Scheduling and sequencing
Download as PPT, PDF87 likes74,906 views
This document discusses various concepts related to operations scheduling. It defines operations scheduling and describes how it involves assigning jobs to work centers and machines, determining start and completion times, allocating resources, and establishing time sequences. It outlines objectives like meeting delivery dates and minimizing costs/inventory. Performance measures used in scheduling like job flow time, makespan, past due jobs and utilization are also defined. Finally, it discusses sequencing jobs at single and multiple workstations using different priority rules.
1 of 34
Downloaded 1,931 times
































Ad
Recommended
TYPES OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT



TYPES OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENTAnkit Prajapati This document outlines different types of strategic management strategies including integration, intensive, diversification, and defensive strategies. Integration strategies involve expanding operations through vertical or horizontal integration. Intensive strategies focus on improving existing products and markets through market penetration, development, or product development. Diversification strategies involve entering new markets or product lines that are related or unrelated. Defensive strategies are used to protect market share and include joint ventures, divestitures, or liquidations.
Agile model



Agile modelDivyaStephen3 The agile model is an iterative and incremental software development process that focuses on quick delivery of working software in short cycles. Requirements are broken into small parts that can be developed incrementally to minimize risk and reduce delivery time. Each iteration is typically 1-4 weeks where a cross-functional team plans, designs, codes, tests, and demos a working product to stakeholders before starting the next iteration. Multiple iterations may be needed to fully develop the product or new features.
Introduction to Groups and Permutation Groups



Introduction to Groups and Permutation GroupsAmit Amola Basic concept of Groups and a detailed understanding of Permutation Groups with examples and solved questions.
Time and Motion Study



Time and Motion StudyVivek Shelke Time and motion studies are a technique used to analyze jobs by recording the times taken to complete individual tasks. This allows for determining the most efficient way to perform tasks and setting productivity standards. They can be implemented in manufacturing, offices, retail stores, and other industries. Benefits include improving productivity, identifying unnecessary activities, balancing workloads, and making recommendations to enhance efficiency. Potential issues include observers lacking competence and workers not fully cooperating with studies. Textile mills commonly use time and motion studies for processes like spinning, warping, weaving, and dyeing to optimize operations.
Reimbursement Expense Receipt Form



Reimbursement Expense Receipt FormRoxas NCHS This document contains a reimbursement expense receipt template. The template includes fields for the entity name, date, fund cluster, and receipt number. It states that the receipt is for an amount received in payment for some purpose, from a payee and their official designation. The payee and a witness must provide their name, signature, and address. Details like inclusive dates or travel purposes should be included for payments related to subsistence, services, rental, or transportation. The document contains the template repeated in full.
Operation management intro



Operation management introStudsPlanet.com This chapter introduces operations management. It defines operations management as managing the systems or processes that create goods and services. The chapter outlines the key functional areas of organizations and how operations management affects a company's ability to compete. It compares manufacturing and service operations, describing their differences in areas like customer contact, input and output variability, and inventory levels. The chapter also discusses the role of the operations manager in making both system design and operation decisions. Finally, it provides an overview of trends impacting operations management like globalization and supply chain management.
Rewards and-recognition-1207897261939764-8



Rewards and-recognition-1207897261939764-8shahzad10 - Nearly 9 out of 10 companies offer recognition programs to acknowledge employee contributions. Recognition programs are generally less expensive than other forms of compensation.
- The key purposes of recognition programs are to motivate high performance, reinforce desired behaviors, and create a positive work culture. Recognition can include both monetary and non-monetary rewards.
- Successful recognition programs have characteristics like senior management support, employee input in design, simplicity, tailored rewards, clear communication, and timely recognition of specific achievements.
Replacement theory



Replacement theoryVILAS ADOLE The document discusses replacement theory, which determines the optimal time to replace equipment or machines that deteriorate over time. It increases maintenance costs as equipment ages. The document provides examples of industries that use replacement theory and outlines the methodology. It presents a sample replacement problem looking at the purchase price, annual running costs, and resale values to determine the year when replacement is most economical based on minimum average total cost. The optimal replacement period is calculated based on rules comparing maintenance costs to average costs or scrap value.
Operation scheduling



Operation schedulingsai precious This document discusses operations scheduling. It begins by introducing operations scheduling and explaining that it involves assigning jobs, resources, and sequencing operations while accounting for deviations. It then discusses key performance measures for schedules such as job flow time, makespan, past due jobs, work-in-process inventory, total inventory, and utilization. The document proceeds to list objectives and functions of operations scheduling such as efficient resource use, on-time delivery, and minimizing costs and inventory. Finally, it briefly outlines types of scheduling like forward and backward, and methods like Johnson's algorithm and the index method.
CAPACITY PLANNING



CAPACITY PLANNINGShilpi Panchal Contents of Presentation-
Capacity Planning:
- Meaning
- Forecasting
- Reasons
- Importance
- Examples
- Capacity Terminology
- Efficiency & Utilization
- Calculation of capacity Utilization
- Determinants of Effective Capacity
- Calculating Processing Requirements
- Capacity Planning Process
- Planning Over a Time Horizon
- Economies of Scale
- Optimal Rate of Output
-Capacity Planning Alternatives Evaluating Models
Cost Volume Analysis: Break-even Analysis
Decision Theory
Financial Analysis
Waiting-Line Analysis
- PROCESS PLANNING
Methods
- INTERACTION OF
PLANNING FUNCTIONS..
-
Facility layout ppt



Facility layout pptAnju Rana The layout facility is the physical location of the various departments/units of the facility within the premises of the facility.
Aggregate planning



Aggregate planningAtif Ghayas Aggregate planning involves developing a preliminary production schedule over the next 6-18 months to satisfy forecasted demand at minimum cost. It considers targeted sales, production levels, inventory levels and backlogs. The objectives are to minimize costs and changes while maximizing profits, customer service and resource utilization. Common strategies are level, which maintains steady output/employment, or chase, which matches demand period to period. Techniques to develop plans include linear programming, linear decision rules and simulation models.
Operations Management : Line Balancing



Operations Management : Line BalancingRohan Bharaj This presentation gives us details about the different methods of Line Balancing.
It also gives an example of Ford Motors and how Line Balancing helped Ford become a powerhouse in the early 1900s
Capacity management



Capacity managementyashodeep more Capacity planning is determining the production capacity needed by a company to meet changing demands. It involves calculating the maximum output that can be produced with available resources, measuring capacity in units, and linking it to workforce planning. Capacity must account for seasonal or unexpected demand changes. There are three types of capacity considered: potential, immediate, and effective. Proper capacity planning ensures a company can meet customer requirements over time.
Production and Operation Management



Production and Operation ManagementJo Balucanag - Bitonio This document discusses production and operations management. It begins with definitions of production management and operations management. It then provides a historical overview of the evolution of the field from Adam Smith's specialization of labor to more modern contributions. The rest of the document defines concepts related to production systems including inputs, transformation processes, outputs, and classifications like job shop, batch, mass, and continuous production.
types of production system



types of production systemram4181 The document discusses two main types of production systems: intermittent and continuous. Intermittent production involves producing goods in small batches based on customer orders, with irregular start/stop cycles. Continuous production aims to produce goods constantly to meet forecasted demand at large scale using standardized processes. Specific intermittent systems include project production (complex one-time orders), job production (custom single units), and batch production (producing in lots based on orders or forecasts). Continuous systems emphasize mass production of standardized goods and process production of a single product.
Capacity planning 



