(SAC2020 SVT-2) Constrained Detecting Arrays for Fault Localization in Combinatorial Testing
- 1. Constrained Detecting Arrays for Fault Localization in Combinatorial Testing Hao Jin[1], Ce Shi[2] and Tatsuhiro Tsuchiya[1] Osaka University[1], Shanghai Lixin University of Accounting and Finance[2] SAC2020-SVT, Brno, March. 31, 2020.
- 2. Combinatorial Testing (CT) • What is CT? – A black-box testing method – Tests all t-way interactions among system components/parameters • Why CT? – In component-based systems or configurable systems, faults are usually involved in interactions among a few (t =1,2,…,6) parameters → up to 50%~95%[1] – Compared to the exhaustive testing, CT test suites can cut off nearly 70% of testing costs (test cases) 2[1]Kuhn et al. An investigation of the applicability of design of experiments to software testing, SEW’02 Can detect many faults with little cost
- 3. Example • Example: A mobile phone product line[2] • Each row represents a parameter of the system • Each parameter has several (≥ 2) values • When a system is developed, each parameter will be assigned a value from its domain 3 F1:Display 0:16MC 1:8MC 2:BW F2:Viewer 0:Graphical 1:Text 2:None F3:Camera 0:2MP 1:1MP 2:None F4:VideoCamera 0:On 1:Off F5:VideoRingtone 0:On 1:Off F1:Display 0 1 2 F2:Viewer 0 1 2 F3:Camera 0 1 2 F4:VideoCamera 0 1 F5:VideoRingtone 0 1 [2] Cohen et al., Constructing interaction test suites for highly-configurable systems in the presence of constraints: a greedy approach, TSE08.
- 4. Example • Test Suite/Test Case • A test suite can be modeled as a matrix • Each row of the matrix represents a test case – A test case returns PASS or FAIL when executed 4 F1 0 1 2 F2 0 1 2 F3 0 1 2 F4 0 1 F5 0 1 No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 1 3 0 1 1 0 1 4 0 2 1 1 0 5 1 0 1 1 1 6 1 1 0 1 1 7 1 2 2 0 0 8 2 0 1 1 1 9 2 1 2 1 0 10 2 2 0 0 1 Can test (cover) the interaction FAIL when executed!
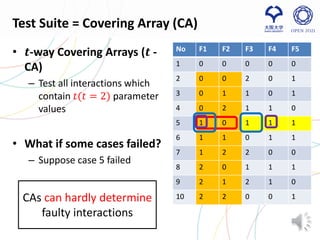
- 5. No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 1 3 0 1 1 0 1 4 0 2 1 1 0 5 1 0 1 1 1 6 1 1 0 1 1 7 1 2 2 0 0 8 2 0 1 1 1 9 2 1 2 1 0 10 2 2 0 0 1 Test Suite = Covering Array (CA) • 𝒕-way Covering Arrays (𝒕 - CA) – Test all interactions which contain 𝑡(𝑡 = 2) parameter values • What if some cases failed? – Suppose case 5 failed 5 Some interactions are suspicious for triggering a fault CAs can hardly determine faulty interactions
- 6. No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 3 0 0 2 1 1 4 0 1 0 1 1 5 0 1 2 0 0 6 0 2 0 0 1 7 0 2 1 1 0 8 1 0 0 0 1 9 1 0 1 1 0 10 1 1 2 1 0 11 1 1 2 1 0 12 1 2 0 1 0 13 1 2 1 0 0 14 1 2 1 1 1 … 22 2 2 2 1 0 No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 3 0 0 2 1 1 4 0 1 0 1 1 5 0 1 2 0 0 6 0 2 0 0 1 7 0 2 1 1 0 8 1 0 0 0 1 9 1 0 1 1 0 10 1 1 2 1 0 11 1 1 2 1 0 12 1 2 0 1 0 13 1 2 1 0 0 14 1 2 1 1 1 … 22 2 2 2 1 0 Locating Faulty Interactions • (𝒅, 𝐭)-Detecting Array (DA) – “𝑡” means that the array can locate 𝑡(𝑡 = 2)-way interactions – “𝑑” means that the array can locate at most 𝑑(𝑑 = 1) interactions • If only one faulty interaction exists, the array can detect it using test results • If more, it can indicate such case 6 After comparing to other cases, one can determine ((F1,0), (F2,0)) is the only faulty interaction. No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 3 0 0 2 1 1 4 0 1 0 1 1 5 0 1 2 0 0 6 0 2 0 0 1 7 0 2 1 1 0 8 1 0 0 0 1 9 1 0 1 1 0 10 1 1 2 1 0 11 1 1 2 1 0 12 1 2 0 1 0 13 1 2 1 0 0 14 1 2 1 1 1 … 22 2 2 2 1 0
