SOLID - Principles of Object Oriented Design
- 1. SOLID PRINCIPLES INGEGNERIA DEL SOFTWARE Università degli Studi di Padova Dipartimento di Matematica Corso di Laurea in Informatica, A.A. 2015 – 2016 [email protected]
- 2. Ingegneria del software mod. B SUMMARY Introduction Single Responsibility Principle Open Closed Principle Liskov Substitution Principle Interface Segregation Principle Dependency Inversion Principle 2Riccardo Cardin
- 3. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTRODUCTION Structured programming and Object-oriented programming Two of the most important revolution of IT industry Everyone uses OO languages, but... Today's programmers are unaware of the principles that are the foundation of Object Orientation Dependency management The art of making code flexible, robust, and reusable It’s too easy to get a bunch of tangled legacy code SOLID principles A set of class design principles that helps to manage dependency 3Riccardo Cardin
- 4. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTRODUCTION SOLID principles Single Responsibility Principle A class should have one, and only one, reason to change Open Closed Principle You should be able to extend a classes behavior, without modifying it Liskov Substitution Principle Derived classes must be substitutable for their base classes Interface Segregation Principle Make fine grained interfaces that are client specific Dependency Inversion Principle Depend on abstractions, not on concretions 4Riccardo Cardin
- 5. Ingegneria del software mod. B SINGLE RESPONSIBILITY PRINCIPLE Also known as cohesion Functional relatedness of the elements of a module A module should have only one reason to change We call this reason of change responsibility Coupled responsibilities Changes to one responsibility may impair or inhibit the class’ ability to meet the others Fragile design that break in unexpected ways Recompilation, test, deploy, … 5Riccardo Cardin
- 6. Ingegneria del software mod. B SINGLE RESPONSIBILITY PRINCIPLE 6Riccardo Cardin Uses Rectangle to help it with the mathematics of geometric shapes. It never draws the rectangle on the screen It definitely draws the rectangle on the screen. The Rectangle class has two responsibilities. • Provides a mathematical model • Renders the rectangle on a GUI
- 7. Ingegneria del software mod. B SINGLE RESPONSIBILITY PRINCIPLE 7Riccardo Cardin Responsibilities are separeted into two completely different classes Renders the rectangle on a GUI Provides a mathematical model
- 8. Ingegneria del software mod. B SINGLE RESPONSIBILITY PRINCIPLE What is really a responsibility? An axis of change is only an axis of change if the changes actually occur The context of the application is also important Needless complexity Should these two responsibilities be separated? That depends upon how the application is changing. 8Riccardo Cardin public interface Modem { public void dial(String pno); public void hangup(); public void send(char c); public char recv(); } Connection management Data communication
- 9. Ingegneria del software mod. B SINGLE RESPONSIBILITY PRINCIPLE Eventually separate responsibilities avoids rigidity They are still coupled in ModemImplementation, but clients don’t need to worry about interface implementations 9Riccardo Cardin
- 10. Ingegneria del software mod. B SINGLE RESPONSIBILITY PRINCIPLE 10Riccardo Cardin
- 11. Ingegneria del software mod. B OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE There are many heuristics in OOD Software entities should be open for extension, but closed for modification You extend behaviour adding new code, not changing the old The Open-Close Principle underlines these heuristics Abstraction is the key Abstract types are the fixed part, derivate classes points of extension 11Riccardo Cardin “All member variables should be private”, “Global variables should be avoided”, “Using run time type identification (RTTI) is dangerous”
- 12. Ingegneria del software mod. B OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE 12Riccardo Cardin Client class must be changed to name the new server class. If we want Client objects to use a different server class, then a new derivative of the AbstractServer class can be created. The Client class can remain unchanged. O C P
- 13. Ingegneria del software mod. B OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE 13Riccardo Cardin public static void drawAll(Shape[] shapes) { for (Shape shape : shapes) { switch (shape.shapeType) { case Square: ((Square) shape).drawSquare(); break; case Circle: ((Circle) shape).drawCircle(); break; } } } Does not conform to the open- closed principle because it cannot be closed against new kinds of shapes. If I wanted to extend this function, I would have to modify the function
- 14. Ingegneria del software mod. B OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE Programs conforming to OCP do not experience «cascade of changes» Changes are obtained adding new code 14Riccardo Cardin public static void drawAll(Shape[] shapes) { for (Shape shape : shapes) { shape.draw(); } } Solution that conforms to open- close principle. To extend the behavior of the drawAll to draw a new kind of shape, all we need do is add a new derivative of the Shape class.
