SQL For PHP Programmers
- 1. Tutorial Day: Nov 11th, 9:00a - 12:30p Dave Stokes MySQL Community Manager [email protected] @Stoker SSQQLL FFoorr PPHHPP PPrrooggrraammmmeerrss
- 2. 2 SSaaffee HHaarrbboorr SSttaatteemmeenntt The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decision. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle.
- 3. 3 The Problem wwiitthh PPHHPP PPrrooggrraammmmeerrss Your are up to date on the latest version of PHP
- 4. 4 The Problem wwiitthh PPHHPP PPrrooggrraammmmeerrss Your are up to date on the latest version of PHP The latest version of Javascript – no problemo!
- 5. 5 The Problem wwiitthh PPHHPP PPrrooggrraammmmeerrss Your are up to date on the latest version of PHP The latest version of Javascript – no problemo! Frameworks – you know two or three or more – plus the ones you wrote yourself
- 6. 6 The Problem wwiitthh PPHHPP PPrrooggrraammmmeerrss Your are up to date on the latest version of PHP The latest version of Javascript – no problemo! Frameworks – you know two or three or more – plus the ones you wrote yourself But roughly 2-3% have had any training in Structured Query Language (SQL)
- 7. 7 So what is SQL?!?!??!?!??!??! http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SQL SQL (/ˈɛs kjuː ˈɛl/ or /ˈsiːkwəl/; Structured Query Language) is a special-purpose programming language designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS), or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS). Originally based upon relational algebra and tuple relational calculus, SQL consists of a data definition language and a data manipulation language. The scope of SQL includes data insert, query, update and delete, schema creation and modification, and data access control.
- 8. 8 Oh Crap!!! He Said 'relational algebra' and 'tuple relational calculus'!
- 10. 10 Relational algebra http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relational_algebra Relational algebra is a family of algebra with a well-founded semantics used for modelling the data stored in relational databases, and defining queries on it. To organize the data, first the redundant data and repeating groups of data are removed, which we call normalized. By doing this the data is organized or normalized into what is called first normal form (1NF). Typically a logical data model documents and standardizes the relationships between data entities (with its elements). A primary key uniquely identifies an instance of an entity, also known as a record.
- 11. 11 Relation Algebra Continued Once the data is normalized and in sets of data (entities and tables), the main operations of the relational algebra can be performed which are the set operations (such as union, intersection, and cartesian product), selection (keeping only some rows of a table) and the projection (keeping only some columns). Set operations are performed in the where statement in SQL, which is where one set of data is related to another set of data.
- 12. 12 Database Normalization Forms 1nf – No columns with repeated or similar data – Each data item cannot be broken down further – Each row is unique (has a primary key) – Each filed has a unique name 2nf – Move non-key attributes that only depend on part of the key to a new table ● Ignore tables with simple keys or no no-key attributes 3nf – Move any non-key attributes that are more dependent on other non-key attributes than the table key to a new table. ● Ignore tables with zero or only one non-key attribute
- 13. 13 In more better English, por favor! 3NF means there are no transitive dependencies. A transitive dependency is when two columnar relationships imply another relationship. For example, person -> phone# and phone# -> ringtone, so person -> ringtone – A → B – It is not the case that B → A – B → C
- 14. 14 And the rarely seen 4nf & 5nf You can break the information down further but very rarely do you need to to 4nf or 5nf
- 15. 15 So why do all this normalization? http://databases.about.com/od/specificproducts/a/normalization.htm Normalization is the process of efficiently organizing data in a database. There are two goals of the normalization process: eliminating redundant data (for example, storing the same data in more than one table ) and ensuring data dependencies make sense (only storing related data in a table). Both of these are worthy goals as they reduce the amount of space a database consumes and ensure that data is logically stored.
