Price PRedictions for Crypto-Assets Using Deep Learning
Download as PPTX, PDF1 like671 views
This slide deck provides an overview of the universe of prediction techniques applied to cryptocurrencies. The content covers emerging prediction models in the deep learning field and how they apply to crypto-assets.
1 of 32
Downloaded 23 times































Ad
Recommended
Cryptocurrency Price Predictions



Cryptocurrency Price Predictionsintotheblock Show me, don’t tell me should be the mantra when it comes to cryptocurrency predictions! A lot of written research but no real world implementations. At IntoTheBlock, we’ve spent months working on predictive models for crypto-assets. We have failed a lot and we have learned a lot. So it is time to show some results!
In this session, we will show you deep neural network architectures that are predicting the price of crypto-assets in real-time based on different goals. We will share some of the lessons we learned trying to predict recent market events and some of the new ideas we are working on. We will showcase different predictive models and reveal some of their most recent predictions.
Find out more at https://app.intotheblock.com/
How does blockchain work



How does blockchain workShishir Aryal This document provides an overview of blockchain technology, how it works, and its applications. It defines blockchain as a decentralized digital ledger consisting of blocks that record transactions across networks so past transactions cannot be altered. The document outlines the history of blockchain, how it provides security through hashing and proof-of-work algorithms, and how cryptocurrencies use blockchain to be immune from counterfeiting without central authorities. It then provides an example of how a basic bitcoin transaction occurs between parties on the blockchain network.
Bitcoin Price Prediction



Bitcoin Price PredictionKadambini Indurkar This document provides an overview of using deep learning algorithms like LSTM and sentiment analysis to predict bitcoin prices. It discusses neural networks and RNNs, why LSTMs are better than RNNs at capturing long-term dependencies. It describes implementing an LSTM model to predict prices from historical data and analyzing sentiment from Twitter tweets. Testing was done and results showed the model could predict prices. Future work includes applying it to other cryptocurrencies and improving performance.
Crypto & Crpyocurrencies Intro



Crypto & Crpyocurrencies IntroTal Shmueli The document provides an overview of cryptocurrencies and digital currencies. It discusses why crypto is important for information security, IP protection, and protection against ransomware. It then outlines a plan to cover Bitcoin and its history, characters, mechanisms, blockchain, symmetric and asymmetric crypto algorithms, breaking crypto difficulties, and comparisons to other digital currencies like Litecoin. Practical exercises on wallets, transfers, and exchanges are also mentioned. Additional advanced topics like SegWit, zero-knowledge proofs, and homomorphic encryption are included as bonuses.
Blockchain Consensus Protocols



Blockchain Consensus ProtocolsMelanie Swan Innovation in Byzantine consensus protocols is helping decentralized networks scale up and become highly performant, possibly faster than centralized networks. Investment growth in Bitcoin and FinTech startups, and enterprise blockchain applications in development in multiple sectors
NFTs - Common Use Cases and Legal Considerations (Japan)



NFTs - Common Use Cases and Legal Considerations (Japan)Joerg Schmidt The presentation outlines common use cases for NFTs, including digital art, collectibles, blockchain games, and IP management. Legal and regulatory considerations can be found on the last few slides.
Ethereum Blockchain explained



Ethereum Blockchain explainedEthWorks Slides for presentation "Mission to disrupt everything", originally presented on Warsaw University of Technology .
artificial intelligence ppt.pptx



artificial intelligence ppt.pptxBrijithaGokula Artificial intelligence
what is AI?
History
foundations of AI
Types of AI
Applications of AI
machine learning and applications
AI Vs Machine learning
Deep learning- advantages and disadvantages
Applications of Deep learning
Why is deep learning better than machine learning
Deep learning vs machine learning
Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
Architecture of ANN
Types of ANN
Applications of ANN
Softwares of ANN and their applications
Introduction to Blockchain



Introduction to BlockchainAIMDek Technologies This document provides an introduction to blockchain technology. It defines key blockchain concepts like blocks, blockchains, consensus algorithms, and mining. It explains how blockchain works through transactions being grouped into blocks and added to the distributed ledger across nodes in the network. Examples of real-world blockchain applications are given for voting systems, supply chain management, and healthcare data sharing. Benefits of blockchain include transparency, decentralization, and open source development, while challenges include limited production experience and need for customer education.
Understanding Blockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology



Understanding Blockchain: Distributed Ledger TechnologySuraj Kumar Jana A complete introduction to Distributed Ledger Technology and Blockchain. Also, get introduced to Hyperledger, an open source permissioned blockchain framework by The Linux Foundation.
Price Predictions for Cryptocurrencies



Price Predictions for CryptocurrenciesJesus Rodriguez This slide deck details some of the lessons we learned building price prediction models for cryptocurrencies. The session provides examples and practical tips about the challenges of price predictions in crypto asset markets.
Fundamental Analysis for Crypto Assets



Fundamental Analysis for Crypto AssetsJesus Rodriguez This document discusses using machine intelligence to analyze crypto-assets. It argues that traditional financial analysis methods do not work for crypto-assets due to a lack of fundamentals data and limited historical price data. It proposes that a new form of technical and quantitative analysis is needed based on blockchain data signals. Machine learning could help identify patterns in blockchain data to better understand and potentially predict the behavior of crypto-assets. The presenter is the CTO of IntoTheBlock and believes machine learning has potential to improve crypto-asset analysis by learning from real-time behavior and correlating on-chain data with price movements.
Presentation on cryptocurrency



Presentation on cryptocurrencyDhruv Gandhi This document provides an overview of cryptocurrency, including definitions of key terms like cryptocurrency and real currency, examples of major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Litecoin, and classifications of cryptocurrencies. It also discusses the benefits of cryptocurrency like fast and cheap transactions, decentralized control, and transparency, as well as risks around implementation challenges, instability, and lack of awareness. Major cryptocurrencies are differentiated based on factors like the algorithms and communities behind them.
Ethereum



EthereumNexThoughts Technologies Ethereum is an open software platform based on blockchain technology that enables developers to
build and deploy decentralized applications.
Ethereum is a distributed public blockchain network.
While the Bitcoin blockchain is used to track ownership of digital currency (bitcoins), the Ethereum
blockchain focuses on running the programming code of any decentralized application.
Ether is a cryptocurrency whose blockchain is generated by the Ethereum platform. Ether can be
transferred between accounts and used to compensate participant mining nodes for computations
performed.
Introduction to Cryptocurrency (Bitcoin)



Introduction to Cryptocurrency (Bitcoin)Kashif Khans Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency created in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a decentralized peer-to-peer network, allowing anonymous transactions at low cost. New bitcoins enter the market only through mining, where users solve mathematical problems. While the legal status of bitcoin varies by country, its popularity has driven demand and market price despite criticism it is a speculative bubble.
An Investor's Guide to Web3 / Crypto / Blockchain



An Investor's Guide to Web3 / Crypto / BlockchainBernard Leong Bernard Leong provided a masterclass on investing in web3. He discussed his own journey in crypto from 2008 to present. He covered the basics of blockchain, different layers and applications. Leong outlined tools for due diligence like Etherscan and Nansen AI. He explained financing models for web3 startups and factors to consider like tokenomics, go-to-market strategies, and regulatory risks. Finally, Leong proposed a model for a $1M web3 angel fund focusing on DeFi, gaming, and SaaS with a mix of angel investing and trading strategies.
Blockchain



BlockchainMohit Singh This document provides an overview of blockchain technology. It discusses that blockchain was first introduced in 2008 as a way to facilitate digital transactions without a central authority. Blockchain uses cryptography, a digital ledger, and a consensus mechanism to securely record transactions. The blockchain is made up of blocks that contain cryptographic hashes linking them together. Miners use proof-of-work to verify transactions and are rewarded with cryptocurrency. Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered, providing transparency and security.
More Than Monitoring: How Observability Takes You From Firefighting to Fire P...



