Switching systems lecture6
- 1. DIT Dar es Salaam institute of Technology (DIT) ETU 07420 Switching Systems Ally, J [email protected]
- 3. DIT To provide a high-speed, low delay multiplexing and switching network to any type of user traffic, such as voice support, data,or video applications. Why do we need a new technology?
- 4. DIT What is ATM? ATM for Telecommunications is Asynchronous Transfer Mode, (not Automatic Teller Machine!). ATM is a flexible high bandwidth, low delay network technology that is capable of handling voice, video and data on a single network; and mostly used in the backbone In general, ATM means that traffic is carried in small, fixed-length packets called cells. A technology that integrates advantages of circuit switch and packet switch. ATM can support any type of user services, such as voice, data, or video service.
- 5. DIT ATM Overview 53byte fixed length cell= 5Bytes cell header+48Bytes payload. ATM must set up virtual connection before communication. ATM network will confer with terminal on parameter of QoS before the connection is set up. Contract 5-Bytes Header 48-Bytes Payload
- 6. DIT ATM can provides both CBR and VBR transport
- 7. DIT Connectionless & Connection- oriented Setup Setup Setup Setup Connectionless: Every packet is transferred from different routes, so the receiving order of packets doesn’t possibly depend on the sending order. Connection-oriented : All packets are transferred from the same route , so the receiving order of packets depends on the sending order. Time delay is fixed.
- 8. DIT ATM Switch Model’s Characteristic Any user’s cell will not be send periodically, and bandwidth will be shared and statistically multiplexed. Many types of service can be transferred in the same time and Quality of Service is supported in an ATM network. Fixed length cell, so switch can be controlled by hardware and high-speed switching is easy to be realized.
- 9. DIT ATM’s Advantage Integration of various services such as voice, image, video, data and multimedia. Standardization of network structures and components. This results in cost savings for network providers. Transmission that is independent of the medium used PDH, SDH, SONET and other media can be used to transport ATM cells. ATM is scaleable, i.e. the bandwidth can be adapted extremely flexibly to meet user requirements. Guaranteed transmission quality to match the service required by the user (quality of service, QoS).
- 10. DIT ATM’s Application In Switching: Traditional Exchange is evolving into Broadband Exchange by ATM’s application In Transmission: ATM virtual path exchange node and ATM Add/Drop Multiplexer In Internet: ATM router applied in IP Switching, Multi-Protocol Label Switching
- 11. DIT ATM Network Model UNI UNI UNI PNNI PNNI NNI NNI NNI NNI NNI NNI NNI ICI Other Network NNI : Network Node Interface UNI : User Node Interface ICI : Inter-carrier Interface PNNI : Private Network Node Interface
- 12. DIT ATM Interfaces The following ATM interfaces have been defined and standardized Private UNI (user-node interface) –specification of the interface between a user’s device (e.g. a workstation) and a private ATM switch Private NNI (network-node interface) –e.g. between private ATM switches needed to support the ATM infrastructure Public UNI–specification of the interface between the user’s device and a provider of a public ATM service Public NNI–interface between ATM switches in public carrier networks. Also referred to as B-ISSI (broadband inter-switching system interface) when applied to the connection between two public switches of the same carrier Also referred to as B-ICI (broadband inter-carrier interface) when applied to the connection between two carriers networks
- 13. DIT ATM Cell
- 14. DIT ATM Cell GFC ( Generic Flow Control): It is intended for control of a possible bus system at the user interface and is not used at the moment. VPI ( Virtual Path Identifier): The VPI contains the second part of the addressing instructions and is of higher priority than the VCI. VCI ( Virtual Channel Identifier): VCI in each case indicates a path section between switching centers or between the switching center and the subscriber. PTI ( Payload Type Identifier): Indicates the type of data in the information field. CLP ( Cell Loss Priority): Determines whether a cell can be preferentially deleted or not in the case of a transmission bottleneck. HEC ( Header Error Control): Provided in order to control and, to some extent, correct errors in the header data that may occur. The HEC is used to synchronize the receiver to the start of the cell.
