Project Allocation Linear Programming Optimisation
0 likes167 views
This document summarizes the formulation, implementation, analysis and evaluation of different integer programming models for optimizing student-project allocation. Model 1 assigns each student to exactly one topic based on their preferences while satisfying supervisor and topic capacity constraints. Model 2 adds penalties to encourage distributing students across more topics without sacrificing preferences. The results are analyzed for student satisfaction and constraint satisfaction. Alternative formulations are reviewed that consider collective satisfaction, fairness and computational cost trade-offs.
1 of 18
Download to read offline


![Problem Formulation: Model #13
Objective Function
Decision Variables
[Binary for assigning topic j to student i]
𝐶𝑖𝑗
∈ {3, 2, 1} is Coefficient of Satisfaction
𝑠j
∈ ℤ+
is the extra capacity for each topic
𝑀𝑗
∈ ℤ+
is the penalty for each 𝑠𝑗
𝑥𝑖𝑗
is 0 if student i is not assigned to topic j
𝑥𝑖𝑗
is 1 if student i is assigned to topic j
where 𝑖 ∈ [1,𝐼] and j ∈ [1,𝐽]
𝑥𝑖𝑗
∈ { 0, 1 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearprogrammingoptimisation-200609230052/85/Project-Allocation-Linear-Programming-Optimisation-3-320.jpg)













Ad
Recommended
Contract lecture



Contract lectureEka Puspita Sari This document provides a summary of the Calculus II course including:
1) The course covers concepts of anti-derivatives, definite integrals, transcendental functions, and integration techniques.
2) The course objectives are for students to understand integral concepts and solve problems logically.
3) Student assessment is based on assignments, quizzes, midterms, and a final exam, with grades ranging from A to E.
Course recommender system



Course recommender systemAakash Chotrani This document describes a course recommender system that aims to recommend courses to students based on their past performance. It does this by using a machine learning algorithm to predict students' grades in courses based on their grades in previous courses. The algorithm trains on a dataset containing students' grades in various courses. It learns weights representing the importance of each previous course on performance in the target course. These weights are used to calculate predicted grades. The algorithm is tested on masked data and iteratively updated to reduce error between predictions and actual grades. The goal is to predict grades with under 10% error to provide good course recommendations. Alternate methods like course-specific and student-specific regression are also described.
Role of cognitive intelligence in coping with examination stress



Role of cognitive intelligence in coping with examination stressMangaleswarasharma Rajini The document describes a study that examined the role of cognitive intelligence in coping with examination stress among Sri Lankan adolescent students. The study used a mixed methods approach, collecting qualitative data through interviews in phase 1 and developing a theoretical model. Phase 2 then quantitatively tested and refined the model through a survey of 357 students, analyzing the data using structural equation modeling. The final accepted structural model supported relationships between language skills and academic self-confidence, academic self-confidence and self-regulated learning, and self-regulated learning and coping with examination stress.
Investigating learning strategies in a dispositional learning analytics conte...



Investigating learning strategies in a dispositional learning analytics conte...Bart Rienties This document discusses a study analyzing how students use worked examples, tutored problem-solving, and untutored problem-solving in an online math tutorial system called SOWISO. The study examines how these learning modes relate to student performance and dispositions. Key findings include: (1) engagement with tutorials and mastery of content strongly predicts exam scores; (2) students frequently use worked examples and rarely use hints for tutored problem-solving; (3) adaptive dispositions correlate with timely preparation and less example use, while maladaptive dispositions correlate with less preparation and more example use.
Achievement test



Achievement testSumi Surendran S This document outlines the process for developing and validating an achievement test in biology. It discusses planning the test by selecting topics, writing questions at different cognitive levels, and constructing a blueprint. Items are developed and analyzed based on difficulty index and discriminating power. A scoring key is prepared and the draft test is administered to a sample. The final test is selected based on item analysis results and validated for content, criterion, and construct validity as well as reliability.
Aied 2013



Aied 2013Roya Hosseini The document describes Knowledge Maximizer (KM), a concept-based problem sequencing tool for exam preparation in Java programming. KM uses an ontology of Java concepts and a student model to select practice problems that will help address gaps in a student's knowledge while maximizing the number of concepts assessed. A classroom study found that while success rates were comparable between KM and other tools, KM pushed students to attempt more complex questions targeting more concepts at once, helping them more efficiently fill gaps in their knowledge.
Achievement test powerpoint97 2003



Achievement test powerpoint97 2003SwathiE6 how to conduct achievement test for student and the steps involved in conducting the test - model blue print.
The Effects of Study Skills Training and Peer Coaching of At-Risk Students on...



The Effects of Study Skills Training and Peer Coaching of At-Risk Students on...Lehman Teaching & Learning Commons 1) The Developmental Algebra Project aimed to reduce attrition and improve pass rates in remedial math courses through study skills training and peer coaching of at-risk students.
2) At-risk students were identified using a diagnostic test, survey, and observations and then assigned peer coaches. Peer coaches met weekly with students to review work and prepare for tests.
3) The treatment group that received study skills training and peer coaching had significantly higher retention rates compared to the control group. However, there was no significant difference in pass rates between the groups. Peer coaching seemed to positively impact pass rates based on number of sessions attended.
CantaNet NCEA Analysis 2012



CantaNet NCEA Analysis 2012sudsnz NCEA Analysis compares student results from virtual classes (VC) to their face-to-face class results. Each reported learning outcome (ROL) is examined and given a numerical value from 1 to 3, with 1 being the best result. These numbers are totaled and converted to percentages at the end. In 2010, two courses had very poor external exam results with almost all students earning N grades, impacting the overall data even though most students did fine in their regular classes. Two other courses also had weak results that year, while the remaining courses performed strongly.
Field testing chunk 1b



Field testing chunk 1bmarjorie manuel Teachers will create an assessment to measure students' problem solving skills after implementing the first part of the TIPS strategy. They will analyze student work and determine the next steps. The meeting will include sharing resources and developing a focus quiz to give students with a word problem and space for justification. Teachers will bring student work and assessment results to the next meeting.
Nctmsecon standards



Nctmsecon standardsAmmamiarihta Tarigan The document outlines standards for secondary mathematics teacher preparation programs. It discusses 7 process standards addressing how mathematics should be approached as a unified whole. It also includes a standard on dispositions addressing candidates' nature as mathematicians and instructors. The document then outlines 8 standards on pedagogical knowledge candidates should possess, including knowledge of mathematical problem solving, reasoning, communication, connections, representations, technology, and pedagogy. It concludes by outlining 7 content standards on number/operation, algebra, geometry, and calculus.
SBAC Performance Task Overview



