Problem Solving Critical Thinking - v5.pptx
- 1. Problem-Solving & Critical Thinking Dr. Magdi Ibrahim Ph.D.
- 3. Learning Objectives By the end of the course, participants will learn the following knowledge, skills and attitudes: • Learn the definitions and concepts of problem-solving. • Study creative problem-solving and brainstorming techniques. • Understand specific tools and techniques to identify problems, research solutions, and analyze results. • Grasp the concepts of critical thinking techniques and develop an organizational problem-solving environment. • Analyze qualities and habits of effective critical thinkers • Establish strategies for overcoming common barriers to critical thinking
- 4. Learning Objectives • Identify and apply key critical thinking strategies to tackle challenges and weather business changes. • Explore a variety of decision-making frameworks to solve personal and professional problems. • Incorporate a formal model into workplace problem-solving efforts. • Use various tools and strategies to generate ideas for workplace problems. • Demonstrate leadership techniques to support problem-solving efforts. • Use collaboration to effectively solve workplace problems.
- 5. Training Outcomes By the end of the course, participants will achieve the following outcomes: • Think through problems before reaching a conclusion. • Ask questions that facilitate better decision-making. • Enhance your judgment in challenging situations. • Employ critical thinking to solve problems, identify opportunities, and effectively manage change.
- 6. Training Outcomes • Explore characteristics of critical thinkers and identify strategies for overcoming common thinking patterns. • Use tools and strategies of critical thinking to match your current workplace situations. • Improve your logic, sharpen your judgment, and make better decisions through critical thinking by exploring alternative solutions to problems. • Discover how to question assumptions, apply sound reasoning, break down complex issues into manageable pieces, and grasp the implications of information.
- 7. Outline Problem solving and critical thinking definitions and concepts. Profile of a problem solver and critical thinker Critical thinking behaviors: active listening and probing Identify and evaluate issues and viewpoints Critical thinking checklist Creative problem solving Creative methods Critical thinking and problem-solving the key to effective decision making
- 8. Outline Lateral thinking techniques The Iceberg Principle and the Understanding- Resolution Ration Problem thinking and critical techniques Problem-solving steps for decision making Individual and collective decision-making traps How to choose: criteria, goals and vision-based decision-making Individual and group decision-making tools and techniques
- 9. Outline Decision-making – practical application to a workplace scenario 6 Hats of thinking Personality styles in decision making – DISC approach Creating an organization's creative thinking culture.
- 11. Definitions and concepts A. What is problem-solving and critical thinking? • The process which we use when we come up with a new idea to face a situation or a problem. • Merging ideas never merged before. • Accidental. • Deliberate. • Developments of products. • Ongoing, continuous investigation, questioning, analysis, training, education, and learning techniques. • https://youtu.be/lhHhwbWEGXQ • https://youtu.be/fPz6uvIbWZE ا
- 12. • Critical thinking is the intellectual process of logically, objectively, and systematically evaluating information to form reasoned judgments, utilizing reasoning, logic, and evidence. It involves: 1.Identifying and questioning assumptions, 2.Applying consistent principles and criteria, 3.Analyzing and synthesizing information, 4.Drawing conclusions based on evidence. • The importance of critical thinking lies in its ability to help individuals make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and differentiate between true and false beliefs.
- 13. B. Profile of a problem solver and critical thinker • Self-knowledge • Knowing what is needed in developing an innovation/ideas for problem-solving • Constantly learning • Asks silly questions sometimes • Curious • What others have done, then explore
- 14. • learning from mistakes • Takes risks • Asks questions • Suggests ideas • Sets targets • Career progression is not his main objective
- 15. • Trusts others • Willing to disagree with others • Prepared to lead • Guided by values • Confident about his ideas • Takes responsibility
- 16. C. Critical thinking and creative problem-solving behavior and mandates • Respect the group • Take your time, don’t push too hard • Focus the group on its objectives • Focus on the future • Link all activities and objectives • Create a stimulating environment
- 17. Exercise – Identify and Evaluate Issues - Analysis & Role Play List down issues –- that are faced daily. Also, business situations are encountered and considered problems that require solutions and proper handling. Conduct a role-play. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
- 18. Role Play guideline tips to Follow 1. Establish a positive and respectful tone during the conversation. 2. Use listening techniques - employ while addressing the concerns. 3. Collaborate with the customer to find mutually agreeable solutions. 4. Address challenges you encounter, and manage to overcome them. 5. What could you do differently in future admin /customer / meetings.
