Programming Methodologies Functions - C Language
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes9 views
This document discusses functions in programming. It defines a function as a block of code that performs a specific task and can be called multiple times. Functions make code more modular, reusable, and easier to debug. There are two types of functions: built-in/library functions that are predefined, and user-defined functions created by the programmer. The document outlines the syntax for defining functions with different parameter and return types, and how to call and prototype functions.
1 of 17
Download to read offline
















Ad
Recommended
Lecture 1_Functions in C.pptx



Lecture 1_Functions in C.pptxKhurramKhan173 1) A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. Functions increase code reusability and improve readability.
2) There are two types of functions - predefined library functions and user-defined functions. User-defined functions are customized functions created by the user.
3) The main() function is where program execution begins. It can call other functions, which may themselves call additional functions. This creates a hierarchical relationship between calling and called functions.
(3) cpp procedural programming



(3) cpp procedural programmingNico Ludwig Check out these exercises: http://de.slideshare.net/nicolayludwig/3-cpp-procedural-programmingexercises
- Procedural Programming
- Predefined and User defined Functions
- Declaration and Definition of Functions
- Procedural and recursive Function Calling
- Namespaces and separated Function Definitions
- A Glimpse of Separated Compilation and Translation Units
VIT351 Software Development VI Unit1



VIT351 Software Development VI Unit1YOGESH SINGH COURSE TITLE: SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT VI
COURSE CODE: VIT 351
TOPICS COVERED:
C STANDARD LIBRARIES
FUNCTIONS IN C
RECURSION
QUIZ SET
Dive into Python Functions Fundamental Concepts.pdf



Dive into Python Functions Fundamental Concepts.pdfSudhanshiBakre1 This document discusses Python functions, including how to define functions with parameters, return values, and docstrings. It covers calling functions and passing arguments, including positional and keyword arguments. The document also discusses built-in functions, user-defined functions, and when to use functions to improve code modularity, reusability, and simplify complex tasks. Tips are provided such as keeping functions short, using descriptive names, testing functions, and taking advantage of features like default arguments.
Functions



FunctionsLakshmi Sarvani Videla Functions allow programmers to break programs into smaller, more manageable units called functions to make programs more modular and easier to write and debug; functions contain elements like a function prototype, parameters, definition, and body; and there are different types of functions like user-defined functions, library functions, and categories of functions based on whether they have arguments or return values.
Functions assignment



Functions assignmentAhmad Kamal The document discusses functions in C++. It defines a function as a named block of code that performs some action. Functions allow code to be reused by calling the function by name. They make programs easier to modify, maintain and develop. The document describes different types of functions like user-defined and built-in functions. It also covers function declaration, definition, scope, passing parameters, and provides examples.
Function C programming



Function C programmingAppili Vamsi Krishna The document discusses C functions, including their definition, types, uses, and implementation. It notes that C functions allow large programs to be broken down into smaller, reusable blocks of code. There are two types of functions - library functions and user-defined functions. Functions are declared with a return type, name, and parameters. They are defined with a body of code between curly braces. Functions can be called within a program and allow code to be executed modularly and reused. Parameters can be passed by value or by reference. Functions can return values or not, and may or may not accept parameters. Overall, functions are a fundamental building block of C that improve code organization, reusability, and maintenance.
Basic information of function in cpu



Basic information of function in cpuDhaval Jalalpara This document discusses user-defined functions in C++. It covers defining functions with return types and parameters, using return statements, function prototypes, and the flow of execution when a function is called. Functions help make programs more modular and understandable by breaking tasks into reusable blocks of code. Defining functions properly allows the compiler to understand how to execute function calls within a program.
arrays.ppt



arrays.pptBharath904863 The document discusses user-defined functions in C programming. It covers topics like function declaration, definition, parameters, return values, function calls, categories of functions, recursion, scope and storage classes of variables in functions. Specifically, it defines a function, explains the need for user-defined functions, and describes the elements and different types of functions.
Funtions of c programming. the functions of c helps to clarify all the tops



Funtions of c programming. the functions of c helps to clarify all the topssameermhr345 functions of c
FUNCTION IN C PROGRAMMING UNIT -6 (BCA I SEM)



