SE Software Requirements Engineering .pptx
- 1. 1 BSc (Hons) in Software Engineering SE1201- Software Requirement Engineering Lecture 03 Use Case Diagrams
- 2. 2 Developing Use-Case Models of Systems A use case is a typical sequence of actions that a user performs in order to complete a given task The objective of use case analysis is to model the system … from the point of view of how users interact with this system … when trying to achieve their objectives. A use case model consists of a set of use cases an optional description or diagram indicating how they are related
- 3. 3 Use Case…. In general, a use case should cover the full sequence of steps from the beginning of a task until the end. A use case should describe the user’s interaction with the system ... not the computations the system performs. A use case should be written so as to be as independent as possible from any particular user interface design. A use case should only include actions in which the actor interacts with the computer.
- 4. 4 Use Case Diagrams Use case diagrams are used to visualize, specify, construct, and document the (intended) behavior of the system, during requirements capture and analysis. Provide a way for developers, domain experts and end-users to Communicate. Serve as basis for testing. Use case diagrams contain use cases, actors, and their relationships.
- 5. 5 Sample Use case diagram Salesperson Customer Place order Check status ACTOR USE CASE SYSTEM BOUNDARY
- 6. 6 Actor An actor is a user of the system playing a particular role. Actors are entities which require help from the system to perform their task or are needed to execute the system’s functions. Actors are not part of the system Actor is shown with a stick figure Actors can be human or automated systems student Employee Customer
- 7. 7 Use Cases Use cases specify desired behavior (Use case is a particular activity a user can do on the system) A use case is a description of a set of sequences of actions, including variants, a system performs to yield an observable result of value to an actor. Each sequence represent an interaction of actors with the system. Use case is represented by an ellipse. Following are two use cases for a University system. Updating Results Enroll
- 8. 8 Use cases… • A use case represents a class of functionality provided by the system • Use cases can be described textually, with a focus on the event flow between actor and system • The textual use case description consists of 6 parts: 1. Unique name 2. Participating actors 3. Entry conditions 4. Exit conditions 5. Flow of events 6. Special requirements. PurchaseTicket
- 9. 9 Textual Use Case Description Example 1. Name: Purchase ticket 2. Participating actor: Passenger 3. Entry condition: Passenger stands in front of ticket distributor Passenger has sufficient money to purchase ticket 4. Exit condition: Passenger has ticket 5. Flow of events: 1. Passenger selects the number of zones to be traveled 2. Ticket Distributor displays the amount due 3. Passenger inserts money, at least the amount due 4. Ticket Distributor returns change 5. Ticket Distributor issues ticket 6. Special requirements: None. Passenger PurchaseTicket
- 10. 10 Use case diagrams Register in Course Add Course Add Course Offering Student Find information about course Professor Actor Registrar Actor Enter Grade for Course
- 11. 11 Guidelines for Drawing Use Case Diagrams Identify the actors and the use cases Prioritize the use cases Develop each use case, starting with the priority ones, writing a description for each Add structure to the use case model: generalization, include and extend relationships and sub-systems
- 12. 12 How to describe a single use case A. Name: Give a short, descriptive name to the use case. B. Actors: List the actors who can perform this use case. C. Goals: Explain what the actor or actors are trying to achieve. D. Preconditions: State of the system before the use case. E. Description: Give a short informal description. F. Related use cases. G. Steps: Describe each step using a 2-column format. H. Postconditions: State of the system.
- 13. 13 Scenarios A scenario is an instance of a use case It expresses a specific occurrence of the use case a specific actor ... at a specific time ... with specific data.
- 14. 14 Scenarios What is a scenario? It is a single logical path in a use case A use case may have one or more scenarios Test cases are developed based on all scenarios in a use case Each scenario has a single point (why?) From every decision point a scenario branch into two or more new paths Good source to write “User Guide” Hint: the complexity of a use case
- 15. 15 How to identify scenarios? Analyze the given textual description Classify events flow into main and exceptional Present and discuss with users Avoid Redundant Scenarios
- 16. 16
- 17. 17 System Boundary System boundary indicates the scope of the system. Anything within the box represents functionality that is in scope and anything outside the box is not
- 18. 18 Use cases and Actors From the perspective of a given actor, a use case does something that is of value to the actor, such as calculate a result or change the state of an object. The Actors define the environments in which the system lives
- 19. 19 Relationships between use cases Generalization - use cases that are specialized versions of other use cases. Include - use cases that are included as parts of other use cases. Enable to factor common behavior. Extend - use cases that extend the behavior of other core use cases. Enable to factor variants.
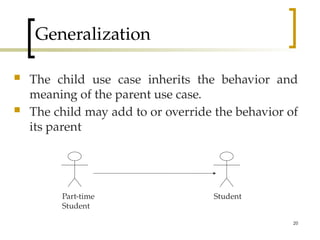
- 20. 20 Generalization The child use case inherits the behavior and meaning of the parent use case. The child may add to or override the behavior of its parent Part-time Student Student
- 21. 21 Include The base use case explicitly incorporates the behavior of another use case at a location specified in the base. The included use case never stands alone. It only occurs as a part of some larger base that includes it. Pay Student Fees Enroll in course Arrange Hostel <<include>> <<include>>
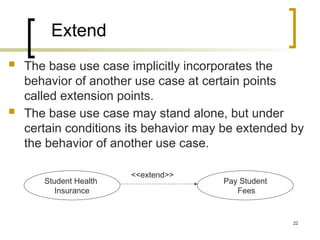
- 22. 22 Extend The base use case implicitly incorporates the behavior of another use case at certain points called extension points. The base use case may stand alone, but under certain conditions its behavior may be extended by the behavior of another use case. Student Health Insurance Pay Student Fees <<extend>>
- 23. 23 Use case relationships Relationship Symbol Meaning Communicates An actor is connected to a use case using a line with no arrowheads Includes A use case contains a behavior that is common to more than one other use case. The arrow points to the common use case Extends A different use case handles exceptions form the basic use case. The arrow points from the extended to the basic use case. Generalizes One UML “thing” is more than another “thing”. The arrow points to the general thing <<include>> <<extend>>