Probability based learning (in book: Machine learning for predictve data analytics)
- 1. Summary: Probability-based Learning (from book: Machine learning for predictve data analytics) Duyen Do 1
- 2. NỘI DUNG Bayes’ Theorem Fundamentals Bayes Prediction Standard Approach: The Naïve Bayes Model Conditional Independence and Factorization Smoothing Extensions and Variations Continuous Features Bayesian Network Summary Q&A Probability basic 2
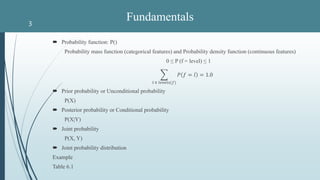
- 3. Probability function: P() Probability mass function (categorical features) and Probability density function (continuous features) 0 ≤ P (f = level) ≤ 1 𝑙 ∈ 𝑙𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑠(𝑓) 𝑃 𝑓 = 𝑙 = 1.0 Prior probability or Unconditional probability P(X) Posterior probability or Conditional probability P(X|Y) Joint probability P(X, Y) Joint probability distribution Example Table 6.1 Fundamentals3
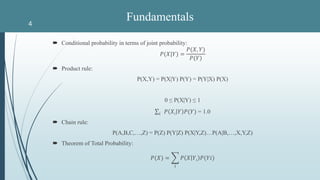
- 4. Conditional probability in terms of joint probability: 𝑃(𝑋|𝑌) = 𝑃(𝑋, 𝑌) 𝑃(𝑌) Product rule: P(X,Y) = P(X|Y) P(Y) = P(Y|X) P(X) 0 ≤ P(X|Y) ≤ 1 𝑖 𝑃 𝑋𝑖 𝑌 𝑃(𝑌) = 1.0 Chain rule: P(A,B,C,…,Z) = P(Z) P(Y|Z) P(X|Y,Z)…P(A|B,…,X,Y,Z) Theorem of Total Probability: 𝑃(𝑋) = 𝑖 𝑃 𝑋 𝑌𝑖 𝑃(𝑌𝑖) Fundamentals4
- 5. Fundamentals: Bayes’s Theorem P(X|Y) = 𝑃(𝑌|𝑋)𝑃(𝑋) 𝑃(𝑌) A doctor inform a patient both bad news and good news: - Bad news: 99% has a serious desease - Good news: the desease is rarely and only 1 in 10,000 people What is actually probability that patient has the desease? Using Bayes’Theorem: 𝑃 𝑑 𝑡 = 𝑃 𝑡 𝑑 𝑃 𝑑 𝑃 𝑡 P(t) = P(t|d)P(d) + P(t|-d)P(-d) = (0.99 * 0.0001) + (0.01 * 0.9999) = 0.0101 P(d|t) = 0.99 ∗0.0001 0.0101 = 0.0098 5
- 6. With P(t=l): the prior probability of target feature t taking the level l P(q[1],…,q[m]): joint probability of descriptive feature P(q[1],…,q[m] | t=l): the conditional probability Example 1: Table 6.1 What is probability a person has MENINGTIS when he/she has HEADACHE=true, FEVER=false, VOMITING=true? => P(m | h, -f, v) Bayesian prediction P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) = 𝑃 𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 𝑡=𝑙)𝑃(𝑡=𝑙) 𝑃(𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 ) 6
- 7. P(m | h, -f, v) = 𝑃 ℎ,−𝑓,𝑣 𝑚)𝑃(𝑚) 𝑃(ℎ,−ℎ,𝑣) P(m) = |{𝐼𝐷5,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}| |{𝐼𝐷1,𝐼𝐷2,𝐼𝐷3,𝐼𝐷4,𝐼𝐷5,𝐼𝐷6,𝐼𝐷7,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷9,𝐼𝐷10}| = 0.3 P(h,-f,v) = |{𝐼𝐷3,𝐼𝐷4,𝐼𝐷6,𝐼𝐷7,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}| |{𝐼𝐷1,𝐼𝐷2,𝐼𝐷3,𝐼𝐷4,𝐼𝐷5,𝐼𝐷6,𝐼𝐷7,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷9,𝐼𝐷10}| = 0.6 P(h, -f, v | m) = P(h|m) P(-f | h,m) P(v | -f, h, m) = |{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}| |{𝐼𝐷5,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}| x |{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}| |{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}| x |{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}| |{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}| = 2 3 x 2 2 x 2 2 = 0.66 P(m | h, -f, v) = (0.66*0.3) / 0.6 = 0.33 P(-m | h, -f, v) = 𝑃 ℎ,−𝑓,𝑣 −𝑚)𝑃(−𝑚) 𝑃(ℎ,−ℎ,𝑣) = 𝑃 ℎ −𝑚)𝑃(−𝑓 ℎ,−𝑚 𝑃 𝑣 −𝑓,ℎ,−𝑚)𝑃(−𝑚) 𝑃(ℎ,−ℎ,𝑣) = 0.667 Bayesian prediction P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) = 𝑃 𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 𝑡=𝑙)𝑃(𝑡=𝑙) 𝑃(𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 ) 7
- 8. Bayesian prediction Maximum a posterior predction: M (q) = arg max P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) = arg max l ∈ 𝑙𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑠( 𝑡) 𝑃 𝑞 1 , … , 𝑞 𝑚 𝑡 = 𝑙)𝑃(𝑡 = 𝑙) 𝑃(𝑞 1 , … , 𝑞 𝑚 ) Bayesian MAP prediction model: M (q) = arg max P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) = arg max l ∈ 𝑙𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑠( 𝑡) 𝑃 𝑞 1 , … , 𝑞 𝑚 𝑡 = 𝑙)𝑃(𝑡 = 𝑙) 8
- 9. Example 2: Table 6.1 What is probability a person has MENINGTIS when he/she has HEADACHE=true, FEVER=true, VOMITING=false? P(m | h, f, -v) = 𝑃 ℎ 𝑚 𝑃 𝑓 ℎ, 𝑚 𝑃 −𝑣 𝑓, ℎ, 𝑚 𝑃(𝑚) 𝑃(ℎ,𝑓,−𝑣) = 0.66 ∗ 0 ∗0 ∗0.3 0.1 = 0.0 P(-m| h, f, -v) = 1.0 – 0.0 = 1.0 Overfit data Bayesian prediction P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) = 𝑃 𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 𝑡=𝑙)𝑃(𝑡=𝑙) 𝑃(𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 ) 9
- 10. Conditional independence when X and Y (independence) share the same cause Z. P(X | Y, Z) = P(X | Z) P(X, Y | Z) = P(X | Z)*P(Y | Z) Chain rule: P(q[1],…,q[m] | t=l) = P(q[1] | t=l)*P(q[2] | t=l)*…*P(q[m] | t=l) = Π P(q[i] | t=l) P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) = Π P(q[i] | t=l) ∗ P(t=l) 𝑃(𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 ) = Joint probability: P(H,F,V,M) = P(M) * P(H|M) * P(F|M) * P(V|M) Conditional independence and Factorization10 If X and Y are independent, then: P(X|Y) = P(X) P(X, Y) = P(X) P(Y)
- 11. Example 2: Table 6.1 What is probability a person has MENINGTIS when he/she has HEADACHE=true, FEVER=true, VOMITING=false? P(m | h, f, -v) = P(h |m) ∗ P(f | m) ∗ P(−v | m) ∗ P(m) 𝑃(ℎ,𝑓,−𝑣) = P(h |m) ∗ P(f | m) ∗ P(−v | m) ∗ P(m) Σ𝑖 𝑃 ℎ 𝑀𝑖 ∗𝑃 𝑓 𝑀𝑖 ∗𝑃 −𝑣 𝑀𝑖 ∗𝑃(𝑀𝑖) = 0.1948 P(-m | h, f, -v) = 0.8052 Conditional independence and Factorization11 If X and Y are independent, then: P(X|Y) = P(X) P(X, Y) = P(X) P(Y)
- 12. Example Table 6.2 Naïve Bayes Model12 MAP (Maximum a posterior): M(q) = arg maxl ∈ levels(t) ((Πi P(q[i] | t=l) * P(t=l))
- 13. Example Table 6.2 CREDIT HISTORY = paid, GUANRANTOR/COAPPLICANT = guarantor, ACCOMMODATION = free? Extensions and Variations: Smoothing13 Laplace smoothing: 𝑃 𝑓 = 𝑙 𝑡) = 𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡 𝑓 = 𝑙 𝑡) + 𝑘 𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡 𝑓 𝑡) + (𝑘 ∗ 𝐷𝑜𝑚𝑎𝑖𝑛 𝑓 )