Capacity planning Abdullah Shahid Capacity planning is the process of determining a company's production capacity needed to meet changing demands. It involves determining the type, amount, and timing of capacity required. Key decisions include selecting the appropriate level and flexibility of facilities while maintaining balance. The process includes estimating future needs, evaluating existing capacity, identifying alternatives, analyzing costs, assessing qualitative factors, selecting an alternative, and monitoring results. Efficiency and utilization are measured by comparing actual output to effective and design capacities. Economies and diseconomies of scale affect costs based on output levels. Cost-volume analysis examines the relationships between costs, revenues, and profits at different volumes.
Production Planning and Control



Production Planning and Controlshrinivas kulkarni This document discusses production planning and control (PPC). It defines PPC as planning, directing, and coordinating a firm's resources to achieve production goals efficiently. PPC involves planning materials, methods, machines, manpower, routing, estimating, scheduling, dispatching, expediting, and evaluating manufacturing operations. It outlines the scope of PPC and discusses key aspects like routing, scheduling, dispatching, follow up/expediting, inspection, and benefits and limitations of PPC.
Capacity planning



Capacity planningAkhil Lal Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands. It involves assessing existing capacity, forecasting future needs, identifying options to modify capacity, evaluating financial and technological alternatives, and selecting the most suitable option. Capacity planning can be classified as long term or short term based on time horizon and finite or infinite based on resources employed. Long term planning accommodates major changes like new products or facilities while short term addresses intermediate fluctuations through overtime or subcontracting. Factors affecting capacity planning include controllable aspects like labor and facilities as well as less controllable issues like absenteeism or machine breakdowns.
Ch17 scheduling



Ch17 schedulingMd. IFTEKHARUL ISLAM The document discusses production and operations management concepts related to work center scheduling. It defines work centers and describes typical scheduling functions like allocating orders and determining sequence. It then covers priority rules for job sequencing, schedule performance measures, and examples of different sequencing methods. Finally, it discusses shop-floor control functions and principles of work center and job shop scheduling.
Scheduling



SchedulingNishant Agrawal Scheduling
Routing
Prioritizing
Dispatching
What is Scheduling ?
Forward Scheduling
Backward Scheduling
Finite LOADING
infinite loading
Schedule Gantt Chart
Line balancing
GOAL AND OBJECTIVE
LINE BALANCING PROCEDURE
Strategies and Costs
as early as possible
as last as possible
work measurement_operation management



work measurement_operation managementSaravanan Murugan This document discusses work measurement techniques. It introduces work measurement as a way to establish standard times for jobs by eliminating ineffective time. It describes the objectives of work measurement as setting standards for costing, scheduling, and incentive plans. The key components of work measurement are explained as elements, performance ratings, allowances, and standard times. Various work measurement techniques are outlined, including time study, synthesis from standard data, predetermined motion time systems, analytical estimating, and work sampling. The uses of work measurement are to compare methods, balance team work, and determine machine-operator relationships.
Presentation on scheduling



Presentation on schedulingGunjan Lal Scheduling involves establishing start and completion times for operations to complete a product by its due date. It aims to systematically arrange production. Key principles include using optimum task sizes, equally loading plants, and normally using work hours in the same sequence. Common scheduling methods are forward and backward, depending on whether scheduling starts from the beginning or end of the process. Scheduling methodology depends on the industry, organization, product, and sophistication required, and can include charts, priority rules, or mathematical programming.
Process design



Process designnavin_sosimple 1) Process design involves planning the processes that transform inputs like resources, information, and time into outputs like products and services.
2) Product and service design influence and are influenced by process design - decisions in one area impact the other. Processes must be designed to effectively produce the products and services.
3) There are different types of processes like project, jobbing, batch, mass, and continuous, as well as service types like professional and mass service, which vary in factors like volume, variety, and skills required. Process mapping and analysis can improve processes.
Cellular layout/Manufacturing



Cellular layout/ManufacturingFahad Ali Cellular Layout/Manufacturing is the concept of lean Management. it involves the concepts for the better production and processing of the Product.
Facility layout



Facility layoutJassi Dutt Facility Layout
Introduction
Layout planning is determining the best physical arrangement of resources within a facility.
It may be defined as a technique of locating machines, processes and plant services within the factory so as to achieve the right quantity and quality of output at the lowest possible cost of manufacturing.
Objective of a good Layout
Provide enough production capacity.
Reduce material handling costs.
Reduce congestion that impedes the movement of people or material.
Reduce hazards to personnel.
Increase employee morale.
Reduce accidents.
Utilize available space effectively & efficiently.
Just In Time (JIT)



Just In Time (JIT)Manoj Subedi This presentation provides an overview of just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing. It discusses the history and origins of JIT in Japan in the 1970s. The key philosophy of JIT is to have "the right material, at the right time, at the right place, and in the exact amount." The presentation outlines the objectives, elements, advantages, and disadvantages of JIT. It also explores how JIT principles can be applied in the service industry through concepts like standard work methods, supplier ties, and automation.
Job shop scheduling



Job shop schedulingSujeet TAMBE This document discusses job shop scheduling, which involves scheduling jobs at general purpose work stations. It describes factors like arrival patterns, number of machines, work sequences, and performance criteria. For arrival patterns, it notes static and dynamic types. For work sequences, it discusses fixed and random types. It provides examples of performance criteria like makespan and machine utilization. It also introduces Gantt charts for scheduling displays and discusses scenarios like scheduling n jobs on 1 machine, n jobs on a flow shop with 2 machines, and n jobs on m machines in general. Heuristics for the n jobs on m machines case include shortest processing time, earliest due date, and critical ratio rules.
Sequencing



SequencingRashmi Navaghane The document describes three problems involving determining the optimal sequence of jobs through multiple machines to minimize the total elapsed time.
For the first problem involving two machines, the optimal sequence is job 2, 1, 6, 5, 4, 3 with a total elapsed time of 85 hours.
The second problem involving three machines is converted to two virtual machines, and the optimal sequence is job 3, 4, 2, 1, 5 with a total elapsed time of 51 hours.
The third problem involving four machines is also converted to two virtual machines, and the optimal sequence is job C, A, B, D with a total elapsed time of 82 hours.
Scheduling



Schedulingahmad bassiouny The document discusses various concepts related to scheduling operations management including objectives, loading, sequencing, monitoring, and advanced planning systems. It provides examples of sequencing rules like FCFS, DDATE, and SPT and compares their performance on a sample problem. Guidelines for selecting rules are outlined. Input/output control and Gantt charts are discussed as monitoring tools. Finally, it briefly covers employee scheduling heuristics.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Operation scheduling



Operation schedulingsai precious This document discusses operations scheduling. It begins by introducing operations scheduling and explaining that it involves assigning jobs, resources, and sequencing operations while accounting for deviations. It then discusses key performance measures for schedules such as job flow time, makespan, past due jobs, work-in-process inventory, total inventory, and utilization. The document proceeds to list objectives and functions of operations scheduling such as efficient resource use, on-time delivery, and minimizing costs and inventory. Finally, it briefly outlines types of scheduling like forward and backward, and methods like Johnson's algorithm and the index method.
CAPACITY PLANNING



CAPACITY PLANNINGShilpi Panchal Contents of Presentation-
Capacity Planning:
- Meaning
- Forecasting
- Reasons
- Importance
- Examples
- Capacity Terminology
- Efficiency & Utilization
- Calculation of capacity Utilization
- Determinants of Effective Capacity
- Calculating Processing Requirements
- Capacity Planning Process
- Planning Over a Time Horizon
- Economies of Scale
- Optimal Rate of Output
-Capacity Planning Alternatives Evaluating Models
Cost Volume Analysis: Break-even Analysis
Decision Theory
Financial Analysis
Waiting-Line Analysis
- PROCESS PLANNING
Methods
- INTERACTION OF
PLANNING FUNCTIONS..
-
Facility layout ppt