More Than Monitoring: How Observability Takes You From Firefighting to Fire P...DevOps.com For some, observability is just a hollow rebranding of monitoring, for others it’s monitoring on steroids. But what if we told you observability is the new way to find out why—not just if—your distributed system or application isn’t working as expected? Today, we see that traditional monitoring approaches can fall short if a system or application doesn’t adequately externalize its state.
This is truer as workloads move into the cloud and leverage ephemeral technologies, such as microservices and containers. To reach observability, IT and DevOps teams need to correlate different sources from logs, metrics, traces, events and more. This becomes even more challenging when defining the online revenue impact of a failed container—after all, this is what really matters to the business.
This webinar will cover:
The differences between observability and monitoring
Why it is a bigger challenge in a multicloud and containerized world
How observability results in less firefighting and more fire prevention
How new platforms can help gain observability (on premises and in the cloud) for containers, microservices and even SAP or mainframes
Quantum Blockchains



Quantum BlockchainsMelanie Swan Cryptography, entanglement, and quantum blocktime: Quantum computing offers a more scalable energy-efficient platform than classical computing and supercomputing, and corresponds more naturally to the three-dimensional structure of atomic reality. Blockchains are a decentralized digital economic system made possible by the 24-7 global nature of the internet.
Ethereum Tutorial - Ethereum Explained | What is Ethereum? | Ethereum Explain...



Ethereum Tutorial - Ethereum Explained | What is Ethereum? | Ethereum Explain...Simplilearn The document provides an overview of Ethereum, including its key features like cryptocurrency (Ether), smart contracts, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), decentralized applications (Dapps), and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). It discusses how Ether is used to pay for transactions and computational resources on the Ethereum network. It also explains how smart contracts are programs that facilitate exchanges without a central authority, and how the EVM executes smart contract code. Dapps are similar to traditional web applications, but run on a distributed network instead of centralized servers.
BLOCKCHAIN



BLOCKCHAINNitish sharma This document discusses blockchain technology and its potential applications. It defines blockchain as a shared, distributed ledger that allows participants in a business network to view transaction records. Blockchain addresses the problem of difficulty monitoring asset ownership and transfers in a trusted network by providing a permissioned, replicated shared ledger. The key properties that enable this are decentralization, strong authentication, and tamper resistance. The document also discusses public versus private blockchains and the challenges and opportunities blockchain poses for financial institutions in validating transactions without third parties.
Hands-on with data visualization in Kibana



Hands-on with data visualization in KibanaElasticsearch Interested in learning how to build charts, maps, dashboards, and reports in Kibana using Elasticsearch data? Learn how to get started with Kibana Lens, use Elastic Maps for detailed geospatial analysis, and create dashboards and PDF reports. We will show you how to get from data to insights with just a few clicks. After the session is complete, you'll have access to a hands-on lab environment so you can try it yourself.
Intro to Time Series 



Intro to Time Series InfluxData This document provides an introduction to time series data and InfluxDB. It defines time series data as measurements taken from the same source over time that can be plotted on a graph with one axis being time. Examples of time series data include weather, stock prices, and server metrics. Time series databases like InfluxDB are optimized for storing and processing huge volumes of time series data in a high performance manner. InfluxDB uses a simple data model where points consist of measurements, tags, fields, and timestamps.
Blockchain



BlockchainSoftware Infrastructure A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It uses cryptography to allow participants to interact securely and anonymously to validate transactions without a central authority. The technology began with Bitcoin and enables applications like cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and decentralized databases. Understanding blockchains requires grasping both technical aspects like distributed databases and consensus algorithms, as well as philosophical concepts like disintermediation.
Crypto 101



Crypto 101Marie Tatibouet If you're a total newbie in the crypto space, take the time to go through this presentation. Lots of helpful resources at the end!
What is Cryptocurrency?



What is Cryptocurrency?Rakesh Ranjan It was my first presentation on cryptocurrency during my sophomore year in college. This presentation covers the basic understanding of cryptocurrency, working of cryptocurrency, bitcoin, blockchain and it's the difference between normal currency and cryptocurrency.
Ethereum-Cryptocurrency (All about Ethereum) 



Ethereum-Cryptocurrency (All about Ethereum) عطاءالمنعم اثیل شیخ This document provides an overview of the Ethereum blockchain platform and smart contracts. It discusses what Ethereum is, how it works, and its key components. The document covers Ethereum wallets, transactions, tokens, and the Solidity programming language for building smart contracts. It provides information on running Ethereum nodes, clients, and testnets. The document serves as training material for a blockchain specialist program.
Introduction to Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)



Introduction to Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)Cygnet Infotech Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) allows businesses to use cloud-based solutions to build, host and use their own blockchain apps. Supply Chain a crucial BaaS use case suffers a major issue of the lack of traceability. BaaS offers transparency and traceability to the Supply Chain. Get in touch with experts of Cygnet to know more.
IntoTheBlock Webinar: Predicting Cryptocurrency Prices Using Deep Learning



IntoTheBlock Webinar: Predicting Cryptocurrency Prices Using Deep Learningintotheblock Check out the slides of our last webinar in which we:
- Show practical lessons and we have learned in our quest to build predictive models for crypto assets.
- Deep dive into different machine learning strategies that have proven successful in different times of the market and will openly discussed the challenges we faced.
- Showcase different prediction models for different crypto-assets and explore some advance ideas for both traders and researchers.
Practical Crypto Asset Predictions rev



Practical Crypto Asset Predictions revJesus Rodriguez This presentations outlines some of the key principles for building deep learning predictive models for crypto assets. The deck includes best practices and lessons learned that provide some perspectives about the challenges and solutions about using deep learning models in the crypto space.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Introduction to Blockchain



Introduction to BlockchainAIMDek Technologies This document provides an introduction to blockchain technology. It defines key blockchain concepts like blocks, blockchains, consensus algorithms, and mining. It explains how blockchain works through transactions being grouped into blocks and added to the distributed ledger across nodes in the network. Examples of real-world blockchain applications are given for voting systems, supply chain management, and healthcare data sharing. Benefits of blockchain include transparency, decentralization, and open source development, while challenges include limited production experience and need for customer education.
Understanding Blockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology



Understanding Blockchain: Distributed Ledger TechnologySuraj Kumar Jana A complete introduction to Distributed Ledger Technology and Blockchain. Also, get introduced to Hyperledger, an open source permissioned blockchain framework by The Linux Foundation.
Price Predictions for Cryptocurrencies