FUNCTION IN C PROGRAMMING UNIT -6 (BCA I SEM)Mansi Tyagi A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. There are two types of functions: library functions and user-defined functions. User-defined functions are created by the programmer to perform specific tasks within a program. Recursion is when a function calls itself during its execution. For a recursive function to terminate, it must have a base case and each recursive call must get closer to the base case. An example is a recursive function to calculate the factorial of a number. Storage classes determine where variables are stored and their scope. The main storage classes are automatic, register, static, and external.
Lecture 11 - Functions



Lecture 11 - FunctionsMd. Imran Hossain Showrov C Programming Language is the most popular computer language and most used programming language till now. It is very simple and elegant language. This lecture series will give you basic concepts of structured programming language with C.
Chapter 11 Function



Chapter 11 FunctionDeepak Singh Functions allow programmers to organize code into reusable blocks. A function performs a specific task and can accept input parameters and return an output. Functions make code more modular and easier to maintain. Functions are defined with a name, parameters, and body. They can be called from other parts of the code to execute their task. Parameters allow functions to accept input values, while return values allow functions to return output to the calling code. Functions can be called by passing arguments by value or reference. The document provides examples and explanations of different types of functions in C++ like inline functions, functions with default arguments, and global vs local variables.
Chapter 1. Functions in C++.pdf



Chapter 1. Functions in C++.pdfTeshaleSiyum The document provides an overview of functions in C++. It discusses the basic concepts of functions including declaring, defining, and calling functions. It covers function components like parameters and arguments. It explains passing parameters by value and reference. It also discusses different types of functions like built-in functions, user-defined functions, and functions with default arguments. Additionally, it covers concepts like scope of variables, return statement, recursion, and automatic vs static variables. The document is intended to teach the fundamentals of functions as building blocks of C++ programs.
Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdfTeshaleSiyum The document provides an overview of functions in C++. It discusses the basic concepts of functions including declaring, defining, and calling functions. It covers different types of functions such as built-in functions, user-defined functions, and functions that return values. The key components of a function like the prototype, definition, parameters, arguments, and return statement are explained. It also describes different ways of passing parameters to functions, including call by value and call by reference. Functions allow breaking down programs into smaller, reusable components, making the code more readable, maintainable and reducing errors.
FUNCTION CPU



FUNCTION CPUKrushal Kakadia This document discusses functions in C programming. It defines functions as a group of statements that perform a specific task and have a name. Main functions must be included in every C program as it is where program execution begins. Functions help facilitate modular programming by dividing programs into smaller parts. Functions can be user-defined or built-in library functions. Parameters can be passed to functions by value or by reference. Functions can call themselves through recursion. Variables have different storage classes like auto, register, static, and external that determine scope and lifetime.
All chapters C++ - Copy.pdfyttttttttttttttttttttttttttttt



All chapters C++ - Copy.pdfytttttttttttttttttttttttttttttjacobdiriba yesmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmklllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllljjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjyesmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmklllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllljjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjyesmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmklllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllljjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjj
C programming language working with functions 1



C programming language working with functions 1Jeevan Raj A function is a named, independent block of code that performs a specific task. Functions allow programmers to break programs into smaller, reusable pieces of code. A function is defined with a name, parameters, a return type, and a body containing statements. Functions can return values to the code where they were called. Functions make programs more modular and organized.
Chapter One Function.pptx



Chapter One Function.pptxmiki304759 This document provides an overview of functions in C++. It defines what a function is, how to declare and define functions, how to call functions, and the differences between passing arguments by value versus by reference. A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. Functions are declared with a return type and parameter list, and defined with a body of code. Arguments can be passed into functions either by value, where the function receives a copy of the argument, or by reference, where any changes to the argument are reflected in the original variable. Well-designed programs use modular functions to organize code into reusable components.
Functions in C.pptx



Functions in C.pptxAshwini Raut Functions are fundamental building blocks of C programs, allowing for modular, structured, and efficient code organization.
c.p function



c.p functiongiri5624 This document discusses functions in C programming. It defines what a function is and different types of functions such as library functions and user-defined functions. It describes the structure of a function including return type, function name, arguments, local variable declaration, executable statements and return statement. It explains how to call functions with or without return values and with arguments. It discusses function prototypes, categories of functions based on arguments and return types, built-in functions, recursive functions, and storage classes. The objectives are to understand functions, write functions, use library functions, and apply storage classes and function concepts.
Unit 3 (1)



Unit 3 (1)Sowri Rajan The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines functions and explains their various parts like declaration, definition, and invocation. It also differentiates between function declaration and definition. Various types of functions are classified based on their inputs and outputs. The key differences between call by value and call by reference are explained with examples. Advantages of pass by reference are also mentioned.
Unit-III.pptx



