Statistical inference for (Python) Data Analysis. An introduction.
2 likes1,987 views
A brief showcase on how Python can help perform statistical inference. Few examples with a short library overview.
1 of 25
Downloaded 39 times






![daftCode sp. z o.o.
NumPy (Example)
Python
>>> # Vector
>>> v = [1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> # scaling vector 2v
>>> v2 = [2*i for i in v]
>>> # Adding vectors v+v2
>>> v3 = [v[i]+v2[i] for i in range(len(v))]
>>> # Vector normalization
>>> mean = sum(v)/len(v)
>>> zero_mean = [(i – mean) for i in v]
>>> std = sum(i**2 for i in zero_mean)/len(v)
>>> normalized = [i/std for i in zero_mean]
Python + NumPy
>>> import numpy as np
>>> # Vector
>>> v = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> # sacling vector 2v
>>> v2 = 2*v
>>> # Adding vectors v+v2
>>> v3 = v2 + v
>>> # Normalization
>>> normalized = v.mean()/v.std()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydata-151116092808-lva1-app6892/85/Statistical-inference-for-Python-Data-Analysis-An-introduction-7-320.jpg)




![daftCode sp. z o.o.
Example 1. Anomaly detection
>>> import numpy as np
>>> values = np.array([…]) # Get values from
>>> # somewhere
>>> values
array([796, 756, 827, 779, 787, 731, 847, 829, 794,
790, 831, 820, 822, 792, 767, 757, 777, 775, 799,
756, 849, 808, 800, 823, 798, 809, 783, 800, 848,
772, 853, 759, 745, 868, 713, 863, 819, 829, 799,
777, 785, 812, 877, 839, 783, 867, 875, 829, 818,
813, 763, 829, 812, 867, 790, 748, 822, 774, 900,
830, 781, 795, 825, 799, 795, 839, 840, 765, 781,
781, 797, 821, 852, 836, 811, 771, 800, 752, 776,
755, 798, 839, 821, 794, 846, 834, 825, 825, 830,
814, 839, 760, 786, 747, 803, 717, 801, 819, 789,
824, 835, 806, 858, 774, 848, 793, 826, 796, 798,
773, 779, 775, 779, 806, 768, 787, 788, 822, 843,
780])
>>> values.max(), values.min()
(900, 713)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydata-151116092808-lva1-app6892/85/Statistical-inference-for-Python-Data-Analysis-An-introduction-12-320.jpg)


![daftCode sp. z o.o.
Example 2. Confidence intervals
● What is the mean number of entries?
● What is the 95% confidence interval for
calculated mean?
>>> # CI simulation
>>> def ci(v, no_reps):
... for i in range(no_reps):
... idx = np.random.randint(0, len(v), size=len(v))
... yield v[idx].mean()
>>> # Get simulated means
>>> gen = ci(values, 10000)
>>> sim_means = np.fromiter(gen, 'float')
>>> # 95% Confidence interval
>>> (ci_low, ci_high) = np.percentile(sim_means, [2.5, 97.5])
>>> print(ci_low, ci_high)
797.942 810.350](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydata-151116092808-lva1-app6892/85/Statistical-inference-for-Python-Data-Analysis-An-introduction-15-320.jpg)
![daftCode sp. z o.o.
Example 3. Comparing distributions
>>> ok = np.array(ok) # non-fraud
>>> fraud = np.array(fraud)
>>> np.median(ok)
140261.0
>>> np.median(fraud)
109883.0
● Unknown distributions:
nonparametric test
>>> ss.mannwhitneyu(ok, fraud)
MannwhitneyuResuls(statistic=54457079.5,
pvalue=1.05701588547616e-59)
● Equalize sample sizes (just to be
sure)
>>> N = len(fraud)
>>> idx = np.arange(0, len(ok))
>>> np.random.shuffle(idx)
>>> ok_subsample = ok[idx[:N]]
>>> ss.mannwhitneyu(ok_subsample, fraud)
>>> MannwhitneyuResult(statistic=3548976.0,
pvalue=3.1818273295679098e-30)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydata-151116092808-lva1-app6892/85/Statistical-inference-for-Python-Data-Analysis-An-introduction-17-320.jpg)

![daftCode sp. z o.o.
Example 4. Bootstrap
>>> # generate statistics
>>> def generate_statistics(vec1, vec2, no_reps=10000):
... all_ = np.r_[vec1, vec2]
... N, M = len(vec1), len(vec2)
... for i in range(no_reps):
... random_indices = np.random.randint(0, M+N, size=M+N)
... tmp1 = all_[random_indices[:M]]
... tmp2 = all_[random_indices[M:]]
... yield np.abs(np.median(tmp1) – np.median(tmp2))
>>> # Initial statistic
>>> stat_0 = np.abs(np.median(ok) – np.median(fraud))
>>> gen = generate_statistics(ok, fraud)
>>> stats = np.fromiter(gen, 'float')
>>> # Get the probability of obtaining statistic larger then initial
>>> np.sum(stats >= stat_0)/len(stats)
0.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydata-151116092808-lva1-app6892/85/Statistical-inference-for-Python-Data-Analysis-An-introduction-19-320.jpg)


![daftCode sp. z o.o.
Example 5. Naive Bayes
>>> # Retrieve probability based on histogram
>>> def get_prob(value, bins, probs):
... idx = np.searchsorted(bins)
... return probs[idx]
>>> N = len(ok) + len(fraud)
>>> P_ok = len(ok)/N
>>> P_fraud = len(fraud)/N
>>> probs_ok, bins_ok = np.histogram(ok, bins=500, normed=True)
>>> probs_fraud, bins_fraud = np.histogram(fraud, bins=bins_ok, normed=True)
>>> # Test!
>>> test_times = np.linspace(0, 1e6, 100000)
>>> detected_as_fraud = 0
>>> detected_as_ok = 0
>>> for el in test_times:
... p_ok = get_prob(el, bins_ok, probs_ok)*P_ok
... p_fr = get_prob(el, bins_fraud, probs_fraud)*P_fraud
... if p_ok > p_fr:
... detected_as_ok += 1
... else:
... detected_as_fraud += 1
>>> print(detected_as_ok, detected_as_fraud)
100000 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydata-151116092808-lva1-app6892/85/Statistical-inference-for-Python-Data-Analysis-An-introduction-22-320.jpg)



Ad
Recommended
NumPy/SciPy Statistics



NumPy/SciPy StatisticsEnthought, Inc. Travis Oliphant, author of NumPy, presents an introduction into NumPy and SciPy tools for statistical analysis including scipy.stats.
Scientific Computing with Python - NumPy | WeiYuan