Facility layout pptAnju Rana The layout facility is the physical location of the various departments/units of the facility within the premises of the facility.
Aggregate planning



Aggregate planningAtif Ghayas Aggregate planning involves developing a preliminary production schedule over the next 6-18 months to satisfy forecasted demand at minimum cost. It considers targeted sales, production levels, inventory levels and backlogs. The objectives are to minimize costs and changes while maximizing profits, customer service and resource utilization. Common strategies are level, which maintains steady output/employment, or chase, which matches demand period to period. Techniques to develop plans include linear programming, linear decision rules and simulation models.
Operations Management : Line Balancing



Operations Management : Line BalancingRohan Bharaj This presentation gives us details about the different methods of Line Balancing.
It also gives an example of Ford Motors and how Line Balancing helped Ford become a powerhouse in the early 1900s
Capacity management



Capacity managementyashodeep more Capacity planning is determining the production capacity needed by a company to meet changing demands. It involves calculating the maximum output that can be produced with available resources, measuring capacity in units, and linking it to workforce planning. Capacity must account for seasonal or unexpected demand changes. There are three types of capacity considered: potential, immediate, and effective. Proper capacity planning ensures a company can meet customer requirements over time.
Production and Operation Management



Production and Operation ManagementJo Balucanag - Bitonio This document discusses production and operations management. It begins with definitions of production management and operations management. It then provides a historical overview of the evolution of the field from Adam Smith's specialization of labor to more modern contributions. The rest of the document defines concepts related to production systems including inputs, transformation processes, outputs, and classifications like job shop, batch, mass, and continuous production.
types of production system



types of production systemram4181 The document discusses two main types of production systems: intermittent and continuous. Intermittent production involves producing goods in small batches based on customer orders, with irregular start/stop cycles. Continuous production aims to produce goods constantly to meet forecasted demand at large scale using standardized processes. Specific intermittent systems include project production (complex one-time orders), job production (custom single units), and batch production (producing in lots based on orders or forecasts). Continuous systems emphasize mass production of standardized goods and process production of a single product.
Capacity planning 



Capacity planning Abdullah Shahid Capacity planning is the process of determining a company's production capacity needed to meet changing demands. It involves determining the type, amount, and timing of capacity required. Key decisions include selecting the appropriate level and flexibility of facilities while maintaining balance. The process includes estimating future needs, evaluating existing capacity, identifying alternatives, analyzing costs, assessing qualitative factors, selecting an alternative, and monitoring results. Efficiency and utilization are measured by comparing actual output to effective and design capacities. Economies and diseconomies of scale affect costs based on output levels. Cost-volume analysis examines the relationships between costs, revenues, and profits at different volumes.
Production Planning and Control



Production Planning and Controlshrinivas kulkarni This document discusses production planning and control (PPC). It defines PPC as planning, directing, and coordinating a firm's resources to achieve production goals efficiently. PPC involves planning materials, methods, machines, manpower, routing, estimating, scheduling, dispatching, expediting, and evaluating manufacturing operations. It outlines the scope of PPC and discusses key aspects like routing, scheduling, dispatching, follow up/expediting, inspection, and benefits and limitations of PPC.
Capacity planning



Capacity planningAkhil Lal Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands. It involves assessing existing capacity, forecasting future needs, identifying options to modify capacity, evaluating financial and technological alternatives, and selecting the most suitable option. Capacity planning can be classified as long term or short term based on time horizon and finite or infinite based on resources employed. Long term planning accommodates major changes like new products or facilities while short term addresses intermediate fluctuations through overtime or subcontracting. Factors affecting capacity planning include controllable aspects like labor and facilities as well as less controllable issues like absenteeism or machine breakdowns.
Ch17 scheduling



Ch17 schedulingMd. IFTEKHARUL ISLAM The document discusses production and operations management concepts related to work center scheduling. It defines work centers and describes typical scheduling functions like allocating orders and determining sequence. It then covers priority rules for job sequencing, schedule performance measures, and examples of different sequencing methods. Finally, it discusses shop-floor control functions and principles of work center and job shop scheduling.
Scheduling



SchedulingNishant Agrawal Scheduling
Routing
Prioritizing
Dispatching
What is Scheduling ?
Forward Scheduling
Backward Scheduling
Finite LOADING
infinite loading
Schedule Gantt Chart
Line balancing
GOAL AND OBJECTIVE
LINE BALANCING PROCEDURE
Strategies and Costs
as early as possible
as last as possible
work measurement_operation management



work measurement_operation managementSaravanan Murugan This document discusses work measurement techniques. It introduces work measurement as a way to establish standard times for jobs by eliminating ineffective time. It describes the objectives of work measurement as setting standards for costing, scheduling, and incentive plans. The key components of work measurement are explained as elements, performance ratings, allowances, and standard times. Various work measurement techniques are outlined, including time study, synthesis from standard data, predetermined motion time systems, analytical estimating, and work sampling. The uses of work measurement are to compare methods, balance team work, and determine machine-operator relationships.
Presentation on scheduling



Presentation on schedulingGunjan Lal Scheduling involves establishing start and completion times for operations to complete a product by its due date. It aims to systematically arrange production. Key principles include using optimum task sizes, equally loading plants, and normally using work hours in the same sequence. Common scheduling methods are forward and backward, depending on whether scheduling starts from the beginning or end of the process. Scheduling methodology depends on the industry, organization, product, and sophistication required, and can include charts, priority rules, or mathematical programming.
Process design



Process designnavin_sosimple 1) Process design involves planning the processes that transform inputs like resources, information, and time into outputs like products and services.
2) Product and service design influence and are influenced by process design - decisions in one area impact the other. Processes must be designed to effectively produce the products and services.
3) There are different types of processes like project, jobbing, batch, mass, and continuous, as well as service types like professional and mass service, which vary in factors like volume, variety, and skills required. Process mapping and analysis can improve processes.
Cellular layout/Manufacturing



Cellular layout/ManufacturingFahad Ali Cellular Layout/Manufacturing is the concept of lean Management. it involves the concepts for the better production and processing of the Product.
Facility layout



Facility layoutJassi Dutt Facility Layout
Introduction
Layout planning is determining the best physical arrangement of resources within a facility.
It may be defined as a technique of locating machines, processes and plant services within the factory so as to achieve the right quantity and quality of output at the lowest possible cost of manufacturing.
Objective of a good Layout
Provide enough production capacity.
Reduce material handling costs.
Reduce congestion that impedes the movement of people or material.
Reduce hazards to personnel.
Increase employee morale.
Reduce accidents.
Utilize available space effectively & efficiently.
Just In Time (JIT)



Just In Time (JIT)Manoj Subedi This presentation provides an overview of just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing. It discusses the history and origins of JIT in Japan in the 1970s. The key philosophy of JIT is to have "the right material, at the right time, at the right place, and in the exact amount." The presentation outlines the objectives, elements, advantages, and disadvantages of JIT. It also explores how JIT principles can be applied in the service industry through concepts like standard work methods, supplier ties, and automation.
Job shop scheduling



Job shop schedulingSujeet TAMBE This document discusses job shop scheduling, which involves scheduling jobs at general purpose work stations. It describes factors like arrival patterns, number of machines, work sequences, and performance criteria. For arrival patterns, it notes static and dynamic types. For work sequences, it discusses fixed and random types. It provides examples of performance criteria like makespan and machine utilization. It also introduces Gantt charts for scheduling displays and discusses scenarios like scheduling n jobs on 1 machine, n jobs on a flow shop with 2 machines, and n jobs on m machines in general. Heuristics for the n jobs on m machines case include shortest processing time, earliest due date, and critical ratio rules.
Viewers also liked (20)
Sequencing



