Skillwise Struts.x
- 2. 2 Struts 2.x
- 3. Agenda Struts Introduction Struts Web Flow Struts Architecture Struts Basic Example Dynamic Method Invocation Multiple Struts.xml files IOC and DI Interceptors Validation Internationalization Control Tags Struts2 with Jquery Build in Interceptor Custom Interceptor I18N
- 4. Struts2 is a free Open Source Framework Apache Struts2 was originally known as WebWork 2. After working independently for several years, the WebWork and Struts communities joined forces to create Struts2. It is based on MVC2 Architecture In Struts 2 FilterDispatcher does the job of Controller. Model contains the data and the business logic. In Struts 2 the model is implemented by the Action component. View is the presentation component of the MVC Pattern. In Struts 2 View is implemented by JSP Struts 2 is a pull-MVC framework. i.e. the data that is to be displayed to user has to be pulled from the Action. The “pull” comes from the views ability to pull data from an action using Value Stack/OGNL. Struts 2 Action class are plain POJO objects thus simplifying the testing of the code. Struts Introduction
- 5. What is MVC ?
- 6. Servlet (Controller) 1. Get Request parameters Business Service (Model) 2. Call Business Service DB Business Service talk to DB JSP (View) 3. Pass the result to the JSP 4. Return Formatted HTML MVC
- 7. Why MVC 1. Business Logic (Model) is separate from controller. 2. View is separate from Controller 3. View is separate from Model Conclusion : MVC Follows Separation of Concern Principal.
- 8. MVC Framework 1. It provide pre-build classes 2. It is a collections of Base classes and Jars 3. They are Extensible 4. Popular Java MVC are Struts 1.x , Struts 2.x , JSF , Wicket , Spring MVC, Play, Grails
- 9. Framework vs Pattern 1. Pattern is the way you can architect your application. 2. Framework provides foundation (base) classes and libraries. 3. Leverage industry best practices.
- 10. MVC1 vs MVC 2
- 11. Struts1 vs Struts2 Flow
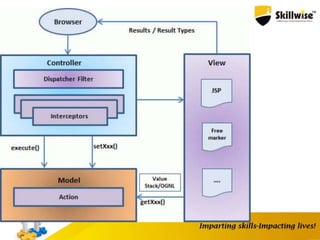
- 14. Struts 2 Web Flow Struts MVC Flow
- 15. Five Core Components: 1. Actions The most basic unit of work that can be associated with a HTTP request coming from a user. 2. Interceptors They provide a way to supply pre-processing and post-processing around the action. They have access to the action being executed, as well as all environmental variables and execution properties. Interceptors are conceptually the same as servlet filters, can be layered and ordered. 3. Value stack / OGNL. The value stack is exactly what it says it is – a stack of objects. OGNL stands for Object Graph Navigational Language, and provides the unified way to access objects within the value stack. 4. Result types Chain, Dispatcher, Freemarker, HttpHeader, Redirect, Redirect-Action, Stream, Velocity, XSLT. If the attribute is not supplied, the default type “dispatcher” is used – this will render a JSP result. 5. View technologies. JSP Velocity Templates Free marker Templates XSLT Transformations Struts 2 Core Components
- 16. Architecture of Struts 2 Struts 2 Architecture is based on WebWork 2 framework. It leverages the standard JEE technologies such as Java Filters, JavaBeans, ResourceBundles, Locales, XML etc in its architecture. It is optional Filter , and it is used to integrate the Struts with SiteMesh Plugin Struts Architecture
- 17. Architecture of Struts 2 Struts 2 Architecture is based on WebWork 2 framework. It leverages the standard JEE technologies such as Java Filters, JavaBeans, ResourceBundles, Locales, XML etc in its architecture. SiteMesh is a web-page layout and decoration framework and web application integration framework to aid in creating large sites consisting of many pages for which a consistent look/feel, navigation and layout scheme is required. Struts Architecture
- 18. Architecture of Struts 2 Struts 2 Architecture is based on WebWork 2 framework. It leverages the standard JEE technologies such as Java Filters, JavaBeans, ResourceBundles, Locales, XML etc in its architecture. The FilterDispatcher filter is called which consults the ActionMapper to determine whether an Action should be invoked Struts Architecture
- 19. Architecture of Struts 2 Struts 2 Architecture is based on WebWork 2 framework. It leverages the standard JEE technologies such as Java Filters, JavaBeans, ResourceBundles, Locales, XML etc in its architecture. If ActionMapper finds an Action to be invoked, the FilterDispatcher delegates control to ActionProxy. Struts Architecture