SBAC Performance Task OverviewGlenn E. Malone, EdD This document provides an overview of performance tasks and classroom activities for online mathematics and English language arts assessments. It defines performance tasks as portions of the test that require students to answer complex, multi-step questions about a topic. Classroom activities are administered separately before performance tasks to familiarize students with relevant topics. The document includes examples of classroom activities and performance task questions in both subjects.
Needs assessment



Needs assessmentMohamed Ibrahim This document discusses the needs assessment process, which is the first step in the Dick and Carey instructional design model. A needs assessment is used to identify instructional goals by determining the gap between desired goals and current status. There are six types of educational needs that can be assessed. The needs assessment aims to identify the problem, causes of the problem, and potential solutions. Determining goals is also discussed - goals should be stated in terms of new skills, knowledge, or attitudes for learners and include what learners will be able to do after instruction. A clear problem description, evidence of causes, and suggested solutions should result from a needs assessment. The importance of determining goals is that it directs all subsequent design decisions by specifying
item analysics



item analysicsPraveen Kumar This document discusses item analysis, which is the process of evaluating the effectiveness of individual multiple choice questions (MCQs) on a test. Item analysis has several objectives, including selecting appropriate questions, determining question difficulty, and ensuring questions can differentiate between more and less capable test takers. It involves arranging test scores and separating respondents into high- and low-scoring groups. Key metrics calculated through item analysis are the difficulty index, which indicates how hard a question is, and the discrimination index, which shows how well a question distinguishes between strong and weak test takers. Item analysis provides useful information for improving test questions and guiding students.
1 elem ccss in-service presentation



1 elem ccss in-service presentationagentry1908 The document provides an overview of the Common Core State Standards including the goals, adoption by states, instructional shifts, implementation timeline, and assessments. It discusses narrowing the standards to focus more deeply on key concepts, building coherence across grade levels, and requiring equal rigor in conceptual understanding, skills, and application. Sample 5th grade math standards on fractions and diagrams are presented. The document emphasizes how the standards complement other initiatives to prepare students for college and careers.
CARP 



CARP slglorioso The document describes a study on using semantic mapping to improve students' vocabulary and SAT scores. It tested the strategy in several high school classes. Results showed that semantic mapping significantly increased students' vocabulary scores and their confidence in using vocabulary words in most classes. The strategy was less effective in chemistry possibly due to lack of routine use. Overall, semantic mapping shows promise as a vocabulary learning strategy to help improve SAT scores when implemented consistently across subjects.
Student created cheat sheets in examinations



Student created cheat sheets in examinationsMichael de Raadt Results of a study that explored the use of student created cheat-sheets and the impact on performance.
AN E XAMINATION OF T HE E FFECTIVENESS OF T EACHING D ATA M ODELLING C ONCEPTS



AN E XAMINATION OF T HE E FFECTIVENESS OF T EACHING D ATA M ODELLING C ONCEPTSIJDMS The effective teaching of data modelling concepts i
s very important; it constitutes the fundament of d
ata-
base planning methods and the handling of databases
with the help of database management languages,
typically SQL. We examined three courses. The stude
nts of two courses prepared for the exam by solving
tests, while the students of the third course prepa
red by solving tasks from a printed exercise book.
The
number of task for the second course was 2.5 times
more than the number of task for the first course.
The
main purpose of our examination was to determine th
e effectiveness of the teaching of data modelling c
on-
cepts, and to decide if there is a significant diff
erence between the results of the three courses. Ac
cording to
our examination, with increasing the number of test
tasks and with the use of exercise book, the resul
ts
became significantly better
Test Blueprint



Test BlueprintDarrin Thomas A test blueprint is a map that outlines the objectives being assessed on a test and the different levels of thinking required to answer each question. It maps objectives to taxonomy and provides details on objectives and statistics on the proportion of questions. Using a test blueprint helps create balanced exams by determining objectives, question types, and cognitive levels being addressed.
FYP ppt



FYP pptAniqa Bano The document describes a student profiling system that uses fuzzy logic and neural networks. It proposes using Fuzzy C-means clustering and Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS) on survey data from students to understand their learning capabilities and create rules for a more personalized learning approach. A survey was conducted with 30 students which formed a dataset for the system. Fuzzy C-means clustering and ANFIS were used to analyze the data and generate inferences. The system aims to improve learning effectiveness through customizing learning based on students' cognitive states and skills.
CONCEPTUAL APPROACH AND SOLVING WORD PROBLEM INVOLVING MULTIPLICATION OF WHOL...



CONCEPTUAL APPROACH AND SOLVING WORD PROBLEM INVOLVING MULTIPLICATION OF WHOL...WayneRavi This study was conducted to determine the effect of conceptual approach on solving word problems involving multiplication of whole numbers as well as addition and subtraction. The study was carried out in Tambongon Elementary School to Fourty-one Grade Two students. Descriptive statistics (mean & SD), paired-sample T-test and ETA2 were used as tools in the analysis of data. Results revealed that there was a significant difference on the pretest and post test scores of conceptual approach. Further, conceptual approach has large effect.
Empowering Pre-Service & New Math Teachers to Use the Common Core Practice St...



Empowering Pre-Service & New Math Teachers to Use the Common Core Practice St...DreamBox Learning How prepared are the K-12 teachers of tomorrow to inspire the next generation of young mathematicians? In this webinar for the edWeb.net Adaptive Math Learning community, attendees learned how essential it is for pre-service teachers to learn, develop, and model the Standards for Mathematical Practice to improve learning for their future students. Ben Braun, Associate Professor of Mathematics at the University of Kentucky, and Tim Hudson, Senior Director of Curriculum Design at DreamBox Learning, discussed ways to ensure that pre-service teachers start their careers understanding how mathematical proficiency requires more than simply content knowledge. Tim and Ben shared ideas for K-12 school leaders and mentor teachers who are responsible for new teacher induction, as well as, implications for college and university faculty teaching both math methods and content courses. They also discussed potential disconnects between pre-service content and methods courses and also eventual in-service expectations, while providing examples of math problems to engage pre-service and new teachers. View the webinar to better understand how to use the Standards for Mathematical Practice.
1a Introduction To Rasch Measurement Model Msm