- 14. Transform continuous feature to categorical feature with: Equal-width binning Equal-frequency binning Example Table 6.11 Extensions and Variations: Continuous feature - Binning14
- 15. A Bayesian network, Bayes network, Bayes(ian) model or probabilistic directed acyclic graphical model is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a structural relationship - a set of random variables and their conditional dependencies - via a directed acyclic graph (DAG) P(A,B) = P(B|A) * P(A) Ex1: P(a, -b) = P(-b|a) * P(a) = 0.7 * 0.4 = 0.28 The probability of an event x1,…,xn P(x1,…,xn) = ∏ P(xi | Parents(xi)) Bayesian Network15 A B P(A=T) P(A=F) 0.4 0.6 A P(B=T | A) P(B=F | A) T 0.3 0.7 F 0.4 0.6
- 16. Ex2: P (a, -b, -c, d) = P(-b|a,-c) * P(-c|d) * P(a) * P(d) = 0.5 * 0.8 * 0.4 * 0.4 = 0.064 Bayesian Network16 A B C D P(D=T) 0.4 P(A=T) 0.4 D P(C=T|D) T 0.2 F 0.5 A C P(B=T|A,C) T T 0.2 T F 0.5 F T 0.4 F F 0.3
- 17. The conditional probability of node xi with n nodes P(xi | x1,…, xi-1, xi+1,…,xn) = P(xi | Parents(xi) ∏ P(xj | Parents(xj)) with j ∈ Children(xi) Ex2: P(c | -a, b, d) = P(c | d) * P(b | -a, c) = 0.2 * 0.4 = 0.08 Bayesian Network17 A B C D P(D=T) 0.4 P(A=T) 0.4 D P(C=T|D) T 0.2 F 0.5 A C P(B=T|A,C) T T 0.2 T F 0.5 F T 0.4 F F 0.3
- 18. P(t |d[1], …, d[n]) = P(t) * ∏ P(d[j] | t) Naïve Bayes Classifier18 Target Descriptive feature 1 Descriptive feature 2 Descriptive feature n
- 19. P(A, B, C) = P(C | A, B) * P(B |A) * P(A) P(A, B, C) = P(A| C, B) * P(B |C) * P(C) Building Bayesian Network19 B C A A C B P(A=T) 0.6 P(C=T) 0.2 A P(B=T|A) T 0.333 F 0.5 C P(B=T|C) T 0.5 F 0.375 A B P(C|A,B) T T 0.25 T F 0.125 F T 0.25 F F 0.25 C B P(A|B,C) T T 0.5 T F 0.5 F T 0.5 F F 0.7
- 20. Building Bayesian Network20 Hybrid approach: 1. Given the topology of the network 2. Induce the CPT What is the best topology structure to give the algorithm as input? Causal graphs Example Table 6.18
- 21. Building Bayesian Network21 A potential causal theory: The more equal in a society, the higher the investment that society will make in health and education, and this in turn result in a lower of corruption SY LE P(CPI|SY, LE) L L 1.0 L H 0 H L 1.0 H H 1.0 CPI GC SC LE GC P(SY=L|GC) L 0.2 H 0.8 GC P(LE=L|GC) L 0.2 H 0.8 B P(GC=L) T 0.5
- 22. Using Bayesian Network make predictions22 M (q) = arg max l ∈ levels(t) BayesianNetwork(t=l,q) Making prediction with missing descriptive feature values: GC = high, SC = high =>? Example Table 6.18




![With P(t=l): the prior probability of target feature t taking the level l
P(q[1],…,q[m]): joint probability of descriptive feature
P(q[1],…,q[m] | t=l): the conditional probability
Example 1:
Table 6.1
What is probability a person has MENINGTIS when he/she has HEADACHE=true, FEVER=false,
VOMITING=true?