- 20. Architecture of Struts 2 Struts 2 Architecture is based on WebWork 2 framework. It leverages the standard JEE technologies such as Java Filters, JavaBeans, ResourceBundles, Locales, XML etc in its architecture. ActionProxy reads the configuration file such as struts.xml. ActionProxy creates an instance of ActionInvocation class and delegates the control. Struts Architecture
- 21. Architecture of Struts 2 Struts 2 Architecture is based on WebWork 2 framework. It leverages the standard JEE technologies such as Java Filters, JavaBeans, ResourceBundles, Locales, XML etc in its architecture. ActionInvocation is responsible to invokes the Interceptors one by one (if required) and then invoke the Action. Struts Architecture
- 22. Architecture of Struts 2 Struts 2 Architecture is based on WebWork 2 framework. It leverages the standard JEE technologies such as Java Filters, JavaBeans, ResourceBundles, Locales, XML etc in its architecture. Once the Action returns, the ActionInvocation is responsible for looking up the proper result associated with the Action result code mapped in struts.xml. Struts Architecture
- 23. Architecture of Struts 2 Struts 2 Architecture is based on WebWork 2 framework. It leverages the standard JEE technologies such as Java Filters, JavaBeans, ResourceBundles, Locales, XML etc in its architecture. The Interceptors are executed again in reverse order and the response is returned to the Filter (In most cases to FilterDispatcher). And the result is then sent to the servlet container which in turns send it back to client Struts Architecture
- 24. Develop Struts First Application
- 25. Struts Basic Example Struts First Program For Creating Struts First Program, You required the Following things a) JDK 1.5 or Higher b) Servlet API and JSP API c) J2EE Compliance Web Server or Application Server d) Download the Following Jar Files from https://struts.apache.org/download.cgi
- 26. Step -1 Struts Filter Entry in web.xml Web.xml <filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter- class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter- class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
- 27. Step -2 Create an Action Class Creating Action
- 28. Step -3 Create a View <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
- 29. Step -4 Create struts.xml File Struts.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> <struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="welcome" class="com.srivastava.basics.HelloAction"> <result name="success">/index.jsp</result> </action> <action name="loginCheck" class="com.srivastava.basics.HelloAction" method="checkLogin" > <result name="login">/welcome.jsp</result> <result name="error"></result> </action> </package> </struts>
- 30. Output
- 37. Struts 1.x v/s Struts 2.x Feature Struts 1.x Struts 2.x Action Classes Struts 1 requires Action classes to extend an abstract base class. A common problem in Struts 1 is programming to abstract classes instead of interfaces. An Struts 2 Action may implement an Action interface, along with other interfaces to enable optional and custom services. Struts 2 provides a base ActionSupport class to implement commonly used interfaces. Albeit, the Action interface is not required. Any POJO object with a execute signature can be used as an Struts 2 Action object. Binding Values into views To access different objects , struts 1 uses the standard jsp implict objects It use valuestack to hold the values and to reterive the value from value stack it use OGNL (Object Graph Navigational Language) Servlet Dependency In action execute method , it has HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse Object, both comes from servlet API Not needed in struts 2 execute method Testablity A major hurdle to testing Struts 1 Actions is that the execute method exposes the Servlet API. A third- party extension, Struts TestCase, offers a set of mock object for Struts 1. Struts 2 Actions can be tested by instantiating the Action, setting properties, and invoking methods. Dependency Injection support also makes testing simpler. No Action Form Struts 1 uses an ActionForm object to capture input. Like Actions, all ActionForms must extend a base class. Since other JavaBeans cannot be used as ActionForms, developers often create redundant classes to capture input. Struts 2 uses Action properties as input properties, eliminating the need for a second input objec Control Of Action Execution Struts 1 supports separate Request Processors (lifecycles) for each module, but all the Actions in the module must share the same lifecycle. Struts 2 supports creating different lifecycles on a per Action basis via Interceptor Stacks.
