Static testing techniques
- 1. Static Testing 1 Principles 2 Lifecycle 4 Dynamic test techniques 3 Static testing 5 Management 6 Tools Software Testing
- 2. Contents Reviews and the test process Types of review Static analysis
- 3. People techniques individual: desk-checking, data-stepping, proof-reading group: Reviews (informal & formal): for consensus Walkthrough: for education Inspection (most formal): to find faults Static techniques do not execute codeStatic techniques do not execute code
- 4. Benefits of reviews Development productivity improvement Reduced development timescales Reduced testing time and cost Lifetime cost reductions Reduced fault levels Improved customer relations etc.
- 5. Reviews are cost-effective 10 times reduction in faults reaching test, testing cost reduced by 50% to 80% Handbook of Walkthroughs, Inspections & Technical Reviews - Freedman & Weinberg reduce faults by a factor of 10 Structured Walkthroughs - Yourdon
- 6. 25% reduction in schedules, remove 80% - 95% of faults at each stage, 28 times reduction in maintenance cost, many others Software Inspection - Gilb & Graham
- 7. What can be Inspected? Anything written down can be Inspected policy, strategy, business plans, marketing or advertising material, contracts system requirements, feasibility studies, acceptance test plans test plans, test designs, test cases, test results
- 8. system designs, logical & physical software code user manuals, procedures, training material
- 9. What can be reviewed? anything which could be Inspected i.e. anything written down plans, visions, “big picture”, strategic directions, ideas project progress work completed to schedule, etc. “Should we develop this” marketing options
- 10. What to review / Inspect? Tests Tests Tests Tests Requirements Design Code Functions Integration T Unit Test Accept. Test System Test
- 11. Costs of reviews Rough guide: 5%-15% of development effort half day a week is 10% Effort required for reviews planning (by leader / moderator) preparation / self-study checking meeting fixing / editing / follow-up recording & analysis of statistics / metrics process improvement (should!)
- 12. Contents Reviews and the test process Types of review Static analysis Static testing 1 2 4 5 3 6
- 13. Types of review of documents Informal Review undocumented widely viewed as useful and cheap (but no one can prove it!) A helpful first step for chaotic organisations. Technical Review: (or peer review) includes peer and technical experts, no management participation. Normally documented, fault-finding. Can be rather subjective.
- 14. Decision-making Review: group discusses document and makes a decision about the content, e.g. how something should be done, go or no-go decision, or technical comments
- 15. Types of review of documents Walkthrough author guides the group through a document and his or her thought processes, so all understand the same thing, consensus on changes to make Inspection: formal individual and group checking, using sources and standards, according to generic and specific rules and checklists, using entry and exit criteria, Leader must be trained & certified, metrics required
- 16. Reviews in general 1 Objectives / goals validation & verification against specifications & standards achieve consensus (excluding Inspection) process improvement (ideal, included in Inspection)
- 17. Reviews in general 2 Activities planning overview / kick-off meeting (Inspection) preparation / individual checking review meeting (not always) follow-up (for some types) metrics recording & analysis (Inspections and sometimes reviews)
- 18. Reviews in general 3 Roles and responsibilities Leader / moderator - plans the review / Inspection, chooses participants, helps & encourages, conducts the meeting, performs follow-up, manages metrics Author of the document being reviewed / Inspected
- 19. Reviewers / Inspectors - specialised fault-finding roles for Inspection Managers - excluded from some types of review, need to plan project time for review / Inspection Others: e.g. Inspection/ review Co-ordinator
- 20. Reviews in general 4 Deliverables Changes (edits) in review product Change requests for source documents (predecessor documents to product being reviewed / Inspected) Process improvement suggestions to the review / Inspection process to the development process which produced the product just reviewed / Inspected Metrics (Inspection and some types of review)
- 21. Reviews in general 5 Pitfalls (they don’t always work!) lack of training in the technique (especially Inspection, the most formal) lack of or quality of documentation - what is being reviewed / Inspected
- 22. Lack of management support - “lip service” - want them done, but don’t allow time for them to happen in project schedules Failure to improve processes (gets disheartening just getting better at finding the same thing over again)
- 23. Inspection is different • the document to be reviewed is given out in advance • typically dozens of pages to review • instructions are "please review this" • not just product, sources • chunk or sample • training, roles