=> P(m | h, -f, v)
Bayesian prediction
P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) =
𝑃 𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 𝑡=𝑙)𝑃(𝑡=𝑙)
𝑃(𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 )
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probability-basedlearning-160820122420/85/Probability-based-learning-in-book-Machine-learning-for-predictve-data-analytics-6-320.jpg)
![P(m | h, -f, v) =
𝑃 ℎ,−𝑓,𝑣 𝑚)𝑃(𝑚)
𝑃(ℎ,−ℎ,𝑣)
P(m) =
|{𝐼𝐷5,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}|
|{𝐼𝐷1,𝐼𝐷2,𝐼𝐷3,𝐼𝐷4,𝐼𝐷5,𝐼𝐷6,𝐼𝐷7,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷9,𝐼𝐷10}|
= 0.3
P(h,-f,v) =
|{𝐼𝐷3,𝐼𝐷4,𝐼𝐷6,𝐼𝐷7,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}|
|{𝐼𝐷1,𝐼𝐷2,𝐼𝐷3,𝐼𝐷4,𝐼𝐷5,𝐼𝐷6,𝐼𝐷7,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷9,𝐼𝐷10}|
= 0.6
P(h, -f, v | m) = P(h|m) P(-f | h,m) P(v | -f, h, m)
=
|{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}|
|{𝐼𝐷5,𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}|
x
|{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}|
|{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}|
x
|{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}|
|{𝐼𝐷8,𝐼𝐷10}|
=
2
3
x
2
2
x
2
2
= 0.66
P(m | h, -f, v) = (0.66*0.3) / 0.6 = 0.33
P(-m | h, -f, v) =
𝑃 ℎ,−𝑓,𝑣 −𝑚)𝑃(−𝑚)
𝑃(ℎ,−ℎ,𝑣)
=
𝑃 ℎ −𝑚)𝑃(−𝑓 ℎ,−𝑚 𝑃 𝑣 −𝑓,ℎ,−𝑚)𝑃(−𝑚)
𝑃(ℎ,−ℎ,𝑣)
= 0.667
Bayesian prediction
P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) =
𝑃 𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 𝑡=𝑙)𝑃(𝑡=𝑙)
𝑃(𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 )
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probability-basedlearning-160820122420/85/Probability-based-learning-in-book-Machine-learning-for-predictve-data-analytics-7-320.jpg)
![Bayesian prediction
Maximum a posterior predction:
M (q) = arg max P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m])
= arg max l ∈ 𝑙𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑠( 𝑡)
𝑃 𝑞 1 , … , 𝑞 𝑚 𝑡 = 𝑙)𝑃(𝑡 = 𝑙)
𝑃(𝑞 1 , … , 𝑞 𝑚 )
Bayesian MAP prediction model:
M (q) = arg max P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m])
= arg max l ∈ 𝑙𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑠( 𝑡)
𝑃 𝑞 1 , … , 𝑞 𝑚 𝑡 = 𝑙)𝑃(𝑡 = 𝑙)
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probability-basedlearning-160820122420/85/Probability-based-learning-in-book-Machine-learning-for-predictve-data-analytics-8-320.jpg)
![Example 2:
Table 6.1
What is probability a person has MENINGTIS when he/she has HEADACHE=true, FEVER=true,
VOMITING=false?
P(m | h, f, -v) =
𝑃 ℎ 𝑚 𝑃 𝑓 ℎ, 𝑚 𝑃 −𝑣 𝑓, ℎ, 𝑚 𝑃(𝑚)
𝑃(ℎ,𝑓,−𝑣)
=
0.66 ∗ 0 ∗0 ∗0.3
0.1
= 0.0
P(-m| h, f, -v) = 1.0 – 0.0 = 1.0
Overfit data
Bayesian prediction
P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) =
𝑃 𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 𝑡=𝑙)𝑃(𝑡=𝑙)
𝑃(𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 )
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probability-basedlearning-160820122420/85/Probability-based-learning-in-book-Machine-learning-for-predictve-data-analytics-9-320.jpg)
![Conditional independence
when X and Y (independence) share the same cause Z.
P(X | Y, Z) = P(X | Z)
P(X, Y | Z) = P(X | Z)*P(Y | Z)
Chain rule:
P(q[1],…,q[m] | t=l) = P(q[1] | t=l)*P(q[2] | t=l)*…*P(q[m] | t=l)
= Π P(q[i] | t=l)
P(t=l | q[1],…,q[m]) =
Π P(q[i] | t=l) ∗ P(t=l)
𝑃(𝑞 1 ,…,𝑞 𝑚 )
= Joint probability:
P(H,F,V,M) = P(M) * P(H|M) * P(F|M) * P(V|M)
Conditional independence and Factorization10
If X and Y are independent, then:
P(X|Y) = P(X)
P(X, Y) = P(X) P(Y)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probability-basedlearning-160820122420/85/Probability-based-learning-in-book-Machine-learning-for-predictve-data-analytics-10-320.jpg)

![Example
Table 6.2
Naïve Bayes Model12
MAP (Maximum a posterior):
M(q) = arg maxl ∈ levels(t) ((Πi P(q[i] | t=l) * P(t=l))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probability-basedlearning-160820122420/85/Probability-based-learning-in-book-Machine-learning-for-predictve-data-analytics-12-320.jpg)





![P(t |d[1], …, d[n]) = P(t) * ∏ P(d[j] | t)
Naïve Bayes Classifier18
Target
Descriptive
feature 1
Descriptive
feature 2
Descriptive
feature n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probability-basedlearning-160820122420/85/Probability-based-learning-in-book-Machine-learning-for-predictve-data-analytics-18-320.jpg)