- 16. 16 Example – Cars Name Gender Color Model Heather F Blue Mustang Heather F White Challenger Eli M Blue F-type Oscar M Blue 911 Dave M Blue Mustang There is redundant information across multiple rows but each row is unique
- 17. 17 2nf – split into tables Name Gender Heather F Eli M Oscar M Dave M Color Model Owner Blue Mustang Heather White Challenger Heather Blue F-type Eli Blue 911 Oscar Blue Mustang Dave Split data into two tables – one for owner data and one for car data
- 18. 18 3nf – split owner and car info into different tables Car_ID Color Model Owner _ID 1 Blue Mustang 1 2 White Challenger 1 3 Blue F-type 2 4 Blue 911 3 5 Blue Mustang 4 The car info is separated from the car info. Note that the car table has a column for the owner's ID from the owner table. Owner_ID Name Gender 1 Heather F 2 Eli M 3 Oscar M 4 Dave M
- 19. 19 But what if White Mustang is shared or 4nf Owner_ID Name Gender 1 Heather F 2 Eli M 3 Oscar M 4 Dave M Car_id Model Color 1 Mustang Blue 2 Challenger White 3 F-type Blue 4 911 Blue Car_id Owner_id 1 1 2 1 3 2 4 3 1 4 Tables for Owner, Car, & Ownership data Now we have a flexible way to search data about owners, cars, and their relations.
- 20. 20 So now what!!! By normalizing to 3nf (or 4th), we are storing the data with no redundancies (or very, very few) Now we need a way to define how the data is stored And a way to manipulate it.
- 21. 21 SQL SQL is a declarative language made up of – DDL – Data Definition Language – DML – Data Manipulation Language SQL was one of the first commercial languages for Edgar F. Codd's relational model, as described in his influential 1970 paper, "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks." --Wikipedia – Codd, Edgar F (June 1970). "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks". Communications of the ACM (Association for Computing Machinery) 13 (6): 377–87. doi:10.1145/362384.362685. Retrieved 2007-06-09.
- 22. 22 Cod versus Codd
- 23. 23 SQL is declarative Describe what you want, not how to process Hard to look at a query to tell if it is efficient by just looks Optimizer picks GPS-like best route – Can pick wrong – traffic, new construction, washed out roads, and road kill! Oh my!!
- 24. 24 SQL is made up of two parts Data Definition Language (DDL) – For defining data structures ●CREATE, DROP, ALTER, and RENAME Data Manipulation Language – Used to SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE data
- 25. 25 DDL Useful commands – DESC[ribe] table – SHOW CREATE TABLE table –
- 26. 26 The stuff in the parenthesis CHAR(30) or VARCHAR(30) will hold strings up to 30 character long. – SQL MODE (more later) tells server to truncate or return error if value is longer that 30 characters – INT(5) tells the server to show five digits of data DECIMAL(5,3) stores five digits with two decimals, i.e. -99.999 to 99.999 FLOAT(7,4) -999.9999 to 999.9999
- 27. 27 Another look at DESC City
- 28. 28 NULL No Value Null is used to indicate a lack of value or no data – Gender : Male, Female, NULL Nulls are very messy in B-tree Indexing, try to avoid Math with NULLs is best avoided
- 29. 29 DESC City in detail Describe table tells us the names of the columns (Fields), the data type, if the column is NULLABLE, Keys, any default value, and Extras.
- 30. 30 Data Types Varies with vendor Usually have types for text, integers, BLOBs, etc. Refer to manual
- 31. 31 MySQL World Database http://dev.mysql.com/doc/index-other.html Used in MySQL documentation, books, on line tutorials, etc. Three tables – City – Country – Country Language
- 32. 32 EER Map
- 33. 33 Simple SELECT Query Result
- 34. 34 Join two tables To get a query that provides the names of the City and the names of the countries, JOIN the two tables on a common data between the two columns (that are hopefully indexed!)
- 35. 35 http://i.imgur.com/hhRDO4d.png – Get a copy!!!
