avoid slowing individual threads. Simultaneous multithreading issues instructions from multiple threads each cycle to better utilize functional units.
CA UNIT IV.pptx



CA UNIT IV.pptxssuser9dbd7e Unit IV discusses parallelism and parallel processing architectures. It introduces Flynn's classifications of parallel systems as SISD, MIMD, SIMD, and SPMD. Hardware approaches to parallelism include multicore processors, shared memory multiprocessors, and message-passing systems like clusters, GPUs, and warehouse-scale computers. The goals of parallelism are to increase computational speed and throughput by processing data concurrently across multiple processors.
archintro.pdf



archintro.pdfGauravDagar13 This document discusses the architecture of parallel computers. It covers hardware issues like the number and type of processors, memory hierarchy, and I/O devices. It also discusses operating system issues in managing resources and supporting hardware features. Programming issues are discussed, like difficulty in programming parallel computers. Flynn's classification of computer architectures is presented, including SISD, SIMD, MIMD, and MISD models. Different types of parallel computers are described such as multi-processors, multi-computers, vector computers, and SIMD computers.
Parallel Programming



Parallel ProgrammingUday Sharma This document discusses parallel programming concepts including threads, synchronization, and barriers. It defines parallel programming as carrying out many calculations simultaneously. Advantages include increased computational power and speed up. Key issues in parallel programming are sharing resources between threads, and ensuring synchronization through locks and barriers. Data parallel programming is discussed where the same operation is performed on different data elements simultaneously.
Parallel Processors (SIMD) 



Parallel Processors (SIMD) Ali Raza This document discusses parallel processors, specifically single instruction multiple data (SIMD) processors. It provides details on vector processors and array processors. Vector processors utilize vector instructions that operate on arrays of data called vectors. They have vector registers, functional units, and load/store units. Array processors perform parallel computations on large data arrays using multiple identical processing elements. The document describes dedicated memory and global memory organizations for array processors. It provides examples of early SIMD machines like ILLIAC IV.
Parallel Processors (SIMD) 



Parallel Processors (SIMD) Ali Raza SIMD (single instruction, multiple data) parallel processors exploit data-level parallelism by performing the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously using a single instruction. Vector processors are a type of SIMD parallel processor that operate on 1D arrays of data called vectors. They contain vector registers that can hold multiple data elements and functional units that perform arithmetic and logical operations in a pipelined fashion on entire vectors. Array processors are another type of SIMD machine composed of multiple identical processing elements that perform computations in lockstep under the control of a single instruction unit. Early examples include the ILLIAC IV and Cray X1 supercomputers. Multimedia extensions like MMX provide SIMD integer operations to improve performance of multimedia applications.
PARALLELISM IN MULTICORE PROCESSORS



PARALLELISM IN MULTICORE PROCESSORSAmirthavalli Senthil Introduction to Multicore processors and other shared memory multiprocessors – Flynn’s classification: SISD, MIMD, SIMD, SPMD and Vector – Hardware multithreading – GPU architecture.
Ad
More from Ismail El Gayar (7)
Neural Networks



Neural NetworksIsmail El Gayar This document provides an overview of artificial neural networks and their application as a model of the human brain. It discusses the biological neuron, different types of neural networks including feedforward, feedback, time delay, and recurrent networks. It also covers topics like learning in perceptrons, training algorithms, applications of neural networks, and references key concepts like connectionism, associative memory, and massive parallelism in the brain.
Why computer engineering



Why computer engineeringIsmail El Gayar Computer engineering is an excellent career choice according to the document for several reasons:
1. There is high market demand and increasing salaries for computer engineers due to growth in fields like computing, networks, biotechnology, and virtual reality. Starting salaries in Egypt are between 2000-3000 LE and higher in other Arab countries.
2. The career offers a wide variety of job opportunities in different work types like software, hardware, networking and different work places like companies, universities, hospitals.
3. There are opportunities for high promotion rates from junior to senior levels and project management roles in just a few years.
4. The work provides comfort and freedom as it takes place in air conditioned offices and allows flexibility in
What is ETL?