- 24. Inspection is different • some people have time to look through it and make comments before the meeting (which is difficult to arrange) • the meeting often lasts for hours entry criteria to meeting, may not be worth holding 2 max., often much shorter
- 25. Inspection is different • "I don't like this" • much discussion, some about technical approaches, some about trivia • don't really know if it was worthwhile, but we keep doing it Rule violations, objective, not subjective • no discussion, highly focused, anti-trivia only do it if value is proven (continually)
- 26. Inspection is more and better entry criteria training optimum checking rate prioritising the words standards process improvement exit criteria quantified estimates of remaining major faults per page typical review early Inspection mature Inspection effectiveness return on investment 10 - 20% unknown 30 - 40% 6 - 8 hrs / Insp hr 80 - 95% 8 - 30 hrs / Insp hr
- 27. The Inspection Process Software Development Stage . . Planning Kick off Ind Chk Meet Edit Change Request Process Improvement Entry Next Software Development Stage Exit
- 28. At first glance.. Here’s a document: review this (or Inspect it)
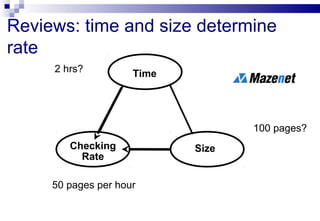
- 29. Reviews: time and size determine rate Time Checking Rate Size 2 hrs? 100 pages? 50 pages per hour Checking Rate
- 30. Review “Thoroughness”? ordinary “review” - finds some faults, one major, fix them, consider the document now corrected and OK major minor minor
- 31. Inspection: time and rate determine size Time Checking Rate Size 2 hrs? Optimum: 1 page* per hour 2 pages (at optimum rate) Size * 1 page = 300 important words
- 32. Inspection Thoroughness Inspection can find deep-seated faults: • all of that type can be corrected • but needs optimum checking rate
- 33. Inspection surprises Fundamental importance of Rules democratically agreed as applying define major issues / faults Slow checking rates Strict entry & exit criteria Fast logging rates Amount of responsibility given to author
- 34. Contents Reviews and the test process Types of review Static analysis
- 35. What can static analysis do? Remember: static techniques do not execute the code A form of automated testing check for violations of standards check for things which may be a fault
- 36. Descended from compiler technology a compiler statically analyses code, and “knows” a lot about it, e.g. variable usage; finds syntax faults static analysis tools extend this knowledge can find unreachable code, undeclared variables, parameter type mis-matches, uncalled functions & procedures, array bound violations, etc.
- 37. Data flow analysis This is the study of program variables variable defined* where a value is stored into it variable used where the stored value is accessed variable is undefined before it is defined or when it goes out of scope *defined should not be confused with declared x = y + z IF a > b THEN read(S) x is defined, y and z are used a and b are used, S is defined
- 38. Data flow analysis faults n := 0 read (x) n := 1 while x > y do begin read (y) write( n*y) x := x - n end Data flow anomaly: n is re-defined without being used Data flow fault: y is used before it has been defined (first time around the loop)
- 39. Control flow analysis Highlights: nodes not accessible from start node infinite loops multiple entry to loops whether code is well structured, i.e. reducible whether code conforms to a flowchart grammar any jumps to undefined labels any labels not jumped to cyclomatic complexity and other metrics
- 40. Unreachable code example Macro definitions (different for different platforms the code runs on) Buffsize: 1000 Mailboxmax: 1000 IF Buffsize < Mailboxmax THEN Error-Exit ENDIF
- 41. Static Analysis finds the THEN clause unreachable, so will flag a fault
- 42. Cyclomatic complexity cyclomatic complexity is a measure of the complexity of a flow graph (and therefore the code that the flow graph represents) the more complex the flow graph, the greater the measure it can most easily be calculated as: complexity = number of decisions + 1
- 43. Which flow graph is most complex? 1 2 3 5 What is the cyclomatic complexity?
- 44. Example control flow graph Result = 0 Right = 0 DO WHILE more Questions IF Answer = Correct THEN Right = Right + 1 ENDIF END DO Result = (Right / Questions) IF Result > 60% THEN Print "pass" ELSE Print "fail” ENDIF do if r=r+1 end init if res pass fail end Pseudo-code:
- 45. Other static metrics lines of code (LOC) operands & operators (Halstead’s metrics) fan-in & fan-out nesting levels function calls OO metrics: inheritance tree depth, number of methods, coupling & cohesion
- 46. Limitations and advantages Limitations: cannot distinguish "fail-safe" code from programming faults or anomalies (often creates overload of spurious error messages) does not execute the code, so not related to operating conditions Advantages: can find faults difficult to "see" gives objective quality assessment of code
- 47. Summary: Key Points Reviews help to find faults in development and test documentation, and should be applied early Types of review: informal, walkthrough, technical / peer review, Inspection Static analysis can find faults and give information about code without executing it