Scientific Computing with Python - NumPy | WeiYuanWei-Yuan Chang This document provides an overview of NumPy, the fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It discusses NumPy's powerful N-dimensional array object and sophisticated broadcasting functions. The document outlines topics including Ndarray, creating and manipulating arrays, array properties, basic operations, matrices, and advanced usages like boolean indexing and masking. NumPy allows efficient storage and manipulation of multi-dimensional data, and integration with languages like C/C++ and Fortran.
Effective Numerical Computation in NumPy and SciPy



Effective Numerical Computation in NumPy and SciPyKimikazu Kato This document provides an overview of effective numerical computation in NumPy and SciPy. It discusses how Python can be used for numerical computation tasks like differential equations, simulations, and machine learning. While Python is initially slower than languages like C, libraries like NumPy and SciPy allow Python code to achieve sufficient speed through techniques like broadcasting, indexing, and using sparse matrix representations. The document provides examples of how to efficiently perform tasks like applying functions element-wise to sparse matrices and calculating norms. It also presents a case study for efficiently computing a formula that appears in a machine learning paper using different sparse matrix representations in SciPy.
Intoduction to numpy



Intoduction to numpyFaraz Ahmed NumPy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python that provides multidimensional array objects and tools to work with arrays. Arrays store values of the same data type and are faster than lists. Two-dimensional arrays are commonly used for exploratory data analysis. Array operations are very fast.
Numpy Talk at SIAM



Numpy Talk at SIAMEnthought, Inc. SciPy and NumPy are Python packages that provide scientific computing capabilities. NumPy provides multidimensional array objects and fast linear algebra functions. SciPy builds on NumPy and adds modules for optimization, integration, signal and image processing, and more. Together, NumPy and SciPy give Python powerful data analysis and visualization capabilities. The community contributes to both projects to expand their functionality. Memory mapped arrays in NumPy allow working with large datasets that exceed system memory.
Python - Numpy/Pandas/Matplot Machine Learning Libraries



Python - Numpy/Pandas/Matplot Machine Learning LibrariesAndrew Ferlitsch Abstract: This PDSG workshop introduces the basics of Python libraries used in machine learning. Libraries covered are Numpy, Pandas and MathlibPlot.
Level: Fundamental
Requirements: One should have some knowledge of programming and some statistics.
Introduction to NumPy (PyData SV 2013)



Introduction to NumPy (PyData SV 2013)PyData NumPy is a Python library used for working with multidimensional arrays and matrices for scientific computing. It allows fast operations on arrays through optimized C code and is the foundation of the Python scientific computing stack. NumPy arrays can be created in many ways and support operations like indexing, slicing, broadcasting, and universal functions. NumPy provides many useful features for linear algebra, Fourier transforms, random number generation and more.
Introduction to numpy Session 1



Introduction to numpy Session 1Jatin Miglani This document is useful when use with Video session I have recorded today with execution, This is document no. 2 of course "Introduction of Data Science using Python". Which is a prerequisite of Artificial Intelligence course at Ethans Tech.
Disclaimer: Some of the Images and content have been taken from Multiple online sources and this presentation is intended only for Knowledge Sharing
NumPy Refresher



NumPy RefresherLukasz Dobrzanski numpy warmup (API and key concepts) ~10min
HTML version: https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/1565687/speak/NumPy%20Refresher/index.html
NumPy



NumPyAbhijeetAnand88 This document contains a presentation by Abhijeet Anand on NumPy. It introduces NumPy as a Python library for working with arrays, which aims to provide array objects that are faster than traditional Python lists. NumPy arrays benefit from being stored continuously in memory, unlike lists. The presentation covers 1D, 2D and 3D arrays in NumPy and basic array properties and operations like shape, size, dtype, copying, sorting, addition, subtraction and more.
Introduction to NumPy for Machine Learning Programmers



Introduction to NumPy for Machine Learning ProgrammersKimikazu Kato Presented at PyData Tokyo Meetup, April 3, 2015.
2015年4月3日PyData Tokyo Meetupでのプレゼン資料です。
NumPyを使って機械学習の実装をするときのコツについてまとめています。
Numpy



NumpyJyoti shukla This document provides an introduction to NumPy, the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python. It discusses what NumPy is, why it is useful compared to regular Python lists, how to define arrays of different dimensions, and how to initialize, manipulate, and perform operations on NumPy arrays. Some key capabilities of NumPy include N-dimensional arrays, broadcasting functions, integration with C/C++ and Fortran code, and tools for linear algebra and Fourier transforms.
Scientific Computing with Python Webinar March 19: 3D Visualization with Mayavi



Scientific Computing with Python Webinar March 19: 3D Visualization with MayaviEnthought, Inc. In this webinar, Didrik Pinte provides an introduction to MayaVi, the 3D interactive visualization library for the open source Enthought Tool Suite. These tools provide scientists and engineers a sophisticated Python development framework for analysis and visualization.
NUMPY 



NUMPY Global Academy of Technology NumPy is a Python library that provides multidimensional array and matrix objects to perform scientific computing. It contains efficient functions for operations on arrays like arithmetic, aggregation, copying, indexing, slicing, and reshaping. NumPy arrays have advantages over native Python sequences like fixed size and efficient mathematical operations. Common NumPy operations include elementwise arithmetic, aggregation functions, copying and transposing arrays, changing array shapes, and indexing/slicing arrays.
Python NumPy Tutorial | NumPy Array | Edureka



Python NumPy Tutorial | NumPy Array | EdurekaEdureka! ( Python Training: https://www.edureka.co/python )
This Edureka Python Numpy tutorial (Python Tutorial Blog: https://goo.gl/wd28Zr) explains what exactly is Numpy and how it is better than Lists. It also explains various Numpy operations with examples.
Check out our Python Training Playlist: https://goo.gl/Na1p9G
This tutorial helps you to learn the following topics:
1. What is Numpy?
2. Numpy v/s Lists
3. Numpy Operations
4. Numpy Special Functions
Introduction to numpy



Introduction to numpyGaurav Aggarwal This document provides an introduction and overview of NumPy, a Python library used for numerical computing. It discusses NumPy's origins and capabilities, how to install NumPy on Linux, key NumPy concepts like the ndarray object, and how NumPy can be used with Matplotlib for plotting. Examples are given of common NumPy operations and functions for arrays, as well as plotting simple graphs with Matplotlib.
Cheat Sheet for Machine Learning in Python: Scikit-learn



Cheat Sheet for Machine Learning in Python: Scikit-learnKarlijn Willems Get started with machine learning in Python thanks to this scikit-learn cheat sheet, which is a handy one-page reference that guides you through the several steps to make your own machine learning models. Thanks to the code examples, you won't get lost!
Pythonで機械学習入門以前



