Practitioner perspective-erp-on-hana-and-fi-analytics 2015
- 1. SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 1 Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics Summary This document provides an introductory and practical overview of FI / AR, as well as, HANA Reporting – via an illustrative “End-to-end HANA Modelling: From SAP FI business process to SAP Report presentation” scenario. Perquisites: For easy reading, basic HANA terminology and Accounting double-entry concept are needed. Please refer to my earlier document for a refresher on fundamental HANA – https://www.scribd.com/doc/248694989/Practitioner-Perspective-HANA-vs-BW7-Modelling
- 2. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 2 Author Bio Benedict Yong is an SAP practitioner, experienced in Business Intelligence Consultation and ERP Support. Due to his varied working exposure in the SAP space, he is able to integrate ERP business processes with cutting-edge reporting technologies. He holds a Masters in ERP (Finance focus), Bachelor of Management (Australia) and a Diploma in Business InfoTech (Singapore). He is familiar with the Consulting and Support environments, with his various Project Lead & Consultant roles. He is situated in Singapore and is bilingual in English and Mandarin. He can be contacted at [email protected]. Note: credits given on the last page.
- 3. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 3 Table of Contents Objective.......................................................................................................................................................4 Introduction ...............................................................................................................................................4 The HANA Advantage ...............................................................................................................................6 HANA Reporting Options...........................................................................................................................7 SAP Finance Overview .................................................................................................................................8 Overview of SAP FI ...................................................................................................................................8 Details of FI Business Process ................................................................................................................10 SAP Techno-functional Analysis..................................................................................................................12 The Payment Business Process ..............................................................................................................12 The Payment SAP Transaction................................................................................................................13 Technology Architecture..............................................................................................................................16 HANA Reporting Landscape....................................................................................................................16 Building a HANA Model ...........................................................................................................................17 Interpreting the Report.............................................................................................................................23 Conclusion..................................................................................................................................................27 Reference...................................................................................................................................................28
- 4. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 4 Objective Introduction SAP ERP is an OLTP system optimized for writing business transactions. It supports real-time operational reporting – albeit having little efficacy. While SAP BW is a reporting and analytics environment, it is positioned to be at the strategic-level reporting. The operational level reporting gap is never properly addressed. Hence, the natural evolution of HANA Live arises. SAP AG defines HANA Live as “Real-Time operational reporting directly on your Suite on HANA system [e.g. ERP on HANA, CRM on HANA] without any redundancy or latency. Alternatively in a sidecar scenario next to your existing SAP Business Suite deployment”. We also need to understand that HANA Live (on ERP) is not the same thing as SAP BW; both in term of physical server, and the reporting space that they serve. They will each serve a different role depending on the requirements of individual organizations. In fact, I manage and architect these two applications within the same organization - ensuring consistent and well-rationalized solution distribution. Here is a generic diagram to show the data flow in HANA Live vs BW: There will probably be questions on: • the technology underlying HANA platform? • how we should position BW with the introduction of HANA? • how does HANA Modeling works step-by-step? Please refer to my earlier document – https://www.scribd.com/doc/248694989/Practitioner-Perspective-HANA-vs-BW7- Modelling – which contains the earlier questions that I had when I first encountered HANA.