- 19. Creative problem-solving and brainstorming techniques A. Creative Methods 1. Evolution: incremental improvement- every new idea is made from other ideas - Every issue that has been dealt with can be looked at again in a better way. 2. Synthesis: Combine two or more ideas into a third new idea
- 20. 3. Revolution: Completely different ideas are sometimes the best 4. Reapplication: Looking at something old in a new way. 5. Changing direction: Shifting attention from one angle of an issue to another. The objective is to dealt with the matter by creating an appropriate solution and not to implement a particular solution.
- 21. B. Brainstorming techniquesاالفكار عصف • A conference technique- obtain the maximum number of ideas- enhances creative thinking and innovation- A sudden inspiration- Abandon- Thrill- Outbreak - Breakthrough- explosion- Imagination- Idea creation- Opportunity- Probortunity- Paradigm- Mind - mapping- Blamestorming.
- 22. C. Rules of Brainstorming • Rule 1: Postpone and withhold your judgment of ideas • Rule 2: Encourage wild and exaggerated ideas • Rule 3: Quantity counts at this stage, not quality • Rule 4: Build on the ideas put forward by others • Rule 5:Every person and every idea has equal worth
- 23. Example of Critical Thinking Tools Fishbone رسم السمكة عظم هيكل مجسم
- 27. Exercise Call for a brainstorming meeting with stakeholders to address and analyze a current situation, a problem, or an opportunity following the proper steps using fishbone analysis and other analytical tools as explained.
- 28. Problem-thinking techniques and developing an organizational problem-solving environment A. How do problem-solving techniques work? • Stimulate original ideas. • New idea = two or more ideas are accidentally or deliberately merged • Problem thinking techniques provide the method for deliberately combining ideas in ways that would not normally come across or think about. • Merging lots of new ideas into a solution.
- 29. B. The problem-thinking techniques 1. The random word technique • Generating new ideas by choosing a random word. • The random word will force you to go in a certain direction in creative thinking. • The skill is to stop your mind from thinking it’s a silly idea. The initial stimulus is the random word itself. • Establish an idea as a bridge between the stimulus and an idea that you could actually use on your issue.
- 30. 2. The random picture technique • The use of a picture as a stimulus instead of a word. • It is easier to use pictures than words • All depends on the situation and the requirements of propor-tunities faced.
- 31. 3. The false rules technique • Implementing rules that have already been applied to a different subject but have not yet been introduced to your own probortunity. • A rule, a quote, an idea, or a suggestion from somewhere else. • It is false because the rule has not been considered as valid before.
- 32. • Forcing yourself to use it will help to direct your thinking about doing things in a different way than you would normally behave. • The stimulus is the false rule for the new ideas. • Establishing a set of ideas based on this stimulus. • Use these ideas as a bridge between the stimulus and a valid idea.
- 33. • Apply the rule directly to your current situation. • Looking at the reason why the rule exists and similarities that could be resulted. • Looking at the benefits of using the rule and why it was created?.
- 34. 4. The random website technique • Choose a random website • Gather the ideas to be used for new ideas • The ideas extracted from the website will be the stimulus to a possible solution • Try to see something on the website which reminds you of your propor-tunity and how it might be solved. • Think of how can use that new situation or object to your advantage.
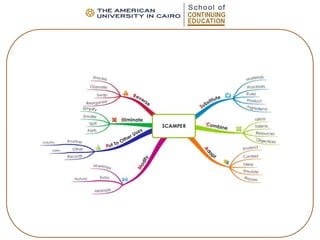
- 35. 5. The SCAMPER technique • Uses a set of directed questions should be answered about your propor-tunity in order to come up with new ideas. • The stimulus comes from forcing yourself to answer questions that you would not normally pose.
- 36. • SCAMPER: – Substitute - Put to other purposes – Combine - Eliminate – Adapt - Rearrange/ Reverse – Modify/distort
- 41. 6. Empathy Map • An empathy map is a collaborative tool teams can use to gain a deeper insight into their customers. Much like a user persona, an empathy map can represent a group of users, such as a customer segment. • The empathy map was originally created by Dave Gray and has gained much popularity within the agile community.
- 43. THE CRITICAL THINKING CHECKLIST 1.Does the logic of the argument make sense? 2.Is it clear how you could falsify the argument? 3.What evidence for the argument has been cited? 4.Is that evidence sufficient, accurate, and relevant? 5.Has the argument been framed in a way to persuade you with emotion rather than convince you with evidence? 6.What’s missing?