1a Introduction To Rasch Measurement Model MsmSaidfudin Mas'udi The document provides an introduction to the Rasch measurement model. It discusses how Rasch analysis can transform ordinal test score data into interval scale data to provide a linear measurement. This overcomes limitations of traditional statistics. The Rasch model conceptualizes measurement as developing a ruler along a continuum of a construct. It establishes probability of a person's response based on their ability and the item difficulty. The model aims to meet criteria for valid measurement including a linear scale, accuracy, validity, replicability and predictive ability.
Reactions to Gamified Training



Reactions to Gamified TrainingMichael Armstrong My poster presentation at the Old Dominion University Graduate Research Appreciation Day 2014 based on my first graduate research project. Participants were given 2 scenarios about different training scenarios - one about traditional PowerPoint lecture training and the other about playing an interactive video game as part of training. Reactions to these scenarios were measured and analyzed. Attitudes towards video games and experience with video games were measured as moderators of the effect of training design on reactions.
CourseEvaluationReport_SPAN102_2015



CourseEvaluationReport_SPAN102_2015Victoriano Pimentel Victoriano Pimentel Rivas received a course evaluation report for his Elementary Spanish II course from Logan Michels of the Office of Institutional Research, Planning and Assessment at Minnesota State University, Mankato. The 12 student evaluations gave the course and instructor overwhelmingly positive reviews, with average ratings above 4.5 out of 5 for most categories. Student comments praised the instructor's enthusiasm, feedback, and use of class time to ensure students learned. A few students suggested providing more opportunities to practice conversational Spanish.
Administering a test, scoring - grading vs marks



Administering a test, scoring - grading vs marksEarnest Lamuel The document discusses various concepts related to administering tests, scoring, grading, and marking. It provides information on:
- The importance of the test administrator's role in creating a calm environment and inspiring confidence in test-takers.
- Different types of tests, such as criterion-referenced tests which measure mastery and norm-referenced tests which provide relative rankings.
- The process of scoring, which determines raw scores, and grading, which assigns symbols or categories to represent performance quality.
- Methods of grading like the analytic method which assigns separate scores to dimensions and the global method which uses general impressions.
- The difference between marking, which awards numbers or symbols to tasks, and
Mat120 syllabus



Mat120 syllabuschellc14 This document provides a course syllabus for MAT 120 - Math For The Behavioral Sciences. The 3-credit course presents arithmetic review, ratios/proportions, percentages, algebra, statistics, and word problems. Students will demonstrate proficiency in interpreting sets, performing number operations, solving equations/inequalities, applying ratios/proportions/percentages, and analyzing/interpreting data. The course grade is based on tests, a final exam, and homework. Tutoring is available for students.
Item and Distracter Analysis



Item and Distracter AnalysisSue Quirante The document discusses item analysis, which is the process of examining test responses to evaluate the quality of individual test items and the test itself. It aims to improve the effectiveness of items used on future tests. Key aspects covered include item difficulty index, item discrimination, and analyzing items based on how well they measure the effects of instruction. The document provides examples and interpretations for calculating various metrics used in item analysis.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
CantaNet NCEA Analysis 2012



CantaNet NCEA Analysis 2012sudsnz NCEA Analysis compares student results from virtual classes (VC) to their face-to-face class results. Each reported learning outcome (ROL) is examined and given a numerical value from 1 to 3, with 1 being the best result. These numbers are totaled and converted to percentages at the end. In 2010, two courses had very poor external exam results with almost all students earning N grades, impacting the overall data even though most students did fine in their regular classes. Two other courses also had weak results that year, while the remaining courses performed strongly.
Field testing chunk 1b



Field testing chunk 1bmarjorie manuel Teachers will create an assessment to measure students' problem solving skills after implementing the first part of the TIPS strategy. They will analyze student work and determine the next steps. The meeting will include sharing resources and developing a focus quiz to give students with a word problem and space for justification. Teachers will bring student work and assessment results to the next meeting.
Nctmsecon standards



Nctmsecon standardsAmmamiarihta Tarigan The document outlines standards for secondary mathematics teacher preparation programs. It discusses 7 process standards addressing how mathematics should be approached as a unified whole. It also includes a standard on dispositions addressing candidates' nature as mathematicians and instructors. The document then outlines 8 standards on pedagogical knowledge candidates should possess, including knowledge of mathematical problem solving, reasoning, communication, connections, representations, technology, and pedagogy. It concludes by outlining 7 content standards on number/operation, algebra, geometry, and calculus.
SBAC Performance Task Overview



SBAC Performance Task OverviewGlenn E. Malone, EdD This document provides an overview of performance tasks and classroom activities for online mathematics and English language arts assessments. It defines performance tasks as portions of the test that require students to answer complex, multi-step questions about a topic. Classroom activities are administered separately before performance tasks to familiarize students with relevant topics. The document includes examples of classroom activities and performance task questions in both subjects.
Needs assessment



Needs assessmentMohamed Ibrahim This document discusses the needs assessment process, which is the first step in the Dick and Carey instructional design model. A needs assessment is used to identify instructional goals by determining the gap between desired goals and current status. There are six types of educational needs that can be assessed. The needs assessment aims to identify the problem, causes of the problem, and potential solutions. Determining goals is also discussed - goals should be stated in terms of new skills, knowledge, or attitudes for learners and include what learners will be able to do after instruction. A clear problem description, evidence of causes, and suggested solutions should result from a needs assessment. The importance of determining goals is that it directs all subsequent design decisions by specifying
item analysics



item analysicsPraveen Kumar This document discusses item analysis, which is the process of evaluating the effectiveness of individual multiple choice questions (MCQs) on a test. Item analysis has several objectives, including selecting appropriate questions, determining question difficulty, and ensuring questions can differentiate between more and less capable test takers. It involves arranging test scores and separating respondents into high- and low-scoring groups. Key metrics calculated through item analysis are the difficulty index, which indicates how hard a question is, and the discrimination index, which shows how well a question distinguishes between strong and weak test takers. Item analysis provides useful information for improving test questions and guiding students.
1 elem ccss in-service presentation



1 elem ccss in-service presentationagentry1908 The document provides an overview of the Common Core State Standards including the goals, adoption by states, instructional shifts, implementation timeline, and assessments. It discusses narrowing the standards to focus more deeply on key concepts, building coherence across grade levels, and requiring equal rigor in conceptual understanding, skills, and application. Sample 5th grade math standards on fractions and diagrams are presented. The document emphasizes how the standards complement other initiatives to prepare students for college and careers.
CARP 