- 5. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 5 The objective of this paper will be to provide a hands-on illustration for “End-to-end HANA Modelling: From SAP FI business process to SAP Report presentation”. We will utilized SAP HANA Modelling techniques and present the data with SAP ALV Grid (ABAP) and SAP Lumira technologies. We will navigate this paper in the following 4 steps: 1. Getting to know HANA Reporting 2. Gaining SAP ERP techno-functional understanding (from double-entry to transactions to tables) 3. Getting to know the architecture of HANA landscape (from data model to processing logic to presentation layer) 4. Integrating the above information and Building a HANA Report
- 6. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 6 The HANA Advantage HANA Reporting has many advantages. We noted two prominent ones: Performance – Data is accessed directly from base tables in-memory. To maximize performance further, HANA introduces the Code-Pushdown paradigm. ABAP programs, traditionally, query the database and perform iterative manipulation of data at the application level. However, modelling done in HANA are performed at the database level. Hence, it is recommended to ‘push-down’ data manipulation (where possible) to the database level – this will reduce the data transfer volume and optimized codes execution. Scalability – Mapping can simply be done with HANA Studio Graphical Interface or HANA ubiquitous SQL Scripting. This is actually one up from SAP BW standard contents which keeps its business logic cryptically embedded into its transformation mapping (one after another). HANA Graphical Interface HANA SQL Scripting
- 7. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 7 HANA Reporting Options HANA Modelling – this allows developer to perform Modelling directly on the base ERP tables (such BSEG, MSEG, VBRP, etcs). Traditionally in BW/ABAP, we build once and seldom perform massive changes as re-engineering takes up considerable effort and checking. Canned reports are acceptable then. HANA means speed, timely and flexible – to take harness this advantage, we have to possess sufficient techno-functional knowledge for agile business requirements. HANA Live Content - HANA Live comes with pre-defined model which we can use on-the-fly. There are many packages that we can import for use. Here are two useful examples: In the “SAP HANA Analytics for ERP” package, there are about 1000+ simple reports (eg. “Billing Document Header”). The reports are developed using HANA Information View Modelling. Refer to help.sap.com for more details: http://help.sap.com/saphelp_hba/helpdata/en/8d/60d3289497430c86bc1465662559c8/conte nt.htm If “SAP Simple Finance Add-On 1.0” is included into Suite on HANA, then the “SAP Smart Financials” advanced package can be imported. This will allow for more analytics level reports to be available (eg Customer Aging Report, Line Item Based Analytics). Refer to help.sap.com for more details: http://help.sap.com/saphelp_sfin100/helpdata/en/cb/f6d652b072ff25e10000000a4450e5/con tent.htm Modelling for Simple Report (“Billing Document Header”) User Interface for Analytics Report (“Overdue Receivables”)
- 8. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 8 SAP Finance Overview Overview of SAP FI SAP Finance (SAP FI) follows the accounting principles closely especially the bookkeeping principles which includes double-entry, control account, sub-ledgers concepts. The end result of financial processes are financial statements. These statements provide an overview of an organization’s profitability and financial position. The SAP FI processes are broken down into: • General Ledger • Account Payable • Account Receivable • Asset Accounting Business transactions can be updated directing into the FI modules or derived from the Logistics modules (SD, MM). The following diagram depicts a generic integration overview of finance with logistics, the finance sub- modules and the key logistics objects:
- 9. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 9 The relationship of General Ledger (GL) and sub-ledgers (AP, AR, AA) are based on accounting concept of “control account”. The GL module provides the total amount owed to creditors, owed by debtors, dollar value of fixed asset classes and the overall Balance Sheet statement. The sub-ledgers provide detail information of which specific vendor we owe what amount, and how many actual machinery we have. If an account is set as reconciliation level, no posting is possible at that account. We have to post it into the sub- ledgers which will rollup back to the total reconciliation account. Each customer (or vendor) has their reconciliation account setup in their Company Code MasterData view – this ensure all postings (except for special GL items) to the customers are reconcilable at the reconciliation level. Additionally, in bookkeeping, we use Debit to add and Credit to minus. SAP uses the debit/credit indicator for this (Debit = S, Credit = H). Here is an illustration of a Balance Sheet statement in the General Ledger and how the sub-modules (AP, AR, AA) are related:
- 10. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 10 Details of FI Business Process For our purpose, we will choose the Account Receivable (AR) process to analyze. What is Account Receivable? The term receivables refer to accrual transactions. Accounts Receivables occur when customer have bill outstanding with us (just as Accounts Payables are from the vendor side). In real business world, many transactions are on accrual basis (instead of cash payment). And there are also agreed payment terms, due baseline dates and prompt discounts. How does Account Receivable works? A typical cash sales transaction will increase bank balance and update sales revenue. (Dr Bank, Cr Sales Revenue). In accounting, all transactions have at least two legs (one debit, one credit) and the net amount of both side will tally. An accrual sales transaction will update sales revenue but instead of increase bank, it increase the debt of the customer – as cash has not yet been received (Dr Customer, Cr Sales Revenue). Only when the customer has done cash payment, we will offset the debt of the customer and increase bank (Cr Customer, Dr Bank). When the two transactions are completed, the customer account will be net zero, resulting in entries similar to those of cash sales (Dr Bank, Cr Sales Revenue). Why go thru such effort if the end result is the same as cash sales? This is to keep the books as updated as per period, for thousands of transactions that are dragged across months and years! Here is an AR double-entry transaction: Customer Samsung (GL = “301300”) bought some goods from us at $3000. Amount received from customer was deposited to DBS bank (GL = “113100”)
- 11. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 11 As mentioned earlier, AR entries can be posted directly from FI or it can be derived from SD. The below diagram depicts the overall flow of AR in relation to SD. Transaction Code (tcode) FD03 and FBL5N are very useful - to view the Customer Master setting and Customer Balance amount, respectively. AR transaction typically starts from a Sales Order in the Sales Cycle (if SAP SD is implemented). However, we can also post direct customer invoice (and credit memo) with FB70 - this creates customer invoice while crediting a revenue account. F-28 is able to pay and clear invoices. Pay means customer outstanding amount is reduced; clear means the paid amount will be matched back to specific invoices. For credit memo, it is an offset figure, there is no money flow. Hence, we need to clear the credit amount to match a specific invoice with F-32.
- 12. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 12 SAP Techno-functional Analysis We shall now move into techno-functional analysis – Mapping Double-entry to SAP Transaction to Database Table. We should know at what stage what transactions are used. And how those transactions are recorded into the database tables. This intricate knowledge will have a direct impact on how we present the data in charts later on. The Payment Business Process • SAP uses document type to control the nature of the document posted. For Customer invoice, by default “DR” (other types include D1, D2, RM, etcs). When a customer is over-invoiced, we post a reduction document known as a Credit Memo, which use “DG” as document type. Payment uses “DZ” document type. • When invoice is posted against a customer, there will be a debit entry (SHKZG = ‘S’) in the BSID table. • When a payment is posted, the entry will be removed from BSID. • However, an invoice can be paid partially, in this case, a credit entry (SHKZG = ‘H’) will be inserted into BSID to offset the original invoiced amount. • After an invoice is fully paid, the entries are removed from BSID and inserted into BSAD.
- 13. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 13 The Payment SAP Transaction We use the tcode FBL5N to view the invoice of a customer. From the illustration, we can see customer 200252 have been invoiced 6 times (document type DR, D1). No payment has been done yet. Entry of open items will be shown in the BSID table. All invoice items are debited.
- 14. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 14 We use the tcode F-28 allow us to post payment against a customer. F-28: Screen 1 F-28: Screen 2 In F-28, we can choose which invoice to knock off. In our example, we choose to perform partial payment. We receive an amount of $15000. We will use it to do One full payment ($7041 / $7041) + One partial payment ($7958 / $9095)
- 15. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 15 In F-28, payment documents has been posted (document type DZ). The full payment amount ($7041) is moved to closed item (Green Status) The partial payment amount ($7958) is included as a credit offset to original invoice ($9095) open item (Red Status). The remaining amount must be paid to move these two lines over to closed item (Green Status) Once F-28 is performed. The first invoice will be removed from BSID table (full payment) and an entry will be inserted into BSAD table. For the second partial payment line, an offset entry will be posted (credit) – entry will still remain in BSID, till full payment.