SequencingRashmi Navaghane The document describes three problems involving determining the optimal sequence of jobs through multiple machines to minimize the total elapsed time.
For the first problem involving two machines, the optimal sequence is job 2, 1, 6, 5, 4, 3 with a total elapsed time of 85 hours.
The second problem involving three machines is converted to two virtual machines, and the optimal sequence is job 3, 4, 2, 1, 5 with a total elapsed time of 51 hours.
The third problem involving four machines is also converted to two virtual machines, and the optimal sequence is job C, A, B, D with a total elapsed time of 82 hours.
Scheduling



Schedulingahmad bassiouny The document discusses various concepts related to scheduling operations management including objectives, loading, sequencing, monitoring, and advanced planning systems. It provides examples of sequencing rules like FCFS, DDATE, and SPT and compares their performance on a sample problem. Guidelines for selecting rules are outlined. Input/output control and Gantt charts are discussed as monitoring tools. Finally, it briefly covers employee scheduling heuristics.
operations scheduling



operations schedulingShriraj Deshpande The document provides information about scheduling techniques for service and manufacturing processes. It discusses front-office and back-office processes, performance measures like flow time and makespan, sequencing jobs using rules like earliest due date and shortest processing time, and priority sequencing rules like critical ratio and slack per remaining operations. Examples are provided to illustrate how to sequence jobs using different rules and compare their performance.
Kanban (1)



Kanban (1)Faraz Patel Kanban is a pull system that uses visual signals to control work in process inventory and optimize material flow. It originated at Toyota in the 1950s to manage production line material flows using cards to signal the need for parts replenishment. Kanban limits work in process inventory by only authorizing production of additional inventory as and when needed, as signaled by empty containers. The key aspects of Kanban include using cards or signals to communicate production orders between processes, standardizing container sizes, and limiting inventory to just what is needed by the downstream process.
Transportation and Assignment



Transportation and AssignmentLokesh Payasi The document discusses transportation and assignment models in operations research. The transportation model aims to minimize the cost of distributing a product from multiple sources to multiple destinations, while satisfying supply and demand constraints. The assignment model finds optimal one-to-one matching between sources and destinations to minimize costs. Some solution methods for transportation problems include the northwest corner method, row minima method, column minima method, and least cost method. The Hungarian method is commonly used to solve assignment problems by finding the minimum cost matching.
Sequencing problems in Operations Research



Sequencing problems in Operations ResearchAbu Bashar The document discusses sequencing problems and various sequencing rules used to optimize outputs when assigning jobs to machines. It describes Johnson's rule for minimizing completion time when scheduling jobs on two workstations. Johnson's rule involves scheduling the job with the shortest processing time first at the workstation where it finishes earliest. It provides an example of applying Johnson's rule to schedule five motor repair jobs at the Morris Machine Company across two workstations. Finally, it discusses Johnson's three machine rule for sequencing jobs across three machines.
An introduction to Game Theory



An introduction to Game TheoryPaul Trafford This presentation is an attempt to introduce Game Theory in one session. It's suitable for undergraduates. In practice, it's best used as a taster since only a portion of the material can be covered in an hour - topics can be chosen according to the interests of the class.
The main reference source used was 'Games, Theory and Applications' by L.C.Thomas. Further notes available at: http://bit.ly/nW6ULD
Product designing strategy



Product designing strategyMegha Jain The document discusses product design strategy and the product development process. It defines standard, customized, and modified product strategies and their objectives. The product development process involves idea development, screening, preliminary design/testing, and final design stages. It also outlines dimensions of product strategy including positioning, repositioning, overlap, scope, design, and elimination. Causes of new product failure and components of an effective product development system are summarized as well.
Aggregate planning and mps om



Aggregate planning and mps omfatuma ahmed The document discusses aggregate planning and master production scheduling. It provides an overview of aggregate planning, including forecasting demand and setting output levels to meet demand. It also discusses developing a master production schedule by disaggregating the aggregate plan into specific end items and timing of production. The master schedule covers a shorter horizon than the aggregate plan, typically 6-8 weeks. It aims to balance demand with capacity and production resources.
Product design and development ch3



Product design and development ch3Kavindra Singh This chapter discusses opportunity identification, which is the first step in the product planning and development processes. It describes three levels of opportunities - improvements to existing products, new products in existing markets/technologies, and entirely new product categories. The chapter outlines a five-step process for identifying opportunities: establishing a charter, generating many opportunities, screening opportunities, developing promising ones, and selecting exceptional opportunities. It then provides techniques for generating opportunities such as following passions, compiling bug lists, studying customers and trends, and imitating but improving competitors. Finally, it discusses factors that influence the quality of identified opportunities and questions to consider when evaluating opportunity quality.
Learning Curve Sample Problem



Learning Curve Sample ProblemCherry Joy Banquicio - The ABC Company has received a production schedule to make 38 ski lift gondola cars over 6 months, with the first unit taking 1000 hours.
- Using a learning curve of 80%, it is estimated that the 38th unit would take around 310 hours to complete.
- The budget provides for a maximum of 30 direct labor employees per month and a total of 15,000 direct labor hours.
- The calculations show the labor hours required each month does not exceed 30 employees, but the total hours required is 16,581, exceeding the budget by 1,581 hours. Therefore, the budget will not be adequate.
TIME STUDY



TIME STUDYchhavi narayan Time study is a work measurement technique that determines the time for a qualified worker to complete a task at a defined level of performance. It involves observing and recording the time required by a worker to perform individual tasks in their regular work. The objectives of time study include increasing productivity, setting labor standards, and determining basic and standard times. It is used to analyze elements of a job, set performance standards, and improve work methods and processes.
operations strategy and competitiveness



operations strategy and competitivenessMeenakshi Singh The document discusses strategic planning and operations strategy. It provides an overview of the strategic planning process, including preparing a mission statement, creating a vision, setting goals, formulating strategies, designing tactics, evaluating performance, and measuring results. It also discusses different types of operations strategies such as competing on price, quality, time, and flexibility. Examples are provided of strategic plans for individuals and companies. The document also covers topics like measuring productivity, types of productivity measures, and ways to improve productivity.
Learning curve



Learning curveFrancisco Gutierrez The document discusses the concept of a learning curve and its application to industries. It shows that human productivity increases with experience, as costs are reduced the more times a task is repeated. For example, a study found that oil refineries achieved 33% higher production than design capacity due to experience. If experience is transferred systematically between employees, the learning curve is accelerated. The document also shows that starting a new industrial operation with experienced personnel through training can significantly reduce initial losses and lead to profits months earlier compared to learning through trial and error alone.
Product design and development ch2



Product design and development ch2Kavindra Singh This document discusses development processes and organizations. It describes core development stages like concept development, architectural design, and detailed design. It also discusses generic concept development processes, product development processes like Tyco's, and organizational types like functional, project, and matrix structures. Finally, it covers traditional design methods and variants of development processes for different product types.
Learning curve



Learning curveJessy Chong The document discusses learning curves, which model how the time and costs to produce a product decrease as a workforce gains experience making it. As a workforce learns, there is a big reduction in the time needed to make additional units. The learning rate expresses the percentage reduction in time, such as an 80% learning curve. There are two methods to calculate learning curves - a tabular approach that calculates average times when output doubles, and an algebraic approach that uses an equation to calculate the time for any unit based on variables like time for the first unit, cumulative output, and the learning factor derived from the learning rate. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating times for single units, ranges of units, and multiple ranges.
Operation strategy at galanze



Operation strategy at galanzeNiilm-Cms The case study discusses a company that failed to properly update its R&D, arrange prototype testing, and understand cultural differences in overseas markets. This led to communication gaps, overstock of unpopular products, and shortages of popular products. To improve, the company must enhance product quality, customer service, adopt a global marketing strategy, maintain proper inventory levels, and strengthen its distribution channels.
C5 process & layout



