Pricing strategies
- 1. Choosing the right pricing strategy Peter Ramsden Paramount Learning Ltd
- 2. Outline Importance of Price Factors affecting Price Pricing Strategies Price demand curves
- 3. What must I consider before setting price? 1. Know how much it costs to make and deliver product or service. Direct and Indirect costs. Fixed and Variable costs. 2. Know your breakeven point 3. Research current prices in the market. 4. Consider your market positioning and competitive advantage as this is likely to impact directly on your choice of pricing strategy.
- 4. Importance of Price Choosing the right pricing strategy strengthens the chance of achieving turnover and profit in line with company objectives.
- 5. Importance of Price Getting it wrong can be painful!
- 6. Importance of Price First impressions Often price creates a first impression of the quality of the product/service and other value based judgements come later. Pricing low can signify cheap and cheerful, pricing high can indicate quality? £5600 £65
- 8. Price Elasticity of Demand Elastic Demand – Products are considered to exist in a market that exhibits elastic demand when a certain percentage change in price results in a larger and opposite percentage change in demand. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10%, the demand for the product is likely to decline by greater than 10%. Inelastic Demand – Products are considered to exist in an inelastic market when a certain percentage change in price results in a smaller and opposite percentage change in demand. For example, if the price of a product increases by 10%, the demand for the product is likely to decline by less than 10%. Elasticity of demand (PED) = % change in demand of good X / % change in price of good X If the PED is greater than one, the good is price elastic. Demand is responsive to a change in price. If for example a 15% fall in price leads to a 30% increase in quantity demanded, the price elasticity = 2. If the PED is less than one, the good is inelastic. Demand is not very responsive to changes in price. If for example a 20% increase in price leads to a 5% fall in quantity demanded, the price elasticity = 0.25
- 10. Prices usually start high and decline as the product reaches maturity Difficult to start prices low and subsequently increase prices later
- 11. The Elements of Cost 1. Direct Materials (Used in the manufacture of 2. Direct Labour the good or service) 3. Direct Expenses Prime or Product Cost 1. Production Overhead Production Cost 1. Research and Development Cost 2. Marketing and Distribution 3. General Administration Total Cost
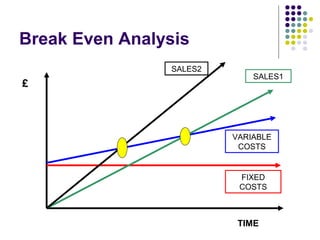
- 12. Break Even Analysis SALES2 SALES1 £ VARIABLE COSTS FIXED COSTS TIME
- 13. Break Even Formulas Profit= Sales – Expenditure Sales - variable costs = Contribution margin Contribution margin - Fixed Costs = Profit Break even = Fixed Costs/Contribution per unit. (Fixed cost + Required Profit)/Contribution per unit = units required to make profit.
- 14. Break Even Calcs Break even = Fixed Costs Contribution per unit Item sold for £3000 with a variable cost of £1500 = Contribution of £1500 Fixed costs of £100,000 means that 66.6 units need to be sold at £3000 before the business breaks even.
- 15. Pricing Strategies Market pricing Competitive Pricing Cost pricing Below market Mark up Parity or Price Matching Margin generation Bundle Breakeven Skimming Loss leader Markdowns Psychological pricing Temporary Prestige Permanent Odd even pricing Payment and delivery Demand terms
- 16. Market Pricing Set prices at or around the middle of the market Fight on other added value areas such as delivery, customer service etc
- 17. Cost Plus Pricing Cost Plus Pricing Cost of materials Cost of labour Add an amount for profit Does not take into account general overhead costs Beware of making loss due to hidden overhead
- 18. Loss Leader Pricing a product below cost to attract customers to higher margin products
- 19. Psychological Pricing Prestige pricing Odd Even Pricing
- 20. Demand Pricing Price varies based on some demand criteria As your output increases/decreases your prices change. Can confuse customers
- 21. Competitive Pricing Matching or beating the market price
- 22. Bundle Pricing Discounts offered to entice client to accept a bundle rather than one part only. Example Product X £3,500 Product Y £4,500 Product Z £7,500 Total £15,500 Bundle Price £14,500 Discount of £1,000 or 6.5%
- 23. Skimming Pricing Client insensitive to price. Works well in an inelastic market. Client needs product. Little or no substitutes available. Innovators, early adopters. Skim the cream off the top.
- 24. Markdowns Temporary Finite life- Offer closes 31/10/08 Can be used to test the market Permanent Often used to get rid of old stock or perishables approaching end of shelf life Fire sale and soiled goods Seasonal Fashions, clothing gardening etc
- 25. Payment and Delivery Terms Considered part of the pricing mix. Cost for payment terms borne by supplier of purchaser depending on terms agreed. Do not forget to take into account credit terms and risk when pricing.
- 26. Pricing Decisions Understand how much it costs to produce or procure a product/service. Ensure that general overhead has been taken into account when setting pricing. Research the typical market price for your product and service and pitch accordingly. Understand your position in the market. High end value, cheap and cheerful or somewhere in between. Set your price level, and review on going.