What is ETL?Ismail El Gayar ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a process that allows companies to consolidate data from multiple sources into a single target data store, such as a data warehouse. It involves extracting data from heterogeneous sources, transforming it to fit operational needs, and loading it into the target data store. ETL tools automate this process, allowing companies to access and analyze consolidated data for critical business decisions. Popular ETL tools include IBM Infosphere Datastage, Informatica, and Oracle Warehouse Builder.
Geographic Information System for Egyptian Railway System(GIS)



Geographic Information System for Egyptian Railway System(GIS)Ismail El Gayar This document provides an overview of geographic information systems (GIS). It defines GIS as a system for capturing, storing, analyzing and presenting spatial data linked to locations. Key points include:
- GIS merges cartography and database technology to store and link map features to attribute data.
- The main components are a database for storing attribute and spatial data, tools for managing and analyzing spatial relationships, and functions for producing maps.
- GIS allows for integration of diverse spatial datasets, visualization, querying, overlay analysis and other functionality to support decision-making.
- Popular GIS software includes ArcGIS, ArcView and AutoCAD Map.
System science documentation



System science documentationIsmail El Gayar This document provides an overview of key concepts in system science and engineering. It begins with an introduction that discusses the motivation for and organization of the document. The first part then defines systems and system concepts like classification, science, engineering, functions, behaviors, structures, properties, characteristics, life cycles and modeling. It also discusses related topics like feedback, thinking processes, statistics, and probability. The second part focuses on a case study of dependability, examining attributes, threats, means of prevention and tolerance of faults, errors and failures. Overall, the document aims to illustrate fundamental system science topics and their applications through examples, models and a dependability case study.
Prolog & lisp



Prolog & lispIsmail El Gayar LISP and PROLOG are early AI programming languages. LISP, created in 1958, uses lists and is functional while PROLOG, created in the 1970s, is logic-based and declarative. Both use recursion and allow programming with lists. They are commonly used for symbolic reasoning, knowledge representation and natural language processing. While different in approach, they both allow developing AI systems through a non-procedural programming style.
Object oriented methodology & unified modeling language



Object oriented methodology & unified modeling languageIsmail El Gayar The document discusses Unified Modeling Language (UML) and object-oriented methodology. It introduces UML, describing it as the standard language for visualizing and modeling software systems. It outlines the main UML diagram types including use case diagrams, class diagrams, sequence diagrams, collaboration diagrams, state machine diagrams, activity diagrams, component diagrams, and deployment diagrams. The document also discusses key concepts of object-oriented methodology such as classes, objects, attributes, and methods.
Recently uploaded (20)
tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdf



tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdffjgm517 descaripcion detallada del avance de las tecnologias en mesopotamia, egipto, roma y grecia.
Andrew Marnell: Transforming Business Strategy Through Data-Driven Insights



Andrew Marnell: Transforming Business Strategy Through Data-Driven InsightsAndrew Marnell With expertise in data architecture, performance tracking, and revenue forecasting, Andrew Marnell plays a vital role in aligning business strategies with data insights. Andrew Marnell’s ability to lead cross-functional teams ensures businesses achieve sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Quantum Computing Quick Research Guide by Arthur Morgan



Quantum Computing Quick Research Guide by Arthur MorganArthur Morgan This is a Quick Research Guide (QRG).
QRGs include the following:
- A brief, high-level overview of the QRG topic.
- A milestone timeline for the QRG topic.
- Links to various free online resource materials to provide a deeper dive into the QRG topic.
- Conclusion and a recommendation for at least two books available in the SJPL system on the QRG topic.
QRGs planned for the series:
- Artificial Intelligence QRG
- Quantum Computing QRG
- Big Data Analytics QRG
- Spacecraft Guidance, Navigation & Control QRG (coming 2026)
- UK Home Computing & The Birth of ARM QRG (coming 2027)
Any questions or comments?
- Please contact Arthur Morgan at [email protected].
100% human made.
Drupalcamp Finland – Measuring Front-end Energy Consumption