C5 process & layouthakimizaki The document discusses various process strategies and tools for analyzing production processes. It describes four main types of process strategies - process focused, repetitive focused, product focused, and mass customization. Each strategy has different characteristics in terms of equipment used, worker skills required, scheduling, and costs. Tools for process design like flow diagrams, process charts, and value stream mapping are also outlined. The goal is to determine the most efficient process strategy to meet customer requirements at low cost.
MARUTI SUZUKI PRODUCT ANALYSIS REPORT



MARUTI SUZUKI PRODUCT ANALYSIS REPORTViʞaƨh ʞumar This document provides a marketing assignment on Maruti Suzuki that includes an introduction, history, and analysis of the 4 P's of Marketing - Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. It discusses Maruti Suzuki's wide range of affordable vehicle offerings across segments, its strategy to offer low prices through efficiency and reduce costs, and its extensive nationwide network of sales and service centers to provide accessibility to customers. The summary analyzes Maruti Suzuki's leadership in the Indian automobile market through its affordable people's cars and extensive distribution network.
Product design and development ch4



Product design and development ch4Kavindra Singh The document provides an overview of the product planning process outlined in Chapter 4 of the textbook "Product Design and Development" by Karl T. Ulrich and Steven D. Eppinger. It discusses identifying product development opportunities, evaluating and prioritizing projects, allocating resources and planning timing. A case study of Xerox's Lakes project to develop a digital copier platform is provided as an example. Key aspects of product planning include developing a portfolio of projects aligned with company strategy, market segmentation, technology roadmaps, and balancing fundamentally new vs. incremental projects.
Ad
Similar to Scheduling and sequencing (20)
Operations Scheduling



Operations SchedulingAshish Jain Operations scheduling is a critical but complicated task for organizations. It involves allocating resources like workers, machines, and materials over time to complete tasks and meet customer demands. Effective scheduling balances performance measures like flow time, inventory levels, and utilization rates. Common scheduling methods include forward and backward scheduling, critical path analysis, and indexing to determine job sequences and machine assignments. The goals of scheduling are to maximize efficiency, output, and profits while minimizing costs, delays, and inventory levels.
schedulingandsequencing-140424065526-phpapp02__1_.ppt



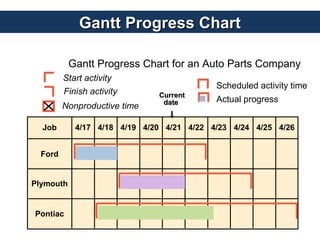
schedulingandsequencing-140424065526-phpapp02__1_.pptVELMURUGANM19 Operations scheduling is critical for meeting customer demands and inventory targets. It involves assigning jobs to work centers, determining start and completion times, allocating resources, and establishing task sequences. Effective scheduling balances performance metrics like flow time, inventory levels, and machine utilization. Priority rules are used to sequence jobs at multiple workstations, though determining the best rule can be complex due to interactions between processes. Gantt charts are useful tools for scheduling and tracking job and workstation progress.
Production planning and control 2019



Production planning and control 2019sserwaniko This document provides information about production planning and control (PPC) and the need for scheduling. It discusses:
- The objectives and benefits of PPC, including cost reduction, optimal resource utilization, and improved customer service.
- The typical functions of scheduling including allocating resources, determining order sequence, measuring performance, and shop floor control.
- Common scheduling methods like Gantt charts, mathematical programming, and priority rules.
- The importance of scheduling bottlenecks to fully utilize constrained resources.
- The need for scheduling to meet customer demands, maximize efficiency, and motivate employees.
Production planning and control



Production planning and controlLaxmikant Deshmukh The document discusses production planning and control functions including process planning, loading, scheduling, dispatching, and follow up. It explains that process planning determines the sequence of operations, loading assigns work to work centers based on schedules, and scheduling determines start and finish times of operations. Dispatching authorizes the start of operations and follow up monitors progress. The document also covers factors that affect production planning like type of product and manufacturing. Different planning functions are needed for job shops, batch production, and mass production. Finally, it discusses scheduling objectives like meeting due dates and maximizing resource utilization.
Scheduling



Schedulingsachin kumar sharma This document discusses operations scheduling, which involves allocating production resources like machines and workers to production orders over time. It covers topics like job shop scheduling terminology, common sequencing rules like shortest processing time and earliest due date, sequencing theory for single and multiple machines, and objectives of operations scheduling such as minimizing costs and tardiness. The document provides examples comparing the results of applying different sequencing rules to a sample job shop scheduling problem.
Scheduling



Schedulingmanobili17 Scheduling involves arranging workloads and allocating resources like machinery, employees, and materials. There are two main types of scheduling: operations scheduling, which assigns jobs and employees to time periods, and flow-shop scheduling for high-volume systems, where identical products flow through standardized processes. For low-volume job shops, scheduling is more complex due to custom orders and uncertain job requirements. Key considerations for both include sequencing jobs effectively and balancing workloads across workstations.
Unit 7 production scheduling 



Unit 7 production scheduling RASHMIPANWAR10 The document discusses production scheduling, which involves determining the products and quantities to be manufactured, the sequence of manufacturing processes, and allocating resources over time. It describes objectives of production control like issuing orders and ensuring instructions are followed. Production scheduling aims to maximize efficiency and reduce costs. Techniques discussed include loading, sequencing using priority rules, Johnson's rule for two work centers, and solving three machine problems if conditions are met. The benefits of scheduling and examples are provided.
7_production-activity-control.pptx



7_production-activity-control.pptxRidhoDarmawan10 Production Activity Control (PAC) is responsible for executing the Master Production Schedule and Materials Requirements Plan. PAC releases work orders to manufacturing and controls the flow of orders through production. It aims to complete orders on time while making efficient use of resources and maintaining low work-in-process inventory. PAC schedules start and completion times for shop orders and develops load profiles for work centers. It implements production plans, monitors performance, and makes adjustments as needed to control production activity.
PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL-Unit 4



PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL-Unit 4prakash0712 The document discusses various production planning and scheduling functions including scheduling, loading, sequencing, expediting, Gantt charts, line of balance, linear scheduling method, batch production scheduling, MRP, kanban, dispatching, progress reporting, and manufacturing lead time. Scheduling determines when operations are performed and works are completed. Loading adds total operation times to planned workstation utilization. Sequencing and dispatching authorize starting operations. Expediting ensures plans meet commitments.
Ppc unit-4-production scheduling



Ppc unit-4-production schedulingkarthi keyan The document discusses several key functions of production scheduling and control including loading work to work centers, sequencing jobs by priority, monitoring capacity and lead times, and generating schedules using methods like Gantt charts, line of balance, and linear scheduling. It also covers batch production scheduling, material requirements planning (MRP), Kanban systems, dispatching work to the shop floor, and reporting on and expediting manufacturing progress.
PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL



PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROLSIVASHANKAR N The document discusses various production scheduling concepts and methods. It describes the functions of loading and scheduling, including determining operation times and adding work to schedules. Common scheduling benefits are outlined as well as tools like Gantt charts, line of balance diagrams, and MRP. Batch production scheduling, linear scheduling, dispatching, progress reporting and manufacturing lead times are also summarized.
unit 4.ppt



unit 4.pptrknatarajan The document discusses various production scheduling concepts and methods. It describes the loading and scheduling process, which involves determining the work required, computing total time needed, and adding it to existing workplans. Scheduling then determines operation start/finish times. Master scheduling and Gantt charts are also referenced. Benefits of scheduling include reduced inventory and setups. MRP, Kanban, dispatching, progress reporting and expediting are additionally summarized.
Unit 4