CARP slglorioso The document describes a study on using semantic mapping to improve students' vocabulary and SAT scores. It tested the strategy in several high school classes. Results showed that semantic mapping significantly increased students' vocabulary scores and their confidence in using vocabulary words in most classes. The strategy was less effective in chemistry possibly due to lack of routine use. Overall, semantic mapping shows promise as a vocabulary learning strategy to help improve SAT scores when implemented consistently across subjects.
Student created cheat sheets in examinations



Student created cheat sheets in examinationsMichael de Raadt Results of a study that explored the use of student created cheat-sheets and the impact on performance.
AN E XAMINATION OF T HE E FFECTIVENESS OF T EACHING D ATA M ODELLING C ONCEPTS



AN E XAMINATION OF T HE E FFECTIVENESS OF T EACHING D ATA M ODELLING C ONCEPTSIJDMS The effective teaching of data modelling concepts i
s very important; it constitutes the fundament of d
ata-
base planning methods and the handling of databases
with the help of database management languages,
typically SQL. We examined three courses. The stude
nts of two courses prepared for the exam by solving
tests, while the students of the third course prepa
red by solving tasks from a printed exercise book.
The
number of task for the second course was 2.5 times
more than the number of task for the first course.
The
main purpose of our examination was to determine th
e effectiveness of the teaching of data modelling c
on-
cepts, and to decide if there is a significant diff
erence between the results of the three courses. Ac
cording to
our examination, with increasing the number of test
tasks and with the use of exercise book, the resul
ts
became significantly better
Test Blueprint



Test BlueprintDarrin Thomas A test blueprint is a map that outlines the objectives being assessed on a test and the different levels of thinking required to answer each question. It maps objectives to taxonomy and provides details on objectives and statistics on the proportion of questions. Using a test blueprint helps create balanced exams by determining objectives, question types, and cognitive levels being addressed.
FYP ppt



FYP pptAniqa Bano The document describes a student profiling system that uses fuzzy logic and neural networks. It proposes using Fuzzy C-means clustering and Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS) on survey data from students to understand their learning capabilities and create rules for a more personalized learning approach. A survey was conducted with 30 students which formed a dataset for the system. Fuzzy C-means clustering and ANFIS were used to analyze the data and generate inferences. The system aims to improve learning effectiveness through customizing learning based on students' cognitive states and skills.
CONCEPTUAL APPROACH AND SOLVING WORD PROBLEM INVOLVING MULTIPLICATION OF WHOL...



CONCEPTUAL APPROACH AND SOLVING WORD PROBLEM INVOLVING MULTIPLICATION OF WHOL...WayneRavi This study was conducted to determine the effect of conceptual approach on solving word problems involving multiplication of whole numbers as well as addition and subtraction. The study was carried out in Tambongon Elementary School to Fourty-one Grade Two students. Descriptive statistics (mean & SD), paired-sample T-test and ETA2 were used as tools in the analysis of data. Results revealed that there was a significant difference on the pretest and post test scores of conceptual approach. Further, conceptual approach has large effect.
Empowering Pre-Service & New Math Teachers to Use the Common Core Practice St...



Empowering Pre-Service & New Math Teachers to Use the Common Core Practice St...DreamBox Learning How prepared are the K-12 teachers of tomorrow to inspire the next generation of young mathematicians? In this webinar for the edWeb.net Adaptive Math Learning community, attendees learned how essential it is for pre-service teachers to learn, develop, and model the Standards for Mathematical Practice to improve learning for their future students. Ben Braun, Associate Professor of Mathematics at the University of Kentucky, and Tim Hudson, Senior Director of Curriculum Design at DreamBox Learning, discussed ways to ensure that pre-service teachers start their careers understanding how mathematical proficiency requires more than simply content knowledge. Tim and Ben shared ideas for K-12 school leaders and mentor teachers who are responsible for new teacher induction, as well as, implications for college and university faculty teaching both math methods and content courses. They also discussed potential disconnects between pre-service content and methods courses and also eventual in-service expectations, while providing examples of math problems to engage pre-service and new teachers. View the webinar to better understand how to use the Standards for Mathematical Practice.
1a Introduction To Rasch Measurement Model Msm



1a Introduction To Rasch Measurement Model MsmSaidfudin Mas'udi The document provides an introduction to the Rasch measurement model. It discusses how Rasch analysis can transform ordinal test score data into interval scale data to provide a linear measurement. This overcomes limitations of traditional statistics. The Rasch model conceptualizes measurement as developing a ruler along a continuum of a construct. It establishes probability of a person's response based on their ability and the item difficulty. The model aims to meet criteria for valid measurement including a linear scale, accuracy, validity, replicability and predictive ability.
Reactions to Gamified Training



Reactions to Gamified TrainingMichael Armstrong My poster presentation at the Old Dominion University Graduate Research Appreciation Day 2014 based on my first graduate research project. Participants were given 2 scenarios about different training scenarios - one about traditional PowerPoint lecture training and the other about playing an interactive video game as part of training. Reactions to these scenarios were measured and analyzed. Attitudes towards video games and experience with video games were measured as moderators of the effect of training design on reactions.
CourseEvaluationReport_SPAN102_2015



CourseEvaluationReport_SPAN102_2015Victoriano Pimentel Victoriano Pimentel Rivas received a course evaluation report for his Elementary Spanish II course from Logan Michels of the Office of Institutional Research, Planning and Assessment at Minnesota State University, Mankato. The 12 student evaluations gave the course and instructor overwhelmingly positive reviews, with average ratings above 4.5 out of 5 for most categories. Student comments praised the instructor's enthusiasm, feedback, and use of class time to ensure students learned. A few students suggested providing more opportunities to practice conversational Spanish.
Administering a test, scoring - grading vs marks



Administering a test, scoring - grading vs marksEarnest Lamuel The document discusses various concepts related to administering tests, scoring, grading, and marking. It provides information on:
- The importance of the test administrator's role in creating a calm environment and inspiring confidence in test-takers.
- Different types of tests, such as criterion-referenced tests which measure mastery and norm-referenced tests which provide relative rankings.
- The process of scoring, which determines raw scores, and grading, which assigns symbols or categories to represent performance quality.
- Methods of grading like the analytic method which assigns separate scores to dimensions and the global method which uses general impressions.
- The difference between marking, which awards numbers or symbols to tasks, and
Mat120 syllabus