Drupalcamp Finland – Measuring Front-end Energy ConsumptionExove How to measure web front-end energy consumption using Firefox Profiler. Presented in DrupalCamp Finland on April 25th, 2025.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in Business



Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in BusinessDr. Tathagat Varma My talk for the Indian School of Business (ISB) Emerging Leaders Program Cohort 9. In this talk, I discussed key issues around adoption of GenAI in business - benefits, opportunities and limitations. I also discussed how my research on Theory of Cognitive Chasms helps address some of these issues
How Can I use the AI Hype in my Business Context?



How Can I use the AI Hype in my Business Context?Daniel Lehner 𝙄𝙨 𝘼𝙄 𝙟𝙪𝙨𝙩 𝙝𝙮𝙥𝙚? 𝙊𝙧 𝙞𝙨 𝙞𝙩 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙜𝙖𝙢𝙚 𝙘𝙝𝙖𝙣𝙜𝙚𝙧 𝙮𝙤𝙪𝙧 𝙗𝙪𝙨𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙨𝙨 𝙣𝙚𝙚𝙙𝙨?
Everyone’s talking about AI but is anyone really using it to create real value?
Most companies want to leverage AI. Few know 𝗵𝗼𝘄.
✅ What exactly should you ask to find real AI opportunities?
✅ Which AI techniques actually fit your business?
✅ Is your data even ready for AI?
If you’re not sure, you’re not alone. This is a condensed version of the slides I presented at a Linkedin webinar for Tecnovy on 28.04.2025.
#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025



#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, transcript, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Big Data Analytics Quick Research Guide by Arthur Morgan



Big Data Analytics Quick Research Guide by Arthur MorganArthur Morgan This is a Quick Research Guide (QRG).
QRGs include the following:
- A brief, high-level overview of the QRG topic.
- A milestone timeline for the QRG topic.
- Links to various free online resource materials to provide a deeper dive into the QRG topic.
- Conclusion and a recommendation for at least two books available in the SJPL system on the QRG topic.
QRGs planned for the series:
- Artificial Intelligence QRG
- Quantum Computing QRG
- Big Data Analytics QRG
- Spacecraft Guidance, Navigation & Control QRG (coming 2026)
- UK Home Computing & The Birth of ARM QRG (coming 2027)
Any questions or comments?
- Please contact Arthur Morgan at [email protected].
100% human made.
Mobile App Development Company in Saudi Arabia



Mobile App Development Company in Saudi ArabiaSteve Jonas EmizenTech is a globally recognized software development company, proudly serving businesses since 2013. With over 11+ years of industry experience and a team of 200+ skilled professionals, we have successfully delivered 1200+ projects across various sectors. As a leading Mobile App Development Company In Saudi Arabia we offer end-to-end solutions for iOS, Android, and cross-platform applications. Our apps are known for their user-friendly interfaces, scalability, high performance, and strong security features. We tailor each mobile application to meet the unique needs of different industries, ensuring a seamless user experience. EmizenTech is committed to turning your vision into a powerful digital product that drives growth, innovation, and long-term success in the competitive mobile landscape of Saudi Arabia.
HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices and Managing Multiuser Environments



HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices and Managing Multiuser Environmentspanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/hcl-nomad-web-best-practices-and-managing-multiuser-environments/
HCL Nomad Web is heralded as the next generation of the HCL Notes client, offering numerous advantages such as eliminating the need for packaging, distribution, and installation. Nomad Web client upgrades will be installed “automatically” in the background. This significantly reduces the administrative footprint compared to traditional HCL Notes clients. However, troubleshooting issues in Nomad Web present unique challenges compared to the Notes client.
Join Christoph and Marc as they demonstrate how to simplify the troubleshooting process in HCL Nomad Web, ensuring a smoother and more efficient user experience.
In this webinar, we will explore effective strategies for diagnosing and resolving common problems in HCL Nomad Web, including
- Accessing the console
- Locating and interpreting log files
- Accessing the data folder within the browser’s cache (using OPFS)
- Understand the difference between single- and multi-user scenarios
- Utilizing Client Clocking
Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdf



Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdfSoftware Company Explore the benefits and features of advanced logistics management software for businesses in Riyadh. This guide delves into the latest technologies, from real-time tracking and route optimization to warehouse management and inventory control, helping businesses streamline their logistics operations and reduce costs. Learn how implementing the right software solution can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and provide a competitive edge in the growing logistics sector of Riyadh.
Procurement Insights Cost To Value Guide.pptx



Procurement Insights Cost To Value Guide.pptxJon Hansen Procurement Insights integrated Historic Procurement Industry Archives, serves as a powerful complement — not a competitor — to other procurement industry firms. It fills critical gaps in depth, agility, and contextual insight that most traditional analyst and association models overlook.
Learn more about this value- driven proprietary service offering here.
Designing Low-Latency Systems with Rust and ScyllaDB: An Architectural Deep Dive



Designing Low-Latency Systems with Rust and ScyllaDB: An Architectural Deep DiveScyllaDB Want to learn practical tips for designing systems that can scale efficiently without compromising speed?
Join us for a workshop where we’ll address these challenges head-on and explore how to architect low-latency systems using Rust. During this free interactive workshop oriented for developers, engineers, and architects, we’ll cover how Rust’s unique language features and the Tokio async runtime enable high-performance application development.
As you explore key principles of designing low-latency systems with Rust, you will learn how to:
- Create and compile a real-world app with Rust
- Connect the application to ScyllaDB (NoSQL data store)
- Negotiate tradeoffs related to data modeling and querying
- Manage and monitor the database for consistently low latencies
Cyber Awareness overview for 2025 month of security



Cyber Awareness overview for 2025 month of securityriccardosl1 Cyber awareness training educates employees on risk associated with internet and malicious emails
Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...



Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...Impelsys Inc. Impelsys provided a robust testing solution, leveraging a risk-based and requirement-mapped approach to validate ICU Connect and CritiXpert. A well-defined test suite was developed to assess data communication, clinical data collection, transformation, and visualization across integrated devices.
2025-05-Q4-2024-Investor-Presentation.pptx



2025-05-Q4-2024-Investor-Presentation.pptxSamuele Fogagnolo Cloudflare Q4 Financial Results Presentation
IEDM 2024 Tutorial2_Advances in CMOS Technologies and Future Directions for C...



IEDM 2024 Tutorial2_Advances in CMOS Technologies and Future Directions for C...organizerofv IEDM 2024 Tutorial2
AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global Trends



AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global TrendsInData Labs In this infographic, we explore how businesses can implement effective governance frameworks to address AI data privacy. Understanding it is crucial for developing effective strategies that ensure compliance, safeguard customer trust, and leverage AI responsibly. Equip yourself with insights that can drive informed decision-making and position your organization for success in the future of data privacy.
This infographic contains:
-AI and data privacy: Key findings
-Statistics on AI data privacy in the today’s world
-Tips on how to overcome data privacy challenges
-Benefits of AI data security investments.
Keep up-to-date on how AI is reshaping privacy standards and what this entails for both individuals and organizations.
UiPath Community Berlin: Orchestrator API, Swagger, and Test Manager API