- 36. 36 Simple join Both City and Country have columns that can be used for JOINs – Country.Code – City.CountryCode
- 37. 37 What happened when you send a query Server receives the query The user is authenticated for permissions – Database, table, and/or column level Syntax Optimizer – Statistics on data – Cost model ● Pick cheapest option (DISK I/O) ● Cardinality of indexes Get the data Sorting/Grouping/etc Data returned
- 38. 38 EXPLAIN EXPLAIN is pre pended to the query to show the results from the optimizer
- 39. 39 VISUAL Explain MySQL Workbench MySQL 5.6/5.7 Uses JSON output from EXPLAIN and turns it into something more visually appealing
- 40. 40 Optimizer Trace { "query_block": { "select_id": 1, "cost_info": { "query_cost": "5779.32" }, "nested_loop": [ { "table": { "table_name": "City", "access_type": "ALL", "rows_examined_per_scan": 4079, "rows_produced_per_join": 4079, "filtered": 100, "cost_info": { "read_cost": "68.72", "eval_cost": "815.80", "prefix_cost": "884.52", "data_read_per_join": "286K" }, "used_columns": [ "Name", "CountryCode", "Population" ] } }, { "table": { "table_name": "Country", "access_type": "eq_ref", "possible_keys": [ "PRIMARY" ], "key": "PRIMARY", "used_key_parts": [ "Code" ], "key_length": "3", "ref": [ "world.City.CountryCode" ], "rows_examined_per_scan": 1, "rows_produced_per_join": 4079, "filtered": 100, "cost_info": { "read_cost": "4079.00", "eval_cost": "815.80", "prefix_cost": "5779.32", "data_read_per_join": "1M" }, "used_columns": [ "Code", "Name"
- 41. 41 MySQL Internals Manual :: 7 The Optimizer :: 7.1 Code and Concepts :: 7.1.2 The Optimizer Code handle_select() mysql_select() JOIN::prepare() setup_fields() JOIN::optimize() /* optimizer is from here ... */ optimize_cond() opt_sum_query() make_join_statistics() get_quick_record_count() choose_plan() /* Find the best way to access tables */ /* as specified by the user. */ optimize_straight_join() best_access_path() /* Find a (sub-)optimal plan among all or subset */ /* of all possible query plans where the user */ /* controls the exhaustiveness of the search. */ greedy_search() best_extension_by_limited_search() best_access_path() /* Perform an exhaustive search for an optimal plan */ find_best() make_join_select() /* ... to here */ JOIN::exec()
- 42. 42 Data and Data types Use the smallest reasonable field – BIGINT are not needed for customer id numbers – Signed/unsigned ● Customer “negative seven four two four three” – All those extra bits have to be moved disk → memory → buffer → Ether → buffer → program CHAR versus VARCHAR – Space and compression – Overhead slight ENUMs and BITs – Have to plan ahead – Sorting issues ● Value of the ENUM
- 43. 43 INTEGER, INT, SMALLINT, TINYINT, MEDIUMINT, BIGINT Type Storage (bytes) Minimum Signed Maximum Signed Minimum Unsigned Maximum Unsigned TINYINT 1 -128 127 0 255 SMALLINT 2 -32768 32767 0 65535 MEDIUMINT 3 -8388608 8388607 0 16777215 INT 4 - 2147483648 2147483647 0 4294967295 BIGINT 8 - 9223372036 854775808 9223372036 854775807 0 1844674407 3709551615
- 44. 44 Creating a table with MySQL command line client CREATE TABLE fooint (a INT(1), b INT(4), c iINT(10)); INSERT INTO fooint (a,b,c) VALUES (1,100,10000); INSERT INTO fooint VALUES (777,777,0); SELECT * from foointg INSERT INTO fooint (a) values (1234567890); SELECT * FROM foointG Note that ; and g are equivalent and G is for vertical output. What happens with INSERT INTO fooint (a) values (12345678900); ??