Unit 4MeganathanJ4 The document discusses various production scheduling concepts and methods. It describes the functions of loading and scheduling, including determining operation times and sequencing work. Common scheduling tools are also explained, such as Gantt charts, which illustrate project schedules and task dependencies. Batch production scheduling and MRP systems are also summarized. Linear scheduling focuses on continuous resource utilization for repetitive activities. The document also discusses dispatching, progress reporting, and manufacturing lead times.
Unit 4



Unit 4Mr.C.Dineshbabu The document discusses various production scheduling concepts and methods. It describes the loading and scheduling process, which involves determining the work required, computing total time needed, and adding it to existing workplans. Scheduling then determines operation start/finish times. Master scheduling and Gantt charts are also referenced. Benefits of scheduling include reduced inventory and setups. MRP, Kanban, dispatching, progress reporting and expediting are additionally summarized.
Unit 4-IE6605 & PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL



Unit 4-IE6605 & PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROLMohanumar S The document discusses various production scheduling concepts and methods. It describes the functions of loading and scheduling, including determining operation times and sequencing work. Common scheduling tools are also explained, such as Gantt charts, which illustrate project schedules and task dependencies. Other scheduling methods covered include line of balance, linear scheduling, batch production scheduling, MRP, Kanban, and dispatching. Progress reporting and expediting are also summarized as important functions to ensure planned performance is achieved.
Unit 4



Unit 4Aravind Ra The document discusses various production scheduling concepts and methods. It describes the loading and scheduling process, which involves determining the work required, computing total time needed, and adding it to existing workplans. Scheduling then determines operation start/finish times. Master scheduling and Gantt charts are also referenced. Benefits of scheduling include reduced inventory and setups. MRP, Kanban, dispatching, progress reporting and expediting are additionally summarized.
Unit 4 PPC



Unit 4 PPCsivaprakash250 The document discusses various production scheduling concepts and methods. It describes the functions of loading and scheduling, including determining operation times and adding work to schedules. Common scheduling benefits are outlined as well as tools like Gantt charts, line of balance diagrams, and MRP. Batch production scheduling, linear scheduling, dispatching, progress reporting and manufacturing lead times are also summarized.
Mba ii pmom_unit-4.2 shop floor planning and control a



Mba ii pmom_unit-4.2 shop floor planning and control aRai University This document discusses shop floor planning and control activities including pre-production planning, common shop floor control activities, and specific techniques like input-output control, Gantt charts, finite and infinite loading, and forward and backward scheduling. It explains that production control departments monitor order progress through the shop by assigning priorities, dispatching lists, tracking work-in-progress, and controlling work flow between centers. Specific techniques like input-output reports, Gantt charts, finite loading based on capacity, and backward scheduling using lead times are discussed.
Types of loading, production & operations management



Types of loading, production & operations managementMahima Mutnuru Types of Loading-
Infinite Loading
Finite Loading
Also know about Scheduling as Loading is an vital part of Scheduling.
Explained with examples.
Important concept in Production and Operation Management.
Ad
More from Akanksha Gupta (6)
BUSINESS PLAN



BUSINESS PLANAkanksha Gupta This document presents a business plan for an event management company called Dreamzz Event Planner owned by two partners. Some key details:
- The company is located in New Delhi and offers services for marriages, birthdays, college events, and corporate parties.
- Services include venue booking, decoration, catering, entertainment, and coordinating other vendors.
- The partners have invested Rs. 300,000 and Rs. 500,000 respectively. They employ 22 workers across various roles.
- The plan estimates costs of assets, daily expenses, projected events and revenues for the first year. Competitor pricing is also compared.
Swot Analysis of indian economy



Swot Analysis of indian economyAkanksha Gupta The document provides a SWOT analysis of the Indian economy. It outlines that India has the 9th largest economy globally and underwent major economic reforms in the 1990s. The strengths of the Indian economy include its robust growth, strong agriculture sector, large workforce, and high savings rate. However, the economy also faces weaknesses such as overdependence on agriculture and monsoon, high poverty and illiteracy rates. There are opportunities to encourage sectors like agriculture, SMEs and infrastructure development. But threats include terrorism, corruption, inflation and the global economic downturn. The document concludes by noting India faces challenges from fiscal deficits, currency depreciation and inflation but hopes for economic improvements.
Mutual fund ppt



Mutual fund pptAkanksha Gupta This document summarizes a study on mutual funds in India with a focus on Reliance Mutual Fund. It discusses what mutual funds are, their advantages, types, investment strategies and the growth of the industry in India. It also provides an overview of Reliance Mutual Fund, including its profile, schemes, findings from the study and conclusions. The study found that many investors remain unaware of mutual funds and their benefits compared to other investment options. It suggests that advisors should focus on educating investors, especially younger ones, to increase awareness and uptake of mutual funds.
measurement and scaling techniques 



measurement and scaling techniques Akanksha Gupta This document discusses different types of measurement scales used in research. There are four main categories of measurement scales: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales. Nominal scales simply classify items into categories, while ordinal scales rank items along a continuum. Interval scales have equal distances between categories to allow comparisons, and ratio scales have a true zero point to enable calculations of ratios. The document provides examples of different types of variables that can be measured on each scale, such as qualitative vs. quantitative variables. It also discusses techniques for developing scales, such as rating and ranking scales.
Ppt management day



Ppt management dayAkanksha Gupta The document discusses the importance of being aware of the past to determine the best path forward. It emphasizes knowing history to make informed decisions about the future. The author signs off thanking the reader for their time.
Class4



Class4Akanksha Gupta This document provides an overview of business environments and factors that influence strategic planning. It discusses the external environment, including general factors like sociocultural, demographic, economic, technological, and political/legal influences. The internal environment and factors under a company's control are also examined. Porter's five competitive forces of rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants that shape industry competition are summarized. The document emphasizes that predicting environmental changes is difficult but contingency planning through scenario models can help companies adapt.
Recently uploaded (20)
Increasing Retail Store Efficiency How can Planograms Save Time and Money.pptx



Increasing Retail Store Efficiency How can Planograms Save Time and Money.pptxAnoop Ashok In today's fast-paced retail environment, efficiency is key. Every minute counts, and every penny matters. One tool that can significantly boost your store's efficiency is a well-executed planogram. These visual merchandising blueprints not only enhance store layouts but also save time and money in the process.
Transcript: #StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tec...



Transcript: #StandardsGoals for 2025: Standards & certification roundup - Tec...BookNet Canada Book industry standards are evolving rapidly. In the first part of this session, we’ll share an overview of key developments from 2024 and the early months of 2025. Then, BookNet’s resident standards expert, Tom Richardson, and CEO, Lauren Stewart, have a forward-looking conversation about what’s next.
Link to recording, presentation slides, and accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/standardsgoals-for-2025-standards-certification-roundup/
Presented by BookNet Canada on May 6, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...



Enhancing ICU Intelligence: How Our Functional Testing Enabled a Healthcare I...Impelsys Inc. Impelsys provided a robust testing solution, leveraging a risk-based and requirement-mapped approach to validate ICU Connect and CritiXpert. A well-defined test suite was developed to assess data communication, clinical data collection, transformation, and visualization across integrated devices.
Build Your Own Copilot & Agents For Devs



Build Your Own Copilot & Agents For DevsBrian McKeiver May 2nd, 2025 talk at StirTrek 2025 Conference.
Manifest Pre-Seed Update | A Humanoid OEM Deeptech In France



Manifest Pre-Seed Update | A Humanoid OEM Deeptech In Francechb3 The latest updates on Manifest's pre-seed stage progress.
How Can I use the AI Hype in my Business Context?