Price Predictions for CryptocurrenciesJesus Rodriguez This slide deck details some of the lessons we learned building price prediction models for cryptocurrencies. The session provides examples and practical tips about the challenges of price predictions in crypto asset markets.
Fundamental Analysis for Crypto Assets



Fundamental Analysis for Crypto AssetsJesus Rodriguez This document discusses using machine intelligence to analyze crypto-assets. It argues that traditional financial analysis methods do not work for crypto-assets due to a lack of fundamentals data and limited historical price data. It proposes that a new form of technical and quantitative analysis is needed based on blockchain data signals. Machine learning could help identify patterns in blockchain data to better understand and potentially predict the behavior of crypto-assets. The presenter is the CTO of IntoTheBlock and believes machine learning has potential to improve crypto-asset analysis by learning from real-time behavior and correlating on-chain data with price movements.
Presentation on cryptocurrency



Presentation on cryptocurrencyDhruv Gandhi This document provides an overview of cryptocurrency, including definitions of key terms like cryptocurrency and real currency, examples of major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Litecoin, and classifications of cryptocurrencies. It also discusses the benefits of cryptocurrency like fast and cheap transactions, decentralized control, and transparency, as well as risks around implementation challenges, instability, and lack of awareness. Major cryptocurrencies are differentiated based on factors like the algorithms and communities behind them.
Ethereum



EthereumNexThoughts Technologies Ethereum is an open software platform based on blockchain technology that enables developers to
build and deploy decentralized applications.
Ethereum is a distributed public blockchain network.
While the Bitcoin blockchain is used to track ownership of digital currency (bitcoins), the Ethereum
blockchain focuses on running the programming code of any decentralized application.
Ether is a cryptocurrency whose blockchain is generated by the Ethereum platform. Ether can be
transferred between accounts and used to compensate participant mining nodes for computations
performed.
Introduction to Cryptocurrency (Bitcoin)



Introduction to Cryptocurrency (Bitcoin)Kashif Khans Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency created in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a decentralized peer-to-peer network, allowing anonymous transactions at low cost. New bitcoins enter the market only through mining, where users solve mathematical problems. While the legal status of bitcoin varies by country, its popularity has driven demand and market price despite criticism it is a speculative bubble.
An Investor's Guide to Web3 / Crypto / Blockchain



An Investor's Guide to Web3 / Crypto / BlockchainBernard Leong Bernard Leong provided a masterclass on investing in web3. He discussed his own journey in crypto from 2008 to present. He covered the basics of blockchain, different layers and applications. Leong outlined tools for due diligence like Etherscan and Nansen AI. He explained financing models for web3 startups and factors to consider like tokenomics, go-to-market strategies, and regulatory risks. Finally, Leong proposed a model for a $1M web3 angel fund focusing on DeFi, gaming, and SaaS with a mix of angel investing and trading strategies.
Blockchain



BlockchainMohit Singh This document provides an overview of blockchain technology. It discusses that blockchain was first introduced in 2008 as a way to facilitate digital transactions without a central authority. Blockchain uses cryptography, a digital ledger, and a consensus mechanism to securely record transactions. The blockchain is made up of blocks that contain cryptographic hashes linking them together. Miners use proof-of-work to verify transactions and are rewarded with cryptocurrency. Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered, providing transparency and security.
More Than Monitoring: How Observability Takes You From Firefighting to Fire P...



More Than Monitoring: How Observability Takes You From Firefighting to Fire P...DevOps.com For some, observability is just a hollow rebranding of monitoring, for others it’s monitoring on steroids. But what if we told you observability is the new way to find out why—not just if—your distributed system or application isn’t working as expected? Today, we see that traditional monitoring approaches can fall short if a system or application doesn’t adequately externalize its state.
This is truer as workloads move into the cloud and leverage ephemeral technologies, such as microservices and containers. To reach observability, IT and DevOps teams need to correlate different sources from logs, metrics, traces, events and more. This becomes even more challenging when defining the online revenue impact of a failed container—after all, this is what really matters to the business.
This webinar will cover:
The differences between observability and monitoring
Why it is a bigger challenge in a multicloud and containerized world
How observability results in less firefighting and more fire prevention
How new platforms can help gain observability (on premises and in the cloud) for containers, microservices and even SAP or mainframes
Quantum Blockchains



Quantum BlockchainsMelanie Swan Cryptography, entanglement, and quantum blocktime: Quantum computing offers a more scalable energy-efficient platform than classical computing and supercomputing, and corresponds more naturally to the three-dimensional structure of atomic reality. Blockchains are a decentralized digital economic system made possible by the 24-7 global nature of the internet.
Ethereum Tutorial - Ethereum Explained | What is Ethereum? | Ethereum Explain...



Ethereum Tutorial - Ethereum Explained | What is Ethereum? | Ethereum Explain...Simplilearn The document provides an overview of Ethereum, including its key features like cryptocurrency (Ether), smart contracts, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), decentralized applications (Dapps), and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). It discusses how Ether is used to pay for transactions and computational resources on the Ethereum network. It also explains how smart contracts are programs that facilitate exchanges without a central authority, and how the EVM executes smart contract code. Dapps are similar to traditional web applications, but run on a distributed network instead of centralized servers.
BLOCKCHAIN



BLOCKCHAINNitish sharma This document discusses blockchain technology and its potential applications. It defines blockchain as a shared, distributed ledger that allows participants in a business network to view transaction records. Blockchain addresses the problem of difficulty monitoring asset ownership and transfers in a trusted network by providing a permissioned, replicated shared ledger. The key properties that enable this are decentralization, strong authentication, and tamper resistance. The document also discusses public versus private blockchains and the challenges and opportunities blockchain poses for financial institutions in validating transactions without third parties.
Hands-on with data visualization in Kibana



Hands-on with data visualization in KibanaElasticsearch Interested in learning how to build charts, maps, dashboards, and reports in Kibana using Elasticsearch data? Learn how to get started with Kibana Lens, use Elastic Maps for detailed geospatial analysis, and create dashboards and PDF reports. We will show you how to get from data to insights with just a few clicks. After the session is complete, you'll have access to a hands-on lab environment so you can try it yourself.
Intro to Time Series 



Intro to Time Series InfluxData This document provides an introduction to time series data and InfluxDB. It defines time series data as measurements taken from the same source over time that can be plotted on a graph with one axis being time. Examples of time series data include weather, stock prices, and server metrics. Time series databases like InfluxDB are optimized for storing and processing huge volumes of time series data in a high performance manner. InfluxDB uses a simple data model where points consist of measurements, tags, fields, and timestamps.
Blockchain



BlockchainSoftware Infrastructure A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It uses cryptography to allow participants to interact securely and anonymously to validate transactions without a central authority. The technology began with Bitcoin and enables applications like cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and decentralized databases. Understanding blockchains requires grasping both technical aspects like distributed databases and consensus algorithms, as well as philosophical concepts like disintermediation.
Crypto 101



Crypto 101Marie Tatibouet If you're a total newbie in the crypto space, take the time to go through this presentation. Lots of helpful resources at the end!
What is Cryptocurrency?