Pythonで機械学習入門以前Kimikazu Kato This document discusses Python and machine learning libraries like scikit-learn. It provides code examples for loading data, fitting models, and making predictions using scikit-learn algorithms. It also covers working with NumPy arrays and loading data from files like CSVs.
Python seaborn cheat_sheet



Python seaborn cheat_sheetNishant Upadhyay The document provides an overview of the Seaborn Python library for statistical data visualization. It discusses preparing data, controlling figure aesthetics, basic plot types like scatter plots and histograms, customizing plots, and using built-in datasets. Key steps include importing libraries, setting the style, loading datasets, and calling plotting functions to visualize relationships in the data.
Python for R Users



Python for R UsersAjay Ohri A side by side comparison of using Python for R users using a standard data science/ analytics workflow
1 seaborn introduction 



1 seaborn introduction YuleiLi3 This document introduces the Seaborn library for statistical data visualization in Python. It discusses how Seaborn builds on Matplotlib and Pandas to provide higher-level visualization functions. Specifically, it covers using distplot to create histograms and kernel density estimates, regplot for scatter plots and regression lines, and lmplot for faceted scatter plot grids. Examples are provided to illustrate customizing distplot, combining different plot elements, and using faceting controls in lmplot.
Numpy tutorial(final) 20160303



Numpy tutorial(final) 20160303Namgee Lee https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-dev/user/quickstart.html
에 내용 중 Shape Manipulation과 Copies And Views 부분에 대한 발표자료.
The Joy of SciPy



The Joy of SciPykammeyer This document provides a summary of the history and capabilities of SciPy. It discusses how SciPy was founded in 2001 by Travis Oliphant with packages for optimization, sparse matrices, interpolation, integration, special functions, and more. It highlights key contributors to the SciPy community and ecosystem. It describes why Python is well-suited for technical computing due to its syntax, built-in array support, and ability to support multiple programming styles. It outlines NumPy's array-oriented approach and benefits for technical problems. Finally, it discusses new projects like Blaze and Numba that aim to further improve the SciPy software stack.
Pandas Cheat Sheet



Pandas Cheat SheetACASH1011 The document is a cheat sheet for data wrangling with pandas, providing syntax and methods for creating and manipulating DataFrames, reshaping and subsetting data, summarizing data, combining datasets, filtering and joining data, grouping data, handling missing values, and plotting data. Key methods described include pd.melt() to gather columns into rows, pd.pivot() to spread rows into columns, pd.concat() to append DataFrames, df.sort_values() to order rows by column values, and df.groupby() to group data.
Python Scipy Numpy



Python Scipy NumpyGirish Khanzode This document provides an overview of the Python programming language. It discusses Python's history and evolution, its key features like being object-oriented, open source, portable, having dynamic typing and built-in types/tools. It also covers Python's use for numeric processing with libraries like NumPy and SciPy. The document explains how to use Python interactively from the command line and as scripts. It describes Python's basic data types like integers, floats, strings, lists, tuples and dictionaries as well as common operations on these types.
Pandas pythonfordatascience



Pandas pythonfordatascienceNishant Upadhyay The document provides an overview of the Pandas library in Python for working with data structures like Series and DataFrames. It covers common operations for selecting, filtering, sorting, applying functions, handling missing data, and reading/writing data to files and databases. These operations allow for easy manipulation and analysis of data in Pandas.
Python matplotlib cheat_sheet



Python matplotlib cheat_sheetNishant Upadhyay Matplotlib is a Python library used for 2D plotting. It can create publication-quality figures in both hardcopy and interactive formats across platforms. The basic steps for creating plots with Matplotlib are: 1) prepare data, 2) create a plot, 3) add elements to the plot, 4) customize the plot, 5) save the plot, and 6) show the plot. Matplotlib provides various functions for plotting different types of data, customizing figures, axes, and layouts.
Python for R developers and data scientists



Python for R developers and data scientistsLambda Tree This is an introductory talk aimed at data scientists who are well versed with R but would like to work with Python as well. I will cover common workflows in R and how they translate into Python. No Python experience necessary.
Python for Scientists



Python for ScientistsAndreas Dewes Python is a multi-paradigm programming language that can be used for scientific applications. It has libraries for tasks like data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. Examples shown include using Python to acquire data from instruments via VISA, analyze data with NumPy and SciPy, and create graphical user interfaces and visualizations with Matplotlib and PyQt. The document provides an overview of Python's capabilities and examples of code for common scientific computing tasks.
Simple APIs and innovative documentation



Simple APIs and innovative documentationPyDataParis Reasons for the succes of Scientific Python
Emmanuelle Gouillart, CNRS/Saint Gobain SVI
@ PyDataParis2016
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
NumPy Refresher



NumPy RefresherLukasz Dobrzanski numpy warmup (API and key concepts) ~10min
HTML version: https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/1565687/speak/NumPy%20Refresher/index.html
NumPy



NumPyAbhijeetAnand88 This document contains a presentation by Abhijeet Anand on NumPy. It introduces NumPy as a Python library for working with arrays, which aims to provide array objects that are faster than traditional Python lists. NumPy arrays benefit from being stored continuously in memory, unlike lists. The presentation covers 1D, 2D and 3D arrays in NumPy and basic array properties and operations like shape, size, dtype, copying, sorting, addition, subtraction and more.
Introduction to NumPy for Machine Learning Programmers



Introduction to NumPy for Machine Learning ProgrammersKimikazu Kato Presented at PyData Tokyo Meetup, April 3, 2015.
2015年4月3日PyData Tokyo Meetupでのプレゼン資料です。
NumPyを使って機械学習の実装をするときのコツについてまとめています。
Numpy



NumpyJyoti shukla This document provides an introduction to NumPy, the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python. It discusses what NumPy is, why it is useful compared to regular Python lists, how to define arrays of different dimensions, and how to initialize, manipulate, and perform operations on NumPy arrays. Some key capabilities of NumPy include N-dimensional arrays, broadcasting functions, integration with C/C++ and Fortran code, and tools for linear algebra and Fourier transforms.
Scientific Computing with Python Webinar March 19: 3D Visualization with Mayavi



Scientific Computing with Python Webinar March 19: 3D Visualization with MayaviEnthought, Inc. In this webinar, Didrik Pinte provides an introduction to MayaVi, the 3D interactive visualization library for the open source Enthought Tool Suite. These tools provide scientists and engineers a sophisticated Python development framework for analysis and visualization.
NUMPY 



NUMPY Global Academy of Technology NumPy is a Python library that provides multidimensional array and matrix objects to perform scientific computing. It contains efficient functions for operations on arrays like arithmetic, aggregation, copying, indexing, slicing, and reshaping. NumPy arrays have advantages over native Python sequences like fixed size and efficient mathematical operations. Common NumPy operations include elementwise arithmetic, aggregation functions, copying and transposing arrays, changing array shapes, and indexing/slicing arrays.
Python NumPy Tutorial | NumPy Array | Edureka