- 15. Ingegneria del software mod. B OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE No program can be 100% closed Closure must be strategic Closure can be gained through abstraction Using interfaces and polimorphim The draw abstract method in the Shape class ...or can be gained in a «data-driven» fashion Sometimes using information configured in external structure can be the only solution What if we want to draw shapes in a specific order that depends from type!? 15Riccardo Cardin
- 16. Ingegneria del software mod. B OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE 16Riccardo Cardin
- 17. Ingegneria del software mod. B OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE Conventions and heuristics derived from OCP Make all member variables private When the member variables of a class change, every function that depends upon them must be changed Encapsulation No global variables (ever) No module that depends upon a global variable can be closed against any other module that might write to that variable There are very few cases that can disobey (i.e. cin, cout) RTTI is dangerous The Shape example shows the bad way to use RTTI But there are also good cases… 17Riccardo Cardin
- 18. Ingegneria del software mod. B LISKOV SUBSTITUTION PRINCIPLE Abstraction and polymorphism At the basis of OOD and OCP What are the characteristics of the best inheritance hierarchies? What are the traps? Liskov Substitution Principle It a special case of the real LSP ;) Violating this principle means violating OCP Function that uses a pointer or reference to a base class, but must know about all the derivatives of that base class. 18Riccardo Cardin Functions that use pointers or references to base classes must be able to use objects of derived classes without knowing it.
- 19. Ingegneria del software mod. B LISKOV SUBSTITUTION PRINCIPLE 19Riccardo Cardin A Square does not need both height and width member variables. Yet it will inherit them anyway. Clearly this is wasteful. Square will inherit the setWidth and setHeight functions. These functions are utterly inappropriate for a Square. But, we could override them... public void setWidth(double width) { super.setWidth(width); super.setHeight(width); } public void setHeight(double height) { this.setWidth(height); }
- 20. Ingegneria del software mod. B LISKOV SUBSTITUTION PRINCIPLE A model, viewed in isolation, can not be meaningfully validated The validity of a model can only be expressed in terms of its clients 20Riccardo Cardin public void f(Rectangle r) { r.setWidth(32); } @Test public void testF() { Rectangle r = new Square(); r.setHeight(15); f(r); // This test will not pass!!! assertEquals(32, r.getWidth); } If we pass a reference to a Square object into this function, and the height will be changed too. This is a clear violation of LSP. The f function does not work for derivatives of its arguments.