UiPath Community Berlin: Orchestrator API, Swagger, and Test Manager APIUiPathCommunity Join this UiPath Community Berlin meetup to explore the Orchestrator API, Swagger interface, and the Test Manager API. Learn how to leverage these tools to streamline automation, enhance testing, and integrate more efficiently with UiPath. Perfect for developers, testers, and automation enthusiasts!
📕 Agenda
Welcome & Introductions
Orchestrator API Overview
Exploring the Swagger Interface
Test Manager API Highlights
Streamlining Automation & Testing with APIs (Demo)
Q&A and Open Discussion
Perfect for developers, testers, and automation enthusiasts!
👉 Join our UiPath Community Berlin chapter: https://community.uipath.com/berlin/
This session streamed live on April 29, 2025, 18:00 CET.
Check out all our upcoming UiPath Community sessions at https://community.uipath.com/events/.
Parallel architecture &programming
- 1. Parallel Architecture & Parallel Programming Submitted: Dr.Hesham El-Zouka By:Eng. Ismail Fathalla El-Gayar
- 2. Content:- • Introduction – Von-Neumann Architecture. – Serial ( Single ) Computational. – Concepts and Terminology • Parallel Architecture – Definition – Benefits & Advantages – Distinguishing Parallel Processors – Multiprocessor Architecture Classifications – Parallel Computer Memory Architectures • Parallel Programming – Definition – Parallel Programming Model – Designing Parallel Programs – Parallel Algorithm Examples – Conclusion • Case Study
- 3. Introduction: • Von-Neumann Architecture Since then, virtually all computers have followed this basic design, which Comprised of four main components: – Memory – Control Unit – Arithmetic Logic Unit – Input/output
- 4. Introduction Serial Computational :- • Traditionally, software has been written for serial computation: To be run on a single computer having a single Central Processing Unit (CPU) • Problem is broken into discrete SERIES of instructions. • Instructions are EXECUTED one after another. • One instruction may execute at any moment in TIME
- 7. Definition: • parallel computing: is the simultaneous use of multiple compute resources to solve a computational problem To be run using multiple CPUs. In which:- - A problem is broken into discrete parts that can be solved concurrently - Each part is further broken down to a series of instructions - Instructions from each part execute simultaneously on different CPUs
- 8. Definition:
- 9. Concepts and Terminology: General Terminology • Task – A logically discrete section of computational work • Parallel Task – Task that can be executed by multiple processors safely • Communications – Data exchange between parallel tasks • Synchronization – The coordination of parallel tasks in real time
- 10. Benefits & Advantages: • Save Time & Money • Solve Larger Problems
- 11. How To Distinguishing Parallel processors: – Resource Allocation: • how large a collection? • how powerful are the elements? • how much memory? – Data access, Communication and Synchronization • how do the elements cooperate and communicate? • how are data transmitted between processors? • what are the abstractions and primitives for cooperation? – Performance and Scalability • how does it all translate into performance? • how does it scale?
- 12. Multiprocessor Architecture Classification : • Distinguishes multi-processor architecture by instruction and data:- • SISD – Single Instruction, Single Data • SIMD – Single Instruction, Multiple Data • MISD – Multiple Instruction, Single Data • MIMD – Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data
- 13. Flynn’s Classical Taxonomy: SISD • Serial • Only one instruction and data stream is acted on during any one clock cycle
- 14. Flynn’s Classical Taxonomy: SIMD • All processing units execute the same instruction at any given clock cycle. • Each processing unit operates on a different data element.
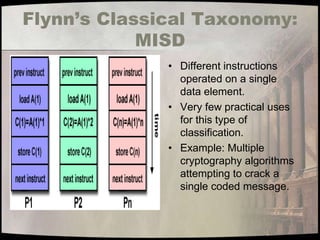
- 15. Flynn’s Classical Taxonomy: MISD • Different instructions operated on a single data element. • Very few practical uses for this type of classification. • Example: Multiple cryptography algorithms attempting to crack a single coded message.