- 45. 45 ALTER, TRUNCATE, and DROP table ALTER TABLE fooint ADD COLUMN id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL FIRST; – Also BEFORE and AFTER SELECT * FROM fooint; TRUNCATE fooint; – Used to remove data but not schema definition DROP TABLE fooint; – Goodbye to table and schema
- 46. 46 Another table CREATE TABLE fooint (id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, name Char(30)); DESC fooint; and SHOW CREATE TABLE foointl INSERT INTO fooint (name) VALUES ('Alpha'),('Beta'), ('Gamma'); SELECT * FROM fooint; – Note the id column incremented automatically
- 47. 47 Foreign Keys CREATE TABLE employee ( e_id INT NOT NULL, name CHAR(20), PRIMARY KEY (e_id) ); CREATE TABLE building ( office_nbr INT NOT NULL, description CHAR(20), e_id INT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (office_nbr), FOREIGN KEY (e_id) REFERENCES employee (e_id) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE);
- 48. 48 More on foreign keys mysql> INSERT INTO employee VALUES (10,'Larry'), (20,'Shemp'), (40,'Moe'); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.04 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> INSERT INTO building VALUES (100,'Corner Office',10), (101,'Lobby',40); Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.04 sec) Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> SELECT * FROM employee; +------+-------+ | e_id | name | +------+-------+ | 10 | Larry | | 20 | Shemp | | 40 | Moe | +------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM building; +------------+---------------+------+ | office_nbr | description | e_id | +------------+---------------+------+ | 100 | Corner Office | 10 | | 101 | Lobby | 40 | +------------+---------------+------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 49. 49 Using foreign keys mysql> SELECT * FROM employee JOIN building ON (employee.e_id=building.e_id); +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ | e_id | name | office_nbr | description | e_id | +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ | 10 | Larry | 100 | Corner Office | 10 | | 40 | Moe | 101 | Lobby | 40 | +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ 2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
- 50. 50 Left Join with foreign keys mysql> SELECT * FROM employee LEFT JOIN building ON (employee.e_id=building.e_id); +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ | e_id | name | office_nbr | description | e_id | +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ | 10 | Larry | 100 | Corner Office | 10 | | 40 | Moe | 101 | Lobby | 40 | | 20 | Shemp | NULL | NULL | NULL | +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 51. 51 Foreign keys keep you from messy data mysql> INSERT INTO building VALUES (120,'Cubicle',77); ERROR 1452 (23000): Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails (`test`.`building`, CONSTRAINT `building_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`e_id`) REFERENCES `employee` (`e_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE) mysql>
- 52. 52 Taking advantage of CASCADE mysql> DELETE FROM employee WHERE e_id=40; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.08 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM employee LEFT JOIN building ON (employee.e_id=building.e_id); +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ | e_id | name | office_nbr | description | e_id | +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ | 10 | Larry | 100 | Corner Office | 10 | | 20 | Shemp | NULL | NULL | NULL | +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+
- 53. 53 Cascade keeping foreign key data updated mysql> UPDATE employee SET e_id=21 WHERE e_id=20; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.04 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 mysql> SELECT * FROM employee LEFT JOIN building ON (employee.e_id=building.e_id); +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ | e_id | name | office_nbr | description | e_id | +------+-------+------------+---------------+------+ | 10 | Larry | 100 | Corner Office | 10 | | 21 | Shemp | NULL | NULL | NULL | +------+-------+------------+-------------
- 54. 54 Indexing MySQL uses mainly B-trees for indexes Great for =, <, >, <=, =>, BETWEEN, some LIKE 'string%'
- 55. 55 13.1.8 CREATE INDEX Syntax CREATE [UNIQUE|FULLTEXT|SPATIAL] INDEX index_name [index_type] ON tbl_name (index_col_name,...) [index_option] [algorithm_option | lock_option] ... index_col_name: col_name [(length)] [ASC | DESC] index_type: USING {BTREE | HASH} index_option: KEY_BLOCK_SIZE [=] value | index_type | WITH PARSER parser_name | COMMENT 'string' algorithm_option: ALGORITHM [=] {DEFAULT|INPLACE|COPY} lock_option: LOCK [=] {DEFAULT|NONE|SHARED|EXCLUSIVE}
- 56. 56 You may not know Can create multi-column indexes – Year,month,day index can be used for ● Year,Month,Day searches ● Year,Month searches ● Year searches – But not day or month, day searches Can index on part of a column – CREATE INDEX ndx1 ON customer (name(10)); NULLs are to be avoided – Extra optimizer steps UNIQUE indexes enforce no duplicates InnoDB will create an index if YOU DO NOT
- 57. 57 13.2.5.2 INSERT … ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE If you specify ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE, and a row is inserted that would cause a duplicate value in a UNIQUE index or PRIMARY KEY, an UPDATE of the old row is performed. For example, if column a is declared as UNIQUE and contains the value 1, the following two statements have identical effect: INSERT INTO table (a,b,c) VALUES (1,2,3) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE c=c+1;
- 58. 58 FIND Asian countries with Population > 5 million EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM Country WHERE Continent = 'Asia' AND Population > 5000000;
- 59. 59 Will indexes make query faster? SELECT * FROM Country WHERE Continent = 'Asia' AND Population > 5000000; Index columns – Population – Continent – Population and Continent – Continent and Population ● Which to pick? Optimizer will look at option that takes the least CPU and I/O ● Statistics from storage engine – Indexes to use, order to join tables, avoiding sorts, is sorting expensive
- 60. 60 Index on Population Alter TABLE Country ADD INDEX p (Population) Down from 239!!