What is Cryptocurrency?Rakesh Ranjan It was my first presentation on cryptocurrency during my sophomore year in college. This presentation covers the basic understanding of cryptocurrency, working of cryptocurrency, bitcoin, blockchain and it's the difference between normal currency and cryptocurrency.
Ethereum-Cryptocurrency (All about Ethereum) 



Ethereum-Cryptocurrency (All about Ethereum) عطاءالمنعم اثیل شیخ This document provides an overview of the Ethereum blockchain platform and smart contracts. It discusses what Ethereum is, how it works, and its key components. The document covers Ethereum wallets, transactions, tokens, and the Solidity programming language for building smart contracts. It provides information on running Ethereum nodes, clients, and testnets. The document serves as training material for a blockchain specialist program.
Introduction to Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)



Introduction to Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)Cygnet Infotech Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) allows businesses to use cloud-based solutions to build, host and use their own blockchain apps. Supply Chain a crucial BaaS use case suffers a major issue of the lack of traceability. BaaS offers transparency and traceability to the Supply Chain. Get in touch with experts of Cygnet to know more.
Similar to Price PRedictions for Crypto-Assets Using Deep Learning (20)
IntoTheBlock Webinar: Predicting Cryptocurrency Prices Using Deep Learning



IntoTheBlock Webinar: Predicting Cryptocurrency Prices Using Deep Learningintotheblock Check out the slides of our last webinar in which we:
- Show practical lessons and we have learned in our quest to build predictive models for crypto assets.
- Deep dive into different machine learning strategies that have proven successful in different times of the market and will openly discussed the challenges we faced.
- Showcase different prediction models for different crypto-assets and explore some advance ideas for both traders and researchers.
Practical Crypto Asset Predictions rev



Practical Crypto Asset Predictions revJesus Rodriguez This presentations outlines some of the key principles for building deep learning predictive models for crypto assets. The deck includes best practices and lessons learned that provide some perspectives about the challenges and solutions about using deep learning models in the crypto space.
Machine Learning for Crypo-Assets



Machine Learning for Crypo-Assetsintotheblock This document discusses using machine learning for analyzing crypto assets. It begins with an introduction to machine learning and the differences between machine learning and statistics. It then discusses using machine learning for scenarios like blockchain deanonymization, investor profiling, factor identification, and price predictions. For each scenario, it provides an example machine learning model and the potential results. The document also discusses challenges for crypto data like lack of labeled datasets and introduces techniques like semi-supervised learning, transfer learning and neural architecture search that are relevant for crypto machine learning.
Bitcoin Price Predictions and Machine Learning: Some New Ideas and Results



Bitcoin Price Predictions and Machine Learning: Some New Ideas and Resultsintotheblock We have continued our work experimenting with cutting edge machine learning models for price predictions in the crypto space and have learned a lot of new things.
During this session we covered:
- The challenges of crypto-asset prediction models
- New trends and ideas we are excited about
- Some techs to follow
- A brief note about DeFi and crypto-quant models
Find out more at https://app.intotheblock.com/
ITB Webinar Series: Why Most Crypto Quant Strategies Fail



ITB Webinar Series: Why Most Crypto Quant Strategies Failintotheblock Quant strategies for crypto seem like a perfect match but does it really work? The reality is that most quant strategies for crypto asset fail. This is particularly true for strategies based in machine learning(ML) methods. But why? From data quality to market inefficiencies, the causes are many.
This session explores the fundamental causes of failure of ML-based quant strategies for crypto assets. We will illustrate each cause in the context of real world examples of crypto trades. Additionally, we will explore new ML techniques that can help to improve ML-based quant strategies in the crypto space.
How To Research Cryptotokens A Step-by-Step Guide.pdf



How To Research Cryptotokens A Step-by-Step Guide.pdfKezex (KZX) Researching cryptotokens involves several crucial steps to ensure informed decisions. First, analyze the project's whitepaper for its goals and technology. Second, evaluate the development team's credibility and experience. Third, examine the token's use case and market demand. Fourth, review the community's engagement and feedback. Fifth, check the project's code and updates on platforms like GitHub. Lastly, assess the token's market performance and historical data to gauge potential risks and rewards.
Types of Blockchain, AI and its future



Types of Blockchain, AI and its futureAarthi Srinivasan Types of Blockchain - permissioned vs. permissionless platforms
Types of AI - Unsupervised, Supervised and Reinforcement Learning, Deep Learning
Future of Blockchain and AI
Better Technical Analysis with Blockchain Indicators



Better Technical Analysis with Blockchain IndicatorsJesus Rodriguez The document discusses how technical analysis of cryptocurrency assets can be improved by incorporating blockchain indicators. It provides examples of how traditional technical analysis indicators like Fibonacci retracement levels, exponential moving averages, and Bollinger bands can be reinforced with complementary blockchain data on in-out money flows, exchange flows, unspent transaction output analysis, and active addresses. By combining on-chain behavioral data with price-based technical analysis, traders may gain a more robust view of market trends and investor sentiment. The document concludes that technical analysis patterns can inform blockchain indicators and vice versa, representing a promising new approach to cryptocurrency market evaluation.
Better Technical Analysis with Blockchain Indicators



Better Technical Analysis with Blockchain Indicatorsintotheblock Technical indicators(TA) remains the dominant method for analyzing trends in crypto-assets. Whether you love or hate TA, we can both agree on two things: it is extremely popular and has some very well-known limitations. It is very common to complement TA strategies with other metrics and indicators in order to improve the analytics. In the case of crypto assets, blockchain metrics provide a very intriguing complement to TA methods.
This session presents a series of blockchain metrics that can complement traditional TA indicators. We show several examples that illustrate how the combination of TA and blockchain indicator leads to more complete, objective and robust analysis about the behavior of crypto assets.
Machine Learning and Blockchain by Director of Product at Target



Machine Learning and Blockchain by Director of Product at TargetProduct School Product Management Event Held at the Product Conference in Silicon Valley.
Aarthi Srinivasan, Director of Product at Target, shared her information on tech singularity. She gave an introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain, and talked about the different types of AI and blockchain. She also discussed the intersection between AI and Blockchain.
Fascinating Metrics About Crypto-Assets



Fascinating Metrics About Crypto-Assetsintotheblock Our CEO keynote at the Crypto Assia Summit.
Key takeaways:
Why crypto assets need a new type of analysis
- Fascinating blockchain indicators
- Blockchain as a complement of order book and future indicators
- Putting it all together: Blockchain indicators + technical analysis
The Rise and Fall of Cryptocurrencies: Defining the Economic and Social Value...