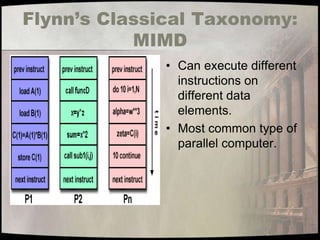
- 16. Flynn’s Classical Taxonomy: MIMD • Can execute different instructions on different data elements. • Most common type of parallel computer.
- 17. Parallel Computer Memory Architectures: Shared Memory Architecture • All processors access all memory as a single global address space. • Data sharing is fast. • Lack of scalability between memory and CPUs
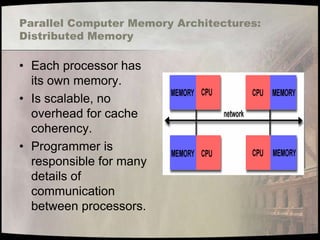
- 18. Parallel Computer Memory Architectures: Distributed Memory • Each processor has its own memory. • Is scalable, no overhead for cache coherency. • Programmer is responsible for many details of communication between processors.
- 20. Parallel Programming Models • Exist as an abstraction above hardware and memory architectures • Examples: – Shared Memory – Threads – Messaging Passing – Data Parallel
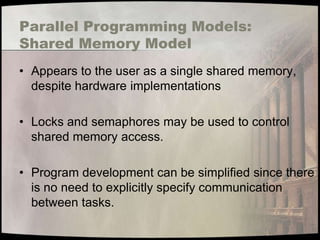
- 21. Parallel Programming Models: Shared Memory Model • Appears to the user as a single shared memory, despite hardware implementations • Locks and semaphores may be used to control shared memory access. • Program development can be simplified since there is no need to explicitly specify communication between tasks.
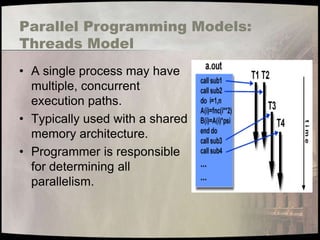
- 22. Parallel Programming Models: Threads Model • A single process may have multiple, concurrent execution paths. • Typically used with a shared memory architecture. • Programmer is responsible for determining all parallelism.
- 23. Parallel Programming Models: Message Passing Model • Tasks exchange data by sending and receiving messages. Typically used with distributed memory architectures. • Data transfer requires cooperative operations to be performed by each process. Ex.- a send operation must have a receive operation. • MPI (Message Passing Interface) is the interface standard for message passing.
- 24. Parallel Programming Models: Data Parallel Model • Tasks performing the same operations on a set of data. Each task working on a separate piece of the set. • Works well with either shared memory or distributed memory architectures.
- 25. Designing Parallel Programs: Automatic Parallelization • Automatic – Compiler analyzes code and identifies opportunities for parallelism – Analysis includes attempting to compute whether or not the parallelism actually improves performance. – Loops are the most frequent target for automatic parallelism.
- 26. Designing Parallel Programs: Manual Parallelization • Understand the problem – A Parallelizable Problem: • Calculate the potential energy for each of several thousand independent conformations of a molecule. When done find the minimum energy conformation. – A Non-Parallelizable Problem: • The Fibonacci Series – All calculations are dependent
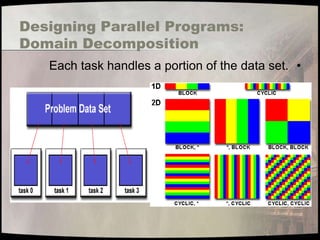
- 27. Designing Parallel Programs: Domain Decomposition Each task handles a portion of the data set. •
- 28. Designing Parallel Programs: Functional Decomposition Each task performs a function of the overall work •
- 29. Conclusion • Parallel computing is fast. • There are many different approaches and models of parallel computing. • Parallel computing is the future of computing.
- 30. References • A Library of Parallel Algorithms, www- 2.cs.cmu.edu/~scandal/nesl/algorithms.html • Internet Parallel Computing Archive, wotug.ukc.ac.uk/parallel • Introduction to Parallel Computing, www.llnl.gov/computing/tutorials/parallel_comp/#Whatis • Parallel Programming in C with MPI and OpenMP, Michael J. Quinn, McGraw Hill Higher Education, 2003 • The New Turing Omnibus, A. K. Dewdney, Henry Holt and Company, 1993
- 31. Case Study Developing Parallel Applications On the Web using Java mobile agents and Java threads
- 32. My References : • Parallel Computing Using JAVA Mobile Agents By: Panayiotou Christoforos, George Samaras ,Evaggelia Pitoura, Paraskevas Evripidou • An Environment for Parallel Computing on Internet Using JAVA By:P C Saxena, S Singh, K S Kahlon