Unit-III.pptxMehul Desai This document discusses functions in C programming. It begins by explaining why programs should be divided into smaller subprograms or functions for manageability. There are two types of functions: library functions which are pre-defined and cannot be modified, and user-defined functions which are created by the user. Every C program must contain a main() function. Functions allow code reusability and modularity. Parameters are used to pass data between functions. The return statement returns data from a function. Local variables are only accessible within their own function.
Functions-Computer programming



Functions-Computer programmingnmahi96 The document discusses top-down design and functions in C programming. It defines top-down design as breaking a large problem down into smaller, more manageable parts or modules. A C program uses functions to implement top-down design, with each function representing a module. The key aspects covered include function declaration, definition, parameters, return values, and recursion. Functions are classified based on whether they return a value and if they accept parameters. Examples demonstrate different types of functions and how to write recursive functions.
Chapter Introduction to Modular Programming.ppt



Chapter Introduction to Modular Programming.pptAmanuelZewdie4 Modular programming involves breaking down a program into individual components (modules) that can be programmed and tested independently. Functions are used to implement modules in C++. Functions must be declared before use so the compiler knows their name, return type, and parameters. Functions are then defined by providing the body of code. Variables used within a function have local scope while variables declared outside have global scope. Functions can pass arguments either by value, where a copy is passed, or by reference, where the address is passed allowing the argument to be modified. Arrays and strings passed to functions are passed by reference as pointers.
How analogue intelligence complements AI



How analogue intelligence complements AIPaul Rowe
Artificial Intelligence is providing benefits in many areas of work within the heritage sector, from image analysis, to ideas generation, and new research tools. However, it is more critical than ever for people, with analogue intelligence, to ensure the integrity and ethical use of AI. Including real people can improve the use of AI by identifying potential biases, cross-checking results, refining workflows, and providing contextual relevance to AI-driven results.
News about the impact of AI often paints a rosy picture. In practice, there are many potential pitfalls. This presentation discusses these issues and looks at the role of analogue intelligence and analogue interfaces in providing the best results to our audiences. How do we deal with factually incorrect results? How do we get content generated that better reflects the diversity of our communities? What roles are there for physical, in-person experiences in the digital world?
Unlocking Generative AI in your Web Apps



Unlocking Generative AI in your Web AppsMaximiliano Firtman Slides for the session delivered at Devoxx UK 2025 - Londo.
Discover how to seamlessly integrate AI LLM models into your website using cutting-edge techniques like new client-side APIs and cloud services. Learn how to execute AI models in the front-end without incurring cloud fees by leveraging Chrome's Gemini Nano model using the window.ai inference API, or utilizing WebNN, WebGPU, and WebAssembly for open-source models.
This session dives into API integration, token management, secure prompting, and practical demos to get you started with AI on the web.
Unlock the power of AI on the web while having fun along the way!
Ad
More Related Content
Similar to Programming Methodologies Functions - C Language (20)
Basic information of function in cpu



Basic information of function in cpuDhaval Jalalpara This document discusses user-defined functions in C++. It covers defining functions with return types and parameters, using return statements, function prototypes, and the flow of execution when a function is called. Functions help make programs more modular and understandable by breaking tasks into reusable blocks of code. Defining functions properly allows the compiler to understand how to execute function calls within a program.
arrays.ppt



arrays.pptBharath904863 The document discusses user-defined functions in C programming. It covers topics like function declaration, definition, parameters, return values, function calls, categories of functions, recursion, scope and storage classes of variables in functions. Specifically, it defines a function, explains the need for user-defined functions, and describes the elements and different types of functions.
Funtions of c programming. the functions of c helps to clarify all the tops



Funtions of c programming. the functions of c helps to clarify all the topssameermhr345 functions of c
FUNCTION IN C PROGRAMMING UNIT -6 (BCA I SEM)



FUNCTION IN C PROGRAMMING UNIT -6 (BCA I SEM)Mansi Tyagi A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. There are two types of functions: library functions and user-defined functions. User-defined functions are created by the programmer to perform specific tasks within a program. Recursion is when a function calls itself during its execution. For a recursive function to terminate, it must have a base case and each recursive call must get closer to the base case. An example is a recursive function to calculate the factorial of a number. Storage classes determine where variables are stored and their scope. The main storage classes are automatic, register, static, and external.
Lecture 11 - Functions