- 15. DIT ATM Connection There are two types of ATM connections Virtual path connections –identified by virtual path identifiers (VPI) Virtual channel connections –identified by a combination of virtual path and circuit identifiers (VPI and VCI) Virtual channels (VC) are the basic unit that carry a stream of ATM cells from one user to another are identified by a virtual channel identifier can be configured statically as PVCs (permanent virtual circuits) that are set up at network configuration time and dynamically as SVCs (switched virtual circuits) that are dynamically configured on-demand can be bundled together into virtual path connections Virtual paths (VP) contain one or more virtual channels are identified by a virtual path identifier are routed through a network as a single entity can be used internally for bundling virtual circuits between switches
- 16. DIT Port 1 VPI=2 VCI=37 VPI=3 VCI=39 NNI UNI UNI ATM Cell Switching ATM Switch Port VPI VCI 1 2 37 2 1 51 Port 2 Port 1 ATM Switch Port VPI VCI 1 1 51 2 3 39 Port 2 ATM TerminalUser B User A ATM Network Node Cell and user’s data change each other VPI=1 VCI=51 ATM Network Node ATM Terminal Cell and user’s data change each other
- 17. DIT Permanent Virtual Channel (PVC): The connections are analogous to leased lines that are switched between certain users. A change can only be made by the network provider. This type of ATM network often forms the initial stage in the introduction of this technology. Switch Virtual Channel (SVC): Users connected to this type of network can set up a connection to the user of their own choice by means of signaling procedures. This can be compared with the process of dialing a telephone number. Signaling In ATM
- 18. DIT Types of ATM Virtual Connection According to the switching mode, ATM Virtual Connection can be classified : VPC (Virtual Path Connection) VCC (Virtual Channel Connection) According to connection establishment, ATM Virtual Connection can be classified: SVC(Switching Virtual Connection) PVC(Permanent Virtual Connection)
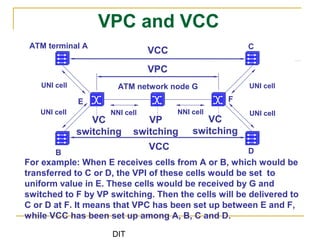
- 19. DIT UNI cell VPC and VCC ATM terminal A C ATM network node G UNI cell NNI cell NNI cell VC switching VCC VPC VCC UNI cell UNI cell B D For example: When E receives cells from A or B, which would be transferred to C or D, the VPI of these cells would be set to uniform value in E. These cells would be received by G and switched to F by VP switching. Then the cells will be delivered to C or D at F. It means that VPC has been set up between E and F, while VCC has been set up among A, B, C and D. E F VP switching VC switching
- 20. DIT Cells Voice Data Video Connection oriented Fast packet switching Statistical multiplexer Supports voice, data and video service Provides QoS Features of ATM
- 21. DIT ATM Protocol Structure Model USER SAAL ATM Layer Physical Layer AAL USER Service and signaling of user Information of user and cell conversion Cell exchange and multiplexing or demultiplexing Frame structure physical medium Impartible management of all layer Independent management of every layer Call connection and Control User information 、 Flow Control and Error Recovery Interface Management Layer Management Control interface User interface
- 22. DIT Three Communications Planes The user plane transports the user data for an application. It uses the physical, ATM and ATM adaptation layers to do this. The control plane takes care of establishing, maintaining and clearing down user connections in the user plane. The key word here is signaling. The management plane includes layer management and plane management. Layer management monitors and coordinates the individual layer tasks. Plane management handles monitoring and coordination tasks in the network.
- 23. DIT ATM Sublayer Model ATM Protocol Stack Model OSI Reference Model User PMD TC PHY ATM AAL CS SAR Interface manage ment 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data link 1 Physical
- 24. DIT Two sublayers: Transmission Convergence Sublayer (TC) transmission frame generation/recovery Processing HEC (Header Error Control) cell delimiting transmission frame adaptation Physical Medium Dependent Sublayer (PMD) Link coding Network physical medium Function of ATM Physical Layer AAL ATM PHY
- 25. DIT Cell switch Quality of Service Processing the cell header Types of payload Multiplexing /Demultiplexing of different connection cell Function of ATM Layer AAL ATM PHY
- 26. DIT Support services for user Segment and reassemble Complete the change between User-PDU and ATM payload Function of ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) AAL ATM PHY
- 27. DIT Function of ATM AAL Overview Function of ATM AAL: Provide a high-speed, low delay multiplexing and switching network to support any type of user service, such as voice, data,or video applications. ATM Payload Constant Bit Rate Data Bursts Variable Bit Rate ATM Cell Multiplexing AAL SDU
- 28. DIT Types of AAL In order to support different types of user services, there are five types of AAL. AAL type 1–meets the needs of class A services AAL type 2–meets the needs of class B services AAL type 3/4-meets the needs of class C and D services AAL type 5–meets the needs of class D services Service type A B C D Bit rate constant variable variable variable Real time YES YES NO NO Connection mode Connection oriented connectionless AAL AAL1 AAL2 AAL3/4 AAL5