- 21. Ingegneria del software mod. B LISKOV SUBSTITUTION PRINCIPLE 21Riccardo Cardin
- 22. Ingegneria del software mod. B LISKOV SUBSTITUTION PRINCIPLE What went wrong? What counts is extrinsic public behavior Behavior that clients depend upon The relation between Square and Rectangle is not a IS-A relation in OOD Design by contract Methods of classes declare preconditions and postconditions (invariants) 22Riccardo Cardin ...when redefining a routine [in a derivative], you may only replace its precondition by a weaker one, and its postcondition by a stronger one. // Rectangle.setWidth(double w) postconditions assert((width == w) && (height == old.height));
- 23. Ingegneria del software mod. B LISKOV SUBSTITUTION PRINCIPLE Design by contract In a derivate class preconditions must not be stronger than in the base class Using base class interface a client knows only base class preconditions In a derivate class postconditions must be stronger than in the base class Derived class must conform to all base class prostcondition. The behaviors and outputs must not violate any of the constraints established for the base class Java and JVM base languages have assert primitive. C++ does not have anything such this 23Riccardo Cardin
- 24. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTERFACE SEGREGATION PRINCIPLE Reducing coupling means to depend upon interfaces, not implementations The risk is to depend upon a «fat» or «polluted» interfaces Fat interfaces are not cohesive Methods can be broken up into groups of functions Clients must view only the part they are interested to Interface Segregation Principle 24Riccardo Cardin Clients should not be forced to depend upon interfaces that they do not use
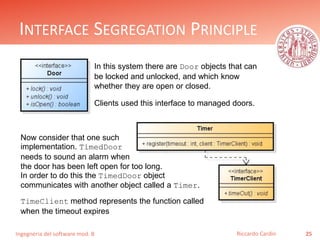
- 25. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTERFACE SEGREGATION PRINCIPLE 25Riccardo Cardin In this system there are Door objects that can be locked and unlocked, and which know whether they are open or closed. Clients used this interface to managed doors. Now consider that one such implementation. TimedDoor needs to sound an alarm when the door has been left open for too long. In order to do this the TimedDoor object communicates with another object called a Timer. TimeClient method represents the function called when the timeout expires
- 26. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTERFACE SEGREGATION PRINCIPLE First solution 26Riccardo Cardin The Door class now depends upon TimerClient. Not all varieties of Door need timing. Moreover, the applications that use those derivatives will have to import the definition of the TimerClient class, even though it is not used. The interface of Door has been polluted with an interface that it does not require. Each time a new interface is added to the base class, that interface must be implemented in derived classes. Default implementations violate the Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)
- 27. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTERFACE SEGREGATION PRINCIPLE 27Riccardo Cardin
- 28. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTERFACE SEGREGATION PRINCIPLE Clients of Door and TimerClient are different The interfaces should remain separate too Sometimes it is the client that forces a change to an interface Also the Door interface have to be changed Clients that does not need timer doors will also be affected The result is a inadvertent coupling between all the clients 28Riccardo Cardin public class Timer { void register(int timeout, int timeOutId, TimerClient client); } public interface TimerClient { // A change to Timer implies a change to TimerClient void timeOut(int timeOudId); }
- 29. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTERFACE SEGREGATION PRINCIPLE Separation by delegation Object form of the Adapter design pattern DoorTimerAdapter translates a Door into a TimerClient Clients of Door and TimerClient are not coupled anymore 29Riccardo Cardin
- 30. Ingegneria del software mod. B INTERFACE SEGREGATION PRINCIPLE Separation through multiple inheritance Class form of the Adapter design pattern Client can use the same object through different and separate interfaces Possible only when multiple inheritance is supported Less types used wrt the solution that uses delegation 30Riccardo Cardin
- 31. Ingegneria del software mod. B DEPENDENCY INVERSION PRINCIPLE Bad design often derives from degradation due to new requirement and maintanance Rigidity – hard to change because every change affects to many part of the system Fragility – when you make a change, unexpected parts of the system break Immobility – It is hard to reuse in another application because it cannot be easily disentangled TNTWIWHDI – That’s not the way I would have done it Interdependence of the modules 31Riccardo Cardin
- 32. Ingegneria del software mod. B DEPENDENCY INVERSION PRINCIPLE 32Riccardo Cardin Consider a simple program that is charged with the task of copying characters typed on a keyboard to a printer. “Read keyboard” and “Write printer” are quite reusable. However the “Copy” module is not reusable in any context that does not involve keyboard and printer public void copy(OutputDevice dev) { int c; while ((c = readKeyboard()) != EOF) if (dev == PRINTER) writePrinter(c); else writeDisk(c); } Violates OCP
- 33. Ingegneria del software mod. B DEPENDENCY INVERSION PRINCIPLE Module containing high level policy should be independent upon low level details modules We have use abstraction to limit dependency 33Riccardo Cardin We have performed dependency inversion. the dependencies have been inverted; the “Copy” class depends upon abstractions, and the detailed readers and writers depend upon the same abstractions. Now we can reuse the “Copy” class, independently of the “Keyboard Reader” and the “Printer Writer”.
