Software Engineering unit 2
- 1. SOFTWARE ENGINEERING UNIT-II ABHIMANYU MISHRA ASSISTANT PROF.(CSE) JETGI 12/31/2016 1Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI
- 2. Requirement Engineering Processes. Feasibility Study. DFD & ER Diagrams. Decision Tables. SRS Document. IEEE Standard For SRS. SQA:Verification & Validation. SQA Plans & Attributes. ISO 9000 Models,SEI-CMM Model. CONTENTS: 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 2
- 3. “Requirement elicitation is the activity during which software requirement are discovered, expressed, and revealed from system requirements”. Its sources may be system requirement documentation, customer or market analysis. Various technologies are used to involved the user on the basis of level of involvement required. The range of variation can be classified in three main styles: a) Consultative Design. b) Representative Design. c) Consensus Design. Software requirement specification: 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 3
- 4. Requirement Gathering SRS Requirement Engineering Requirement Analysis Requirement Document Requiremen t Review Problem Solving Fig-Software Elicitation 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 4
- 5. Requirement Gathering-In this phase requirement are going to identified. Requirement Analysis- Analysis of requirement are done in order to identify in consistency, defect or missing requirement. Requirement Process-Review process is followed for correct out or improved the quality of SRS. CLASSIFICATION OF COMPONENT; 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 5
- 6. This is a process in which people from client &contractor organization both involved for checking the requirements for omission. Different parts of document are checked by different people involved in this type of activities. Various activities performed during user needs review process are: Plan a review Review meeting Follow-up actions Checking for redundancy Completeness Consistency Review & Management of User needs: 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 6
- 7. “Management of user needs is not a simple task it depends upon various issues of different organization”. This can be done in following steps: Collecting organization history-The performance of organization, future plan, organization goal. Current problem understanding-There must be clear understanding of the currently known issues and what are the expectations of management. Know your user profile-It is important to know user who operate the system. Most organization charts do not give information pertaining the user. The profile of each of these user group is vastly different as far as capability and exposure of technology concerned. Management Needs: 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 7
- 8. When we are developing a system we know weather proposed system will be feasible or not i.e. practically implementable or not? It may be possible that the proposed system may not be implementable due to many reasons like it may take long time in development than the specified time limit, cost may increase than proposed. There may be several types of feasibility depending on the aspects they covers. Some of them are: • Technical Feasibility • Operation Feasibility • Economical Feasibility 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 8
- 9. Phases of Feasibility: Technical feasibility-The technical feasibility study basically centers on alternatives for hardware, software and design approach to determine the functional aspects of system. The technical issues raised during feasibility are: a) Does the necessary technology exist. b) Does the proposed equipment have technical capacity to hold data. c) Can the system be expended, if developed? d) Are there technical guarantee of accuracy, reliability and security of data Operational feasibility-Operational feasibility is a measure of how people are able to work with system. This type of feasibility demands if the system will work when developed and installed. 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 9
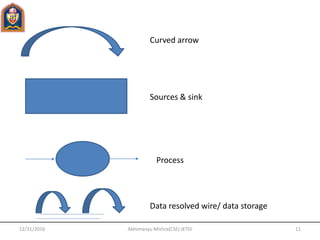
- 10. Data Flow Diagram: A DFD is also known as “bubble sort” has the purpose of clarifying system requirements and identifying major transformation. It shows the flow of data through a system. It is a graphical tool because it present a picture. It present a system or software at any level of abstraction. Four simple notation are used to complete a DFD- i. Data Flow-The data flow is used to describe the movement of information from a part of system to another part. ii. Process-A circle or bubble represents a process that transform incoming data to outgoing data. iii. External Entity- A square defines a source or destination of system data. External entities represents any entity that supplies information from the system. iv. Data Store- The data store is used to collect data at rest or a temporary repository of data. 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 10
- 11. Curved arrow Sources & sink Process Data resolved wire/ data storage 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 11
- 12. Entity Relationship Diagram: The entity relationship data model is based on a perception of a real word that consist of a basic objects, called entity, and of relationships among these objects. An entity is a object or thing in the real world that is distinguishable from other objects. An entity have a set of attributes. A relationship is an association among several entities. ER diagram consist of following major component- i. Rectangle-which represent entity sets. ii. Ellipse-which represent attributes. iii. Diamond-which represent relationship sets. iv. Lines-which link attributes to entity set and to relationship sets. 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 12
- 13. Rectangle Ellipses Diamond Lines Fig- E-R Representation12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 13