- 44. CRITICAL THINKING: QUESTIONS TO ASK • Clarity: Could you elaborate further on that point? Could you express that point in another way? Could you give me an illustration? Could you give me an example? • Accuracy: Is that really true? How could we check that? How could we find out if that is true? • Precision: Could you give me more details? Could you be more specific? (note that a statement can be both clear and accurate without being specific – Relevance: How is that connected with the question? How does that bear on the issue?
- 45. • Depth: How does your answer address the complexities of the question? How are you taking into account the problems of the question? Is that dealing with the most significant factors? • Breadth: Do we need to consider another point of view? Is there another way to look at this question? What would this look like from a conservative standpoint? What would this look like from the point of view of … (fill in the dots). • Logic: Does that really make sense? Does that follow from what you said? How does that follow? Before you implied this and now you are saying that – how can both be true? CRITICAL THINKING: QUESTIONS TO ASK
- 46. Group Excercise Critical Thinking Check List
- 47. Problem solving mechanism What is it for? • Facing a situation • Choose a solution – optimum / best/ suitable • To solve a problem • Overcome uncertainty through knowledge and training
- 49. Decision making for Problem Solving – detailed 10 Steps 1. State the decision to be made and decide who should make it. 2. Assemble the decision makers and organize for the decision by designating a group facilitator and recorder.
- 50. 3. State the decision to be made and explore the context: a. Tie the decision to a goal or an objective that the decision is oriented to achieving. b. Explore the causes of the situation which give rise to the need for a decision to be made. c. Determine the impact of not deciding. d. Remind the group of the type of decision and why this type was selected. e. Specify the criteria for evaluating the decision. ا Decision making for Problem-Solving -10 Steps
- 51. 4. Identify optional decisions. 5. Describe the effects of each option and select the best option or combination of aspects of each option. 6. Select the right option (optimal/suitable). 7. Plan implementation of the decision. Decision making for Problem Solving -10 Steps
- 52. 8. Plan communication of decisions to those not present who need to know. 9. Plan a review of the decision at a future date in which you will apply the criteria you identified under 3. e. above. 10. Review the process used to make the decision in the meeting to improve it. Decision making for Problem-Solving -10 Steps
- 53. Exercise Apply 10 problem-solving steps for decision-making on a business matter that you are considering.
- 54. Type of problems and decisions made in organizations • Daily problems – detailed • Global problems – overall • Reactive decisions – after event • Proactive decisions – before event
- 55. Exercise Call for a meeting with stakeholders to address and analyze a current conflict, a controversial issue following problem-solving steps.
- 56. Types of problems decision-makers face in business األعمال مجال في القرار صناع يواجهها التي المشاكل أنواع • Non-Crisis An issue that requires resolution but does not simultaneously have the importance and immediacy characteristics of a crisis. • Crisis A serious difficulty requiring immediate action
- 57. Exercise • Apply problem-thinking techniques to solve a situation or a problem or a current burning issue related.
- 58. Reactive and proactive problem-solving models واالستباقية التفاعلية المشكالت حل نماذج – Define the problem – Collect information – Develop options – Choose the best option – Plan – Execute – Follow up
- 59. Exercise Consider a recent problem by applying reactive and proactive problem-solving steps. حل خطوات تطبيق خالل من حديثة مشكلة في فكر واالستباقية التفاعلية المشكالت.