The Rise and Fall of Cryptocurrencies: Defining the Economic and Social Value...Petar Radanliev This paper contextualises the common queries of "why is crypto crashing?" and "why is crypto down?", the research transcends beyond the frequent market fluctuations to unravel how cryptocurrencies fundamentally work and the step-by-step process on how to create a cryptocurrency.
What Are the Trends Shaping the Future of Crypto Launchpad Development in 2025



What Are the Trends Shaping the Future of Crypto Launchpad Development in 2025Blockchainx In this PPT about Trends Shaping the Future of Crypto Launchpad Development in 2025 by BlockchainX
Beyond Bitcoin_ Crypto Investment in Altcoins.docx



Beyond Bitcoin_ Crypto Investment in Altcoins.docxcryptotrend16 Bitcoin may be the king of crypto, but it's far from the only investment worth considering. Altcoins—alternative cryptocurrencies—offer incredible opportunities for portfolio diversification, high-growth potential, and innovative blockchain applications. But with thousands of options available, how do you pick the right ones?
This in-depth guide, “Beyond Bitcoin: Crypto Investment in Altcoins,” explores everything you need to know about investing in altcoins. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just stepping into the crypto space, this article provides actionable insights to help you navigate the altcoin market with confidence.
We break down the key reasons why altcoins matter, including their role in portfolio diversification, DeFi growth, and emerging blockchain technologies. You’ll learn how to evaluate altcoins effectively, analyzing factors like technology, tokenomics, and developer activity.
Want to trade altcoins successfully? This guide covers trading strategies, risk management techniques, and expert-backed market insights to help you make smarter investment decisions. Plus, we highlight the power of crypto communities, market sentiment, and real-time trading signals in shaping altcoin trends.
Backed by Investors Collective’s commitment to providing expert insights and real-time updates, this article ensures you’re well-equipped to make informed investment choices. We also tackle frequently asked questions about altcoin investing, covering everything from staking rewards to security best practices.
If you're looking to go beyond Bitcoin and unlock the full potential of the crypto market, this guide is a must-read. Join the Investors Collective community, stay ahead of the curve, and start investing in altcoins with confidence today!
7th Webinar: Patterns, Predictions and Fascinating Metrics from Cryptocurrenc...



7th Webinar: Patterns, Predictions and Fascinating Metrics from Cryptocurrenc...intotheblock Our CTO & Co- Founder, Jesus Rodriguez unveils a series of new and unique analytics for order book datasets from cryptocurrency exchanges.
We highlight some unique insights that arise when combining exchange order books and blockchain datasets.
Finally, we show how order book metrics can be used
2019 tokens tokens everywhere tokens



2019 tokens tokens everywhere tokensJeff Flowers This document provides an overview of cryptoeconomics and tokenization. It defines coins and tokens, explaining that tokens are objects built on blockchains for specific purposes as defined by their creators. The document discusses the goals of tokenization, including funding, governance models, and novel business interactions. It outlines some properties of blockchains that make them suitable for business systems, such as guaranteed execution and access controls. However, it notes that many token-based systems fail because they do not properly model usage or consider emission controls. The document emphasizes the need to explain token functionality within economic frameworks for financial and legal purposes. It defines cryptoeconomics as merging cryptography and economic incentives to secure processes and foster engagement.
How to Conduct Fundamental Analysis on Cryptocurrencies



How to Conduct Fundamental Analysis on CryptocurrenciesSFC Today How to Conduct Fundamental Analysis on Cryptocurrencies
Managing Initial Coin Offerings



Managing Initial Coin OfferingsDr. Nikolaus Lipusch The document presents a taxonomy of Initial Coin Offering (ICO) processes developed through an empirical and conceptual research methodology. The taxonomy identifies four key dimensions of ICO processes: defining the market, determining token functionality and development, determining the token sales model, and user communication and engagement. It then provides examples of process characteristics within each dimension. The results show three common clusters of ICOs based on their goals and process characteristics: customer-centric service innovators, financial service innovators, and platform innovators. The taxonomy contributes a theoretical understanding of ICO processes and provides practical guidance for entrepreneurs conducting ICOs.
Ico processes n_li



Ico processes n_linikinew1 The document presents a taxonomy of Initial Coin Offering (ICO) processes developed through an empirical and conceptual research methodology. The taxonomy identifies four key dimensions of ICO processes: defining the market, determining token functionality and development, determining the token sales model, and user communication and engagement. It then provides examples of process characteristics within each dimension. The results show three common clusters of ICOs based on their goals and process characteristics: customer-centric service innovators, financial service innovators, and platform innovators. The taxonomy contributes a theoretical understanding of ICO processes and provides practical guidance for entrepreneurs conducting ICOs.
Bitcoin Price Prediction and Forecasting



Bitcoin Price Prediction and ForecastingIRJET Journal This document discusses predicting bitcoin price movements using machine learning techniques. It proposes using LSTM neural networks combined with sentiment analysis of tweets and Reddit posts to analyze factors influencing bitcoin prices. The methodology involves data collection, preprocessing, sentiment analysis to classify tweets as positive, neutral or negative, and training LSTM models on historic price data. The trained models would allow investors to predict bitcoin price changes and limit potential losses. Evaluation of the models found LSTM to have better performance than other techniques for this volatile cryptocurrency data. With further expansion and testing of models on more diverse data, this approach aims to more accurately forecast bitcoin and other cryptocurrency prices.
Ad
More from Jesus Rodriguez (20)
The Emergence of DeFi Micro-Primitives



The Emergence of DeFi Micro-PrimitivesJesus Rodriguez DeFi is moving towards more granular "micro-primitives" that break down protocols into smaller, modular units. Examples include Uniswap v4 hooks, EigenLayer marketplaces, and Flashbots' decomposed MEV roles. Micro-primitives enable composability but increase complexity and the attack surface. While they can enrich functionality, there is a risk of further fragmenting DeFi without capturing value through applications.
ChatGPT, Foundation Models and Web3.pptx



ChatGPT, Foundation Models and Web3.pptxJesus Rodriguez This presentation presents an overview of the challenges and opportunities of generative artificial intelligence in Web3. It includes a brief research history of generative AI as well as some of its immediate applications in Web3.
DeFi Opportunities and Challenges in the Current Crypto Market



DeFi Opportunities and Challenges in the Current Crypto MarketJesus Rodriguez This session explores some of the key opportunities and challenges of decentralized finance in lights of the recent changes in the crypto market.
MEV Deep Dive .pptx



MEV Deep Dive .pptxJesus Rodriguez Maximal extractable value(MEV) is one of the most debated topics in crypto. This session discusses some of the technical architectures, opportunities and challenges that MEV traders and developers should explore.
Quant in Crypto Land



Quant in Crypto LandJesus Rodriguez This session explores the unique aspects of quantitative trading strategies applied to cryptocurrencies. The session covers topics such as challenges of crypto quant strategies, DeFi and many others.
The Polygon Blockchain by the Numbers



The Polygon Blockchain by the NumbersJesus Rodriguez This presentation shows some cool analytics about the recent adoption of the Polygon blockchain and draws some comparison to the Ethereum blockchain.
Social Analytics for Cryptocurrencies 



Social Analytics for Cryptocurrencies Jesus Rodriguez This session discusses the impact that some of the newest trends in natural language understanding can have in the analysis of crypto-assets
DeFi Quant Yield-Generating Strategies



DeFi Quant Yield-Generating StrategiesJesus Rodriguez Yield farming or liquidity mining have been at the core of the recent boom of DeFi protocols. From a trading perspective, yield-generating strategies are producing incredibly attractive returns compared to similar strategies traditional capital markets. How to build yield-generating DeFi strategies that correctly balance risk-rewards?
This session discusses the new world of DeFi quant yield-generating strategies. We discuss key building blocks required to implement intelligent DeFi quant strategies in an institutional-grade manner. The session will discuss how to think about elements such as risk quantification, back testing , simulations , protocol interactions and many others in the context of DeFi yield-generating strategies.
High Frequency Trading and DeFi