How Can I use the AI Hype in my Business Context?Daniel Lehner 𝙄𝙨 𝘼𝙄 𝙟𝙪𝙨𝙩 𝙝𝙮𝙥𝙚? 𝙊𝙧 𝙞𝙨 𝙞𝙩 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙜𝙖𝙢𝙚 𝙘𝙝𝙖𝙣𝙜𝙚𝙧 𝙮𝙤𝙪𝙧 𝙗𝙪𝙨𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙨𝙨 𝙣𝙚𝙚𝙙𝙨?
Everyone’s talking about AI but is anyone really using it to create real value?
Most companies want to leverage AI. Few know 𝗵𝗼𝘄.
✅ What exactly should you ask to find real AI opportunities?
✅ Which AI techniques actually fit your business?
✅ Is your data even ready for AI?
If you’re not sure, you’re not alone. This is a condensed version of the slides I presented at a Linkedin webinar for Tecnovy on 28.04.2025.
AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global Trends



AI and Data Privacy in 2025: Global TrendsInData Labs In this infographic, we explore how businesses can implement effective governance frameworks to address AI data privacy. Understanding it is crucial for developing effective strategies that ensure compliance, safeguard customer trust, and leverage AI responsibly. Equip yourself with insights that can drive informed decision-making and position your organization for success in the future of data privacy.
This infographic contains:
-AI and data privacy: Key findings
-Statistics on AI data privacy in the today’s world
-Tips on how to overcome data privacy challenges
-Benefits of AI data security investments.
Keep up-to-date on how AI is reshaping privacy standards and what this entails for both individuals and organizations.
Heap, Types of Heap, Insertion and Deletion



Heap, Types of Heap, Insertion and DeletionJaydeep Kale This pdf will explain what is heap, its type, insertion and deletion in heap and Heap sort
Quantum Computing Quick Research Guide by Arthur Morgan



Quantum Computing Quick Research Guide by Arthur MorganArthur Morgan This is a Quick Research Guide (QRG).
QRGs include the following:
- A brief, high-level overview of the QRG topic.
- A milestone timeline for the QRG topic.
- Links to various free online resource materials to provide a deeper dive into the QRG topic.
- Conclusion and a recommendation for at least two books available in the SJPL system on the QRG topic.
QRGs planned for the series:
- Artificial Intelligence QRG
- Quantum Computing QRG
- Big Data Analytics QRG
- Spacecraft Guidance, Navigation & Control QRG (coming 2026)
- UK Home Computing & The Birth of ARM QRG (coming 2027)
Any questions or comments?
- Please contact Arthur Morgan at [email protected].
100% human made.
Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdf



Complete Guide to Advanced Logistics Management Software in Riyadh.pdfSoftware Company Explore the benefits and features of advanced logistics management software for businesses in Riyadh. This guide delves into the latest technologies, from real-time tracking and route optimization to warehouse management and inventory control, helping businesses streamline their logistics operations and reduce costs. Learn how implementing the right software solution can enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and provide a competitive edge in the growing logistics sector of Riyadh.
AI EngineHost Review: Revolutionary USA Datacenter-Based Hosting with NVIDIA ...



AI EngineHost Review: Revolutionary USA Datacenter-Based Hosting with NVIDIA ...SOFTTECHHUB I started my online journey with several hosting services before stumbling upon Ai EngineHost. At first, the idea of paying one fee and getting lifetime access seemed too good to pass up. The platform is built on reliable US-based servers, ensuring your projects run at high speeds and remain safe. Let me take you step by step through its benefits and features as I explain why this hosting solution is a perfect fit for digital entrepreneurs.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in Business



Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in BusinessDr. Tathagat Varma My talk for the Indian School of Business (ISB) Emerging Leaders Program Cohort 9. In this talk, I discussed key issues around adoption of GenAI in business - benefits, opportunities and limitations. I also discussed how my research on Theory of Cognitive Chasms helps address some of these issues
2025-05-Q4-2024-Investor-Presentation.pptx



2025-05-Q4-2024-Investor-Presentation.pptxSamuele Fogagnolo Cloudflare Q4 Financial Results Presentation
Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD



Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure ADVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Cybersecurity Identity and Access Solutions using Azure AD
tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdf



tecnologias de las primeras civilizaciones.pdffjgm517 descaripcion detallada del avance de las tecnologias en mesopotamia, egipto, roma y grecia.
HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices and Managing Multiuser Environments



HCL Nomad Web – Best Practices and Managing Multiuser Environmentspanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/hcl-nomad-web-best-practices-and-managing-multiuser-environments/
HCL Nomad Web is heralded as the next generation of the HCL Notes client, offering numerous advantages such as eliminating the need for packaging, distribution, and installation. Nomad Web client upgrades will be installed “automatically” in the background. This significantly reduces the administrative footprint compared to traditional HCL Notes clients. However, troubleshooting issues in Nomad Web present unique challenges compared to the Notes client.
Join Christoph and Marc as they demonstrate how to simplify the troubleshooting process in HCL Nomad Web, ensuring a smoother and more efficient user experience.
In this webinar, we will explore effective strategies for diagnosing and resolving common problems in HCL Nomad Web, including
- Accessing the console
- Locating and interpreting log files
- Accessing the data folder within the browser’s cache (using OPFS)
- Understand the difference between single- and multi-user scenarios
- Utilizing Client Clocking
Role of Data Annotation Services in AI-Powered Manufacturing



Role of Data Annotation Services in AI-Powered ManufacturingAndrew Leo From predictive maintenance to robotic automation, AI is driving the future of manufacturing. But without high-quality annotated data, even the smartest models fall short.
Discover how data annotation services are powering accuracy, safety, and efficiency in AI-driven manufacturing systems.
Precision in data labeling = Precision on the production floor.
Splunk Security Update | Public Sector Summit Germany 2025



Splunk Security Update | Public Sector Summit Germany 2025Splunk Splunk Security Update
Sprecher: Marcel Tanuatmadja
Technology Trends in 2025: AI and Big Data Analytics