Mat120 syllabuschellc14 This document provides a course syllabus for MAT 120 - Math For The Behavioral Sciences. The 3-credit course presents arithmetic review, ratios/proportions, percentages, algebra, statistics, and word problems. Students will demonstrate proficiency in interpreting sets, performing number operations, solving equations/inequalities, applying ratios/proportions/percentages, and analyzing/interpreting data. The course grade is based on tests, a final exam, and homework. Tutoring is available for students.
Similar to Project Allocation Linear Programming Optimisation (20)
Item and Distracter Analysis



Item and Distracter AnalysisSue Quirante The document discusses item analysis, which is the process of examining test responses to evaluate the quality of individual test items and the test itself. It aims to improve the effectiveness of items used on future tests. Key aspects covered include item difficulty index, item discrimination, and analyzing items based on how well they measure the effects of instruction. The document provides examples and interpretations for calculating various metrics used in item analysis.
1 Saint Leo University MAT 131 College Mathemati.docx



1 Saint Leo University MAT 131 College Mathemati.docxaryan532920 1
Saint Leo University
MAT 131
College Mathematics
Course Description:
Topics include critical thinking, number theory, measurement, percentages, geometry, counting
methods, probability, and statistics.
Prerequisite:
None
Textbooks:
Blitzer, B. (2011). Thinking mathematically with Mymathlab plus access (6th ed.). Boston, MA:
Pearson-Prentice Hall. ISBN-13: 978-0-321-86732-2
White, J., & White, S. (2015). Thinking critically to solve problems: Combining values and
college mathematics. Boston, MA: Pearson-Prentice Hall. ISBN-13: 978-1-5115-3917-3
The MyMathLab Plus access code includes Thinking Mathematically (Blitzer) eBook
access, so purchasing the physical Blitzer textbook is optional.
Learning Outcomes:
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
1. Solve problems involving data analysis and probability and obtain a better sense of
community when interpreting studies that relate to the world around them.
2. Use concepts that relate to number sense, concepts, and operations.
3. Use measurement techniques and demonstrate knowledge of geometry and spatial
sense.
4. Use basic problem-solving strategies.
5. Explore how mathematics can be used to enhance community.
Core Value:
Students will be learning the mathematical skills for solving problems and then investigate how
those skills and solutions can be used to enhance community.
Community: Saint Leo University develops hospitable Christian learning communities
everywhere we serve. We foster a spirit of belonging, unity, and interdependence based on
mutual trust and respect to create socially responsible environments that challenge all of us to
listen, to learn, to change, and to serve.
2
Evaluation:
In determining the final grade, the following weights will apply:
Problem Sets (7 @ 2% each) 14%
Quizzes (4 @ 2% each) 8%
Exams (2 @ 13% each) 26%
Final Test 20%
Discussions (8 @ 1% each) 8%
Group Project 12%
Individual Project 12%
Total 100%
Module Breakdown of Percentages:
Module 1: Problem Set 1 = 2%, Discussion = 1%
Module 2: Problem Set 2 = 2%, Discussion = 1%, Quiz 1 = 2%, Exam 1= 13%,
Module 3: Problem Set 3 = 2%, Discussion = 1%
Module 4: Problem Set 4 = 2%, Discussion = 1%, Quiz 2 = 2%, Group Project = 12%
Module 5: Problem Set 5 = 2%, Discussion = 1%
Module 6: Problem Set 6 = 2%, Discussion = 1%, Quiz 3 = 2%, Exam 2 = 13%
Module 7: Problem Set 7 = 2%, Discussion = 1%
Module 8: Discussion = 1%, Quiz 4 = 2%, Final Test = 20%, Individual Project = 12%
Grading Scale:
Grade Score (%)
A 94-100
A- 90-93
B+ 87-89
B 84-86
B- 80-83
C+ 77-79
C 74-76
C- 70-73
D+ 67-69
D 60-66
F 0-59
A minimum grade of “C” is needed to fulfill the degree requirement.
MyMathLab:
Most of your assignments for this course will be completed in MyMathLab, which is designed to ...
PLANNING CLASSROOM TESTS AND ASSESSMENTS



PLANNING CLASSROOM TESTS AND ASSESSMENTSSANA FATIMA This document discusses planning classroom tests and assessments. It outlines 8 steps for planning tests: 1) determining the purpose, 2) developing test specifications, 3) selecting item types, 4) preparing items, 5) assembling the test, 6) administering the test, 7) appraising the test, and 8) using results. Different types of assessments are described including pre-tests, formative assessments, and post-tests. Guidelines are provided for developing test blueprints and selecting appropriate item types such as essay, short answer, and objective items.
SEU Management the Blue Sky Project Case Questions.docx



SEU Management the Blue Sky Project Case Questions.docxwrite5 1. The document provides instructions for an assignment on project management for a college course. It includes a case study from the textbook on a project called the Blue Sky Project and asks students to answer 3 questions about the case study.
2. The questions ask how a project manager would respond to issues, what mistakes were made, and lessons learned from the case study related to project management concepts. The assignment is due by a specified date and guidelines are provided on formatting, references, and plagiarism.
3. Additional details are given on assignment requirements and objectives to understand project management concepts, monitor and control projects, and work effectively in a team.
Donors Choose Project (1)



Donors Choose Project (1)Fernando Hidalgo This document discusses predicting whether education projects on DonorsChoose.org will be funded. It presents a classification problem using DonorsChoose data from 2002 to present. Features like project price, number of students, school details are analyzed. Logistic regression achieved the best accuracy score of 0.811. Further feature analysis found the top 5 predictive features were total price, funding eligibility, and resource type. Using only these 5 features, logistic regression accuracy improved to 0.8171. While the model performance increased over the baseline, concerns were noted that the most predictive features cannot be changed without fabrication. Suggestions to improve the model include adding essay/material text and using location-based census data.
Umap17 learner modelingforintegrationskills_yunhuang



Umap17 learner modelingforintegrationskills_yunhuangYun Huang Complex skill mastery requires not only acquiring individual basic component skills, but also practicing integrating such basic skills. However, traditional approaches to knowledge modeling, such as Bayesian Knowledge Tracing, only trace knowledge of each decomposed basic component skill. This risks early assertion of mastery or ineffective remediation failing to address skill integration. We propose a diagnostic Bayesian network based on a hierarchical integration graph for learner knowledge modeling. We assess the value of such a model from four aspects: performance prediction, parameter plausibility, expected instructional effectiveness, and real-world recommendation helpfulness. Our experiments with a Java programming dataset and a user study based on a Java programming tutor show that proposed model significantly improves two popular multiple skill knowledge tracing models on all these four aspects. Our work serves as a first step towards building skill application context sensitive learner model for modeling and promoting students’ robust learning.
Achievement test - Teacher Made Test and Standardized Test - Characteristics,...