Python NumPy Tutorial | NumPy Array | EdurekaEdureka! ( Python Training: https://www.edureka.co/python )
This Edureka Python Numpy tutorial (Python Tutorial Blog: https://goo.gl/wd28Zr) explains what exactly is Numpy and how it is better than Lists. It also explains various Numpy operations with examples.
Check out our Python Training Playlist: https://goo.gl/Na1p9G
This tutorial helps you to learn the following topics:
1. What is Numpy?
2. Numpy v/s Lists
3. Numpy Operations
4. Numpy Special Functions
Introduction to numpy



Introduction to numpyGaurav Aggarwal This document provides an introduction and overview of NumPy, a Python library used for numerical computing. It discusses NumPy's origins and capabilities, how to install NumPy on Linux, key NumPy concepts like the ndarray object, and how NumPy can be used with Matplotlib for plotting. Examples are given of common NumPy operations and functions for arrays, as well as plotting simple graphs with Matplotlib.
Cheat Sheet for Machine Learning in Python: Scikit-learn



Cheat Sheet for Machine Learning in Python: Scikit-learnKarlijn Willems Get started with machine learning in Python thanks to this scikit-learn cheat sheet, which is a handy one-page reference that guides you through the several steps to make your own machine learning models. Thanks to the code examples, you won't get lost!
Pythonで機械学習入門以前



Pythonで機械学習入門以前Kimikazu Kato This document discusses Python and machine learning libraries like scikit-learn. It provides code examples for loading data, fitting models, and making predictions using scikit-learn algorithms. It also covers working with NumPy arrays and loading data from files like CSVs.
Python seaborn cheat_sheet



Python seaborn cheat_sheetNishant Upadhyay The document provides an overview of the Seaborn Python library for statistical data visualization. It discusses preparing data, controlling figure aesthetics, basic plot types like scatter plots and histograms, customizing plots, and using built-in datasets. Key steps include importing libraries, setting the style, loading datasets, and calling plotting functions to visualize relationships in the data.
Python for R Users



Python for R UsersAjay Ohri A side by side comparison of using Python for R users using a standard data science/ analytics workflow
1 seaborn introduction 



1 seaborn introduction YuleiLi3 This document introduces the Seaborn library for statistical data visualization in Python. It discusses how Seaborn builds on Matplotlib and Pandas to provide higher-level visualization functions. Specifically, it covers using distplot to create histograms and kernel density estimates, regplot for scatter plots and regression lines, and lmplot for faceted scatter plot grids. Examples are provided to illustrate customizing distplot, combining different plot elements, and using faceting controls in lmplot.
Numpy tutorial(final) 20160303



Numpy tutorial(final) 20160303Namgee Lee https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-dev/user/quickstart.html
에 내용 중 Shape Manipulation과 Copies And Views 부분에 대한 발표자료.
The Joy of SciPy



The Joy of SciPykammeyer This document provides a summary of the history and capabilities of SciPy. It discusses how SciPy was founded in 2001 by Travis Oliphant with packages for optimization, sparse matrices, interpolation, integration, special functions, and more. It highlights key contributors to the SciPy community and ecosystem. It describes why Python is well-suited for technical computing due to its syntax, built-in array support, and ability to support multiple programming styles. It outlines NumPy's array-oriented approach and benefits for technical problems. Finally, it discusses new projects like Blaze and Numba that aim to further improve the SciPy software stack.
Pandas Cheat Sheet



Pandas Cheat SheetACASH1011 The document is a cheat sheet for data wrangling with pandas, providing syntax and methods for creating and manipulating DataFrames, reshaping and subsetting data, summarizing data, combining datasets, filtering and joining data, grouping data, handling missing values, and plotting data. Key methods described include pd.melt() to gather columns into rows, pd.pivot() to spread rows into columns, pd.concat() to append DataFrames, df.sort_values() to order rows by column values, and df.groupby() to group data.
Python Scipy Numpy



Python Scipy NumpyGirish Khanzode This document provides an overview of the Python programming language. It discusses Python's history and evolution, its key features like being object-oriented, open source, portable, having dynamic typing and built-in types/tools. It also covers Python's use for numeric processing with libraries like NumPy and SciPy. The document explains how to use Python interactively from the command line and as scripts. It describes Python's basic data types like integers, floats, strings, lists, tuples and dictionaries as well as common operations on these types.
Pandas pythonfordatascience



Pandas pythonfordatascienceNishant Upadhyay The document provides an overview of the Pandas library in Python for working with data structures like Series and DataFrames. It covers common operations for selecting, filtering, sorting, applying functions, handling missing data, and reading/writing data to files and databases. These operations allow for easy manipulation and analysis of data in Pandas.
Python matplotlib cheat_sheet



Python matplotlib cheat_sheetNishant Upadhyay Matplotlib is a Python library used for 2D plotting. It can create publication-quality figures in both hardcopy and interactive formats across platforms. The basic steps for creating plots with Matplotlib are: 1) prepare data, 2) create a plot, 3) add elements to the plot, 4) customize the plot, 5) save the plot, and 6) show the plot. Matplotlib provides various functions for plotting different types of data, customizing figures, axes, and layouts.
Python for R developers and data scientists



Python for R developers and data scientistsLambda Tree This is an introductory talk aimed at data scientists who are well versed with R but would like to work with Python as well. I will cover common workflows in R and how they translate into Python. No Python experience necessary.
Similar to Statistical inference for (Python) Data Analysis. An introduction. (20)
Python for Scientists



Python for ScientistsAndreas Dewes Python is a multi-paradigm programming language that can be used for scientific applications. It has libraries for tasks like data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. Examples shown include using Python to acquire data from instruments via VISA, analyze data with NumPy and SciPy, and create graphical user interfaces and visualizations with Matplotlib and PyQt. The document provides an overview of Python's capabilities and examples of code for common scientific computing tasks.
Simple APIs and innovative documentation



Simple APIs and innovative documentationPyDataParis Reasons for the succes of Scientific Python
Emmanuelle Gouillart, CNRS/Saint Gobain SVI
@ PyDataParis2016
Python for Scientific Computing -- Ricardo Cruz



Python for Scientific Computing -- Ricardo Cruzrpmcruz This document discusses Python for scientific computing. It provides notes on NumPy, the fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. NumPy allows vectorized mathematical operations on multidimensional arrays in a simple and efficient manner. The notes cover common NumPy operations and syntax as compared to MATLAB and R. Pandas is also introduced as a package for data manipulation and analysis based on the concept of data frames from R. Examples are given of generating fake data to demonstrate modeling capabilities in Python.
Numpy_Pandas_for beginners_________.pptx