- 7. Incorporating Constraints • Due to the real-world requirements or restrictions, there may exist constraints among parameters • Constraints: A mobile phone product line[2] • Test cases must satisfy constraints 7[2] Cohen et al., Constructing interaction test suites for highly-configurable systems in the presence of constraints: a greedy approach, TSE08. Constraints Graphical viewer requires color display 2MP camera requires color display Graphical viewer not support 2MP camera 8MC display not support 2MP camera Video camera requires a camera and a color display Video ringtones cannot occur with NO video camera The combination (16MC, Text, 2MP camera) will not be supported Constraints 𝑭 𝟐 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟏 ≠ 𝟐 𝑭 𝟑 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟏 ≠ 𝟐 𝑭 𝟐 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟑 ≠ 𝟎 𝑭 𝟏 = 𝟏 → 𝑭 𝟑 ≠ 𝟎 𝑭 𝟒 = 𝟎 → (𝑭 𝟑 ≠ 𝟐 ∧ 𝑭 𝟏 ≠ 𝟐) 𝑭 𝟓 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟒 = 𝟎 ¬(𝑭 𝟏 = 𝟎 ∧ 𝑭 𝟐 = 𝟏 ∧ 𝑭 𝟑 = 𝟎)
- 8. Interaction Validity • Invalid Interactions – Test cases must satisfy system constraints – Invalid: Interactions which violate the constraints cannot be tested ((F4,1), (F5,0)) CONFLICTS 𝑭 𝟓 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟒 = 𝟎 8 No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 3 0 0 1 1 1 4 0 0 2 1 1 5 0 1 1 0 0 6 0 1 1 0 1 7 0 1 1 1 1 8 0 1 2 1 1 9 0 2 0 0 0 .. Invalid interactions cannot appear in a test case Exclude such invalid interactions from locating ability
- 9. Masking • Masking – Constraints may make faulty interactions unlocatable 9 Constraints: 𝑭 𝟓 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟒 = 𝟎 All test cases covering ((F1,1),(F5,0)) also cover ((F1,1),(F4,0)) If ((F1,0),(F4,0)) is faulty, can’t determine ((F1,0),(F5,0)) No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 3 0 0 1 1 1 4 0 0 2 1 1 5 0 1 1 0 0 6 0 1 1 0 1 7 0 1 1 1 1 8 0 1 2 1 1 9 0 2 0 0 0 ..
- 10. Constrained Detecting Arrays (CDA) • (1,2)-CDA – ALL rows satisfy constraints – Invalid interactions do not appear in any rows – For faulty interactions which are not masked by other interactions, CDAs can locate them as DAs can 10 No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 2 1 1 3 0 1 1 0 0 4 0 1 1 0 1 5 0 1 2 1 1 6 0 2 0 0 0 7 0 2 0 0 1 8 0 2 0 1 1 9 0 2 1 1 1 10 1 0 1 0 0 11 1 0 1 0 1 12 1 0 1 1 1 13 1 0 2 1 1 14 1 1 1 0 0 … 21 2 2 2 1 1 Exclude all the conflicts caused by constraints CDAs preserve all benefits of DAs
- 11. Constrained Detecting Arrays (CDA) • Invalid Interactions – Not appear in any rows – ((F4,1),(F5,0)) • Interactions masked by other interactions – Inherently unlocatable – ((F1,0),(F4,0)) masks ((F1,0),(F5,0)) • Interactions not masked by other interactions – Locatable as in DAs 11 No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 2 1 1 3 0 1 1 0 0 4 0 1 1 0 1 5 0 1 2 1 1 6 0 2 0 0 0 7 0 2 0 0 1 8 0 2 0 1 1 9 0 2 1 1 1 10 1 0 1 0 0 11 1 0 1 0 1 12 1 0 1 1 1 13 1 0 2 1 1 14 1 1 1 0 0 … 21 2 2 2 1 1 No F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 1 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 2 1 1 3 0 1 1 0 0 4 0 1 1 0 1 5 0 1 2 1 1 6 0 2 0 0 0 7 0 2 0 0 1 8 0 2 0 1 1 9 0 2 1 1 1 10 1 0 1 0 0 11 1 0 1 0 1 12 1 0 1 1 1 13 1 0 2 1 1 14 1 1 1 0 0 … 21 2 2 2 1 1
- 12. Generating CDAs using an SMT solver • An SMT Solver – A tool which can check the satisfiability of a propositional logic formula – If the formula is satisfiable, the tool can return a value assignment for the variables in the formula – A frequently applied method for constraint handling in CT 12 ¬(𝑭 𝟏 = 𝟎 ∧ 𝑭 𝟐 = 𝟏 ∧ 𝑭 𝟑 = 𝟎) SMT solver 𝑭 𝟏 = 𝟏 𝑭 𝟐 = 𝟏 𝑭 𝟑 = 𝟎 SAT