Achievement test - Teacher Made Test and Standardized Test - Characteristics,...Suresh Babu Achievement test - Teacher Made Test and Standardized Test - Characteristics, Steps in Construction (blueprint) and Standardization, Types of Test Items - objective, short answer and long answer- its merits and demerits.
SE-IT MINI PROJECT SYLLABUS



SE-IT MINI PROJECT SYLLABUSnikshaikh786 The document outlines the program structure for the second year of engineering studies at the University of Mumbai. It details the courses, credits, teaching and examination schemes for Semesters III and IV. It includes guidelines for a Mini Project that students must complete in groups of 3-4 over the two semesters to identify problems, propose solutions, build prototypes, and demonstrate their work. The Mini Project aims to develop students' problem-solving, communication, and lifelong learning skills through hands-on work addressing societal needs.
micro testing teaching learning analytics



micro testing teaching learning analyticsMartin Schön Development of adaptive microlearning apps for testing competence in multiplication tables, educational data mining edm, learning analytics
joe beck cald talk.ppt



joe beck cald talk.pptEverMontoya2 Computer tutors provide detailed interaction data that can be used for educational data mining to assess students and improve tutoring. The Project LISTEN reading tutor collects extensive data on student speech, help requests, tutor actions and more. This data is used to predict student help requests using classification models, infer student subword knowledge like grapheme-phoneme mappings using knowledge tracing, and assess students' reading proficiency. Future work includes improving these assessment capabilities and developing a more comprehensive model of student knowledge.
Exams evaluate students. Who’s evaluating exams? Data-Informed Exam Design



Exams evaluate students. Who’s evaluating exams? Data-Informed Exam DesignG. Alex Ambrose 2019 Midwest Scholarship of Teaching & Learning (SOTL) conference presentation. The goal of this presentation is to share our data-informed approach to re-engineer the exam design, delivery, grading, and item analysis process in order to construct better exams that maximize all students potential to flourish. Can we make the use of exam analytics so easy and time efficient that faculty clearly see the benefit? For more info see our blog at https://kaneb.nd.edu/real/
Smarter balanced sampleitems_webinar



Smarter balanced sampleitems_webinarMelissa Laramie This document discusses Smarter Balanced sample test items and performance tasks that demonstrate the rigor and complexity expected by the Common Core State Standards. It provides an overview of the Smarter Balanced assessment system and components, including claims and item types. Examples of English language arts and mathematics items for various grades are shown and described. The document also outlines Washington State's transition to Smarter Balanced assessments and the related timeline.
Achievment Test.pptx



Achievment Test.pptxpreranadataverificat The document discusses different types of achievement tests, including their purpose, characteristics, and construction. It defines achievement tests as assessments of developed knowledge or skills that measure a student's current proficiency. The key types discussed are teacher-made tests, which are constructed by teachers, and standardized tests, which are developed by testing experts. The document outlines the steps to construct valid and reliable achievement tests, including planning, developing a design and blueprint, writing questions, and analyzing items. It also compares the strengths and weaknesses of different question formats like objective, short answer, and essay.
LAK21 Data Driven Redesign of Tutoring Systems (Yun Huang)



LAK21 Data Driven Redesign of Tutoring Systems (Yun Huang)Yun Huang This is the slides for our paper in LAK '21 conference:
Yun Huang, Nikki G. Lobczowski, J. Elizabeth Richey, Elizabeth A. McLaugh- lin, Michael W. Asher, Judith M. Harackiewicz, Vincent Aleven, and Kenneth R. Koedinger. 2021. A General Multi-method Approach to Data-Driven Re- design of Tutoring Systems. In LAK21: 11th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference (LAK21), April 12–16, 2021, Irvine, CA, USA. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3448139.3448155
Abstract: Analytics of student learning data are increasingly important for continuous redesign and improvement of tutoring systems and courses. There is still a lack of general guidance on converting analytics into better system design, and on combining multiple methods to maximally improve a tutor. We present a multi-method approach to data-driven redesign of tutoring systems and its empirical evaluation. Our approach systematically combines existing and new learning analytics and instructional design methods. In particular, our methods involve identifying difficult skills and creating focused tasks for learning these difficult skills effectively following content redesign strategies derived from analytics. In our past work, we applied this approach to redesigning an algebraic modeling unit and found initial evidence of its effectiveness. In the current work, we extended this approach and applied it to redesigning two other tutor units in addition to a second iteration of redesigning the previously redesigned unit. We conducted a one-month classroom experiment with 129 high school students. Compared to the origi- nal tutor, the redesigned tutor led to significantly higher learning outcomes, with time mainly allocated to focused tasks rather than original full tasks. Moreover, it reduced over- and under-practice, yielded a more effective practice experience, and selected skills progressing from easier to harder to a greater degree. Our work provides empirical evidence of the effectiveness and generality of a multi-method approach to data-driven instructional redesign.
Test Administration, Test administration, Test-taking Strategies



Test Administration, Test administration, Test-taking StrategiesSarah Cruz The document provides guidance on revising and administering tests, as well as understanding student test-taking strategies. It discusses checking venues and materials for test administration and conducting quantitative and qualitative item analyses to evaluate difficulty, discrimination, and alignment to objectives when revising tests. It also notes that students typically read questions first and rely on matching and prior knowledge when answering, so practice tests can help orient them to task requirements.
Math grade 2 training



Math grade 2 trainingAnthony Smith The document provides guidance for teachers administering 2nd grade math performance assessments aligned to Common Core standards. It explains that assessments will be administered in September (pre) and May-June (post) and scored using an online system called LinkIt. It provides instructions for logging into LinkIt and outlines which assessment tasks should be administered individually versus to the whole class. Rubrics will be used to score student performance on each task.
Vjai paper reading201808-acl18-simple-and_effective multi-paragraph reading c...



Vjai paper reading201808-acl18-simple-and_effective multi-paragraph reading c...Dat Nguyen This paper proposes two approaches for document-level question answering: a pipeline approach and a confidence-based approach. The pipeline approach selects a single paragraph and extracts an answer from it. The confidence-based approach assigns confidence scores to answers from multiple paragraphs and returns the highest scoring answer. The paper experiments with different training methods for the confidence model and evaluates on several datasets, finding the shared normalization and no-answer option methods perform best. Error analysis shows the model still struggles with connecting statements across sentences and paragraphs.
Analyzing Test Results in STEM Education



Analyzing Test Results in STEM Educationhypz2004 Analyzing Test Results in STEM Education
This presentation explores data analysis techniques for evaluating test results in STEM education. It covers statistical methods, performance trends, and assessment strategies to enhance learning outcomes. By interpreting student performance data, educators can identify gaps, adjust teaching approaches, and improve overall instructional effectiveness in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics subjects.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
CTS EXCEPTIONSPrediction of Aluminium wire rod physical properties through AI...