Numpy_Pandas_for beginners_________.pptxAbhi Marvel slide conatin the numpy related stuff, which is use full for thr beginners to understand
Machine Learning on Code - SF meetup



Machine Learning on Code - SF meetupsource{d} This document discusses machine learning on source code. It begins by defining machine learning on source code as applying machine learning where the input data is source code. It then discusses some of the challenges of applying machine learning to source code, including data retrieval and analysis. Finally, it provides examples of potential use cases like predicting the next token in code, learning to represent programs with graphs, and building tools to assist with code reviews.
Statistical Machine Learning for Text Classification with scikit-learn and NLTK



Statistical Machine Learning for Text Classification with scikit-learn and NLTKOlivier Grisel This document discusses using machine learning algorithms and natural language processing tools for text classification tasks. It covers using scikit-learn and NLTK to extract features from text, build predictive models, and evaluate performance on tasks like sentiment analysis, topic categorization, and language identification. Feature extraction methods discussed include bag-of-words, TF-IDF, n-grams, and collocations. Classifiers covered are Naive Bayes and linear support vector machines. The document reports typical accuracy results in the 70-97% range for different datasets and models.
Numpy_Cheat_Sheet.pdf



Numpy_Cheat_Sheet.pdfSkyNerve The NumPy library provides tools for working with multidimensional arrays in Python. It allows for creating, manipulating, and analyzing arrays. NumPy arrays can be created from data, imported/exported from files, reshaped, transposed, concatenated, split, and have elements added or removed. Arithmetic, logical, statistical and linear algebra operations can be performed on arrays.
Arrays basics



Arrays basicssudhirvegad The slide will give introduction to Arrays with C Programming language. It is useful to the beginners to work with.
Lec1



Lec1Nikhil Chilwant The document discusses data structures and algorithms. It defines key concepts like algorithms, programs, data structures, and asymptotic analysis. It explains how to analyze algorithms to determine their efficiency, including analyzing best, worst, and average cases. Common notations for describing asymptotic running time like Big-O, Big-Omega, and Big-Theta are introduced. The document provides examples of analyzing sorting algorithms like insertion sort and calculating running times. It also discusses techniques for proving an algorithm's correctness like assertions and loop invariants.
Regression and Classification with R



Regression and Classification with RYanchang Zhao This document discusses building regression and classification models in R, including linear regression, generalized linear models, and decision trees. It provides examples of building each type of model using various R packages and datasets. Linear regression is used to predict CPI data. Generalized linear models and decision trees are built to predict body fat percentage. Decision trees are also built on the iris dataset to classify flower species.
The System of Automatic Searching for Vulnerabilities or how to use Taint Ana...



The System of Automatic Searching for Vulnerabilities or how to use Taint Ana...Positive Hack Days This document discusses using taint analysis to automatically find vulnerabilities. It describes Alex Bazhanyuk and Nikita Tarakanov, who work on security research projects. Their presentation covers the System of Automatic Searching for Vulnerabilities (SASV), which uses taint analysis, BitBlaze tools like TEMU and VINE, and the STP constraint solver to automatically find vulnerabilities. SASV traces target programs, converts the traces to intermediate language code, and uses path exploration and symbolic execution to generate new test inputs that maximize code coverage and have the potential to trigger vulnerabilities.
Comparing EDA with classical and Bayesian analysis.pptx



Comparing EDA with classical and Bayesian analysis.pptxPremaGanesh1 This document provides an overview of exploratory data analysis (EDA) techniques and commonly used tools. It discusses classical and Bayesian statistical analysis approaches as well as EDA. Popular Python libraries for EDA include NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib and Seaborn. NumPy allows working with multidimensional arrays and matrices while Pandas facilitates working with structured data. The document also provides examples of creating arrays and dataframes, loading data from files, and analyzing datasets using these tools.
app4.pptx



app4.pptxsg4795 The WiMAX (IEEE 802.16e) standard offers peak data rates of 128Mbps downlink and
56Mbps uplink over 20MHz wide channels whilst the new standard in development, 4G
WiMAN-Advanced (802.16m) is targeting the requirements to be fully 4G using 64Q QAM,
BPSK and MIMO technologies to reach the 1Gbps rate. It is predicted that in an actual
deployment, using 4X2 MIMO in an urban microcell application using a 20 MHz TDD
channel, the 4G WiMAN-Advanced system will be able to support 120Mbps downlink and
60Mbps uplink per site concurrently. WiMAX applications are already in use in many countries
globally but research in 2010 gave results that showed only just over 350 set ups were actually
in use. Many previous WiMAX operators were found to have moved to LTE along with Yota,
who were the largest WiMAX operator in the world.
A Map of the PyData Stack



A Map of the PyData StackPeadar Coyle An exploration of what tools to use to extract insights out of your small/medium/big data in Python. And what the future will bring.
Introduction to Tensorflow



Introduction to TensorflowTzar Umang An introduction to Google's AI Engine, look deeper into Artificial Networks and Machine Learning. Appreciate how our simplest neural network be codified and be used to data analytics.
Machine Learning With R



Machine Learning With RDavid Chiu This document discusses using machine learning with R for data analysis. It covers topics like preparing data, running models, and interpreting results. It explains techniques like regression, classification, dimensionality reduction, and clustering. Regression is used to predict numbers given other numbers, while classification identifies categories. Dimensionality reduction finds combinations of variables with maximum variance. Clustering groups similar data points. R is recommended for its statistical analysis, functions, and because it is free and open source. Examples are provided for techniques like linear regression, support vector machines, principal component analysis, and k-means clustering.
Decision Tree.pptx



Decision Tree.pptxRamakrishna Reddy Bijjam The document discusses decision trees and their use in R. It contains 3 key points:
1. Decision trees can be used to predict outcomes like spam detection based on input variables. The nodes represent choices and edges represent decision rules.
2. An example creates a decision tree using the 'party' package in R to predict reading skills based on variables like age, shoe size, and native language.
3. The 'rpart' package can also be used to create and visualize decision trees, as shown through an example predicting insurance fraud based on rear-end collisions.
Numerical tour in the Python eco-system: Python, NumPy, scikit-learn



Numerical tour in the Python eco-system: Python, NumPy, scikit-learnArnaud Joly We first present the Python programming language and the NumPy package for scientific computing. Then, we devise a digit recognition system highlighting the scikit-learn package.
NumPy.pptx