High Frequency Trading and DeFiJesus Rodriguez This session presents some ideas, lessons learned and techniques used to build high frequency trading strategies in decentralized finance(DeFi). The deck describes some key practical tips that can help quants build HFT strategies for the new word of DeFi.
Simple DeFi Analytics Any Crypto-Investor Should Know About 



Simple DeFi Analytics Any Crypto-Investor Should Know About Jesus Rodriguez This session provides an overview of basic indicators that will help traders and investors better understand DeFi protocols. The session covers unique analytics and visualizations that reveal fascinating insights the top DeFi projects in the market.
15 Minutes of DeFi Analytics



15 Minutes of DeFi AnalyticsJesus Rodriguez This session provides an overview of analytics for decentralized finance(DeFi) protocols. The session also outlines some ideas about the future of market intelligence and DeFi.
DeFi Trading Strategies: Opportunities and Challenges



DeFi Trading Strategies: Opportunities and ChallengesJesus Rodriguez This deck discusses some ideas about trading opportunities in the DeFi ecosystem as well as the challenges and risks. The content presents a conceptual framework to think about DeFi quant strategies
Fascinating Metrics and Analytics About Cryptocurrencies



Fascinating Metrics and Analytics About CryptocurrenciesJesus Rodriguez This document discusses the need for a new approach to analyzing cryptocurrency assets using data science. It argues that cryptocurrencies generate far more behavioral data than traditional assets through their public ledgers. This rich blockchain data can provide insights into metrics like the number of traders profiting from each asset, how long investors hold assets, geographic trading patterns, and concentration among large holders. The document presents examples of data analyses for various cryptocurrencies that could help monitor market trends, predict price movements, and identify risks around exchanges. In conclusion, it advocates applying data science to simplify cryptocurrency analysis and unlock insights from their unique blockchain datasets.
Demystifying Centralized Crypto Exchanges using Data Science



Demystifying Centralized Crypto Exchanges using Data ScienceJesus Rodriguez
Centralized exchanges are one of the most obscure and difficult to understand elements in the crypto landscape. From fake volumes to transaction transformations, centralized exchanges introduce a level of obfuscation that challenges even the most sophisticated analytic techniques. How can we learn to identify and understand the behavior of centralized crypto exchanges?
This session showcases a series of machine learning and data visualization techniques that help us better understand some of the patterns of crypto exchanges. Using gorgeous data visualizations, we will walk you through a journey that clearly illustrates how exchanges process transactions and distribute crypto-assets across their different addresses. Finally, we will illustrate how certain behaviors of crypto exchanges become relevant to specific patterns in the crypto market.
Crypto assets are a data science heaven rev



Crypto assets are a data science heaven revJesus Rodriguez This session provides an outline of data science techniques for crypto-assets. The content introduces the notion of crypto asset fundamental analysis and highlights some shocking data about crypto-assets
Implementing Machine Learning in the Real World



Implementing Machine Learning in the Real WorldJesus Rodriguez This document outlines 15 lessons learned from building large-scale machine learning systems in the real world. Some key challenges discussed include data scientists not being well-suited for engineering work, traditional development methodologies not working for machine learning, the difficulty of data labeling and feature extraction, and the complexities of training, executing, operationalizing, and securing machine learning models at scale. The document provides ideas to address these challenges such as establishing separate data science and engineering teams, implementing automated data labeling strategies, leveraging centralized feature stores, and adopting techniques like transfer learning and continual learning.
Blockchain in the enterprise



Blockchain in the enterpriseJesus Rodriguez The document discusses key considerations for enterprise blockchain implementations, including selecting a blockchain platform, runtime, and complementary technology stacks. It analyzes popular permissioned blockchain platforms like Hyperledger Fabric, Sawtooth, and Corda and cloud services from Azure, AWS, IBM and others. It also reviews relevant technology stacks for integration, testing, data storage, access and security. The conclusion recommends starting small and iterating when establishing a blockchain strategy to address challenges of real-world solutions.
The Future of Security Tokens: Myths and Realities



The Future of Security Tokens: Myths and RealitiesJesus Rodriguez This presentation provides a glimpse into the future of security tokens both from a technological and market standpoint.
Decentralized AI for the Rest of Us



Decentralized AI for the Rest of UsJesus Rodriguez Decentralized AI aims to address challenges with centralized AI models, including data and model centralization, transparency issues, and the "rich get richer" problem. The presentation discusses several foundational technologies needed for decentralized AI, including homomorphic encryption, GAN cryptography, secure multi-party computation, and federated learning. It also notes the roles of blockchains and crypto tokens in incentivizing contributions and coordination in decentralized AI networks. Several existing platforms working on decentralized AI applications and services are briefly described.
10 Things I Wish I Dad Known Before Scaling Deep Learning Solutions



10 Things I Wish I Dad Known Before Scaling Deep Learning SolutionsJesus Rodriguez This document provides an overview of practical lessons learned on the implementation of large scale deep learning solutions.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
How analogue intelligence complements AI



How analogue intelligence complements AIPaul Rowe
Artificial Intelligence is providing benefits in many areas of work within the heritage sector, from image analysis, to ideas generation, and new research tools. However, it is more critical than ever for people, with analogue intelligence, to ensure the integrity and ethical use of AI. Including real people can improve the use of AI by identifying potential biases, cross-checking results, refining workflows, and providing contextual relevance to AI-driven results.
News about the impact of AI often paints a rosy picture. In practice, there are many potential pitfalls. This presentation discusses these issues and looks at the role of analogue intelligence and analogue interfaces in providing the best results to our audiences. How do we deal with factually incorrect results? How do we get content generated that better reflects the diversity of our communities? What roles are there for physical, in-person experiences in the digital world?
Quantum Computing Quick Research Guide by Arthur Morgan



Quantum Computing Quick Research Guide by Arthur MorganArthur Morgan This is a Quick Research Guide (QRG).
QRGs include the following:
- A brief, high-level overview of the QRG topic.
- A milestone timeline for the QRG topic.
- Links to various free online resource materials to provide a deeper dive into the QRG topic.
- Conclusion and a recommendation for at least two books available in the SJPL system on the QRG topic.
QRGs planned for the series:
- Artificial Intelligence QRG
- Quantum Computing QRG
- Big Data Analytics QRG
- Spacecraft Guidance, Navigation & Control QRG (coming 2026)
- UK Home Computing & The Birth of ARM QRG (coming 2027)
Any questions or comments?
- Please contact Arthur Morgan at [email protected].
100% human made.
Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...



Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...Impelsys Inc. Impelsys provided a robust testing solution, leveraging a risk-based and requirement-mapped approach to validate ICU Connect and CritiXpert. A well-defined test suite was developed to assess data communication, clinical data collection, transformation, and visualization across integrated devices.
TrsLabs - Fintech Product & Business Consulting



TrsLabs - Fintech Product & Business ConsultingTrs Labs Hybrid Growth Mandate Model with TrsLabs
Strategic Investments, Inorganic Growth, Business Model Pivoting are critical activities that business don't do/change everyday. In cases like this, it may benefit your business to choose a temporary external consultant.
An unbiased plan driven by clearcut deliverables, market dynamics and without the influence of your internal office equations empower business leaders to make right choices.
Getting things done within a budget within a timeframe is key to Growing Business - No matter whether you are a start-up or a big company
Talk to us & Unlock the competitive advantage
#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025



#StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tech Forum 2025BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, transcript, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Mobile App Development Company in Saudi Arabia



Mobile App Development Company in Saudi ArabiaSteve Jonas EmizenTech is a globally recognized software development company, proudly serving businesses since 2013. With over 11+ years of industry experience and a team of 200+ skilled professionals, we have successfully delivered 1200+ projects across various sectors. As a leading Mobile App Development Company In Saudi Arabia we offer end-to-end solutions for iOS, Android, and cross-platform applications. Our apps are known for their user-friendly interfaces, scalability, high performance, and strong security features. We tailor each mobile application to meet the unique needs of different industries, ensuring a seamless user experience. EmizenTech is committed to turning your vision into a powerful digital product that drives growth, innovation, and long-term success in the competitive mobile landscape of Saudi Arabia.
2025-05-Q4-2024-Investor-Presentation.pptx



2025-05-Q4-2024-Investor-Presentation.pptxSamuele Fogagnolo Cloudflare Q4 Financial Results Presentation
Transcript: #StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tec...



Transcript: #StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tec...BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, presentation slides, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global Trends



AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global TrendsInData Labs In this infographic, we explore how businesses can implement effective governance frameworks to address AI data privacy. Understanding it is crucial for developing effective strategies that ensure compliance, safeguard customer trust, and leverage AI responsibly. Equip yourself with insights that can drive informed decision-making and position your organization for success in the future of data privacy.
This infographic contains:
-AI and data privacy: Key findings
-Statistics on AI data privacy in the today’s world
-Tips on how to overcome data privacy challenges
-Benefits of AI data security investments.
Keep up-to-date on how AI is reshaping privacy standards and what this entails for both individuals and organizations.
AI Changes Everything – Talk at Cardiff Metropolitan University, 29th April 2...



AI Changes Everything – Talk at Cardiff Metropolitan University, 29th April 2...Alan Dix Talk at the final event of Data Fusion Dynamics: A Collaborative UK-Saudi Initiative in Cybersecurity and Artificial Intelligence funded by the British Council UK-Saudi Challenge Fund 2024, Cardiff Metropolitan University, 29th April 2025
https://alandix.com/academic/talks/CMet2025-AI-Changes-Everything/
Is AI just another technology, or does it fundamentally change the way we live and think?
Every technology has a direct impact with micro-ethical consequences, some good, some bad. However more profound are the ways in which some technologies reshape the very fabric of society with macro-ethical impacts. The invention of the stirrup revolutionised mounted combat, but as a side effect gave rise to the feudal system, which still shapes politics today. The internal combustion engine offers personal freedom and creates pollution, but has also transformed the nature of urban planning and international trade. When we look at AI the micro-ethical issues, such as bias, are most obvious, but the macro-ethical challenges may be greater.
At a micro-ethical level AI has the potential to deepen social, ethnic and gender bias, issues I have warned about since the early 1990s! It is also being used increasingly on the battlefield. However, it also offers amazing opportunities in health and educations, as the recent Nobel prizes for the developers of AlphaFold illustrate. More radically, the need to encode ethics acts as a mirror to surface essential ethical problems and conflicts.
At the macro-ethical level, by the early 2000s digital technology had already begun to undermine sovereignty (e.g. gambling), market economics (through network effects and emergent monopolies), and the very meaning of money. Modern AI is the child of big data, big computation and ultimately big business, intensifying the inherent tendency of digital technology to concentrate power. AI is already unravelling the fundamentals of the social, political and economic world around us, but this is a world that needs radical reimagining to overcome the global environmental and human challenges that confront us. Our challenge is whether to let the threads fall as they may, or to use them to weave a better future.
HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices and Managing Multiuser Environments



HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices and Managing Multiuser Environmentspanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/hcl-nomad-web-best-practices-and-managing-multiuser-environments/
HCL Nomad Web is heralded as the next generation of the HCL Notes client, offering numerous advantages such as eliminating the need for packaging, distribution, and installation. Nomad Web client upgrades will be installed “automatically” in the background. This significantly reduces the administrative footprint compared to traditional HCL Notes clients. However, troubleshooting issues in Nomad Web present unique challenges compared to the Notes client.
Join Christoph and Marc as they demonstrate how to simplify the troubleshooting process in HCL Nomad Web, ensuring a smoother and more efficient user experience.
In this webinar, we will explore effective strategies for diagnosing and resolving common problems in HCL Nomad Web, including
- Accessing the console
- Locating and interpreting log files
- Accessing the data folder within the browser’s cache (using OPFS)
- Understand the difference between single- and multi-user scenarios
- Utilizing Client Clocking
The Evolution of Meme Coins A New Era for Digital Currency ppt.pdf



The Evolution of Meme Coins A New Era for Digital Currency ppt.pdfAbi john Analyze the growth of meme coins from mere online jokes to potential assets in the digital economy. Explore the community, culture, and utility as they elevate themselves to a new era in cryptocurrency.
Drupalcamp Finland – Measuring Front-end Energy Consumption



Drupalcamp Finland – Measuring Front-end Energy ConsumptionExove How to measure web front-end energy consumption using Firefox Profiler. Presented in DrupalCamp Finland on April 25th, 2025.
Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdf



Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdfSoftware Company Explore the benefits and features of advanced logistics management software for businesses in Riyadh. This guide delves into the latest technologies, from real-time tracking and route optimization to warehouse management and inventory control, helping businesses streamline their logistics operations and reduce costs. Learn how implementing the right software solution can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and provide a competitive edge in the growing logistics sector of Riyadh.
Technology Trends in 2025: AI and Big Data Analytics



Technology Trends in 2025: AI and Big Data AnalyticsInData Labs At InData Labs, we have been keeping an ear to the ground, looking out for AI-enabled digital transformation trends coming our way in 2025. Our report will provide a look into the technology landscape of the future, including:
-Artificial Intelligence Market Overview
-Strategies for AI Adoption in 2025
-Anticipated drivers of AI adoption and transformative technologies
-Benefits of AI and Big data for your business
-Tips on how to prepare your business for innovation
-AI and data privacy: Strategies for securing data privacy in AI models, etc.
Download your free copy nowand implement the key findings to improve your business.
Increasing Retail Store Efficiency How can Planograms Save Time and Money.pptx



Increasing Retail Store Efficiency How can Planograms Save Time and Money.pptxAnoop Ashok In today's fast-paced retail environment, efficiency is key. Every minute counts, and every penny matters. One tool that can significantly boost your store's efficiency is a well-executed planogram. These visual merchandising blueprints not only enhance store layouts but also save time and money in the process.
Semantic Cultivators : The Critical Future Role to Enable AI