- 38. Multiple Struts.xml File We can include other struts.xml-format files from a bootstrap struts.xml file <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"> <struts> <include file=“advice.xml"/> <include file=“contract.xml"/> <include file=“dms.xml"/> </struts>
- 42. UI in Struts 2
- 43. Designing UI in Struts 2 The form Tag Eg. <s:form action=“actionname” method =“post”> </s:form> The textfield tag <s:textfield name=“userid” label =“userid” /> The TextArea tag <s:textarea name=“address” label=“Address” cols=“15” rows=“2” /> UI
- 44. The password tag <s:password name=“password” label=“Password” /> The Checkbox Tag <s:checkbox name=“cricket” label=“Cricket” fieldValue=“C”/> <s:checkbox name=“hockey” label=“Hockey” fieldValue=“H”/> The Radio Tag <s:radio name=“m_status” label=“Marital Status” list=“{‘Single’,’Married’}” /> The Hidden Tag <s:hidden name=“empid” value=“Some Value” /> UI
- 45. The Combo box <s:combobox label=“Country" headerKey="-1" headerValue="--- Select ---" list=“country" name=“country" /> class Action extends ActionSupport { private List<String> country; public void setCountry(List<String> country) { } public List<String> getCountryList() { } } The submit tag <s:submit/> The datetimepicker tag <s:datetimepicker name=“dob” label =“Date of Birth” displayFormat="dd MMMM, yyyy" /> UI
- 46. Using Freemarker template for Creating Custom UI
- 47. FreeMarker is a "template engine"; a generic tool to generate text output To Print the Values in FTL Welcome ${user} If condition in FTL <#if field.formatType??> </#if> Loops in FTL <#list tabList as page> </#list> Freemarker
- 48. Creating Own Components Using FTL Eg. Creating Password Field Using FTL <input type="password" <#rt/> name="${parameters.name?default("")?html}"<#rt/> <#if parameters.get("size")??> size="${parameters.get("size")?html}"<#rt/> </#if> <#if parameters.maxlength??> maxlength="${parameters.maxlength?html}"<#rt/> </#if> <#if parameters.id??> id="${parameters.id?html}"<#rt/> </#if> <#if parameters.get("size")??> size="${parameters.get("size")?html}"<#rt/> </#if> <#if parameters.onblur??> onblur="${parameters.onblur?html}"<#rt/> </#if> /> NOTE: Store your FTL File in public-html template finnonepro Freemarker
- 49. Calling FTL using <s:component tag> , place in JSP File <s:component template="password.ftl" theme="finnonepro" id="28000005" name="FW_SC_PW_OodPW"> <s:param name="maxlength" value="'20'"/> <s:param name="size" value="'12'"/> <s:param name="mandatory" value="'Y'"/> </s:component> Freemarker
- 50. IOC (Inversion of Control) and DI (Dependency Injection) IOC and DI are programming design patterns, which are used to reduce coupling in programming. It follow the Following Principle: a) You do not need to create your objects. You need to only describe how they should be created. (This think is done by ObjectFactory) To enable the IOC in Struts a) Using an Enabler Interface Eg. SessionAware, ApplicationAware etc. IOC (Inversion of Control)
- 51. IOC (Inversion of Control)
- 52. Exercise: Create an Online Shopping Application, where user can login and register if the User is New. Once User login in the System , the Application display the items to the User , so User can choose it and buy the desire item. The Selected Item has the given features like Item Name , Size , Color , Quantity and Price. Once the User buy the selected item , the final bill is generated and display to the User
- 53. Interceptor Interceptor is used for seperation of core functionality code in the form of Interceptors makes Action more lightweight. The purpose of Interceptors is to allow greater control over controller layer and separate some common logic that applies to multiple actions. All framework interceptors defined in struts-default.xml Interceptors
- 54. Alias Interceptor Alias Interceptor This interceptor alias a named parameter to a different parameter name. Suppose your jsp having two textfield name t1 and t2 and in your action class you defined t3 and t4 variable , so alias interceptor can map t1 with t3 alias and t2 with t4 alias.