- 61. 61 A reading from the Book of MySQL – Chapter 8 Optimization READ this section of the MySQL Manual – Hardware – Configuration – Queries – Locking – Benchmarkings Set InnoDb Buffer Cache Size to 75-80% of system RAM Move Logs off disks/controllers with data Use bigger stronger machines for replication slaves Looking at SSDs, FusionIO cards Monitor! Monitor! Monitor!
- 62. 62 ALTER TABLE Country ADD INDEX C (continent) 42 is better than 239 or 54
- 63. 63 CREATE INDEX cpidx ON Country (continent, Population) Event better still!
- 64. 64 CREATE INDEX pcidx on Country (Population,continent) FORCING the use of the new index shows it is not optimal.
- 65. 65 Index-es Indexes need maintenance – Run OPTIMIZE TABLE when system quiet – Each INSERT/DELETE takes overhead ● Slows you down – Therefore remove unused indexes – MySQL Utilities mysqlindexcheck to look for unused index on long running systems (do not use AFTER a restart) ● Use good naming convention, document – Statistics can be saved/reloaded at shutdown/reboot ● After a reboot w/o saving, the system is going to need to rebuild stats from scratch, run slower – Log queries not using Indexes ● Not all of these are bad, just recognize them
- 67. 67 Transactions You will need to use a transactional storage engine like InnoDB, NDB You need to START a transaction, do the work and COMMIT to record the changes or ROLLBACK to cancel the recording. To avoid using ROLLBACK, you can employ the following strategy: – Use LOCK TABLES to lock all the tables you want to access. – Test the conditions that must be true before performing the update. – Update if the conditions are satisfied. – Use UNLOCK TABLES to release your locks. Note – This solution does not handle the situation when someone kills the threads in the middle of an update. In that case, all locks are released but some of the updates may not have been executed.
