Quantitative Math
- 2. To use the VAM method to obtain an initial basic feasible solution to a problem. To recognize problems that have alternative least-cost solutions. To find alternate least-cost solutions when they exist.
- 4. Topics to be discussed: Ways of Allocating Goods Assignment Method Let’s do This!
- 5. Initial allocation entails assigning numbers to satisfy supply and demand constraints. In order to allocate and assign goods, there are three (3) ways available. The Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- 6. Different WAYS of Allocating Goods 1. THE NORTH-WEST CORNER METHOD 2. THE LEAST-COST METHOD OF ALLOCATION 3. VOGEL’S APPROXIMATION METHOD
- 7. North-West Corner method of Allocation
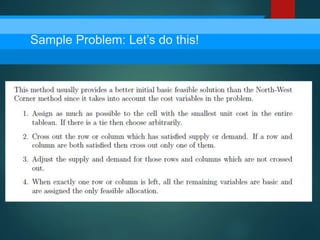
- 8. The north-west corner method for finding an initial feasible solution involves the following steps:
- 9. NORTH-WEST CORNER METHOD a) Start in a cell at the upper-left corner, place a quantity of goods in this cell that equals the smaller of the row total or the column total in the transportation b) If the smaller number is the row total, the 1st row is exhausted. Go to the 2nd. If the smaller number is the column total, the 1st column is exhausted. Go to the 2nd column.
- 10. NORTH-WEST CORNER METHOD c) If you have gone to the 2nd row, allocate enough goods to the cell in row 2, column 1, to exhaust the column d) Continue this manner, utilizing the smaller of the row total and the column total, until you reach the lower right-hand corner. You should place numbers in a number of cells equal to the number of columns + the number of rows -1(C+R-1); unless the problem is degenerated.
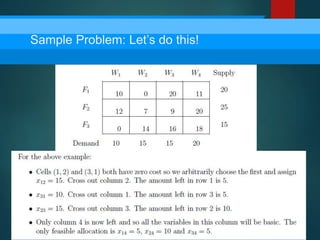
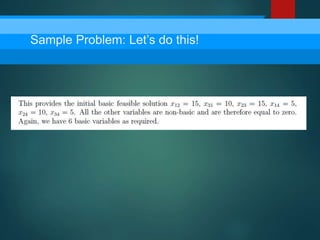
- 11. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 12. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 13. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 14. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 15. Least-Cost method of Allocation
- 16. how? it’s easier than you think.
- 17. INTUITIVE LOWEST-COST METHOD The intuitive method makes initial allocations based on lowest cost. This straightforward approach uses the following steps: 1. Identify the cell with lowest cost. Break any ties for the lowest cost arbitrarily. 2. Allocate as many units as possible to that cell without exceeding the supply or demand. Then cross out that row or column (or both) that is exhausted by this assignment.
- 18. 3. Find the cell with the lowest cost from the remaining (not crossed out) cells. 4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 until it has been allocated Rule being applied: Least cost method
- 19. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 20. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 21. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 22. Third method ? Vogel’s Approximation method of Allocation
- 23. This method also costs into account. In allocation, five steps are involved in applying this heuristic.
- 24. Steps to follow: 1. Determine the difference between the lowest two cells in all rows and columns (including dummies if they are unbalanced). 2. Identify the row column with the largest difference ties that may be broken arbitrarily.
- 25. 3. Allocate as much as possible to the lowest-cost cell in the row or column with the highest difference. 4. Stop the process if all row and column requirements are met. If not, go to the next step. 5. Recalculate the difference between the two lowest cell remaining in all rows and columns. Any row and column with zero supply or demand should not be used in calculating further differences. Then go to step 2.
- 26. The Vogel’s Approximation Method (VAM) usually produces an optimal or near-optimal starting solution. One study found that VAM yields an optimum solution in 80% of the sample problems tested.
- 27. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 28. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 29. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 30. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 32. how? it’s easier than you think.
- 33. Assignment Method Another type of purpose is the algorithm used in linear programming. It is concerned in allocating the jobs to each of the workers for minimum cost.
- 34. 1) The assignment problem is the problem of assigning n workers to n jobs. In such a way that only one worker is assigned to each job, each job has one. The workers assigned to it and the cost of completing all of the jobs are minimized.
- 35. 2. The assignment method is the standard procedure for solving the assignment problem on the basis of the assignment table.
- 36. There are three main steps to follow in solving an assignment problem: 1. Subtract the smallest cost from each entry in each row. If each zero can now be assigned in a one to one correspondence with the “workers”, an optimal solution is obtained. If cannot, go to step 2. 2. Subtract the smallest cost in each column. If the zero entries can now be distributed in a one to one correspondence with the “workers”, an optimal solution is obtained or reached. If not, go to step 3.
- 37. 3. Cover the zero entries by vertical or horizontal lines, using the least number of lines possible. (This can be done by covering first the row or column having the most number of zeros). Subtract the smallest uncovered cost from each uncovered cost but add it to the entry found at the intersection of the lines. If the assignment is already possible an optimal solution is reached. If not, repeat step 3. An assignment is optimum if the number of lines is equal to the number of rows or the number of columns.
- 38. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 39. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 40. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 41. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 42. Sample Problem: Let’s do this!
- 43. Jessica MagadiaEtrataJ E M Submitted To:
- 44. THE END THANK YOU FOR LISTENING! GROUP 5