Lecture 11 - FunctionsMd. Imran Hossain Showrov C Programming Language is the most popular computer language and most used programming language till now. It is very simple and elegant language. This lecture series will give you basic concepts of structured programming language with C.
Chapter 11 Function



Chapter 11 FunctionDeepak Singh Functions allow programmers to organize code into reusable blocks. A function performs a specific task and can accept input parameters and return an output. Functions make code more modular and easier to maintain. Functions are defined with a name, parameters, and body. They can be called from other parts of the code to execute their task. Parameters allow functions to accept input values, while return values allow functions to return output to the calling code. Functions can be called by passing arguments by value or reference. The document provides examples and explanations of different types of functions in C++ like inline functions, functions with default arguments, and global vs local variables.
Chapter 1. Functions in C++.pdf



Chapter 1. Functions in C++.pdfTeshaleSiyum The document provides an overview of functions in C++. It discusses the basic concepts of functions including declaring, defining, and calling functions. It covers function components like parameters and arguments. It explains passing parameters by value and reference. It also discusses different types of functions like built-in functions, user-defined functions, and functions with default arguments. Additionally, it covers concepts like scope of variables, return statement, recursion, and automatic vs static variables. The document is intended to teach the fundamentals of functions as building blocks of C++ programs.
Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chapter1-230901115452-13a8ca1c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Chapter_1.__Functions_in_C++[1].pdfTeshaleSiyum The document provides an overview of functions in C++. It discusses the basic concepts of functions including declaring, defining, and calling functions. It covers different types of functions such as built-in functions, user-defined functions, and functions that return values. The key components of a function like the prototype, definition, parameters, arguments, and return statement are explained. It also describes different ways of passing parameters to functions, including call by value and call by reference. Functions allow breaking down programs into smaller, reusable components, making the code more readable, maintainable and reducing errors.
FUNCTION CPU



FUNCTION CPUKrushal Kakadia This document discusses functions in C programming. It defines functions as a group of statements that perform a specific task and have a name. Main functions must be included in every C program as it is where program execution begins. Functions help facilitate modular programming by dividing programs into smaller parts. Functions can be user-defined or built-in library functions. Parameters can be passed to functions by value or by reference. Functions can call themselves through recursion. Variables have different storage classes like auto, register, static, and external that determine scope and lifetime.
All chapters C++ - Copy.pdfyttttttttttttttttttttttttttttt



All chapters C++ - Copy.pdfytttttttttttttttttttttttttttttjacobdiriba yesmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmklllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllljjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjyesmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmklllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllljjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjyesmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmklllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllljjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjj
C programming language working with functions 1



C programming language working with functions 1Jeevan Raj A function is a named, independent block of code that performs a specific task. Functions allow programmers to break programs into smaller, reusable pieces of code. A function is defined with a name, parameters, a return type, and a body containing statements. Functions can return values to the code where they were called. Functions make programs more modular and organized.
Chapter One Function.pptx



Chapter One Function.pptxmiki304759 This document provides an overview of functions in C++. It defines what a function is, how to declare and define functions, how to call functions, and the differences between passing arguments by value versus by reference. A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. Functions are declared with a return type and parameter list, and defined with a body of code. Arguments can be passed into functions either by value, where the function receives a copy of the argument, or by reference, where any changes to the argument are reflected in the original variable. Well-designed programs use modular functions to organize code into reusable components.
Functions in C.pptx



Functions in C.pptxAshwini Raut Functions are fundamental building blocks of C programs, allowing for modular, structured, and efficient code organization.
c.p function



c.p functiongiri5624 This document discusses functions in C programming. It defines what a function is and different types of functions such as library functions and user-defined functions. It describes the structure of a function including return type, function name, arguments, local variable declaration, executable statements and return statement. It explains how to call functions with or without return values and with arguments. It discusses function prototypes, categories of functions based on arguments and return types, built-in functions, recursive functions, and storage classes. The objectives are to understand functions, write functions, use library functions, and apply storage classes and function concepts.
Unit 3 (1)



Unit 3 (1)Sowri Rajan The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines functions and explains their various parts like declaration, definition, and invocation. It also differentiates between function declaration and definition. Various types of functions are classified based on their inputs and outputs. The key differences between call by value and call by reference are explained with examples. Advantages of pass by reference are also mentioned.
Unit-III.pptx