- 68. 68 CREATE TABLE account (id int not null, balance decimal(6,2) default 0) INSERT INTO account VALUES (1,1000.10), (2,400), (3,0), (15,.99); START TRANSACTION; UPDATE account SET balance = 1010.10 WHERE id = 1; UPDATE account SET balance = 300 WHERE id=2; COMMIT; START TRANSACTION UPDATE account SET balance=1000 WHERE ID=3; ROLLBACK;
- 69. 69 AUTOCOMMIT AUTOCOMMIT is set to 1 by default or 'do things as I type them mode'. – START TRANSACTION overrides – Some APIs like JDBC have own way to handle transactions (see chapter 23 in MySQL docs) AUTOCOMMIT set to 0 requires a COMMIT to store changes Some statements cannot be rolled back. In general, these include data definition language (DDL) statements, such as those that create or drop databases, those that create, drop, or alter tables or stored routines Some statements cause an implicit commit – DDL, user account changes, transaction control or locking statements, data loading, and replication control statements,
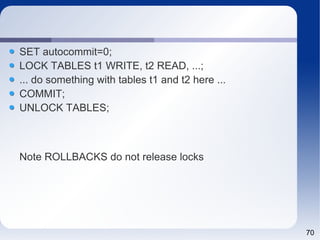
- 70. 70 SET autocommit=0; LOCK TABLES t1 WRITE, t2 READ, ...; ... do something with tables t1 and t2 here ... COMMIT; UNLOCK TABLES; Note ROLLBACKS do not release locks
- 71. 71 SET autocommit=0; LOCK TABLES t1 WRITE, t2 READ, ...; ... do something with tables t1 and t2 here ... COMMIT; UNLOCK TABLES; Note ROLLBACKS do not release locks
- 72. 72 Scaling MySQL
- 73. 73 First steps of scaling ✔ Upgrade MySQL versions ✔ 5.5 is 25% faster than 5.1 ✔ 5.6 is 20% faster ✔ 5.7 will be faster still ✔ Memory ✔ DISKS ✔ Move logs to different platters, controllers Move large databases to own disks ✔ TUNE queries ✔ Scale horizontally especially is server is old ✔ Use bigger, more powerful boxes for replicants ✔ Optimize network
- 74. 74 Read/Write Splitting – Scale READS
- 75. MySQL Fabric HA, shards, Write scaling ● Lets you shard and reshard ● Very new ● Looking for feedback ● Released in May Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 75 All rights reserved.
- 76. Why does that query take so LONG!!! ● I only want the top N customers! ● And I want them sorted by last name, first name, middle name, postal code, and average purchase! Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 76 All rights reserved. The stuff on the right hand side of the WHERE clause may seem like a great way to prune down the number of records for a query BUT that is not always the case.
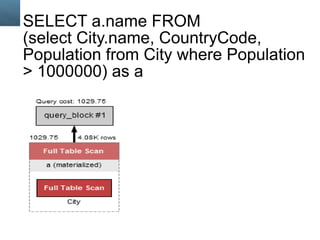
- 77. Query we want to 'prune' Select City.name AS 'City', Country.name AS 'Country', City.Population AS 'Pop' FROM City JOIN Country ON (City.CountryCode = Country.Code) Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 77 All rights reserved.
- 78. The Stats! Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 78 All rights reserved. Total cost is about 5780. Bad news is that we have a Full Table Scan on City but that was expected. Good news is that we have 1 read on Country using the Primary key to get record we need to match on the join.
- 79. Now we only want the top ten! LIMIT 10 Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 79 All rights reserved. But the cost is still 5780!?!?! The server has to run through ALL the records to get just the first ten. So LIMIT does not buy us any speed in this case.
- 80. ORDER BY Country Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 80 All rights reserved. Oh no! The cost jumps to 9858! And we have to open a temp table and then sort that file (expensive)
- 81. WHERE City.Population > 1000000 Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 81 All rights reserved. Nope. The server is doing the join first and then tossing away the records that are <= 1000000
- 82. SELECT a.name FROM (select City.name, CountryCode, Population from City where Population > 1000000) as a Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 82 All rights reserved.
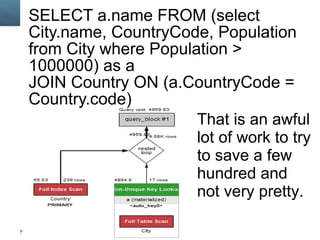
- 83. SELECT a.name FROM (select City.name, CountryCode, Population from City where Population > 1000000) as a JOIN Country ON (a.CountryCode = Country.code) Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 83 All rights reserved. That is an awful lot of work to try to save a few hundred and not very pretty.
- 84. The World is too small ● The World database is too small and already too optimized to gain much more performance. ● So lets create a new database and copy the date to get 100K+ records; – CREATE TABLE bigcity LIKE city; – INSERT INTO bigcity SELECT * FROM city; INSERT INTO bigcity SELECT NULL,Name,CountryCode,District,Population FROM bigcity; <many times> Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 84 All rights reserved.