CTS EXCEPTIONSPrediction of Aluminium wire rod physical properties through AI...ThanushsaranS Prediction of Aluminium wire rod physical properties through AI, ML
or any modern technique for better productivity and quality control.
computer organization and assembly language.docx



computer organization and assembly language.docxalisoftwareengineer1 computer organization and assembly language : its about types of programming language along with variable and array description..https://www.nfciet.edu.pk/
GenAI for Quant Analytics: survey-analytics.ai



GenAI for Quant Analytics: survey-analytics.aiInspirient Pitched at the Greenbook Insight Innovation Competition as apart of IIEX North America 2025 on 30 April 2025 in Washington, D.C.
Join us at survey-analytics.ai!
AI Competitor Analysis: How to Monitor and Outperform Your Competitors



AI Competitor Analysis: How to Monitor and Outperform Your CompetitorsContify AI competitor analysis helps businesses watch and understand what their competitors are doing. Using smart competitor intelligence tools, you can track their moves, learn from their strategies, and find ways to do better. Stay smart, act fast, and grow your business with the power of AI insights.
For more information please visit here https://www.contify.com/
How iCode cybertech Helped Me Recover My Lost Funds



How iCode cybertech Helped Me Recover My Lost Fundsireneschmid345 I was devastated when I realized that I had fallen victim to an online fraud, losing a significant amount of money in the process. After countless hours of searching for a solution, I came across iCode cybertech. From the moment I reached out to their team, I felt a sense of hope that I can recommend iCode Cybertech enough for anyone who has faced similar challenges. Their commitment to helping clients and their exceptional service truly set them apart. Thank you, iCode cybertech, for turning my situation around!
[email protected]
Safety Innovation in Mt. Vernon A Westchester County Model for New Rochelle a...



Safety Innovation in Mt. Vernon A Westchester County Model for New Rochelle a...James Francis Paradigm Asset Management By James Francis, CEO of Paradigm Asset Management
In the landscape of urban safety innovation, Mt. Vernon is emerging as a compelling case study for neighboring Westchester County cities. The municipality’s recently launched Public Safety Camera Program not only represents a significant advancement in community protection but also offers valuable insights for New Rochelle and White Plains as they consider their own safety infrastructure enhancements.
Perencanaan Pengendalian-Proyek-Konstruksi-MS-PROJECT.pptx



Perencanaan Pengendalian-Proyek-Konstruksi-MS-PROJECT.pptxPareaRusan planning and calculation monitoring project
Principles of information security Chapter 5.ppt



Principles of information security Chapter 5.pptEstherBaguma Principles of information security Chapter 5.ppt
Day 1 - Lab 1 Reconnaissance Scanning with NMAP, Vulnerability Assessment wit...



Day 1 - Lab 1 Reconnaissance Scanning with NMAP, Vulnerability Assessment wit...Abodahab IHOY78T6R5E45TRYTUYIU
Data Science Courses in India iim skills



Data Science Courses in India iim skillsdharnathakur29 This comprehensive Data Science course is designed to equip learners with the essential skills and knowledge required to analyze, interpret, and visualize complex data. Covering both theoretical concepts and practical applications, the course introduces tools and techniques used in the data science field, such as Python programming, data wrangling, statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization.
Thingyan is now a global treasure! See how people around the world are search...



Thingyan is now a global treasure! See how people around the world are search...Pixellion We explored how the world searches for 'Thingyan' and 'သင်္ကြန်' and this year, it’s extra special. Thingyan is now officially recognized as a World Intangible Cultural Heritage by UNESCO! Dive into the trends and celebrate with us!
Deloitte Analytics - Applying Process Mining in an audit context



Deloitte Analytics - Applying Process Mining in an audit contextProcess mining Evangelist Mieke Jans is a Manager at Deloitte Analytics Belgium. She learned about process mining from her PhD supervisor while she was collaborating with a large SAP-using company for her dissertation.
Mieke extended her research topic to investigate the data availability of process mining data in SAP and the new analysis possibilities that emerge from it. It took her 8-9 months to find the right data and prepare it for her process mining analysis. She needed insights from both process owners and IT experts. For example, one person knew exactly how the procurement process took place at the front end of SAP, and another person helped her with the structure of the SAP-tables. She then combined the knowledge of these different persons.
Safety Innovation in Mt. Vernon A Westchester County Model for New Rochelle a...