Technology Trends in 2025: AI and Big Data AnalyticsInData Labs At InData Labs, we have been keeping an ear to the ground, looking out for AI-enabled digital transformation trends coming our way in 2025. Our report will provide a look into the technology landscape of the future, including:
-Artificial Intelligence Market Overview
-Strategies for AI Adoption in 2025
-Anticipated drivers of AI adoption and transformative technologies
-Benefits of AI and Big data for your business
-Tips on how to prepare your business for innovation
-AI and data privacy: Strategies for securing data privacy in AI models, etc.
Download your free copy nowand implement the key findings to improve your business.
Scheduling and sequencing
- 1. SCHEDULING AND SEQUENCING -Presented by Akanksha Gupta
- 2. Scheduling • Scheduling: The allocation of resources over time to accomplish specific tasks. • Demand scheduling: A type of scheduling whereby customers are assigned to a definite time for order fulfillment. • Workforce scheduling: A type of scheduling that determines when employees work. • Operations scheduling: A type of scheduling in which jobs are assigned to workstations or employees are assigned to jobs for specified time periods.
- 3. Introduction Operations scheduling is critical to the success of an organization; however, it can be a very complicated task. Effective schedules are needed to meet promised customer delivery dates or inventory targets. It covers the following areas in particular: - assign job to a particular work center/ machine - time of assignment of job and completion - allocation of resources like manpower and materials - time sequence of operations - feedback and control function to take care of deviations
- 4. Work Centre • A work center is an area in a business in which productive resources are organized and work is completed • Can be a single machine, a group of machines, or an area where a particular type of work is done
- 5. Performance Measures From the manager’s perspective, identifying the performance measures to be used in selecting a schedule is important. If the overall goals of the organization are to be achieved, the schedules should reflect managerially acceptable performance measures. The following list describes the most common performance measures used in operations scheduling. Job Flow Time: The amount of shop time for the job is called job flow time. It is the sum of the moving time between operations, waiting time for machines or work orders, process time (including setups), and delays resulting from machine breakdowns, component unavailability, and the like.
- 6. Performance Measures Makespan: The total amount of time required to complete a group of jobs is called makespan. Past Due: The measure past due can be expressed as the amount of time by which a job missed its due date (also referred to as tardiness) or as the percentage of total jobs processed over some period of time that missed their due dates. Work-in-Process Inventory: Any job in a waiting line, moving from one operation to the next, being delayed for some reason, being processed, or residing in component or subassembly inventories is considered to be work-in-process inventory.
- 7. Performance Measures Total Inventory: The sum of scheduled receipts and on-hand inventories is the total inventory. Utilization: The percent of work time productively spent by a machine or worker is called utilization. These performance measures often are interrelated. An understanding of the interactions of job flow time, makespan, past due, WIP inventory, total inventory, and utilization can make scheduling easier.
- 9. Objectives of Operations Scheduling • Making efficient use of the labour. • Making best possible use of the equipments that are available for the use. • Increasing the profit. • Increasing the output. • Improving the service level.
- 10. Objectives of Operations Scheduling • Maximizing the delivery performance i.e. meeting the delivery dates. • Minimizing the inventory. • Reducing the manufacturing time. • Minimizing the production costs. • Minimizing the worker costs.
- 11. Functions of Operations Scheduling • Allocation of the resources. • Shop floor control. • Making maximum use of the plant at minimum possible cost. • Ensure that the needs of the manpower are optimum. • Determination of the sequence of the jobs.
- 12. Functions of Operations Scheduling • Specifying the start and the end time for each job (actively scheduled). • Getting quick feedback from the shops regarding the delays and the various interruptions. • Possess up – to – date information for the availability of the materials, expected delivery dates etc. • Possess up – to – date data on the machine regarding its breakdown, servicing etc.
- 13. Types of Scheduling Types of Operations Scheduling are as follows: 1. Forward operations scheduling – • Classified on the basis of the time. • All the activities are scheduled from the date of the planned order release. • First task of the job is scheduled. • Its subsequent task is scheduled on the scheduled completion of the first task. • Like this, accordingly all the tasks of the job are scheduled.
- 14. Types of Scheduling 2. Backward operations scheduling – • Also classified on the basis of the time. • Activities are scheduled from the date or the planned receipt date. • The last activity is scheduled first. • Time of the start of the last task is considered as the time for the start of the previous activity.
- 15. Shop Floor Control (SFC) Schedule and monitor day-to-day job shop production • Also called production control and production activity control (PAC) • Performed by production control department • Loading - check availability of material, machines, and labor • Sequencing - release work orders to shop and issue dispatch lists for individual machines • Monitoring - maintain progress reports on each job until it is complete
- 16. Loading Process of assigning work to limited resources • Perform work with most efficient resources • Use assignment method of linear programming to determine allocation
- 17. Sequencing • Prioritize jobs assigned to a resource • If no order specified use first-come first-served (FCFS) • Other Sequencing Rules • FCFS - first-come, first-served • LCFS - last come, first served • DDATE - earliest due date • CUSTPR - highest customer priority • SETUP - similar required setups • SLACK - smallest slack • CR - smallest critical ratio • SPT - shortest processing time • LPT - longest processing time
- 18. Sequencing Jobs • Operations schedules are short-term plans designed to implement the sales and operations plan • An operation with divergent flows is often called a job shop – Low-to medium-volume production – Utilizes job or batch processes – The front office would be the equivalent for a service provider – Difficult to schedule because of the variability in job routings and the continual introduction of new jobs to be processed
- 19. Sequencing Jobs • An operation with line flow is often called a flow shop – Medium- to high-volume production – Utilizes line or continuous flow processes – The back office would be the equivalent for a service provider – Tasks are easier to schedule because the jobs have a common flow pattern through the system
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. ShippingDepartment RawMaterials Legend: Batch of parts Workstation Job Shop Sequencing Figure J.1 – Diagram of a Manufacturing Job Shop Process
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. • First-come, first-served (FCFS) • Earliest due date (EDD) • Critical ratio (CR) Priority Sequencing Rules A ratio less than 1.0 implies that the job is behind schedule A ratio greater than 1.0 implies the job is ahead of schedule The job with the lowest CR is scheduled next CR = (Due date) – (Today’s date) Total shop time remaining
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. • Shortest processing time (SPT) • Slack per remaining operations (S/RO) Priority Sequencing Rules The job with the lowest S/RO is scheduled next S/RO = Due date Today’s date Total shop time remaining– – Number of operations remaining
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. • Single-dimension rules • A job’s priority assignment based only on information waiting for processing at the individual workstation (e.g., FCFS, EDD, and SPT) Sequencing One Workstation
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Multiple-Dimension Rules • The priority rules CR and S/RO incorporate information about the remaining workstations S/RO is better than EDD with respect to the percentage of jobs past due but usually worse than SPT and EDD with respect to average job flow times CR results in longer job flow times than SPT, but CR also results in less variance in the distribution of past due hours No choice is clearly best; each rule should be tested in the environment for which it is intended
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. • Identifying the best priority rule to use at a particular operation in a process is a complex problem because the output from one operation becomes the input to another • Computer simulation models are effective tools to determine which priority rules work best in a given situation Multiple Workstations
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. • In single-workstation scheduling, the makespan is the same regardless of the priority rule chosen • In the scheduling of two or more workstations in a flow shop, the makespan varies according to the sequence chosen • Determining a production sequence for a group of jobs to minimize the makespan has two advantages – The group of jobs is completed in minimum time – The utilization of the two-station flow shop is maximized Scheduling a Two-Station Flow Shop
- 27. Scheduling Jobs for Multiple Workstations • Priority sequencing rules can be used to schedule more than one operation. Each operation is treated independently. • Identifying the best priority rule to use at a particular operation in a process is a complex problem because the output from one process becomes the input for another. • Computer simulation models are effective tools to determine which priority rules work best in a given situation. • When a workstation becomes idle, the priority rule is applied to the jobs waiting for that operation, and the job with the highest priority is selected. • When that operation is finished, the job is moved to the next operation in its routing, where it waits until it again has the highest priority.
- 28. Scheduling Problems • One machine, many jobs • Two machines, many jobs • Three machines, many jobs • Many machines, many jobs
- 29. One machine, many jobs • Total time is independent of sequence • SPT minimizes average flow time • Examples- Mumbai airport
- 30. Two machines, many jobs • All Jobs follow same sequence – Johnson’s Rule • Jobs have different sequence – Jackson’s Rule • Johnson’s 3 machine rule
- 31. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Johnson’s Rule • Minimizes makespan when scheduling a group of jobs on two workstations Step 1: Scan the processing time at each workstation and find the shortest processing time among the jobs not yet scheduled. If two or more jobs are tied, choose one job arbitrarily. Step 2: If the shortest processing time is on workstation 1, schedule the corresponding job as early as possible. If the shortest processing time is on workstation 2, schedule the corresponding job as late as possible. Step 3: Eliminate the last job scheduled from further consideration. Repeat steps 1 and 2 until all jobs have been scheduled.
- 32. Gantt Progress ChartGantt Progress Chart Plymouth Ford Pontiac Job 4/20 4/22 4/23 4/24 4/25 4/264/214/17 4/18 4/19 CurrentCurrent datedate Scheduled activity time Actual progress Start activity Finish activity Nonproductive time Gantt Progress Chart for an Auto Parts Company
- 33. Gantt Workstation ChartGantt Workstation Chart Gantt Workstation Chart for Hospital Operating Rooms
- 34. Thank You


