Ad
Programming
- 2. Objectives After viewing this presentation, the learner will be able to… • Given a task, create pseudocode • Given pseudocode, create a flowchart • Define/describe these terms: program, compile vs. interpret, loop, variable, function, syntax, code, debug, IF THEN ELSE
- 3. What is programming? Series of instructions to a computer to accomplish a task Instructions must be written in a way the computer can understand Programming languages are used to write programs
- 4. What is programming? Once the code (language) of a program has been written, it must be executed (run, started). You may need to type the name of the program to start it, or use a word like RUN and the name of the program (in the old days, anyway).
- 5. What is programming? Some programming languages (like Java or C++) require the code to be compiled (translated to binary) before it can be started. Others (like JavaScript) are interpreted, meaning that each command is translated separately when the program is started.
- 6. What is a programming language? Set of commands that a computer has been “taught” to understand Languages that look like “machine code” (e.g., 82A8: jsr r5,@#82AE 82AC: sob r0,8296) are used for… • Writing games • Writing application programs (like Excel) Other languages look like English (“high level,” e.g., PRINT “HELLO”) • Logo • JavaScript • And many more
- 7. What does programming look like? Here are some examples of an instruction to print the word HI • Logo PR [HI] • JavaScript alert(“HI”); • FORTRAN PRINT “HI” • BASIC PRINT “HI” • COBOL DISPLAY ‘HI’. • C++ printf(“HI”); • Pascal WRITELN(‘HI’); • Assembly XPRNT MESSAGE1 Language MESSAGE1 DC ‘HI’
- 8. How do you write a program? Decide what steps are needed to complete the task Write the steps in pseudocode (written in English) or as a flowchart (graphic symbols) Translate into the programming language Try out the program and “debug” it (fix if necessary)
- 9. What is pseudocode? List of steps written in English Like the instructions for a recipe Must be in the right sequence • Imagine saying “bake the cake” and then “mix it up”
- 10. Sample Pseudocode Task: add two numbers Pseudocode: • Start • Get two numbers • Add them • Print the answer • End
- 11. What does a flowchart look like? The pseudocode from the previous slide would look like this as a flowchart: Start Get 2 numbers Add them Print answer End
- 12. What are those funny symbols? START/END INPUT/OUTPUT PROCESS DECISION
- 13. What are those funny symbols? START/END Used at the beginning and end of each flowchart.
- 14. What are those funny symbols? INPUT/OUTPUT Shows when information/data comes into a program or is printed out. What are those funny symbols?
- 15. What are those funny symbols? PROCESS Used to show calculations, storing of data in variables, and other “processes” that take place within a program. What are those funny symbols?
- 16. What are those funny symbols? DECISION Used to show that the program must decide whether something (usually a comparison between numbers) is true or false. YES and NO (or T/F) branches are usually shown. What are those funny symbols? Y N X>7?
- 17. Another Sample: Calculating Age Pseudocode: • Start • Get year born • Calculate age • Print age • If age > 50 print OLD • End
- 18. Another Sample: Calculating Age Flowchart • Start • Get year born • Calculate age • Print age • If age > 50 print OLD • End Get yr Calc age Print age Age>50?OLD Y N Start End
- 19. Elements of a Program All programming languages have certain features in common. For example: • Variables • Commands/Syntax (the way commands are structured) • Loops • Decisions • Functions Each programming language has a different set of rules about these features.
- 20. Variables Variables are part of almost every program. A variable is a “place to put data” and is usually represented by a letter or a word. (Think of a variable as a Tupperware container with a label on it.) Variable names cannot contain spaces. Some programming languages have very specific limits on variable names.
- 21. Variables Usually there are several ways to put information into a variable. The most common way is to use the equal sign (=). X = Y + 7 means take the value of Y, add 7, and put it into X. COUNT=COUNT + 2 means take the current value of COUNT, add 2 to it, and make it the new value of COUNT.
- 22. Variables Sometimes you must specify the type of data that will be placed in a variable. Here are some examples of data types: • Numeric (numbers of all kinds) • String (text, “strings of letters”) • Integer (whole numbers) • Long (large numbers) • Boolean (true/false)
- 23. Variables Variables may be classified as global or local. A global variable is one that can be shared by all parts of a program, including any functions or sub-programs. A local variable is one that is used only within a certain part of the program, for example, only in one function or sub-program.
- 24. Commands/Syntax Programming languages are truly languages. They have rules about grammar, spelling, punctuation, etc. You need to learn the rules of a programming language, just as you learned to speak and write English.
- 25. Loops A loop is a repetition of all or part of the commands in a program. A loop often has a counter (a variable) and continues to repeat a specified number of times. A loop may also continue until a certain condition is met (e.g., until the end of a file or until a number reaches a set limit)
- 26. Decisions You saw a flowchart symbol for decisions. A program often needs to decide whether something is true or false in order to see which way to continue. Programs often use IF (or IF THEN or IF THEN ELSE) statements to show a decision.
- 27. Decisions An IF statement always has a condition to check, often a comparison between a variable and a number. The IF statement also must specify what to do if the condition/comparison is true. These instructions (for “true”) may come after the word THEN, or they may simply be listed.