- 29. DIT Service Types of ATM layer CBR (Constant bit rate) Intended to support real-time applications requiring tightly constrained delay variation (e.g. voice, video) VBR-NRT (Variable bit rate-non real time) Intended for non-real-time applications with bursty traffic (e.g. multimedia-email) VBR-RT (VBR-real time) intended for real-time applications with bursty traffic (e.g. compressed video/voice) UBR (Unspecified bit rate) Represents a “best-effort service intended for non-real-time applications that do not require tightly constrained delay or delay variation and are tolerant to cell loss ( widely used today for TCP/IP) ABR (Available bit rate) similar to UBR but enhanced to handle applications that require a minimum bandwidth requirement (e.g. email and file transfer)
- 30. DIT (IP over ATM) IPOA Protocol Stack ATM network Physical layer IP address is mapped to PVC or SVC User application ATM AAL IP TCP/UDP ATM AAL IP TCP/UDP IP packet is transferred to ATM Payload User application
- 31. DIT TCP/IP Process App DataTCP Header TCP header App DataIP Header IP Header TCP Header App DataLLC SAR-SDU#1 SAR-SDU#2 SAR-SDU#3 SAR-PDU#4 SAR-PDU#5 TCP IP SNAP/LLC AAL5 CS SAR ATM PHY Cell header will be added to SAR-PDU, whose VPI and VCI depends on the map table of IP address to PVC/SVC. Then ,the cells will be sent to Physical Layer. Perform the transmission of ATM cells via physical media. LLC IP Header TCP Header App Data PAD CPCS-PDU Tail
- 32. DIT Thanks! Technology changes but communication lasts.
Editor's Notes
- #5: ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) is a high speed packet switching technology. It supports any kind of service. ATM is a flexible high bandwidth, low delay network technology that is:Capable of handling voice, video and data on a single network; and Generally used in the backbone
- #6: VPI:Virtual Path Identifier VCI:Virtual Channel Identifier ATM is a circuit switched procedure The connection through ATM network is called as “virtual”, since it does not exist physically, but it is present only in the form of routing tables in the switching center.
- #9: Here statistical multiplexing means, TS are not fixed. Information is sent over several TS may these are adjacent or may be different.
- #14: Why two fields? think VPI as a bundle of virtual channels. (256 VPI on one link) the individual virtual channels have unique VCIs. The VCI values may be reused in each virtual path
- #15: GFC ( Generic Flow Control): Supports the configuration of the subscriber equipment. It is intended for the control of a possible bus system at the user interface. VPI ( Virtual Path Identifier): VPI contains the second part of the addressing instructions and is of higher priority than the VCI. This allows the rapid direction of the cells through the network. ATM cross-connects the cell stream in various directions based on VPI. The VPI and VCI are assigned by the switching centers when the call is being established. VCI ( Virtual Channel Identifier): This field contains part of the addressing instructions. All cells belonging to the same virtual channel have the same VCI. VCI indicates a path section between switching centers or between switching center and subscriber. PTI ( Payload Type Identifier): A distinction is made between network and user information. CLP ( Cell Loss Priority): The contents of this field determines whether a cell can be preferentially deleted or not during congestion. CLP=0 Lower priority CLP=1 Higher priority HEC ( Header Error Control): The HEC is used to synchronize the receiver to the start of the cell. CRC code is also sent over it (x8+x2+x+1) There are cells for transmitting the signaling information and OAM cells.
- #16: There are two types of ATM connections Virtual path connections –identified by virtual path identifiers (VPI) Virtual channel connections –identified by a combination of virtual path and circuit identifiers (VPI and VCI) Virtual channels (VC) are the basic unit that carry a stream of ATM cells from one user to another are identified by a virtual channel identifier can be concatenated can be configured statically or dynamicallyStatically as PVCs (permanent virtual circuits) that are set up at network configuration time Dynamically as SVCs (switched virtual circuits) that are dynamically configured on-demand can be bundled together into virtual path connections Virtual paths (VP) contain one or more virtual channels are identified by a virtual path identifier are routed through a network as a single entity can be used internally for bundling virtual circuits between switches
- #20: PVC: Permanent Virtual Channel, A PVC in the usual meaning is a VC that is not signaled by the end points. Both of the endpoint (user) VC values are manually provisioned. The link-by-link route through the network is also manually provisioned. If any equipment fails, the PVC is down, unless the underlying physical network (SONET, for example) can re-route below ATM. SVC: A SVC is established by UNI signaling methods. So an SVC is a request oriented connection initiated by the user. If some equipment in the path fails, the SVC is broken and would have to be reconnected.
