React and Flux life cycle with JSX, React Router and Jest Unit Testing
- 1. ReactJS + Flux + JSX + Jest Eswara K Palakollu@Sapient Learn Isomorphic React and Flux Life cycle in detail.
- 2. ReactJS
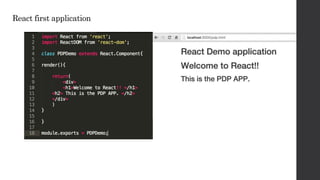
- 3. What is React? • Reactjs is a java script library for building composable, maintainable and testable user interfaces. • React covers just view ‘V’ in MVC pattern.
- 4. How does React work? React abstracts application DOM and maintains Virtual DOM in memory for handling in-page interactions and updates from server. React compares previous state of Virtual DOM with new state of Virtual DOM and updates physical DOM with the changed elements. Physical DOM always reflect up to date application state and react updates virtual DOM whenever application state changes and which internally updates physical DOM. React Virtual DOM Physical DOM Application Events Events Only changed elements
- 5. Why React? • Fast • Unidirectional data flow from parent components to child components. • Isomorphic • Easy to debug & testable • SPA friendly. • Can co-exist with other frameworks and easy to try it out. • Use JSX with familiar HTML like syntax for writing react applications.
- 7. React at client side (Non-SEO / SPA)
- 8. React at server side (SEO)
- 9. JSX • JSX is a ECMASCRIPT syntactic extension similar to HTML and XML. • JSX helps to write secure java script with familiar HTML like syntax. • JSX transpilers help to compile JSX syntactic code into pure java script for execution on browsers. • React JSX transpiler can be used to compile react JSX code into pure java script for execution. • <ProductImage href=“image.jpeg”></ ProductImage>
- 10. JSX – Syntax • Use Upper case for custom tags <ProductImage><image href=“./image.jpeg”/> </ProductImage> • Use lower case for html tags <image href=“./image.jpeg” /> • Self Closing - <ProductImage href=“./image.jpeg” /> • Child elements - <Product><ProductImage href=“./image.jpeg” /> </Product> • Pass properties - <ProductImage href=“./image.jpeg” /> • Spread attributes <ProductImage {…this.props} /> • Attribute expression <ProductImage href={this.props.href} />
- 11. Get hands dirty.
- 13. Tools and packages • Using ECMA6 compatible REACT API and differences to ECMA5 are called out later. • react, react-addons-test-utils • react-dom, react-dom/server • react-router • flux • babel frameworks • jest – unit testing • webpack
- 14. React APIs • React.Component API covers component life cycle methods discussed in the coming sections. • ReactDOM – This package provides DOM specific methods such as rendering DOM at client side and server side for SEO benefits. render() method will be the primary and mandatory method used in this API for rendering components on client side. renderToString() [react-dom/server] method will be useful to render the component on server side and send HTML to client side for client side binding and event listeners. findDOMNode() method is useful for reading DOM elements. Mostly refs and event listeners will cover most of the needs. renderToStaticMarkup() [react-dom/server] method is useful for sending pure html to client without any react hooks. unmountComponentAtNode() method will serve opposite of render() method to unmount the rendered component from DOM.
- 15. React Component life cycle
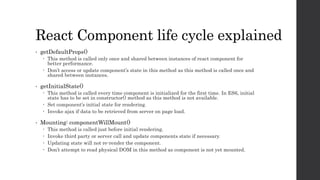
- 16. React Component life cycle explained • getDefaultProps() This method is called only once and shared between instances of react component for better performance. Don’t access or update component’s state in this method as this method is called once and shared between instances. • getInitialState() This method is called every time component is initialized for the first time. In ES6, initial state has to be set in constructor() method as this method is not available. Set component’s initial state for rendering. Invoke ajax if data to be retrieved from server on page load. • Mounting: componentWillMount() This method is called just before initial rendering. Invoke third party or server call and update components state if necessary. Updating state will not re-render the component. Don’t attempt to read physical DOM in this method as component is not yet mounted.
- 17. React Component life cycle explained • Mounting: componentDidMount() This method is called just after initial rendering. Integrate with third party or AJAX calls to server or analytics etc. Access refs and DOM elements in this method. • Updating: componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) Updating component state / props will trigger re-rendering of View. Updating component state / pros is allowed here. Updating props from parent can trigger re-rendering of updated child component. • Updating: shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps,nextState) Return false if rendering of changed state / props is not needed. By default this method returns true always unless there is a performance reason to return try by comparing previosProps and nextProps If it returns true componentWillUpdate() and componentDidUpdate() will be called otherwise not called.
- 18. React Component life cycle explained • Updating: componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState) This method is invoked before rendering when new props or state being received. Updating state is not allowed in this method. Use componentWillReceiveProps() for updating state. • Updating: componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) This method is invoked right after component nextProps rendered successfully. DOM can be accessed in this method. Third party calls or ajax server calls can be invoked in this method. Application state / props can be accessed and updated in this method.