- 34. Ingegneria del software mod. B DEPENDENCY INVERSION PRINCIPLE Dependency Inversion Principle Important policy decisions are in high level modules It’s these modules we want to be able to reuse Template method design pattern In layered application, each layer should expose a proper level of abstraction (interface) A naive implementation can force wrong dependency among modules 34Riccardo Cardin High level modules should not depend upon low level modules. Both should depend upon abstractions. Abstractions should not depend upon details. Details should depend upon abstractions.
- 35. Ingegneria del software mod. B DEPENDENCY INVERSION PRINCIPLE 35Riccardo Cardin The high level policy class uses a lower level Mechanism; which in turn uses a detailed level utility class. The Policy Layer is sensitive to changes all the way down in the Utility Layer. Each of the lower level layers are represented by an abstract class. Each of the higher level classes uses the next lowest layer through the abstract interface. Thus, none of the layers depends upon any of the other layers.
- 36. Ingegneria del software mod. B DEPENDENCY INVERSION PRINCIPLE 36Riccardo Cardin
- 37. Ingegneria del software mod. B REFERENCES The Principles of OOD http://butunclebob.com/ArticleS.UncleBob.PrinciplesOfOod Chap. 8 “The Single-Responsibility Principle (SRP)”, Agile Principles, Patterns, and Practices in C#, Robert C. Martin, 2006, Prentice Hall Chap. 9 “The Open/Closed Principle (OCP)”, Agile Principles, Patterns, and Practices in C#, Robert C. Martin, 2006, Prentice Hall Chap. 10 “The Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)”, Agile Principles, Patterns, and Practices in C#, Robert C. Martin, 2006, Prentice Hall Chap. 11 “The Dependency-Inversion Principle (DIP)”, Agile Principles, Patterns, and Practices in C#, Robert C. Martin, 2006, Prentice Hall Chap. 12 “The Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)”, Agile Principles, Patterns, and Practices in C#, Robert C. Martin, 2006, Prentice Hall 37Riccardo Cardin













![Ingegneria del software mod. B
OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE
13Riccardo Cardin
public static void drawAll(Shape[] shapes) {
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
switch (shape.shapeType) {
case Square:
((Square) shape).drawSquare();
break;
case Circle:
((Circle) shape).drawCircle();
break;
}
}
}
Does not conform to the open-
closed principle because it
cannot be closed against new
kinds of shapes. If I wanted to
extend this function, I would
have to modify the function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidprinciplesofobject-orienteddesign-160405054559/85/SOLID-Principles-of-Object-Oriented-Design-13-320.jpg)
![Ingegneria del software mod. B
OPEN-CLOSE PRINCIPLE
Programs conforming to OCP do not experience
«cascade of changes»
Changes are obtained adding new code
14Riccardo Cardin
public static void drawAll(Shape[] shapes) {
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
shape.draw();
}
}
Solution that conforms to open-
close principle. To extend the
behavior of the drawAll to draw
a new kind of shape, all we need
do is add a new derivative of the
Shape class.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidprinciplesofobject-orienteddesign-160405054559/85/SOLID-Principles-of-Object-Oriented-Design-14-320.jpg)







![Ingegneria del software mod. B
LISKOV SUBSTITUTION PRINCIPLE
What went wrong?
What counts is extrinsic public behavior
Behavior that clients depend upon
The relation between Square and Rectangle is not a IS-A
relation in OOD
Design by contract
Methods of classes declare preconditions and
postconditions (invariants)
22Riccardo Cardin
...when redefining a routine [in a derivative], you may only replace its
precondition by a weaker one, and its postcondition by a stronger one.
// Rectangle.setWidth(double w) postconditions
assert((width == w) && (height == old.height));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solidprinciplesofobject-orienteddesign-160405054559/85/SOLID-Principles-of-Object-Oriented-Design-22-320.jpg)