Safety Innovation in Mt. Vernon A Westchester County Model for New Rochelle a...James Francis Paradigm Asset Management
Ad
Project Allocation Linear Programming Optimisation
- 1. Optimisation of Student-Project Allocation BMAN60101 Mathematical Programming and Optimisation 2019-20 Group 4 Math Myth
- 2. TASK 1 2 3 4 5 Problem Formulation as Integer Optimisation Model Model Implementation using Excel Solver Analysis & Interpretation of Results: Difficulty & Properties of Constraints Extending Model with Optional Property Evaluation of Alternative Formulations
- 3. Problem Formulation: Model #13 Objective Function Decision Variables [Binary for assigning topic j to student i] 𝐶𝑖𝑗 ∈ {3, 2, 1} is Coefficient of Satisfaction 𝑠j ∈ ℤ+ is the extra capacity for each topic 𝑀𝑗 ∈ ℤ+ is the penalty for each 𝑠𝑗 𝑥𝑖𝑗 is 0 if student i is not assigned to topic j 𝑥𝑖𝑗 is 1 if student i is assigned to topic j where 𝑖 ∈ [1,𝐼] and j ∈ [1,𝐽] 𝑥𝑖𝑗 ∈ { 0, 1 }
- 4. Problem Formulation: Model #14 Max. Internal Supervisors’ Supervision Capacity Max. External Supervisors’ Supervision Capacity Min. External Supervisors’ Supervision Capacity 𝜎k is the maximum supervision capacity for internal supervisor, k 𝜎q is the maximum supervision capacity for external supervisor, q tkj is a binary for student being assigned to the topic j of internal supervisor, k tqj is a binary for student being assigned to the topic j of external supervisor, q s.t.:
- 5. s.t.: Problem Formulation: Model #15 Total no. of topics assigned to student i Max. Topic Capacity 𝑠j ∈ ℤ+ is the extra capacity for each topic 𝛼𝑗 is the maximum capacity for topic j
- 6. Implementation: Model #1 Survey #1 Matrix allow all combination of students and topics. E.g. Each student can be assigned to any topic xij = 1, if student is assigned to topic j xij = 0, if student is not assigned to topic j Coefficient of Satisfaction, Cij Allocation of topics to each student (Output)Coefficient of Preference Score of each student (Input) 1st choice = 3 2nd choice = 2 3rd choice = 1 6
- 7. . . Implementation: Model #1 Survey #1 . Student Supervisor Topic • Each student is assigned to exactly one topic • Student is assigned to a topic that he/she finds acceptable ID One Topic per Student Student Satisfaction 1 1 = 1 1 ≥ 1 2 1 1 3 1 3 1 1 3 1 --- --- --- --- --- 10 1 1 2 1 Topic # of Student ≤ Topic Capacity 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 0 2 --- --- --- 10 1 2 *Solver output *Solver output • Each topic has limited capacity Supervisor # of student Max Min E Margaret 1 ≤ 1 ≥ 1 Sylvia 2 4 1 Pierre 1 2 1 I Alan 2 = 2 Gabriel 2 2 Li Bai 2 2 *Solver output • Every supervisor is assigned at least to one student • No more students than maximum Supervisor capacity • Internal supervisor is prioritized 7
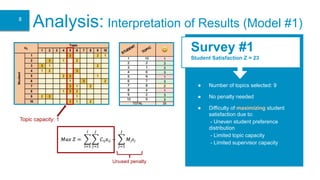
- 8. Analysis: Interpretation of Results (Model #1) Survey #1 Student Satisfaction Z = 23 ● Number of topics selected: 9 ● No penalty needed ● Difficulty of maximizing student satisfaction due to: - Uneven student preference distribution - Limited topic capacity - Limited supervisor capacity Topic capacity: 1 Unused penalty 8
- 9. Analysis: Interpretation of Results (Model #1) ● Supervisor Constraint : as an internal supervisor, Gabriel should be assigned to two students. ● Topic Constraint: topic 6 has limited capacity of 1 Infeasible solution because of unsatisfied constraints. Survey #2 2 Solver could not find a feasible solution 9 1
- 10. Analysis: Interpretation of Results (Model #1) The problem can be solved Survey #2 ● More capacity allocated to topic 6 ● Adding 1 penalty 10
- 11. Problem Formulation: Model #2 Optional Property: - Avoid too many students assigned to the same topic without sacrificing students’ preferences, if possible Approach: - Add a penalty to a topic that has no student’s assignment - Allow flexibility in the future by adjusting the size of the penalties 11 𝑀2𝑗 is a penalty applied to topic j when student is not assigned to the topic. 𝑦𝑗 is a binary variable 𝑀1𝑗 ≪ 𝑀2𝑗 𝑦𝑗 = 0 when topic j is assigned with at least 1 student 𝑦𝑗 = 1 when student is not assigned to topic j
- 12. . Analysis: Properties of Constraints (Model #2) Topic Topic # of Student ≤ Max. Capacity Min. Capacity 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 3 0 2 1 --- --- --- --- 10 1 2 1 *Solver output • Each topic has max. and min. capacity 12
- 13. Analysis: Interpretation of Results (Model #2) Student Satisfaction = 23 Survey #1 No penalty for increasing topic capacity 13 ● Reach max. topic distribution ● Same student allocation as Model #1 ● Not possible to improve the student satisfaction and topic distribution with the given data (Survey #1) and constraints 𝑀1𝑗 ≪ 𝑀2𝑗 No penalty for topics that isn’t assigned to any students
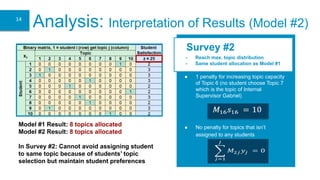
- 14. Model #1 Result: 8 topics allocated Model #2 Result: 8 topics allocated In Survey #2: Cannot avoid assigning student to same topic because of students’ topic selection but maintain student preferences ● 1 penalty for increasing topic capacity of Topic 6 (no student choose Topic 7 which is the topic of Internal Supervisor Gabriel) ● No penalty for topics that isn’t assigned to any students - Reach max. topic distribution - Same student allocation as Model #1 Survey #2 Analysis: Interpretation of Results (Model #2) 14
- 15. Evaluation: Review of Alternatives15 References: Chiarandini et al., Handling Preferences in Student-Project Allocation, 2019 A. A. Anwar and A. S. Baha, Student Project Allocation Using Integer Programming, 2003 COLLECTIVE SATISFACTION ● ORDERED WEIGHTED AVERAGING ● LEXICOGRAPHIC OPTIMISATION FAIRNESS / INDIVIDUAL WELFARE Promote egalitarianism in the outcome MINIMAX / MAXIMIN CRITERION ● Student that receives worst is assigned project with preference as high as possible ● Minimize the max preferenced value attained by any student (weighted sum of preference) PARETO EFFICIENCY Resource allocation optimisation COMPUTATIONAL COST Within a minute in the MILP Solver TRADE-OFF Conciliate equity & global utility
- 16. ALTERNATIVES Evaluation: Review of Alternatives16 References: Chiarandini et al., Handling Preferences in Student-Project Allocation, 2019 A. A. Anwar and A. S. Baha, Student Project Allocation Using Integer Programming, 2003 A. Higher collective satisfactions value -> Greedy Maximum Matchings: Assign higher score to 1st choice B. Different ways of collecting data of students preference C. Minimisation Objective: number of projects supervised by each supervisor A. More likely give result of more students get their 1st choice (e.g. 7 students get 1st choice and 3 get 3rd, rather than 4 students get 1st choice, 4 get 2nd, and 2 get 3rd) B. Increase number of choices and collect data of skills / experience, multi-attribute model with OWA C. Distribute projects more evenly among supervisors
- 17. Thank you Q&A
- 18. Appendix: Model #2 with Survey #1 18 Effect of the Penalty Size : - Both penalties are too small (e.g. penalties = 1) - Easy for the model to break the constraints Result: - Better student satisfaction of 25 - Break one constraint on topic 6 - Lower topic distribution 23 25 No allocation for Topic 7 𝑀1𝑗 = 𝑀2𝑗