NumPy.pptxEN1036VivekSingh NumPy is a Python package that provides multidimensional array and matrix objects as well as tools to work with these objects. It was created to handle large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices efficiently. NumPy arrays enable fast operations on large datasets and facilitate scientific computing using Python. NumPy also contains functions for Fourier transforms, random number generation and linear algebra operations.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Bonk coin airdrop_ Everything You Need to Know.pdf



Bonk coin airdrop_ Everything You Need to Know.pdfHerond Labs The Bonk airdrop, one of the largest in Solana’s history, distributed 50% of its total supply to community members, significantly boosting its popularity and Solana’s network activity. Below is everything you need to know about the Bonk coin airdrop, including its history, eligibility, how to claim tokens, risks, and current status.
https://blog.herond.org/bonk-coin-airdrop/
Artificial Intelligence Applications Across Industries



Artificial Intelligence Applications Across IndustriesSandeepKS52 Artificial Intelligence is a rapidly growing field that influences many aspects of modern life, including transportation, healthcare, and finance. Understanding the basics of AI provides insight into how machines can learn and make decisions, which is essential for grasping its applications in various industries. In the automotive sector, AI enhances vehicle safety and efficiency through advanced technologies like self-driving systems and predictive maintenance. Similarly, in healthcare, AI plays a crucial role in diagnosing diseases and personalizing treatment plans, while in financial services, it helps in fraud detection and risk management. By exploring these themes, a clearer picture of AI's transformative impact on society emerges, highlighting both its potential benefits and challenges.
From Chaos to Clarity - Designing (AI-Ready) APIs with APIOps Cycles



From Chaos to Clarity - Designing (AI-Ready) APIs with APIOps CyclesMarjukka Niinioja Teams delivering API are challenges with:
- Connecting APIs to business strategy
- Measuring API success (audit & lifecycle metrics)
- Partner/Ecosystem onboarding
- Consistent documentation, security, and publishing
🧠 The big takeaway?
Many teams can build APIs. But few connect them to value, visibility, and long-term improvement.
That’s why the APIOps Cycles method helps teams:
📍 Start where the pain is (one “metro station” at a time)
📈 Scale success across strategy, platform, and operations
🛠 Use collaborative canvases to get buy-in and visibility
Want to try it and learn more?
- Follow APIOps Cycles in LinkedIn
- Visit the www.apiopscycles.com site
- Subscribe to email list
-
OpenTelemetry 101 Cloud Native Barcelona



OpenTelemetry 101 Cloud Native BarcelonaImma Valls Bernaus A brief introduction to OpenTelemetry, with a practical example of auto-instrumenting a Java web application with the Grafana stack (Loki, Grafana, Tempo, and Mimir).
Generative Artificial Intelligence and its Applications



Generative Artificial Intelligence and its ApplicationsSandeepKS52 The exploration of generative AI begins with an overview of its fundamental concepts, highlighting how these technologies create new content and ideas by learning from existing data. Following this, the focus shifts to the processes involved in training and fine-tuning models, which are essential for enhancing their performance and ensuring they meet specific needs. Finally, the importance of responsible AI practices is emphasized, addressing ethical considerations and the impact of AI on society, which are crucial for developing systems that are not only effective but also beneficial and fair.
Leveraging Foundation Models to Infer Intents



Leveraging Foundation Models to Infer IntentsKeheliya Gallaba Invited Talk at RAISE 2025: Requirements engineering for AI-powered SoftwarE Workshop co-located with ICSE, the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Software Engineering.
Abstract: Foundation Models (FMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in various natural language tasks. However, their ability to accurately capture stakeholder requirements remains a significant challenge for using FMs for software development. This paper introduces a novel approach that leverages an FM-powered multi-agent system called AlignMind to address this issue. By having a cognitive architecture that enhances FMs with Theory-of-Mind capabilities, our approach considers the mental states and perspectives of software makers. This allows our solution to iteratively clarify the beliefs, desires, and intentions of stakeholders, translating these into a set of refined requirements and a corresponding actionable natural language workflow in the often-overlooked requirements refinement phase of software engineering, which is crucial after initial elicitation. Through a multifaceted evaluation covering 150 diverse use cases, we demonstrate that our approach can accurately capture the intents and requirements of stakeholders, articulating them as both specifications and a step-by-step plan of action. Our findings suggest that the potential for significant improvements in the software development process justifies these investments. Our work lays the groundwork for future innovation in building intent-first development environments, where software makers can seamlessly collaborate with AIs to create software that truly meets their needs.
Top 5 Task Management Software to Boost Productivity in 2025



Top 5 Task Management Software to Boost Productivity in 2025Orangescrum In this blog, you’ll find a curated list of five powerful task management tools to watch in 2025. Each one is designed to help teams stay organized, improve collaboration, and consistently hit deadlines. We’ve included real-world use cases, key features, and data-driven insights to help you choose what fits your team best.
Providing Better Biodiversity Through Better Data



Providing Better Biodiversity Through Better DataSafe Software This session explores how FME is transforming data workflows at Ireland’s National Biodiversity Data Centre (NBDC) by eliminating manual data manipulation, incorporating machine learning, and enhancing overall efficiency. Attendees will gain insight into how NBDC is using FME to document and understand internal processes, make decision-making fully transparent, and shine a light on underlying code to improve clarity and reduce silent failures.
The presentation will also outline NBDC’s future plans for FME, including empowering staff to access and query data independently, without relying on external consultants. It will also showcase ambitions to connect to new data sources, unlock the full potential of its valuable datasets, create living atlases, and place its valuable data directly into the hands of decision-makers across Ireland—ensuring that biodiversity is not only protected but actively enhanced.
How Insurance Policy Management Software Streamlines Operations



How Insurance Policy Management Software Streamlines OperationsInsurance Tech Services Insurance policy management software transforms complex, manual insurance operations into streamlined, efficient digital workflows, enhancing productivity, accuracy, customer service, and profitability for insurers. Visit https://www.damcogroup.com/insurance/policy-management-software for more details!
Async-ronizing Success at Wix - Patterns for Seamless Microservices - Devoxx ...



Async-ronizing Success at Wix - Patterns for Seamless Microservices - Devoxx ...Natan Silnitsky In a world where speed, resilience, and fault tolerance define success, Wix leverages Kafka to power asynchronous programming across 4,000 microservices. This talk explores four key patterns that boost developer velocity while solving common challenges with scalable, efficient, and reliable solutions:
1. Integration Events: Shift from synchronous calls to pre-fetching to reduce query latency and improve user experience.
2. Task Queue: Offload non-critical tasks like notifications to streamline request flows.
3. Task Scheduler: Enable precise, fault-tolerant delayed or recurring workflows with robust scheduling.
4. Iterator for Long-running Jobs: Process extensive workloads via chunked execution, optimizing scalability and resilience.
For each pattern, we’ll discuss benefits, challenges, and how we mitigate drawbacks to create practical solutions
This session offers actionable insights for developers and architects tackling distributed systems, helping refine microservices and adopting Kafka-driven async excellence.
Who will create the languages of the future?