Unit-III.pptxMehul Desai This document discusses functions in C programming. It begins by explaining why programs should be divided into smaller subprograms or functions for manageability. There are two types of functions: library functions which are pre-defined and cannot be modified, and user-defined functions which are created by the user. Every C program must contain a main() function. Functions allow code reusability and modularity. Parameters are used to pass data between functions. The return statement returns data from a function. Local variables are only accessible within their own function.
Functions-Computer programming



Functions-Computer programmingnmahi96 The document discusses top-down design and functions in C programming. It defines top-down design as breaking a large problem down into smaller, more manageable parts or modules. A C program uses functions to implement top-down design, with each function representing a module. The key aspects covered include function declaration, definition, parameters, return values, and recursion. Functions are classified based on whether they return a value and if they accept parameters. Examples demonstrate different types of functions and how to write recursive functions.
Chapter Introduction to Modular Programming.ppt



Chapter Introduction to Modular Programming.pptAmanuelZewdie4 Modular programming involves breaking down a program into individual components (modules) that can be programmed and tested independently. Functions are used to implement modules in C++. Functions must be declared before use so the compiler knows their name, return type, and parameters. Functions are then defined by providing the body of code. Variables used within a function have local scope while variables declared outside have global scope. Functions can pass arguments either by value, where a copy is passed, or by reference, where the address is passed allowing the argument to be modified. Arrays and strings passed to functions are passed by reference as pointers.
Recently uploaded (20)
How analogue intelligence complements AI



How analogue intelligence complements AIPaul Rowe
Artificial Intelligence is providing benefits in many areas of work within the heritage sector, from image analysis, to ideas generation, and new research tools. However, it is more critical than ever for people, with analogue intelligence, to ensure the integrity and ethical use of AI. Including real people can improve the use of AI by identifying potential biases, cross-checking results, refining workflows, and providing contextual relevance to AI-driven results.
News about the impact of AI often paints a rosy picture. In practice, there are many potential pitfalls. This presentation discusses these issues and looks at the role of analogue intelligence and analogue interfaces in providing the best results to our audiences. How do we deal with factually incorrect results? How do we get content generated that better reflects the diversity of our communities? What roles are there for physical, in-person experiences in the digital world?
Unlocking Generative AI in your Web Apps



Unlocking Generative AI in your Web AppsMaximiliano Firtman Slides for the session delivered at Devoxx UK 2025 - Londo.
Discover how to seamlessly integrate AI LLM models into your website using cutting-edge techniques like new client-side APIs and cloud services. Learn how to execute AI models in the front-end without incurring cloud fees by leveraging Chrome's Gemini Nano model using the window.ai inference API, or utilizing WebNN, WebGPU, and WebAssembly for open-source models.
This session dives into API integration, token management, secure prompting, and practical demos to get you started with AI on the web.
Unlock the power of AI on the web while having fun along the way!
Viam product demo_ Deploying and scaling AI with hardware.pdf



Viam product demo_ Deploying and scaling AI with hardware.pdfcamilalamoratta Building AI-powered products that interact with the physical world often means navigating complex integration challenges, especially on resource-constrained devices.
You'll learn:
- How Viam's platform bridges the gap between AI, data, and physical devices
- A step-by-step walkthrough of computer vision running at the edge
- Practical approaches to common integration hurdles
- How teams are scaling hardware + software solutions together
Whether you're a developer, engineering manager, or product builder, this demo will show you a faster path to creating intelligent machines and systems.
Resources:
- Documentation: https://on.viam.com/docs
- Community: https://discord.com/invite/viam
- Hands-on: https://on.viam.com/codelabs
- Future Events: https://on.viam.com/updates-upcoming-events
- Request personalized demo: https://on.viam.com/request-demo
HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices und Verwaltung von Multiuser-Umgebungen



HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices und Verwaltung von Multiuser-Umgebungenpanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/hcl-nomad-web-best-practices-und-verwaltung-von-multiuser-umgebungen/
HCL Nomad Web wird als die nächste Generation des HCL Notes-Clients gefeiert und bietet zahlreiche Vorteile, wie die Beseitigung des Bedarfs an Paketierung, Verteilung und Installation. Nomad Web-Client-Updates werden “automatisch” im Hintergrund installiert, was den administrativen Aufwand im Vergleich zu traditionellen HCL Notes-Clients erheblich reduziert. Allerdings stellt die Fehlerbehebung in Nomad Web im Vergleich zum Notes-Client einzigartige Herausforderungen dar.
Begleiten Sie Christoph und Marc, während sie demonstrieren, wie der Fehlerbehebungsprozess in HCL Nomad Web vereinfacht werden kann, um eine reibungslose und effiziente Benutzererfahrung zu gewährleisten.
In diesem Webinar werden wir effektive Strategien zur Diagnose und Lösung häufiger Probleme in HCL Nomad Web untersuchen, einschließlich
- Zugriff auf die Konsole
- Auffinden und Interpretieren von Protokolldateien
- Zugriff auf den Datenordner im Cache des Browsers (unter Verwendung von OPFS)
- Verständnis der Unterschiede zwischen Einzel- und Mehrbenutzerszenarien
- Nutzung der Client Clocking-Funktion
fennec fox optimization algorithm for optimal solution



fennec fox optimization algorithm for optimal solutionshallal2 Imagine you have a group of fennec foxes searching for the best spot to find food (the optimal solution to a problem). Each fox represents a possible solution and carries a unique "strategy" (set of parameters) to find food. These strategies are organized in a table (matrix X), where each row is a fox, and each column is a parameter they adjust, like digging depth or speed.
Play It Safe: Manage Security Risks - Google Certificate



Play It Safe: Manage Security Risks - Google CertificateVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Play It Safe: Manage Security Risks - Google Certificate
The No-Code Way to Build a Marketing Team with One AI Agent (Download the n8n...



The No-Code Way to Build a Marketing Team with One AI Agent (Download the n8n...SOFTTECHHUB The No-Code Way to Build a Marketing Team with One AI Agent (Download the n8n Template Free)
UiPath Automation Suite – Cas d'usage d'une NGO internationale basée à Genève



UiPath Automation Suite – Cas d'usage d'une NGO internationale basée à GenèveUiPathCommunity Nous vous convions à une nouvelle séance de la communauté UiPath en Suisse romande.
Cette séance sera consacrée à un retour d'expérience de la part d'une organisation non gouvernementale basée à Genève. L'équipe en charge de la plateforme UiPath pour cette NGO nous présentera la variété des automatisations mis en oeuvre au fil des années : de la gestion des donations au support des équipes sur les terrains d'opération.
Au délà des cas d'usage, cette session sera aussi l'opportunité de découvrir comment cette organisation a déployé UiPath Automation Suite et Document Understanding.
Cette session a été diffusée en direct le 7 mai 2025 à 13h00 (CET).
Découvrez toutes nos sessions passées et à venir de la communauté UiPath à l’adresse suivante : https://community.uipath.com/geneva/.
Zilliz Cloud Monthly Technical Review: May 2025



Zilliz Cloud Monthly Technical Review: May 2025Zilliz About this webinar
Join our monthly demo for a technical overview of Zilliz Cloud, a highly scalable and performant vector database service for AI applications
Topics covered
- Zilliz Cloud's scalable architecture
- Key features of the developer-friendly UI
- Security best practices and data privacy
- Highlights from recent product releases
This webinar is an excellent opportunity for developers to learn about Zilliz Cloud's capabilities and how it can support their AI projects. Register now to join our community and stay up-to-date with the latest vector database technology.
UiPath Agentic Automation: Community Developer Opportunities



UiPath Agentic Automation: Community Developer OpportunitiesDianaGray10 Please join our UiPath Agentic: Community Developer session where we will review some of the opportunities that will be available this year for developers wanting to learn more about Agentic Automation.
AI 3-in-1: Agents, RAG, and Local Models - Brent Laster



AI 3-in-1: Agents, RAG, and Local Models - Brent LasterAll Things Open Presented at All Things Open RTP Meetup
Presented by Brent Laster - President & Lead Trainer, Tech Skills Transformations LLC
Talk Title: AI 3-in-1: Agents, RAG, and Local Models
Abstract:
Learning and understanding AI concepts is satisfying and rewarding, but the fun part is learning how to work with AI yourself. In this presentation, author, trainer, and experienced technologist Brent Laster will help you do both! We’ll explain why and how to run AI models locally, the basic ideas of agents and RAG, and show how to assemble a simple AI agent in Python that leverages RAG and uses a local model through Ollama.
No experience is needed on these technologies, although we do assume you do have a basic understanding of LLMs.
This will be a fast-paced, engaging mixture of presentations interspersed with code explanations and demos building up to the finished product – something you’ll be able to replicate yourself after the session!
Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD



Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure ADVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD
The Future of Cisco Cloud Security: Innovations and AI Integration



The Future of Cisco Cloud Security: Innovations and AI IntegrationRe-solution Data Ltd Stay ahead with Re-Solution Data Ltd and Cisco cloud security, featuring the latest innovations and AI integration. Our solutions leverage cutting-edge technology to deliver proactive defense and simplified operations. Experience the future of security with our expert guidance and support.
GDG Cloud Southlake #42: Suresh Mathew: Autonomous Resource Optimization: How...