- 85. SELECT countrycode, sum(Population) FROM bigcity GROUP BY CountryCode; ● Takes .343 seconds ● ALTER TABLE bigcity ADD INDEX cc_pop (CountryCode,Population); ● Now takes .156 seconds Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 85 All rights reserved.
- 86. Zipcode – from a free zipcode database SELECT city, state, zipcode FROM zip WHERE zipcode = '76262'; Pretend out app provides the us postal code given the city and state data. Here no indexes. Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 86 All rights reserved.
- 87. Indexing city and state only. ● CREATE INDEX csidx ON zip (city(8),state(2)); /* only use first 8 on name and 2 Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 87 All rights reserved. for state*/ ● SELECT city, state, zipcode FROM zip WHERE city='Roanoke' and state='TX';
- 88. Good optimization Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 88 All rights reserved. The optimizer uses the city and state from the index we created to know where to dive into the data. Some indexes will be able to supply all the data so there will be no need to dive into the data.
- 89. Composite and Compound Indexes ● Composite index covers all the columns in the filter, join and select criteria. All of these columns are stored on all of the index pages accordingly in the index B-tree. ● Compound index covers all the filter and join key columns in the B-tree, keeping the select columns only on the leaf pages as they will not be searched, only extracted! This saves space and creates smaller index pages (and is faster). Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 89 All rights reserved.
- 90. NoSQL ● No Schema – Teenager with all belongings in center of room – Does not scale easily – ACID compliance not important – Effective for some jobs but watch out if you need an AND or an OR Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 90 All rights reserved.
- 91. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NoSQL A NoSQL (often interpreted as Not Only SQL) database provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases. Motivations for this approach include simplicity of design, horizontal scaling and finer control over availability. The data structure (e.g. key-value, graph, or document) differs from the RDBMS, and therefore some operations are faster in NoSQL and some in RDBMS. There are differences though, and the particular suitability of a given NoSQL DB depends on the problem it must solve (e.g., does the solution use graph algorithms?). Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 91 All rights reserved.
- 92. Key/value pair ● A key-value pair (KVP) is a set of two linked data items: a key, which is a unique identifier for some item of data, and the value, which is either the data that is identified or a pointer to the location of that data. http://searchenterprisedesktop.techtarget.com/definition/key-value-pair ● Berkeley Database (Sleepycat) 1986 – Hash table Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 92 All rights reserved.
- 93. Graph Databases ● In computing, a graph database is a database that uses graph structures with nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data. A graph database is any storage system that provides index-free adjacency. This means that every element contains a direct pointer to its adjacent elements and no index lookups are necessary http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_database Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 93 All rights reserved.
- 94. Document Databases A document-oriented database is a computer program designed for storing, retrieving, and managing document-oriented information, also known as semi-structured data. Document-oriented databases are one of the main categories of NoSQL databases and the popularity of the term "document-oriented database" (or "document store") has grown with the use of the term NoSQL itself. In contrast to relational databases and their notions of"Tables" and "Relations" (between Tables), these systems are designed around an abstract notion of a "Document". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document-oriented_database Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 94 All rights reserved.
- 95. Hybrids Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 95 All rights reserved.
- 96. Bypassing syntax checking and optimizer upto 9x faster than SQL Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 96 All rights reserved.
- 97. Paradigm Shifting w/o a clutch ● SQL is a declarative language ● PHP is procedural/object orientated ● Square Pegs for Round Holes Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 97 All rights reserved.
- 98. Object Relation Mapper ● Adds another layer – Easier to learn SQL – Not as expressive as SQL – ORMs are a hammer in a world of nails and blasting caps – If you can not solve problem with an object, adding another object is not going to help Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 98 All rights reserved.
- 99. Query Rewrite plugin or How To Fix your ORM's lousy SQL mysql < <plugin directory>/install_rewriter_plugin.sql INSERT INTO query_rewrite.rewrite_rules( pattern, replacement ) VALUES ( 'SELECT ?', 'SELECT ? + 1' ); Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 99 All rights reserved.