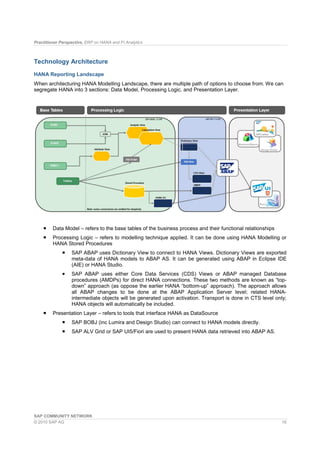
- 16. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 16 Technology Architecture HANA Reporting Landscape When architecturing HANA Modelling Landscape, there are multiple path of options to choose from. We can segregate HANA into 3 sections: Data Model, Processing Logic, and Presentation Layer. Data Model – refers to the base tables of the business process and their functional relationships Processing Logic – refers to modelling technique applied. It can be done using HANA Modelling or HANA Stored Procedures SAP ABAP uses Dictionary View to connect to HANA Views. Dictionary Views are exported meta-data of HANA models to ABAP AS. It can be generated using ABAP in Eclipse IDE (AIE) or HANA Studio. SAP ABAP uses either Core Data Services (CDS) Views or ABAP managed Database procedures (AMDPs) for direct HANA connections. These two methods are known as “top- down” approach (as oppose the earlier HANA “bottom-up” approach). The approach allows all ABAP changes to be done at the ABAP Application Server level; related HANA- intermediate objects will be generated upon activation. Transport is done in CTS level only; HANA objects will automatically be included. Presentation Layer – refers to tools that interface HANA as DataSource SAP BOBJ (inc Lumira and Design Studio) can connect to HANA models directly. SAP ALV Grid or SAP UI5/Fiori are used to present HANA data retrieved into ABAP AS.
- 17. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 17 Building a HANA Model Up till now, we have gained sufficient knowledge of the FI process and the HANA landscape. We shall apply this knowledge into building a “Customer Days Outstanding Report”. • Data will be taken from base tables BSID / BSAD. • The tables will be join using HANA Analytical View. • The presentation layer will be in SAP ALV Grid and SAP Lumira. The report will be using the following key fields: Column Description Table/Field Customer Customer BSID.KUNNR Baseline Date Used to track the due date BSID.ZFBDT Debit/Credit Indicator Debit/Credit indicator BSID.SHKZG Amount Posting Amount (value depends on context, such as document type, debit/credit indicator) BSID.DMBTR DUE_AMT If Debit/Credit = ‘H’, DUE_DAY = Amount X (-1) else DUE_DAY = Amount Calculated Keyfigure DUE_DAY DUE_DAY = Baseline Date – Today Calculated Keyfigure GRADE If (Baseline Date – Today) < 100 Grade = ‘A’ Elseif (Baseline Date – Today) < 150 Grade = ‘B’ Else Grade = ‘C’ Calculated Attribute
- 18. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 18 In HANA Studio, we will do a left-inner join between BSID and BSAD. However for “Customer Days Outstanding Report”, fields used will mainly come from BSID – as it contain all the outstanding amount. The result of the Analytical View can be seen in “data preview” tab. This figure should tally with the FBL5N balance
- 19. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 19 Presentation Layer using SAP ABAP (using Dictionary View) In ABAP in Eclipse IDE (AIE), we can generate Dictionary View and code/compile ABAP altogether. We will need AIE or HANA Studio (ABAP Perspective) to export HANA View into Dictionary View. Output is shown i the illustration
- 20. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 20 With Dictionary View available in ABAP AS, we can easily display the values with standard ALV Grid.
- 21. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 21 The AIE also allows development of CDS View (aka DDL Source Object) and AMDP ABAP Class. The below shows a simple CDS View scripting that reference our earlier Dictionary View. During the CDS View creation, an SQLView will be automatically created to access HANA. Likewise for AMDP Class, a DB Procedure object will be automatically created to access HANA. Alternatively, we can just do SQL scripting onto the base tables in the CDS View and this view can be called by ABAP subsequently.
- 22. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 22 Presentation Layer using SAP Lumira Visualization In Lumira, we are able to visualize the Amount outstanding per Customer breakdown by Aging Grade.
- 23. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 23 Interpreting the Report Upon close analysis of the chart for 5 customers, we can see that the most recent posting (Grade A), are negative in value. This is because those are partial payments – it has not been fully knocked off. It really depends on how the users wish to represent this data. It can be totally fine this way, or user may request we adjust the modelling to do a net offset.