GDG Cloud Southlake #42: Suresh Mathew: Autonomous Resource Optimization: How...James Anderson Autonomous Resource Optimization: How AI is Solving the Overprovisioning Problem
In this session, Suresh Mathew will explore how autonomous AI is revolutionizing cloud resource management for DevOps, SRE, and Platform Engineering teams.
Traditional cloud infrastructure typically suffers from significant overprovisioning—a "better safe than sorry" approach that leads to wasted resources and inflated costs. This presentation will demonstrate how AI-powered autonomous systems are eliminating this problem through continuous, real-time optimization.
Key topics include:
Why manual and rule-based optimization approaches fall short in dynamic cloud environments
How machine learning predicts workload patterns to right-size resources before they're needed
Real-world implementation strategies that don't compromise reliability or performance
Featured case study: Learn how Palo Alto Networks implemented autonomous resource optimization to save $3.5M in cloud costs while maintaining strict performance SLAs across their global security infrastructure.
Bio:
Suresh Mathew is the CEO and Founder of Sedai, an autonomous cloud management platform. Previously, as Sr. MTS Architect at PayPal, he built an AI/ML platform that autonomously resolved performance and availability issues—executing over 2 million remediations annually and becoming the only system trusted to operate independently during peak holiday traffic.
Enterprise Integration Is Dead! Long Live AI-Driven Integration with Apache C...



Enterprise Integration Is Dead! Long Live AI-Driven Integration with Apache C...Markus Eisele We keep hearing that “integration” is old news, with modern architectures and platforms promising frictionless connectivity. So, is enterprise integration really dead? Not exactly! In this session, we’ll talk about how AI-infused applications and tool-calling agents are redefining the concept of integration, especially when combined with the power of Apache Camel.
We will discuss the the role of enterprise integration in an era where Large Language Models (LLMs) and agent-driven automation can interpret business needs, handle routing, and invoke Camel endpoints with minimal developer intervention. You will see how these AI-enabled systems help weave business data, applications, and services together giving us flexibility and freeing us from hardcoding boilerplate of integration flows.
You’ll walk away with:
An updated perspective on the future of “integration” in a world driven by AI, LLMs, and intelligent agents.
Real-world examples of how tool-calling functionality can transform Camel routes into dynamic, adaptive workflows.
Code examples how to merge AI capabilities with Apache Camel to deliver flexible, event-driven architectures at scale.
Roadmap strategies for integrating LLM-powered agents into your enterprise, orchestrating services that previously demanded complex, rigid solutions.
Join us to see why rumours of integration’s relevancy have been greatly exaggerated—and see first hand how Camel, powered by AI, is quietly reinventing how we connect the enterprise.
Reimagine How You and Your Team Work with Microsoft 365 Copilot.pptx



Reimagine How You and Your Team Work with Microsoft 365 Copilot.pptxJohn Moore M365 Community Conference 2025 Workshop on Microsoft 365 Copilot
GyrusAI - Broadcasting & Streaming Applications Driven by AI and ML