- 100. Better Example ● SELECT patientId, time FROM patient_records WHERE patientId > 1000 AND patientId < 2000 AND time < “2014-09-08” AND illness = ”Headache” ORDER BY time LIMIT 1; ● SELECT patiendId, time FROM patient_records WHERE patientId > 1000 AND patientID < 2000 AND time < “2014-09-08” AND illness = ”Acrocephalosyndactylia” * ORDER BY time LIMIT 1; Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 100 All rights reserved.
- 101. The Rules for the rewrite INSERT INTO query_rewrite.rewrite_rules ( pattern, pattern_database, replacement ) VALUES ( # Pattern 'SELECT patientid, time ' || 'FROM patient_records ' || 'WHERE patientid > ? AND patientid < ? ' || 'AND time < ? AND illness = ? ' || 'ORDER BY time LIMIT 1', # Database 'health_clinic', # Replacement 'SELECT patientid, time ' || 'FROM patient_records FORCE INDEX(patientIdIdx) ' || 'WHERE patientid > ? AND patientid < ? ' || 'AND time < ? AND illness = ? ' || 'ORDER BY time LIMIT 1'); Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 101 All rights reserved.
- 102. Recommended Books ● High Performance MySQL, 3rd Edition Baron Schwartz, Peter Zaitsev & Vadim Tkachenko ● SQL Antipatterns – Bill Karwin ● SQL and Relational Theory – CJ Date ● Effective MySQL Replication Techniques in Depth – Ronald Bradford Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 102 All rights reserved.
- 103. Q/A ● Slideshare.net/davestokes ● @stoker ● [email protected] Copyright © 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 103 All rights reserved.

























![25
DDL
Useful commands
– DESC[ribe] table
– SHOW CREATE TABLE table
–](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql4php-141202131544-conversion-gate02/85/SQL-For-PHP-Programmers-25-320.jpg)













![40
Optimizer Trace
{
"query_block": {
"select_id": 1,
"cost_info": {
"query_cost": "5779.32"
},
"nested_loop": [
{
"table": {
"table_name": "City",
"access_type": "ALL",
"rows_examined_per_scan": 4079,
"rows_produced_per_join": 4079,
"filtered": 100,
"cost_info": {
"read_cost": "68.72",
"eval_cost": "815.80",
"prefix_cost": "884.52",
"data_read_per_join": "286K"
},
"used_columns": [
"Name",
"CountryCode",
"Population"
]
}
},
{
"table": {
"table_name": "Country",
"access_type": "eq_ref",
"possible_keys": [
"PRIMARY"
],
"key": "PRIMARY",
"used_key_parts": [
"Code"
],
"key_length": "3",
"ref": [
"world.City.CountryCode"
],
"rows_examined_per_scan": 1,
"rows_produced_per_join": 4079,
"filtered": 100,
"cost_info": {
"read_cost": "4079.00",
"eval_cost": "815.80",
"prefix_cost": "5779.32",
"data_read_per_join": "1M"
},
"used_columns": [
"Code",
"Name"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql4php-141202131544-conversion-gate02/85/SQL-For-PHP-Programmers-40-320.jpg)














![55
13.1.8 CREATE INDEX Syntax
CREATE [UNIQUE|FULLTEXT|SPATIAL] INDEX index_name
[index_type]
ON tbl_name (index_col_name,...)
[index_option]
[algorithm_option | lock_option] ...
index_col_name:
col_name [(length)] [ASC | DESC]
index_type:
USING {BTREE | HASH}
index_option:
KEY_BLOCK_SIZE [=] value
| index_type
| WITH PARSER parser_name
| COMMENT 'string'
algorithm_option:
ALGORITHM [=] {DEFAULT|INPLACE|COPY}
lock_option:
LOCK [=] {DEFAULT|NONE|SHARED|EXCLUSIVE}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql4php-141202131544-conversion-gate02/85/SQL-For-PHP-Programmers-55-320.jpg)