Semantic Cultivators : The Critical Future Role to Enable AIartmondano By 2026, AI agents will consume 10x more enterprise data than humans, but with none of the contextual understanding that prevents catastrophic misinterpretations.
Big Data Analytics Quick Research Guide by Arthur Morgan



Big Data Analytics Quick Research Guide by Arthur MorganArthur Morgan This is a Quick Research Guide (QRG).
QRGs include the following:
- A brief, high-level overview of the QRG topic.
- A milestone timeline for the QRG topic.
- Links to various free online resource materials to provide a deeper dive into the QRG topic.
- Conclusion and a recommendation for at least two books available in the SJPL system on the QRG topic.
QRGs planned for the series:
- Artificial Intelligence QRG
- Quantum Computing QRG
- Big Data Analytics QRG
- Spacecraft Guidance, Navigation & Control QRG (coming 2026)
- UK Home Computing & The Birth of ARM QRG (coming 2027)
Any questions or comments?
- Please contact Arthur Morgan at [email protected].
100% human made.
Price PRedictions for Crypto-Assets Using Deep Learning
- 1. Crypto-Asset predictions, challenges and crazy ideas using deep learning
- 2. Agenda ❖ A gentle introduction to predictions in capital markets ❖ Prediction In crypto assets ❖ Myths and realities of crypto asset predictions ❖ Time series vs. deep learning architectures ❖ Some ideas to explore
- 3. INTRODUCING Predictions are the holy grail of machine intelligence applied to financial markets…
- 4. INTRODUCING Predictions focus on forecasting the performance of one or a group of assets based on a specific set of attributes….
- 5. INTRODUCING There are two main schools of thought to approach asset predictions in capital markets…
- 7. Asset-Based Predictions Ex: Predict the price of Bitcoin in the next 12 hours Focus on predicting the performance of a single asset based on a specific criteria Typically factors in specific characteristics of the target asset
- 8. 8 Asset-Based Predictions Pros • Rich models based on the specific characteristics of an asset • Possible to achieve high levels of accuracy during short periods of time • Simpler to retrain and validate Cons • Exposure to a single asset within a market • Hard to assemble in cohesive portfolios • Becomes challenging to combine different predictions as part of portfolios
- 9. Factor-Based Predictions Ex: Predict is cryptos with strong momentum will outperform in the next 24 hours Focus on predicting the performance of a group of assets based on a set of factors Typical factors include aspects such as value, momentum, carry, volatility, quality, etc…
- 10. 10 Factor-Based Predictions Pros • Minimum exposure to a single asset within a market • Ability to formulate sophisticated thesis across an entire portfolio • Exposure to non-correlated factors and hedging models Cons • Prediction models need to ignore unique characteristics of a given asset • Prediction models might miss unique investment opportunities in a specific asset within the portfolio
- 11. Price Predictions in Crypto Assets
- 12. 12 Benefits and Challenges of Predictive Models for Crypto Assets Benefits • Asymmetrical opportunity to uncover alpha generating strategies • Unique data sources • Irrational market with massive potential upsides Challenges • Small and inaccurate datasets • Fake volumes and wash trading • Lack of labeled datasets • Limited non-correlated factors • Inability to leverage existing quant models • Black swan events • Irrational markets
- 14. Predictions Based on Order Book Datasets 14 Focus on predicting short term performance fluctuations for an asset or a factor Leverage attributes such as price, volume as well as order book bids, asks and trades Models are vulnerable to the poor quality of crypto exchange order book datasets
- 15. Predictions Based on Blockchain Datasets 15 Focus on predicting medium to long term performance trends on a crypto-asset or a factor Leverage attributes such as hash rates, exchange flows, wallet balances, etc. Models are very unique to crypto assets and can’t take advantage of existing quant research
- 16. Predictions Based on Derivative Contracts 16 Focus on predicting the short or medium-term impact of derivative contracts in crypto markets Current prediction models would necessarily be asset based Unique insights when combined with blockchain datasets
- 17. Predictions Based on Protocol Contracts 17 Focus on medium to long term predictions of the performance of specific protocol By definition, prediction models will be asset based Vulnerable to unexpected changes and versions of a given protocol
- 18. Predictions Based on Alternative Asset Datasets 18 Focus on short term predictions based on sources like Twitter, Telegram, News, etc. Leverage natural language understanding techniques to extract information from text data sources. Largely used as a complement to more sophisticated prediction models
- 20. 20 The Super Predictor Myth Myth • A single attribute can predict the price of a crypto asset • Ex: NVT score can predict the price of Bitcoin…. Reality • Most prediction models require a combination of many factors
- 21. 21 The Super Model Myth Myth • A single model can predict the price of a crypto asset across different market conditions • Ex: A model based on technical that can regularly predict the price of Bitcoin Reality • Most models only work under specific market conditions and they tend to overfit for those
- 22. 22 The Price-Volume Myth Myth • All characteristics of a crypto asset are captured in price and volume sentiment Reality • Blockchchain and derivatives datasets offer unique insights about crypto assets that are impossible to capture in price and volume models
- 23. Predictive Model Approaches: Time Series vs. Machine Learning
- 24. Time Series Prediction Models 24 Statistical models that focus on predicting a variable based on linear correlations with other attributes of the dataset The value of the predictor attributes in the future should be known in advance Most algorithms are based on variation of linear regressions Ex: predict the price of Bitcoin based on the expected settlements in Bitcoin futures Algorithms: ARIMA, ARIMAX, VARMAX
- 25. Machine Learning Prediction Models 25 Neural network architectures that forecast a variable based on hierarchical, non-linear relationships between other predictors Analyze complex relationships in sophisticated datasets Different schools of thought: supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, reinforcement, etc More prompt to discover alpha in efficient markets Proven algorithms for financial markets: long-short- term memory networks, convolutional neural networks, multi-layer perceptrons
- 26. INTRODUCING IntoTheBlock Predictions: Democratize machine learning predictions for crypto-assets for the mainstream investor
- 27. 27 What we are doing? : Building a series of deep learning models based on different datasets: order book, futures, blockchain data
- 28. The Process 28 Deep Learning Process for Crypto Predictions Prepare dataset Extract features Train model Deploy model Evaluate predictions
- 29. Example: CNN+LSTM for Order Book Data • The input is an image of the order book from multiple exchanges • A CNN layers detecting features for the order book data • A time distributed layer identifies patterns for a specific timeframe • A LSTM layer that aggregates all the individual patterns into a target prediction 29
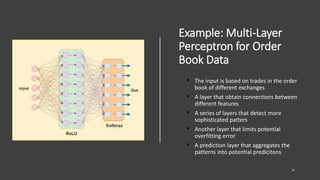
- 30. Example: Multi-Layer Perceptron for Order Book Data • The input is based on trades in the order book of different exchanges • A layer that obtain connections between different features • A series of layers that detect more sophisticated patters • Another layer that limits potential overfitting error • A prediction layer that aggregates the patterns into potential predicitons
- 31. 31 Summary ● Crypto assets offer a blank canvas for prediction models ● There are different data sources of predictions for crypto assets: order book, futures, blockchain, alternative … ● The two main schools of thought for prediction are : time series and machine/deep learning ● ITB is working on prediction models for crypto assets based on deep learning