Who will create the languages of the future?Jordi Cabot Will future languages be created by language engineers?
Can you "vibe" a DSL?
In this talk, we will explore the changing landscape of language engineering and discuss how Artificial Intelligence and low-code/no-code techniques can play a role in this future by helping in the definition, use, execution, and testing of new languages. Even empowering non-tech users to create their own language infrastructure. Maybe without them even realizing.
Revolutionize Your Insurance Workflow with Claims Management Software



Revolutionize Your Insurance Workflow with Claims Management SoftwareInsurance Tech Services Claims management software enhances efficiency, accuracy, and satisfaction by automating processes, reducing errors, and speeding up transparent claims handling—building trust and cutting costs. Explore More - https://www.damcogroup.com/insurance/claims-management-software
Essentials of Resource Planning in a Downturn



Essentials of Resource Planning in a DownturnOnePlan Solutions In a tight labor market and tighter economy, PMOs and resource managers must ensure that every team member is focused on the highest-value work. This session explores how AI reshapes resource planning and empowers organizations to forecast capacity, prevent burnout, and balance workloads more effectively, even with shrinking teams.
COBOL Programming with VSCode - IBM Certificate



COBOL Programming with VSCode - IBM CertificateVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ COBOL Programming with VSCode - IBM Certificate
Marketo & Dynamics can be Most Excellent to Each Other – The Sequel



Marketo & Dynamics can be Most Excellent to Each Other – The SequelBradBedford3 So you’ve built trust in your Marketo Engage-Dynamics integration—excellent. But now what?
This sequel picks up where our last adventure left off, offering a step-by-step guide to move from stable sync to strategic power moves. We’ll share real-world project examples that empower sales and marketing to work smarter and stay aligned.
If you’re ready to go beyond the basics and do truly most excellent stuff, this session is your guide.
Automating Map Production With FME and Python



Automating Map Production With FME and PythonSafe Software People still love a good paper map, but every time a request lands on a GIS team’s desk, it takes time to create that perfect, individual map—even when you're ready and have projects prepped. Then come the inevitable changes and iterations that add even more time to the process. This presentation explores a solution for automating map production using FME and Python. FME handles the setup of variables, leveraging GIS reference layers and parameters to manage details like map orientation, label sizes, and layout elements. Python takes over to export PDF maps for each location and template size, uploading them monthly to ArcGIS Online. The result? Fresh, regularly updated maps, ready for anyone to grab anytime—saving you time, effort, and endless revisions while keeping users happy with up-to-date, accessible maps.
FME for Climate Data: Turning Big Data into Actionable Insights



FME for Climate Data: Turning Big Data into Actionable InsightsSafe Software Regional and local governments aim to provide essential services for stormwater management systems. However, rapid urbanization and the increasing impacts of climate change are putting growing pressure on these governments to identify stormwater needs and develop effective plans. To address these challenges, GHD developed an FME solution to process over 20 years of rainfall data from rain gauges and USGS radar datasets. This solution extracts, organizes, and analyzes Next Generation Weather Radar (NEXRAD) big data, validates it with other data sources, and produces Intensity Duration Frequency (IDF) curves and future climate projections tailored to local needs. This presentation will showcase how FME can be leveraged to manage big data and prioritize infrastructure investments.
Key AI Technologies Used by Indian Artificial Intelligence Companies



Key AI Technologies Used by Indian Artificial Intelligence CompaniesMypcot Infotech Indian tech firms are rapidly adopting advanced tools like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to drive innovation. These key AI technologies enable smarter automation, data analysis, and decision-making. Leading developments are shaping the future of digital transformation among top artificial intelligence companies in India.
For more information please visit here https://www.mypcot.com/artificial-intelligence
Software Engineering Process, Notation & Tools Introduction - Part 3