- 55. Step-1 Create JSP File
- 56. Step-2 Create Action Class
- 57. Step-3 Entry in Struts.xml File
- 60. ExecuteAndWait Interceptor While running a long action, the user may get impatient in case of a long delay in response. To avoid this, the execAndWait Interceptor is used, which runs a long running action in the background and display a page with a Loading to the user.
- 61. Step -1 Create JSP
- 62. Step -2 Create Action
- 63. Step -3 Create Wait.jsp
- 64. Step -4 Create struts.xml an initial delay in millis to wait before the wait page is shown Used for waking up at certain intervals to check if the background process is already done. Default is 100 millis
- 65. Exception Interceptor The Struts 2 framework provides the functionality of exception handling through the Interceptor. Instead of displaying stack trace for the exception to the user, it is always good to show a nicely designed page describing the real problem to the user.
- 66. Step -1 Create JSP
- 67. Step -2 Create Action Class
- 69. Step -4 exception jsp file
- 70. Creating Own Interceptor This framework provides the flexibility to create own interceptor classes to enable additional logic which can be separated and refused in the Interceptor stack of different action classes. The Custom interceptor class need to be defined in the struts.xml file.
- 71. Step -1 Create Interceptor Java File
- 72. Step -2 Entry in struts.xml file
- 73. Validation Framework Struts 2 based on a validation framework, which is provided by Xwork. The Validation framework uses external metadata in the form of XML files to describe what validation should be performed on your action. Struts2 Validation Framework allows us to separate the validation logic from actual Java/JSP code, where it can be reviewed and easily modified later. Validation can be perform a) Programmatic b) XML Meta Data Validation Framework
- 74. Validation Using XML Meta-Data
- 75. Step -1 Create JSP
- 76. Step -2 Create Action Class
- 77. Step -3 create validation.xml file
- 78. Step -3 create validation.xml file
- 79. Step -4 struts.xml Note: validation.xml file placed in the same location , where Action is placed and it is same name as action name and end with validation.xml file
- 80. Programmatic Validation It is written in the Actionclass by overriding the validate method , this method calls automatically when user submit the page, it is call before the execute method , and if any error occurred , it return the “input” as a result , otherwise it execute the execute method of the action
- 81. Step -1 Create an Action Override the validate method it comes from Validateable interface, which is implemented by ActionSupport class
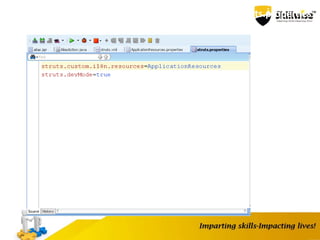
- 82. Internationalization Internationalization is a technique for application development that support multiple languages and data formats without having to rewrite programming logic. Create different languages application resource property file’s and these files name end with country language code Note: Also Specify the application resource name and path in struts.properties file, the path is required if you are not placed in application resoource file in the src folder
- 85. Create JSP File
- 86. Changing Browser Language 1 2 3
- 88. Control Tags