- 19. Unidirectional data flow in React • In react, data flows in one direction from parent to child components using props. • React renders data using component state and the properties sent by parent react component to it. • Component state is maintained by this.state variable and initialised in constructor() aka getIntitialState() in ES5 version. • Properties are usually passed to the component by its parent and this.props will hold all the properties passed by parent. • getDefaultProperties() will be used to initialise the properties and it is invoked only once and shared between instances.
- 20. Get hands dirty.
- 22. Application state • React maintains application state at component level and sends required state attributes to child components via props. • Every time application state changes the changed state is passed to child components to update the views again. • this.state – holds the component state received from server or set by component. • this.props – holds the properties sent by its parent and any callbacks needed to call for updating state in parent that will trigger updated props to this component for updating view again.
- 23. this.state = {title: ‘I am the initial state’}; • State (this.state) in react refers to component state that will be rendered in View by ReactDOM. • State can be changed by calling this.setState(). React rerenders the component when the state is updated. this.setState({title: ‘I am the updated state’}); this.setState({title: ‘I am the updated state with callback’,function(){}); • State is private to the component unlike this.props and it can be managed by using react life cycle methods. • While mounting use componentWillMount() method to update state before initial rendering. • While updating the state after initial rendering, use componentWillReceiveProps() before re-rendering or componentDidUpdate() for accessing and updating DOM after rendering based on user or server interaction. • Never assign state to this.state directly instead use this.setState() as updating this.state doesn’t invoke react life cycle correctly.
- 24. this.props • React props are owned and maintained by parent component. • Parent component sends state to child react components as properties for rendering. • Child tags or html content between opening and closing tags can be accessed using this.props.children. • <ProductImage href=“image.jpeg”> <img src=“image.jpeg”></img> </ProductImage> • this.props.children will give <img src=“image.jpeg”></img> tag. • When this.props are updated, parent broadcasts the change to all its child tags that will invoke componentWillReceiveProps() life cycle method.
- 25. rest and spread props {a,b,…rest} • Take advantage of ECMA6 arrays destructuring to use rest or spread the properties sent by parent. • let {href , title} = this.props; //spread the required attributes from props • let {href , title, …more} = this.props; //…more holds the rest of the attributes apart from spread attributes href and title.
- 26. render(){return <h1>hello</h1>)} • render() is the must have function and only mandatory method in every react component. • render must return HTML content or another react child component for rendering. • Render can only render one element for now due to syntactic issues with java script. If multiple elements need to be rendered, surround all the elements with a div or any other element as per the need. render(){ return { <div> <h1>Product Description</h1> <p>print product description here.</p> <ProductMoreDetails id={this.props.product.id} /> </div> } }
- 27. Get hands dirty.
- 28. refs • React provide refs (references) to access DOM after component is displayed. • Avoid using refs as react manages keep component displayed correctly at all times and there shouldn’t be any need to manipulate DOM manually. • Usually accessing DOM may not be required given that react manages updating the DOM when props are propagated from parent or state changes. • In some cases other parts of the bigger application may need to reference DOM to further action. • this.refs. render(){ return { <div> <h1>Product Description</h1> <p ref=“productDescription”>print product description here.</p> </div> } }
- 29. key attribute • Key attribute optimizes rendering of ordered or unordered list of elements on the page. • If a dropdown has 20 elements and one of the element changed. React will compare the difference using Virtual DOM which eventually end of updating all the items in the dropdown. • Key attribite will help react to identify the changes correctly and update only the changed elements instead of re-rendering unchanged elements. • <ul> • <li key=“sku1”>SKU1</li> • <li key=“sku2”>SKU2</li> • <li key=“sku3”>SKU3</li> • <li key=“sku4”>SKU4</li> • </ul> • React removes “sku1” and inserts “sku5” without touching other elements in the list. <ul> <li key=“sku5”>SKU5</li> <li key=“sku2”>SKU2</li> <li key=“sku3”>SKU3</li> <li key=“sku4”>SKU4</li> </ul>
- 30. Other attributes • forceUpdate() – It forced react to render without calling shouldComponentUpdate() method. • propTypes() – It allows to type check input prop types before getDefaultProps() is called. For performance reasons this method should only be checked in development environment.
- 31. ECMA5 vs ECMA6 • React latest 0.14.x supports ECMA6 and few life cycle methods have deprecated from API. I have omitted the api methods that may be removed completely from ECMA6 version. • ECMA5 ES2015(aka ECMA6) React.createClass() used for creating react component classes. var App = React.createClass({ }); Extend React.Component class to create custom components. class App extends React.Component{} Deprecated methods to stay way from using: replaceState() isMounted() getDOMNode() isMounted() setProps() replaceProps()
- 32. React SEO – Server side rendering • Isomorphic react provides SEO support for compiling HTML at server side and bid the non-seo components at client side. • ReactDOM API provides functionality for executing react component on server side.