Software Engineering Process, Notation & Tools Introduction - Part 3Gaurav Sharma Software Engineering Process, Notation & Tools Introduction
Ad
Statistical inference for (Python) Data Analysis. An introduction.
- 1. daftCode sp. z o.o. Statistical inference for (Python) Data Analysis. An introduction Piotr Milanowski
- 2. daftCode sp. z o.o. Statistical inference? Wait, why? ● Quantify a level of trust for values you obtain ● Compare values ● Infer validity of provided data
- 3. daftCode sp. z o.o. Buzz phrases for this talk ● Probability ● Distribution ● Random variable ● Significance ● Hypothesis testing ● Statistic
- 4. daftCode sp. z o.o. Part 1. Preparation.
- 5. daftCode sp. z o.o. Building Python statistical stack ● Necessary modules: Numpy Scipy ● Helpful modules: Pandas Matplotlib
- 6. daftCode sp. z o.o. NumPy ● http://www.numpy.org ● Numerical library ● Optimized for speed and memory efficiency ● Many useful and intuitive functionalities, and methods (especially for multidimensional arrays)
- 7. daftCode sp. z o.o. NumPy (Example) Python >>> # Vector >>> v = [1, 2, 3, 4] >>> # scaling vector 2v >>> v2 = [2*i for i in v] >>> # Adding vectors v+v2 >>> v3 = [v[i]+v2[i] for i in range(len(v))] >>> # Vector normalization >>> mean = sum(v)/len(v) >>> zero_mean = [(i – mean) for i in v] >>> std = sum(i**2 for i in zero_mean)/len(v) >>> normalized = [i/std for i in zero_mean] Python + NumPy >>> import numpy as np >>> # Vector >>> v = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) >>> # sacling vector 2v >>> v2 = 2*v >>> # Adding vectors v+v2 >>> v3 = v2 + v >>> # Normalization >>> normalized = v.mean()/v.std()
- 8. daftCode sp. z o.o. SciPy ● http://www.scipy.org ● A set of scientific libraries for signal analysis (scipy.signal), image analysis (scipy.ndimage), Fourier transform (scipy.fftpack), linear algebra (scipy.linalg), integration (scipy.integrate)….. ● Here: scipy.stats
- 9. daftCode sp. z o.o. Pandas & Matplotlib ● http://pandas.pydata.org ● Great datastructures with helpful methods ● http://matplotlib.org/ ● Visualization library
- 10. daftCode sp. z o.o. Part 2. Examples
- 11. daftCode sp. z o.o. Eaxample 1. Anomaly detection. ● Data: number of daily page entries from 3 months ● Question: should we be suspicious if for a given day we have 800, 850 and 900 entries?
- 12. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 1. Anomaly detection >>> import numpy as np >>> values = np.array([…]) # Get values from >>> # somewhere >>> values array([796, 756, 827, 779, 787, 731, 847, 829, 794, 790, 831, 820, 822, 792, 767, 757, 777, 775, 799, 756, 849, 808, 800, 823, 798, 809, 783, 800, 848, 772, 853, 759, 745, 868, 713, 863, 819, 829, 799, 777, 785, 812, 877, 839, 783, 867, 875, 829, 818, 813, 763, 829, 812, 867, 790, 748, 822, 774, 900, 830, 781, 795, 825, 799, 795, 839, 840, 765, 781, 781, 797, 821, 852, 836, 811, 771, 800, 752, 776, 755, 798, 839, 821, 794, 846, 834, 825, 825, 830, 814, 839, 760, 786, 747, 803, 717, 801, 819, 789, 824, 835, 806, 858, 774, 848, 793, 826, 796, 798, 773, 779, 775, 779, 806, 768, 787, 788, 822, 843, 780]) >>> values.max(), values.min() (900, 713)
- 13. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 1. Anomaly detection ● Assumption: values are drawn from Poisson distribution ● What is the probability of obtaining 800, 850, 900 for Poisson distribution fitted to this data? ● What is threshold value? ● scipy.stats.poisson (and many other distributions)
- 14. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 1. Anomaly detection >>> import scipy.stats as ss >>> # Calculating distribution parameter >>> mu = values.mean() >>> # Check for 800 >>> 1 – ss.poisson.cdf(800, mu) # equal to ss.poisson.sf(800, mu) 0.548801 >>> # Check for 900 >>> 1 – ss.poisson.cdf(900, mu) 0.00042 >>> # Check for 850 >>> 1 – ss.poisson.cdf(850, mu) 0.05205 >>> # Threshold for magical 5% >>> ss.poisson.ppf(0.95, mu) 851 ● 3 lines of code (read data, calculate distribution parameter, calculate threshold), and the detector is ready!
- 15. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 2. Confidence intervals ● What is the mean number of entries? ● What is the 95% confidence interval for calculated mean? >>> # CI simulation >>> def ci(v, no_reps): ... for i in range(no_reps): ... idx = np.random.randint(0, len(v), size=len(v)) ... yield v[idx].mean() >>> # Get simulated means >>> gen = ci(values, 10000) >>> sim_means = np.fromiter(gen, 'float') >>> # 95% Confidence interval >>> (ci_low, ci_high) = np.percentile(sim_means, [2.5, 97.5]) >>> print(ci_low, ci_high) 797.942 810.350
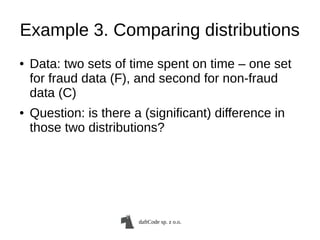
- 16. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 3. Comparing distributions ● Data: two sets of time spent on time – one set for fraud data (F), and second for non-fraud data (C) ● Question: is there a (significant) difference in those two distributions?
- 17. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 3. Comparing distributions >>> ok = np.array(ok) # non-fraud >>> fraud = np.array(fraud) >>> np.median(ok) 140261.0 >>> np.median(fraud) 109883.0 ● Unknown distributions: nonparametric test >>> ss.mannwhitneyu(ok, fraud) MannwhitneyuResuls(statistic=54457079.5, pvalue=1.05701588547616e-59) ● Equalize sample sizes (just to be sure) >>> N = len(fraud) >>> idx = np.arange(0, len(ok)) >>> np.random.shuffle(idx) >>> ok_subsample = ok[idx[:N]] >>> ss.mannwhitneyu(ok_subsample, fraud) >>> MannwhitneyuResult(statistic=3548976.0, pvalue=3.1818273295679098e-30)
- 18. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 4. Bootstrap ● The same data and question as previous ● Test without any build-in tests ● Hypothesis 0: both datasets are drawn from the same distribution ● Mix them together, draw two new datasets (with replacement), calculate statistic (difference in median) ● Probability of obtaining statistic larger or equal to the initial one (from original data)
- 19. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 4. Bootstrap >>> # generate statistics >>> def generate_statistics(vec1, vec2, no_reps=10000): ... all_ = np.r_[vec1, vec2] ... N, M = len(vec1), len(vec2) ... for i in range(no_reps): ... random_indices = np.random.randint(0, M+N, size=M+N) ... tmp1 = all_[random_indices[:M]] ... tmp2 = all_[random_indices[M:]] ... yield np.abs(np.median(tmp1) – np.median(tmp2)) >>> # Initial statistic >>> stat_0 = np.abs(np.median(ok) – np.median(fraud)) >>> gen = generate_statistics(ok, fraud) >>> stats = np.fromiter(gen, 'float') >>> # Get the probability of obtaining statistic larger then initial >>> np.sum(stats >= stat_0)/len(stats) 0.0
- 20. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 5. Naive Bayes ● Can we classify fraud based on time spent on a page? ● Using Naive Bayes: P(F|t) ~ P(t|F)P(F) P(C|t) ~ P(t|C)P(C) ● P(t|F), P(t|C) are sample distributions P(C), P(F)
- 21. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 5. Naive Bayes P(t∣C) P(t∣F)
- 22. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 5. Naive Bayes >>> # Retrieve probability based on histogram >>> def get_prob(value, bins, probs): ... idx = np.searchsorted(bins) ... return probs[idx] >>> N = len(ok) + len(fraud) >>> P_ok = len(ok)/N >>> P_fraud = len(fraud)/N >>> probs_ok, bins_ok = np.histogram(ok, bins=500, normed=True) >>> probs_fraud, bins_fraud = np.histogram(fraud, bins=bins_ok, normed=True) >>> # Test! >>> test_times = np.linspace(0, 1e6, 100000) >>> detected_as_fraud = 0 >>> detected_as_ok = 0 >>> for el in test_times: ... p_ok = get_prob(el, bins_ok, probs_ok)*P_ok ... p_fr = get_prob(el, bins_fraud, probs_fraud)*P_fraud ... if p_ok > p_fr: ... detected_as_ok += 1 ... else: ... detected_as_fraud += 1 >>> print(detected_as_ok, detected_as_fraud) 100000 0
- 23. daftCode sp. z o.o. Example 5. Naive Bayes ● NB doesn't seem to work that well in this example ● Better results by just putting a threshold ● But still, several lines of code and classifier ready!
- 24. daftCode sp. z o.o. Almost at the end. Just one more slide… and it's a summary!
- 25. daftCode sp. z o.o. Summary ● Statistical inference is used to compare and validate values ● It gives some quantification, but there still is a room for subjective decisions (p-values, priors) ● It is quite easy to do statistics in Python when you have proper tools