- 13. Our Approach • Using the properties of an SMT solver to obtain a CDA – Convert the conditions for an array to become a CDA into a propositional logic formula – The conditions: • All 𝑛 test cases satisfy constraints • All valid interactions appear in the array • Interactions not masked by other interactions are locatable 13 𝑎11 ⋯ 𝑎1𝑘 ⋮ ⋱ ⋮ 𝑎 𝑛1 ⋯ 𝑎 𝑛𝑘 ∧ 𝐶𝑜𝑟𝑒𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠(𝑎11, … , 𝑎 𝑛𝑘) SMT solver 0 ⋯ 2 ⋮ ⋱ ⋮ 2 ⋯ 1 A CDA instance
- 14. Advantages of the Approach • Able to obtain a minimal (optimal) CDA – As explained above, in order to reduce the test cost, a smaller sized test suite is preferable – By decreasing the size n one by one, the approach is able to find the minimal CDA 14 Our Approach If satisfiable 𝒏 = 𝒏 − 𝟏 If unsatisfiable The last satisfiable instance is an optimal CDA
- 15. How to obtain a suitable initial size 𝒏? • The approach needs an initial size of the array – The initial size should be larger than the size of a minimal CDA – A smaller initial size can reduce times of repetition of SAT checking • We use the size of a (𝒅 + 𝒕)-Constrained Covering Array (CCA) as the initial size – The idea comes from our conjecture that a (𝑑 + 𝑡)-CCA is already a (𝑑, 𝑡)-CDA – We omit the proof here – There are many high-speed generation methods for CCAs 15
- 16. Experiments • Experiments in brief – Experiments executed for 30 benchmarks – Frequently used benchmarks in the field of CT – The timeout was set to 30 minutes – (1,2)-CDAs were generated for the benchmarks – We wrote a program in the C++ language – We used • A machine with Intel Core i7-8700 CPU, 64GB memory and Ubuntu 18.04LTS OS. • The Z3 SMT solver (https://github.com/Z3Prover/z3) • The CIT-BACH tool [3] as the CCA generator 16 [3] Tatsuhiro Tsuchiya, Using binary decision diagrams for constraint handling in combinatorial interaction testing. CoRR abs/1907.01779. arXiv:1907.01779.
- 17. Experiment Results 17 Problem ID 3-CCA size CDA size SAT time UNSAT time 1 8 8 0.21 0.23 2 25 25 1.05 T.O. 3 60 24 1,324.29 T.O. 4 13 12 4.94 169.05 5 77 53 1,471.80 T.O. 6 11 10 13.86 49.20 7 24 14 395.55 T.O. 8 33 28 828.68 T.O. 9 54 54 1,137.43 T.O. 10 45 43 1,457.51 T.O. 11 27 26 1,363.48 T.O. 12 18 18 517.14 T.O.
- 18. Based on the Experiment Results • Our approach is able to generate a minimal CDA – For small sized benchmarks, the method we proposed is able to generate a minimal CDA • The generation is time-consuming – For 18 of the 30 benchmarks, the approach could not find even a non-optimal CDA • The checking for UNSAT sizes consumes most of the time – From benchmark No. 2, it can be found that UNSAT checking consumes most of the time 18
- 19. Conclusion and Future Works • Conclusion – Proposed a new mathematical concept called Constrained Detecting Arrays which are able to locate faults – Proposed an SMT-based method for generating (minimal) CDAs • Future works – For real-life usage, the method should scale to large problems – Instead of generating optimal sized arrays, but generate arrays in a short time • Use heuristic algorithm, etc. 19
- 20. Thank you 20
![Constrained Detecting Arrays for
Fault Localization in
Combinatorial Testing
Hao Jin[1], Ce Shi[2] and Tatsuhiro Tsuchiya[1]
Osaka University[1],
Shanghai Lixin University of
Accounting and Finance[2]
SAC2020-SVT, Brno, March. 31, 2020.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sac2020v4-2-200326061554/85/SAC2020-SVT-2-Constrained-Detecting-Arrays-for-Fault-Localization-in-Combinatorial-Testing-1-320.jpg)
![Combinatorial Testing (CT)
• What is CT?