- #24: SSCS:Service Special Convergence Sublayer CPCS:Common Part Convergence Sublayer CS:Convergence Sublayer SAR:Segmentation And Reassembly AAL:ATM Adaptation Layer PHY: Physical Layer TC:Transmission Convergence Sublayer PMD:Physical Medium Dependent Sublayer
- #25: Physical Layer The physical layer is responsible for placing and removing cells from the physical transport medium. Standards for physical interfaces to various media exist and are discussed later. SONET/SDH based transmission media are the most common for transmission of ATM. The physical layer performs two types of functions: -Functions associated with the structure or format of the info to be transmitted and other specific functions (e.g. multiplexing). These functions are independent of the transmission medium. -Functions associated with the transmission of signals over a particular medium (e.g. line coding for a particular medium). These functions are dependent on the transmission medium
- #26: ATM Layer -provides services to higher layers (e.g. multiplexing ATM connections on to a single connection) and facilitates the forwarding of ATM cells through the network by the setting of parameters in the ATM cell header (e.g. prioritization, traffic management). -delivers ATM cells to the physical layer for transport -A number of parameters are set at the ATM layer that determine quality of service and traffic management Quality of Service (QoS) refers to a collection of performance parameters whose values have to do with the speed and accuracy/reliability characteristics of the ATM connection. Negotiable parameters (determined by customer) ppCDV –peak to peak cell transfer delay variation Max CTD –maximum cell transfer delay CLR –cell loss ratio Non-negotiable parameters(determined by service provider) CER –cell error ratio CMR –cell mis-insertion rate SECBR –severely errored cell block ratio Traffic parametersdefine characteristics of the traffic to be offered over the ATM connection. PCR –peak cell rate SCR –sustainable cell rate MBS –maximum burst rate MCR –minimum cell rate ICR –initial cell rate
- #27: ATM adaptation Layer -The AAL maps higher-level data (e.g. legacy technologies) onto ATM cells making the data suitable for transport through the ATM network and isolates higher layers from the ATM layer. These functions are performed on the user side.
- #28: ATM adaptation Layer -The AAL maps higher-level data (e.g. legacy technologies) onto ATM cells making the data suitable for transport through the ATM network and isolates higher layers from the ATM layer. These functions are performed on the user side. -The concept of Service Classes is used to define traffic corresponding to specific combinations of: timing relations between source and destination (required/not required) constant vs. variable bit rate connection mode (connection oriented vs. connectionless oriented) -Defined service classes are: Class A –synchronous, connection oriented, constant bit rate (e.g. DS, DS3 circuit emulation) Class B –synchronous, connection oriented variable bit rate (e.g. packet video) Class C –asynchronous, connection oriented, variable bit rate (e.g. frame relay) Class D –asynchronous, connectionless, variable bit rate (e.g. SMDS) -AAL protocols are defined to handle one of more of the above service classes and create properly formatted ATM cells. There is no stipulation that rigidly binds an AAL protocol to a service class. AAL type 1–meets the needs of class A services Provides for the acceptance of user info at a fixed rate and delivery of this info at the destination at the same fixed rate and indication of loss or errored information AAL type 2–meets the needs of class B services Designed to carry low bit rate, variable-length, delay-sensitive packets AAL type 3/4-meets the needs of class C and D services Designed to carry variable bit rates with no timing relationship AAL type 5–meets the needs of class C services Simplified and more efficient than 3/4 -simple and efficient data protocol
- #29: -The concept of Service Classes is used to define traffic corresponding to specific combinations of: timing relations between source and destination (required/not required) constant vs. variable bit rate connection mode (connection oriented vs. connectionless oriented) -Defined service classes are: Class A –synchronous, connection oriented, constant bit rate (e.g. DS, DS3 circuit emulation) Class B –synchronous, connection oriented variable bit rate (e.g. packet video) Class C –asynchronous, connection oriented, variable bit rate (e.g. frame relay) Class D –asynchronous, connectionless, variable bit rate (e.g. SMDS) -AAL protocols are defined to handle one of more of the above service classes and create properly formatted ATM cells. There is no stipulation that rigidly binds an AAL protocol to a service class. AAL type 1–meets the needs of class A services Provides for the acceptance of user info at a fixed rate and delivery of this info at the destination at the same fixed rate and indication of loss or errored information AAL type 2–meets the needs of class B services Designed to carry low bit rate, variable-length, delay-sensitive packets AAL type 3/4-meets the needs of class C and D services Designed to carry variable bit rates with no timing relationship AAL type 5–meets the needs of class C services Simplified and more efficient than 3/4 -simple and efficient data protocol
- #31: IP Over ATM
- #32: This page reference page :AAL5 Process. Reference:RFC1483 SNAP: Sub-network Access Protocol LLC: Low Layer Compatability