GyrusAI - Broadcasting & Streaming Applications Driven by AI and MLGyrus AI Gyrus AI: AI/ML for Broadcasting & Streaming
Gyrus is a Vision Al company developing Neural Network Accelerators and ready to deploy AI/ML Models for Video Processing and Video Analytics.
Our Solutions:
Intelligent Media Search
Semantic & contextual search for faster, smarter content discovery.
In-Scene Ad Placement
AI-powered ad insertion to maximize monetization and user experience.
Video Anonymization
Automatically masks sensitive content to ensure privacy compliance.
Vision Analytics
Real-time object detection and engagement tracking.
Why Gyrus AI?
We help media companies streamline operations, enhance media discovery, and stay competitive in the rapidly evolving broadcasting & streaming landscape.
🚀 Ready to Transform Your Media Workflow?
🔗 Visit Us: https://gyrus.ai/
📅 Book a Demo: https://gyrus.ai/contact
📝 Read More: https://gyrus.ai/blog/
🔗 Follow Us:
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/gyrusai/
Twitter/X - https://twitter.com/GyrusAI
YouTube - https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCk2GzLj6xp0A6Wqix1GWSkw
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/GyrusAI
Ad
Programming Methodologies Functions - C Language
- 1. ICT 1405 Programming Methodologies 8. Functions
- 2. Function? ● Also known as procedure or subroutine in other programming languages. ● A function is a group of statements that together perform a task. ● A function can be called many times. ● A function is a block of code that only runs when it is called.
- 3. Why do we need function? ● Reduce code redundancy. ○ If functionality is performed at multiple places in software, then rather than writing the same code, again and again, it can create a function and call it everywhere. ● Make code modular. ○ It becomes really simple to read and use the code if the code is divided into functions ● Provide abstraction. ○ Can use library functions without knowing about their internal work.
- 4. Advantages of Functions ● Easier to Code ○ A lengthy program can be divided into small functions. ○ A function is written for a specific task. ○ A programmer can focus the attention on a specific problem. ● Easier to Modify ○ If there is an error in the program, it is corrected in the corresponding function.
- 5. ● Easier to Maintain & Debug ○ Each function contains independent source code. ○ A change in one part of the code does not affect other parts. ○ In case of an error, the infected function is debugged only. ○ The user does not need to examine the whole program. ● Reusability ○ They can be executed many times, can call a function whenever it needs. ○ It can be executed in different parts of the program to display the line repeatedly.
- 6. ● Less Programming Time ○ A program may be made up of many functions, which are written as independent programs. ○ Different programmers can work on different functions simultaneously, which saves a lot of time in the long run.
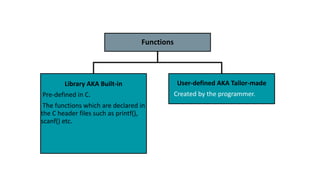
- 7. Functions Library AKA Built-in Pre-defined in C. The functions which are declared in the C header files such as printf(), scanf() etc. User-defined AKA Tailor-made Created by the programmer.
- 8. Declaration of a function ● Syntax: return_type function_name (parameter1, parameter2,...) { //code to be executed }
- 9. ● return_type : Data type specifier of the data returned by the function. ● function_name : The identifier by which it will be possible to call the function. ● Parameters : ○ Each parameter consists of a data type specifier followed by an identifier. (for example: int age) ● Allow passing arguments to the function when it is called. ● Different parameters are separated by commas. ● Function's body contains statement/s. It is a block of statements surrounded by braces { }.
- 10. Functions Built-in User-defined No return type - No parameters With return type - no parameter/s. With parameter/s - no return type. With parameter/s and return type.
- 11. No Parameter/s - No Return Type Syntax: void functionName (){ //function implementation } Example: void addition(){ int total = 0; int x = 10; int y = 20; total = x + y; printf(“Total is : %d” , total); }
- 12. With Return Type - No Parameter Syntax: returnType functionName (){ //function implementation //return statement } Example: int addition(){ int total = 0; int x = 10; int y = 20; total = x + y; return total; }
- 13. With Parameter/s - No Return Type Syntax: void functionName (dataType parameter1, dataType parameter2){ //function implementation } Example: void addition(int x, int y){ int total = 0; total = x + y; printf(“Total is : %d” , total); }
- 14. With Parameter/s and Return Type. Syntax: returnType functionName (dataType parameter1, dataType parameter2){ //function implementation //return statement } Example: int addition(int x, int y){ int total = 0; total = x + y; return total; }
- 15. Calling the Function ● Calling or invoking the function locates the function in the memory, furnishing it with arguments and causing it to execute. ● When a function is called then the control passed to the function where it is actually defined. ● The actually statements are executed and control passed again to the calling program. Syntax: variable= function_name(argument1, argument1, …, argumentN);
- 16. Prototyping a Function ● While writing a program, function cannot be used without specifying its type or without telling the compiler about it. ● Therefore, before calling a function, it must be either declared or defined. ● Thus, declaring a function before calling a function is called function declaration or prototype which tells the compiler that at some point of the program we will use the function of the name specified in the prototype. Syntax: returnType functionName(dataType, dataType, … ); OR returnType functionName(dataType parameter1, dataType parameter2, … );
- 17. END