– A black-box testing method
– Tests all t-way interactions among system
components/parameters
• Why CT?
– In component-based systems or configurable systems, faults
are usually involved in interactions among a few (t =1,2,…,6)
parameters → up to 50%~95%[1]
– Compared to the exhaustive testing, CT test suites can cut off
nearly 70% of testing costs (test cases)
2[1]Kuhn et al. An investigation of the applicability of design of experiments to
software testing, SEW’02
Can detect many faults with little cost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sac2020v4-2-200326061554/85/SAC2020-SVT-2-Constrained-Detecting-Arrays-for-Fault-Localization-in-Combinatorial-Testing-2-320.jpg)
![Example
• Example: A mobile phone product line[2]
• Each row represents a parameter of the system
• Each parameter has several (≥ 2) values
• When a system is developed, each parameter will be
assigned a value from its domain
3
F1:Display 0:16MC 1:8MC 2:BW
F2:Viewer 0:Graphical 1:Text 2:None
F3:Camera 0:2MP 1:1MP 2:None
F4:VideoCamera 0:On 1:Off
F5:VideoRingtone 0:On 1:Off
F1:Display 0 1 2
F2:Viewer 0 1 2
F3:Camera 0 1 2
F4:VideoCamera 0 1
F5:VideoRingtone 0 1
[2] Cohen et al., Constructing interaction test suites for highly-configurable systems
in the presence of constraints: a greedy approach, TSE08.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sac2020v4-2-200326061554/85/SAC2020-SVT-2-Constrained-Detecting-Arrays-for-Fault-Localization-in-Combinatorial-Testing-3-320.jpg)


![Incorporating Constraints
• Due to the real-world requirements or restrictions,
there may exist constraints among parameters
• Constraints: A mobile phone product line[2]
• Test cases must satisfy constraints
7[2] Cohen et al., Constructing interaction test suites for highly-configurable systems
in the presence of constraints: a greedy approach, TSE08.
Constraints
Graphical viewer requires color display
2MP camera requires color display
Graphical viewer not support 2MP camera
8MC display not support 2MP camera
Video camera requires a camera and a color display
Video ringtones cannot occur with NO video camera
The combination (16MC, Text, 2MP camera) will not be supported
Constraints
𝑭 𝟐 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟏 ≠ 𝟐
𝑭 𝟑 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟏 ≠ 𝟐
𝑭 𝟐 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟑 ≠ 𝟎
𝑭 𝟏 = 𝟏 → 𝑭 𝟑 ≠ 𝟎
𝑭 𝟒 = 𝟎 → (𝑭 𝟑 ≠ 𝟐 ∧ 𝑭 𝟏 ≠ 𝟐)
𝑭 𝟓 = 𝟎 → 𝑭 𝟒 = 𝟎
¬(𝑭 𝟏 = 𝟎 ∧ 𝑭 𝟐 = 𝟏 ∧ 𝑭 𝟑 = 𝟎)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sac2020v4-2-200326061554/85/SAC2020-SVT-2-Constrained-Detecting-Arrays-for-Fault-Localization-in-Combinatorial-Testing-7-320.jpg)








![Experiments
• Experiments in brief
– Experiments executed for 30 benchmarks
– Frequently used benchmarks in the field of CT
– The timeout was set to 30 minutes
– (1,2)-CDAs were generated for the benchmarks
– We wrote a program in the C++ language
– We used
• A machine with Intel Core i7-8700 CPU, 64GB memory and Ubuntu
18.04LTS OS.
• The Z3 SMT solver (https://github.com/Z3Prover/z3)
• The CIT-BACH tool [3] as the CCA generator
16
[3] Tatsuhiro Tsuchiya, Using binary decision diagrams for constraint handling in
combinatorial interaction testing. CoRR abs/1907.01779. arXiv:1907.01779.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sac2020v4-2-200326061554/85/SAC2020-SVT-2-Constrained-Detecting-Arrays-for-Fault-Localization-in-Combinatorial-Testing-16-320.jpg)



















