- 24. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 24 The more interesting question is what will the graph looks like if we have completely covered the partial payment. Again, this requires techno-functional investigation. Looking at FBL5N, we need to payment $1136 = $9095 - $7958 We will use F-28 to post the remaining amount for the partial payment.
- 25. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 25 The transaction will move the two open postings into close item. Entries updated in BSAD.
- 26. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 26 The closing the partial payment for Customer 20052 will result in a shorter due amount The screen before closing the partial payment The screen after closing the partial payment
- 27. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 27 Conclusion The evolution of the HANA technology has improved our developmental productivity and business efficacy. HANA offers greater flexibility with more refined and in-time development environment and approaches. We are free to choose among different presentation tools and coding approaches. The new breed of HANA ‘developer’ will need strong foundation in data modelling concept (including the ability to discern between operational and strategic reporting), in-depth techno-functional knowledge, specific technological knowledge (SQL, ABAP, Client Scripting).
- 28. Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK © 2010 SAP AG 28 Reference 1. Practitioner Perspective, Modelling HANA vs BW7 https://www.scribd.com/doc/248694989/Practitioner-Perspective-HANA-vs-BW7-Modelling 2. SAP HANA Live Overview and Installation http://help.sap.com/hba 3. “SAP HANA Live for SAP ERP” Add-On http://help.sap.com/saphelp_hba/helpdata/en/8d/60d3289497430c86bc1465662559c8/content.htm 4. “SAP Simple Finance” Add-On http://help.sap.com/saphelp_sfin100/helpdata/en/cb/f6d652b072ff25e10000000a4450e5/content.htm 5. SAP Smart Business for the SAP Simple Finance Add-On http://help.sap.com/saphelp_ssb_sfin_100/helpdata/en/60/671753bf213047e10000000a44538d/fram eset.htm 6. SAP End-to-End Development (ABAP) Example in SAP NetWeaver 7.4 & SAP HANA http://www.sdn.sap.com/irj/scn/go/portal/prtroot/docs/library/uuid/b01089ed-dead-3110-f28e- caa12aeb5e27?QuickLink=index&overridelayout=true&59223304044850 7. SAP ABAP CDS - Language Elements http://help.sap.com/abapdocu_740/en/index.htm?file=abencds_annotations.htm




![Practitioner Perspective, ERP on HANA and FI Analytics
SAP COMMUNITY NETWORK
© 2010 SAP AG 4
Objective
Introduction
SAP ERP is an OLTP system optimized for writing business transactions. It supports real-time operational
reporting – albeit having little efficacy. While SAP BW is a reporting and analytics environment, it is
positioned to be at the strategic-level reporting. The operational level reporting gap is never properly
addressed. Hence, the natural evolution of HANA Live arises.
SAP AG defines HANA Live as “Real-Time operational reporting directly on your Suite on HANA system [e.g.
ERP on HANA, CRM on HANA] without any redundancy or latency. Alternatively in a sidecar scenario next
to your existing SAP Business Suite deployment”.
We also need to understand that HANA Live (on ERP) is not the same thing as SAP BW; both in term of
physical server, and the reporting space that they serve. They will each serve a different role depending on
the requirements of individual organizations. In fact, I manage and architect these two applications within the
same organization - ensuring consistent and well-rationalized solution distribution.
Here is a generic diagram to show the data flow in HANA Live vs BW:
There will probably be questions on:
• the technology underlying HANA platform?
• how we should position BW with the introduction of HANA?
• how does HANA Modeling works step-by-step?
Please refer to my earlier document – https://www.scribd.com/doc/248694989/Practitioner-Perspective-HANA-vs-BW7-
Modelling – which contains the earlier questions that I had when I first encountered HANA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practitioner-perspective-erp-on-hana-and-fi-analytics2015-200124051323/85/Practitioner-perspective-erp-on-hana-and-fi-analytics-2015-4-320.jpg)