Predicting Method Crashes with Bytecode Operations
- 1. Predicting Method Crashes with Bytecode Operations Sunghun Kim Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, China Thomas Zimmermann Microsoft Research, USA Rahul Premraj VU University Amsterdam, The Netherlands Nicolas Bettenburg Queen’s University, Canada Shivkumar Shivaji University of California, Santa Cruz, USA © Microsoft Corporation
- 3. capture and replay + prediction © Microsoft Corporation
- 4. Capture and Replay © Microsoft Corporation
- 5. ReCrash Technique Goal: Convert a crash into a set of unit tests 1. Monitoring: maintain a shadow stack – Contains a copy of each method argument – On program crash, write the shadow stack to a file 2. Test generation: create many unit tests For each stack frame, create one unit test: – Invoke the method using arguments from the shadow stack – If the test does not reproduce the crash, discard the test Slide from: http://www.slideshare.net/hunkim/recrash-making- crashes-reproducible-by-preserving-object-states © Microsoft Corporation
- 6. Cost of Monitoring Key cost of ReCrash: copying arguments to shadow stack Tradeoff: less information in shadow stack ⇒ lower chance of reproducing crashes Monitor fewer methods: Ignore methods not likely to crash © Microsoft Corporation
- 7. ReCrash+ Technique Goal: Convert a crash into a set of unit tests 1. Monitoring: maintain a shadow stack – Contains a copy of each method argument for methods predicted to crash – On program crash, write the shadow stack to a file 2. Test generation: create many unit tests For each stack frame, create one unit test: – Invoke the method using arguments from the shadow stack – If the test does not reproduce the crash, discard the test Slide adapted from: http://www.slideshare.net/hunkim/recrash- making-crashes-reproducible-by-preserving-object-states © Microsoft Corporation
- 9. crash defect prediction © Microsoft Corporation
- 10. From Defect to Crash 1. The programmer creates a defect – an error in the code. 2. When executed the defect creates an infection – an error in the state. 3. The infection propagates. 4. The infection causes a crash. Slide adapted from companion materials to Why Programs Fail, 2nd Edition. A Guide to Systematic Debugging, by Andreas Zeller, Morgan Kauffman. © Microsoft Corporation
- 11. Approach Identify crashed methods Gene © Microsoft Corporation
- 12. Approach Generate features from Bytecode © Microsoft Corporation
- 13. Approach features from Bytecode Build model © Microsoft Corporation
- 14. Step 1: Identify Crashed Methods infoZilla Bug report infoZilla image by Nicolas © Microsoft Corporation Bettenburg
- 15. Step 1: Identify Crashed Methods infoZilla Bug report infoZilla image by Nicolas © Microsoft Corporation Bettenburg
- 16. Step 2: Generate Features Bytecode Control flow graph (basic blocks) © Microsoft Corporation
- 17. Step 2: Generate Features © Microsoft Corporation
- 18. Step 3: Build Classifier © Microsoft Corporation
- 19. Experiments 1. Evaluating crash prediction – Within-project classification – Cross-project classification – Significant features (see paper) – Impact of “throws” statements (see paper) 2. Reproducing crashes with ReCrash+ © Microsoft Corporation
- 20. Evaluating Crash Prediction • Within-project classification: ten-fold cross validation • Cross-project validation: train on one project and test on the other • Baseline: complexity metrics Size of Method (in Bytes), Number of Conditional Statements, Number of Scalar Locals, Number of Vector Locals, Length of Local Identifiers, McCabe Complexity, Data Structure Complexity, Nesting Level Complexity, Halstead complexity measures © Microsoft Corporation
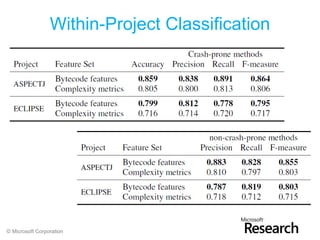
- 21. Within-Project Classification © Microsoft Corporation
- 22. Cross-Project Classification © Microsoft Corporation
- 23. Reproducing Crashes • Train classifier using the ECLIPSE corpus • Classify methods from a different project called SVNKit. – 2,347 methods of which 27% were classified as crash-prone • Apply ReCrash+: monitor only those methods predicted to be crash-prone – Three crashes from original ReCrash paper © Microsoft Corporation
- 24. Reproducing Crashes All 3 crashes from SVNKit were successfully reproduced by ReCrash+. Runtime overhead decreased: © Microsoft Corporation
- 25. Reproducing Crashes Only a subset of methods had to be monitored: © Microsoft Corporation
- 26. Conclusion • Monitoring crash-prone methods reduced the overhead significantly at almost no cost. • Opportunity for capture and replay tools to reduce overhead with prediction models. • Value of project’s history for the identification of crash-prone methods. • Potential value of Bytecode features for prediction models. © Microsoft Corporation