- 61. Group Exercise Role Play 6 Hats of Thinking
- 62. How to influence others in Problem Solving with the DISC model " ديسك التأثير "نموذج
- 63. Style 1: Dominance – High “D” Style • Demonstrates a cool, independent, and competitive nature • When working alone, completes tasks and projects with impressive speed • Is swift with action and decision-making • Takes control and gets impatient with slow action or lack thereof • Wants the freedom to manage self and others • Demonstrates low tolerance for people’s feelings and attitudes • Does not readily embrace advice • Performs extremely well in administrative tasks بمفردك العمل وتنافسيةعند ومستقلة رائعة طبيعة ُظهري، - القرار واتخاذ التصرف في سريع مذهلة بسرعة والمشاريع المهام يكمل عدمه أو العمل بطء بسبب صبره وينفد األمور زمام يتولى واآلخر نفسه إدارة في الحرية يريد ومواقفهم الناس مشاعر مع التسامح انخفاض ُظهريين اإلدارية المهام في للغاية جيد بشكل بسهولةيؤدي النصيحة يتقبل ال
- 64. Style 2: Influence – High “I” Style • Demonstrates spontaneity and decisiveness • Enjoys participating • Doesn’t enjoy working alone • Tends towards exaggeration and generalization • Is inclined to dream and get others excited about the dream • Easily hops from activity to activity • Works with others with speed and excitement • Looks for admiration and recognition • Possesses excellent influencing skills والحسم العفوية يظهر بالمشاركة يستمتع - والتعميم المبالغة إلى يميل بمفرده بالعمل يستمتع ال- للحلم اآلخرين حماس وإثارة الحلم إلى يميل وإثارة بسرعة اآلخرين مع آخريعمل إلى نشاط من بسهولة يقفز ممتازة تأثير مهارات والتقديريمتلك اإلعجاب عن يبحث
- 65. Style 3: Steadiness – High “S” Style • Takes it slow when it comes to actions and decisions • Enjoys close and deep relationships • Is averse to workplace conflict • Demonstrates strong listening skills and support of others • Has great ability to counsel others • Is not naturally strong at goal setting and giving direction • Has a knack for gaining people’s buy-in and support • Works with others in a slow and cohesive manner • Looks for safety and belongingness والقرارت باإلجراءات األمر يتعلق عندما ببطء األمر يأخذ وعميقة وثيقة بعالقات يتمتع العمل مكان في الصراع يكره اآلخرين ودعم قوية استماع مهارات ُظهري لآلخر المشورة تقديم على كبيرة قدرة لديه التوجيهات وإعطاء األهداف تحديد في طبيعي بشكل قويًا ينليس ودعمهم الناس تأييد لكسب موهبة لديه ومتماسكة بطيئة بطريقة اآلخرين مع يعمل واالنتماء األمان عن يبحث
- 66. Style 4: Conscientious – High “C” Style • Marked by caution in taking action and making decisions • Enjoys organization and structure • Does not enjoy involvement • Asks lots of questions about task and project details • Thrives best in a work environment that’s task-oriented, objective, and intellectually stimulating • Does not want to be wrong and, thus, may collect too much data and overanalyze • Works slowly, precisely, and alone • Demonstrates excellent problem-solving skills القرارات واتخاذ اإلجراءات اتخاذ في بالحذر يتميز والهيكل بالتنظيم يتمتع ة بالمشاركة يتمتع والمشروع المهمة تفاصيل حول األسئلة من الكثير يطرح اًيفكر ومحفزة وموضوعية المهام نحو موجهة عمل بيئة في أفضل بشكل يزدهر التحليل في ويبالغ البيانات من الكثير يجمع قد وبالتالي ،اًئمخط يكون أن يريد ال وحده ،وبدقة ،ببطء يعمل المشكالت حل في ممتازة مهارات ظهرُي
- 67. Role Play Exercise ديسك نموذج استخدمDISC
- 68. Group Project العمل فرق في مشروع • Work on a current problem or a development opportunity to solve and decide about the situation. • Use a flip chart to present and draw your idea solution in a logical road map. الموقف لحل تطويرية فرصة أو حالية مشكلة على العمل بشأنه القرار واتخاذ. خارطة في ورسمه فكرتك حل لعرض الورقي اللوح استخدم منطقية طريق.
- 69. Take charge of your creative energy “To enjoy enduring success we should travel a little in advance of the world.” Lynda Curtin
- 70. Thanking you for your participation
- 71. References Reference List Charles Conn, Robert McLean (2019).” Bullet proof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything “. John Wiley & Sons Inc. Garrette, Bernard, Phelps, Corey, and Sibony, Olivier. (2021).” Cracked it.: How to solve big problems and sell solutions like top strategy consultants”. Amazon.com. Heath, Dan (2022). “Upstream: The Quest to Solve Problems Before They Happen”. Amazon. Com. Herman, E. Amy (2020). “Fixed: How to Perfect the Fine Art of Problem Solving”. Amazon.com Knapp, Jake, Zeratsky, John et al (2020). “Sprint: How to Solve Big Problems and Test New Ideas in Just Five Days”. Aamzon.com Watanabe, Ken (2020). “Problem Solving 101: A Simple Book for Smart People”. Amazon.com Wedell-Wedellsborg, Thomas (2021). “What’s Your Problem? To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve” Amazon.com. V. Anton, Spraul (2021). “Think Like a Programmer: An Introduction to Creative Problem Solving”. Aamzon.com