- 28. Decisions In an IF THEN statement, when the condition is false, the program simply ignores the THEN commands and continues to the next line. In an IF THEN ELSE statement, commands are given for both the true and false conditions.
- 29. Functions In most programming languages, small sub- programs are used to perform some of the tasks. These may be called functions, subroutines, handlers, or other such terms. Functions often have names (e.g., getName or CALCTAX).
- 30. Functions A function generally gets information from the main program, performs some task, and returns information back to the program. Functions follow the same rules of syntax, etc. as the main program. JavaScript code is primarily made of a series of functions.
- 31. Hints for Writing Code “Code” means writing the program in the appropriate language Be sure the code is exact (spelling, capitals/lower case, punctuation, etc). Write part of the code, try it, then write more.
- 32. Debugging To “debug” means to try a program, then fix any mistakes. Virtually no program works the first time you run it. There are just too many places to make errors. When you are debugging a program, look for spelling and punctuation errors. Fix one error at a time, then try the program again.
- 33. Self-Check A computer program is… • A series of instructions to accomplish something • A TV show • Written in Egyptian hieroglyphics • Can be written any way you want to
- 34. Self-Check A computer program is… • A series of instructions to accomplish something • A TV show • Written in Egyptian hieroglyphics • Can be written any way you want to
- 35. Self-Check To “compile” a program means to… • Translate it into English • Translate it into binary code • Pile up the punch cards used for the program • Run the program as it was written
- 36. Self-Check To “compile” a program means to… • Translate it into English • Translate it into binary code • Pile up the punch cards used for the program • Run the program as it was written
- 37. Self-Check Pseudocode is… • The program as it is written in a programming language • The results of a program that makes secret codes • The logic of a program written in English • The logic of a program shown in a chart
- 38. Pseudocode is… • The program as it is written in a programming language • The results of a program that makes secret codes • The logic of a program written in English • The logic of a program shown in a chart Self-Check
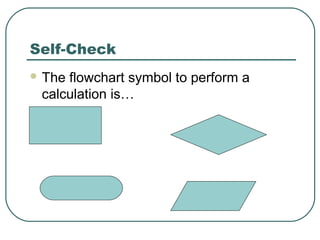
- 39. Self-Check The flowchart symbol to perform a calculation is…
- 40. Self-Check The flowchart symbol to perform a calculation is…
- 41. Self-Check The flowchart symbol to show a decision is…
- 42. Self-Check The flowchart symbol to show a decision is…
- 43. Self-Check Look at the flowchart section below. If the variable X is 5, what will print (K or 1st)? X > 5? YN Print “1st”Print “K”
- 44. Self-Check Look at the flowchart section below. If the variable X is 5, what will print (K or 1st)? X > 5? YN Print “1st”Print “K” K will be printed. The answer to the question “Is X greater than 5?” is NO, since X is equal to (not greater than) 5.
- 45. Self-Check Choose the correct flowchart symbol for each of these statements. AGE>65? Calc. Tax START Print NAME
- 46. Self-Check Choose the correct flowchart symbol for each of these statements. AGE>65? Calc. Tax START Print NAME
- 47. Self-Check A function in a program is… • Something from trigonometry, like COSINE • A sub-program, usually performing one task • A way to check the accuracy of a program (a “function check”)
- 48. Self-Check A function in a program is… • Something from trigonometry, like COSINE • A sub-program, usually performing one task • A way to check the accuracy of a program (a “function check”)
- 49. Self-Check A variable in a program is… • A letter or word that represents a place to store data • A decision made within a program • A small sub-program used to find errors
- 50. Self-Check A variable in a program is… • A letter or word that represents a place to store data • A decision made within a program • A small sub-program used to find errors
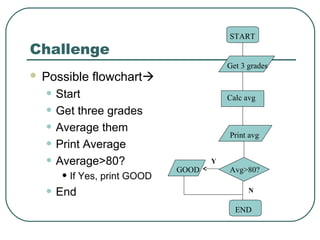
- 51. Challenge Try to write pseudocode and create a flowchart for a program that calculates the average of three grades and prints the average. The word GOOD should be printed only if the average is more than 80.
- 52. Challenge Possible pseudocode • Start • Get three grades • Average them • Print Average • Average>80? • If Yes, print GOOD • End
- 53. Challenge Possible flowchart • Start • Get three grades • Average them • Print Average • Average>80? • If Yes, print GOOD • End START END Get 3 grades Calc avg Print avg Avg>80?GOOD Y N







![What does programming
look like?
Here are some examples of an instruction to
print the word HI
• Logo PR [HI]
• JavaScript alert(“HI”);
• FORTRAN PRINT “HI”
• BASIC PRINT “HI”
• COBOL DISPLAY ‘HI’.
• C++ printf(“HI”);
• Pascal WRITELN(‘HI’);
• Assembly XPRNT MESSAGE1
Language MESSAGE1 DC ‘HI’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-150217230026-conversion-gate01/85/Programming-7-320.jpg)