- 14. Advantages of E-R Model- It is easy and simple to understand with minimal training. Therefore the model can be used by the db designer to communicate design to end user. It has explicitly linkages between entities. In the ER model it is possible to find a connection from one node to all the other nodes. Disadvantages of E-R Model- Limited constraint representation. Limited relationship representation. No representation of data. Loss of information. 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 14
- 15. Decision Table: A major drawback to decision tree is the lack of information in its format to tell us what other combination of conditions of test. To overcome from this drawback decision table is used. A decision table is a table of contingencies for defining a problem and the action to be taken. It is a single representation of the relationships between conditions and action. A Decision table consist two parts:- i. Stub- The stub part is divided into “upper quadrant” and “lower quadrant” called condition and action stub. ii. Entry- The entry part are also divided into “upper quadrant” and “lower quadrant”. 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 15
- 16. Post paid condition Rules Prepaid Full talk time Pay before service Pay after service Reduction of service T F T F T F T F F Fig- Decision table 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 16
- 17. IEEE Standards of SRS: The SRS development is a collaborative effort for designing a software project which is further converted into SRS document. Several organizations have a proposed their basic structure and the components for SRS. IEEE has given basic structure for software development. Sample of a basic SRS outline: i. Introduction- purpose Document convention Intended audiences References Additional information 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 17
- 18. Overall description- Product perspective Product function User environment Design Assumptions & depended External interface requirement- User interface Hardware interface Software interface Communication protocols and interfaces System features- Description and priority Action/result Functional requirements 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 18
- 19. Software Quality Assurance: Software Quality assurance plan is a standard activity which ensure the quality goals of the organization. It gives details and template on all activities, which have become part of the standard implementation. The SQA plan include the following: • Project planning • Models of data, classes and object, processes, design architecture • SRS • Test plans for testing SRS • User manuals online help etc. • Audit & Review In SQA plan 3 kinds of activities performed: • Organization specific • Software specific • Customer Specific 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 19
- 20. Software verification refers to a set of activities that ensure that software correctly implements a specific function i.e. “Are we building the product right”. Software validation is concerned with showing that the requirements actually define the system that the customer wants. It refers to a set of activities that ensure that the software that is going to be build is traceable to customer requirements. “Are we building the right product”. Traditionally software verification & validation is define as system engineering methodology to ensure that quality is built into software during development. The analysis and test activities are performed by V & V evaluates and assess the software product. Verification & Validation: 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 20
- 21. ISO Certificate 9000 ISO 9000 certification serves as reference for contact between independent parties. The ISO 9000 standard specifies the guidelines for maintaining for a quality system. The ISO standard mainly addresses operational aspects and organizational aspects . Such as responsibility, reporting, etc. It is important to realize that ISO 9000 standard is a set of guideline for the production process and is not directly concerned with product itself. ISO 9000 is a series of three standards: ISO 9001, ISO 9002 and ISO 9003. The different types of software industries to which the different ISO standard apply are as: i. ISO 9001-This standard applies to the organization engaged in design, development and servicing of goods. ii. ISO 9002- This organization applies to those which do not design product but are only involved in production. iii. ISO 9003- This standard applies to organizations involved only in installation and testing of the product. 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 21
- 22. Capability Maturity Model: The capability maturity model is not a software life cycle model. Instead it is a strategy for improving the software process, irrespective of actual life cycle model used. The CMM has been developed by Software engineering institute(SEI) at Carnegie Mellon university in 1987. There are five level of maturity: i. Initial ii. Repeatable iii. Define iv. Manage v. Optimizing 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 22
- 23. Classification of levels of maturity: i. Initial- At the level 1 the process followed by the organizations are not well defined. They are immature. As aresult of stable environment is not available for software development. ii. Repeatable- The level 2 focuses on establishing basic project management policies. iii. Design- At this level standard process to be used across the organization are defined and documented. iv. Manage- At this level of CMM quantitative quality goals are set for the organization for the software product as well as software processes. v. Optimizing- Establishing strategies and plan for quantitative understanding of software project. 12/31/2016 Abhimanyu Mishra(CSE) JETGI 23