- 33. React DOM API • ReactDOM – This package provides DOM specific methods such as rendering DOM at client side and server side for SEO benefits. render() method will be the primary method used in this API for rendering components on client side. renderToString() [react-dom/server] method will be useful to render the component on server side and send HTML to client side for client side binding and event listeners. findDOMNode() method is useful for reading DOM elements. Mostly refs and event listeners will cover most of the needs. renderToStaticMarkup() [react-dom/server] method is useful for sending pure html to client without any react hooks. unmountComponentAtNode() method will serve opposite of render() method to unmount the rendered component from DOM. Renders <DemoApp/> in the div ‘reactDemoApp’ present in the html.
- 34. React at client side (SEO)
- 35. Get hands dirty
- 36. JEST • Jest is BDD unit testing framework built over Jasmine for testing react and flux applications. • Automatically mocks all the require modules. • Why JEST not Jasmine, directly copied from JEST site (refer jest site for detailed tutorial): Jest provides you with multiple layers on top of Jasmine: Automatically finds tests to execute in your repo Automatically mocks dependencies for you when running your tests Allows you to test asynchronous code synchronously Runs your tests with a fake DOM implementation (via jsdom) so that your tests can run on the command line Runs tests in parallel processes so that they finish sooner •
- 37. JEST - example
- 38. Get hands dirty
- 39. React Routing (react-router) • React router (react-router) is useful for implementing routing in SPA applications at client side. • Ideal for using it in SPA application for handling different routes. • It has dependency on history api for managing URLs in the browser history. • react-router exports react components for creating routing on client site. • React-router api provides following components Router - route level node for nesting routes. Route - individual route IndexRoute – default route if there is no root level route set Redirect – to handle redirects in the router • Refer this link for full api: https://github.com/rackt/react-router/
- 40. react-router- usage • import {Router, Route, IndexRoute,Redirect} from 'react-router'
- 41. FLUX Unidirectional Data flow Architecture
- 42. What is Flux? • Flux is an application architecture pattern from Facebook for building client side web applications using unidirectional data flow. • Data in flux application flows in single direction Source:https://facebook.github.io/flux
- 43. Flux Architecture Explained • Dispatcher Responsible for dispatching actions to all the callbacks registered by stores themselves with dispatcher. Doesn’t have any logic on its own. • Store Stores register callbacks with dispatcher with action type. Use waitFor() to maintain dependencies between stores in an event StoreB needs to be invoked before StoreA. Connect with server to get and update application state. • Action / Action Creators Responsible for invoking dispatcher with appropriate event type. Generate actions in response to event listeners. • React View Components Listening to change events, retrieve data and send it to all its child components for rendering changes.
- 44. React + Flux life cycle
- 45. JEST for Flux • Jest provides an easy way to test flux applications. • Detailed API is available at this location. • https://facebook.github.io/flux/docs/testing-flux-applications.html
- 46. JEST Dispatcher Test Example
- 47. References - Best for getting deeper understanding • React JS https://facebook.github.io/react/docs/getting-started.html • React JEST https://facebook.github.io/jest/docs/tutorial-react.html • es2015 http://people.mozilla.org/~jorendorff/es6-draft.html#sec-constructor • Flux https://facebook.github.io/flux/docs/overview.html
- 48. Call to action • Practice Rect and Flux combination • Read about React Native. https://facebook.github.io/react-native/
- 49. Thank You Hope it helps at least a little.
Editor's Notes
- #38: Walkthrough this example












![React APIs
• React.Component API covers component life cycle methods discussed in the
coming sections.
• ReactDOM – This package provides DOM specific methods such as
rendering DOM at client side and server side for SEO benefits.
render() method will be the primary and mandatory method used in this API for
rendering components on client side.
renderToString() [react-dom/server] method will be useful to render the component
on server side and send HTML to client side for client side binding and event
listeners.
findDOMNode() method is useful for reading DOM elements. Mostly refs and event
listeners will cover most of the needs.
renderToStaticMarkup() [react-dom/server] method is useful for sending pure html
to client without any react hooks.
unmountComponentAtNode() method will serve opposite of render() method to
unmount the rendered component from DOM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactjs-flux-160117101746/85/React-and-Flux-life-cycle-with-JSX-React-Router-and-Jest-Unit-Testing-14-320.jpg)

















![React DOM API
• ReactDOM – This package provides DOM specific methods such as
rendering DOM at client side and server side for SEO benefits.
render() method will be the primary method used in this API for rendering
components on client side.
renderToString() [react-dom/server] method will be useful to render the component
on server side and send HTML to client side for client side binding and event
listeners.
findDOMNode() method is useful for reading DOM elements. Mostly refs and event
listeners will cover most of the needs.
renderToStaticMarkup() [react-dom/server] method is useful for sending pure html
to client without any react hooks.
unmountComponentAtNode() method will serve opposite of render() method to
unmount the rendered component from DOM.
Renders <DemoApp/> in the
div ‘reactDemoApp’ present
in the html.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactjs-flux-160117101746/85/React-and-Flux-life-cycle-with-JSX-React-Router-and-Jest-Unit-Testing-33-320.jpg)















