Ad
Syntax
- 1. Syntax – Intro and Overview CS331
- 2. Syntax • Syntax defines what is grammatically valid in a programming language – Set of grammatical rules – E.g. in English, a sentence cannot begin with a period – Must be formal and exact or there will be ambiguity in a programming language • We will study three levels of syntax – Lexical • Defines the rules for tokens: literals, identifiers, etc. – Concrete • Actual representation scheme down to every semicolon, i.e. every lexical token – Abstract • Description of a program’s information without worrying about specific details such as where the parentheses or semicolons go
- 3. BNF Grammar • BNF = Backus-Naur Form to specify a grammar – Equivalent to a context free grammar • Set of rewriting rules (a rule that can be applied multiple times) defined on a set of nonterminal symbols, a set of terminal symbols, and a start symbol – Terminals, ∑ : Basic alphabet from which programs are constructed. E.g., letters, digits, or keywords such as “int”, “main”, “{“, “}” – Nonterminals, N : Identify grammatical categories – Start Symbol: One of the nonterminals which identifies the principal category. E.g., “Sentence” for english, “Program” for a programming language
- 4. Rewriting Rules • Rewriting Rules, ρ – Written using the symbols and | | is a separator for alternative definitions, i.e. “OR” is used to define a rule, i.e. “IS” – Format • LHS RHS1 | RHS2 | RHS3 | … • LHS is a single nonterminal • RHS is any sequence of terminals and nonterminals
- 5. Sample Grammars • Grammar for subset of English Sentence Noun Verb Noun Jack | Jill Verb eats | bites • Grammar for a digit Digit 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |7 |8 |9 • Grammar for signed integers SignedInteger Sign Integer Sign + | - Integer Digit | Digit Integer • Grammar for subset of Java Assignment Variable = Expression Expression Variable | Variable + Variable | Variable – Variable Variable X | Y
- 6. Derivation • Process of parsing data using a grammar – Apply rewrite rules to non-terminals on the RHS of an existing rule – To match, the derivation must terminate and be composed of terminals only • Example Digit 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |7 |8 |9 Integer Digit | Digit Integer – Is 352 an Integer? Integer → Digit Integer → 3 Integer → 3 Digit Integer → 3 5 Integer → 3 5 Digit → 3 5 2 Intermediate formats are called sentential forms This was called a Leftmost Derivation since we replaced the leftmost nonterminal symbol each time (could also do Rightmost)
- 7. Derivation and Parse Trees • The derivation can be visualized as a parse tree Integer Digit Integer Digit Integer 3 5 Digit 2
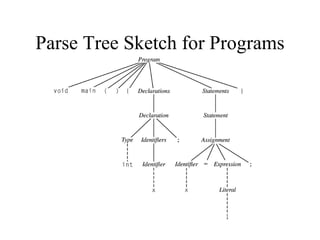
- 8. Parse Tree Sketch for Programs
- 9. BNF and Languages • The language defined by a BNF grammar is the set of all strings that can be derived – Language can be infinite, e.g. case of integers • A language is ambiguous if it permits a string to be parsed into two separate parse trees – Generally want to avoid ambiguous grammars – Example: • Expr Integer | Expr + Expr | Expr * Expr | Expr - Expr • Parse: 3*4+1 – Expr * Expr → Integer * Expr → 3 * Expr → 3 * Expr+Expr → … 3 * 4 + 1 – Expr + Expr → Expr + Integer → Expr + 1 Expr * Expr +1 → … 3 * 4 + 1
- 10. Ambiguity • Example for AmbExp Integer | AmbExp – AmbExp 2-3-4
- 11. Ambiguous IF Statement Dangling ELSE: if (x<0) if (y<0) { y=y-1 } else { y=0 }; Does the else go with the first or second if?
- 13. How to fix ambiguity? • Use explicit grammar without ambiguity – E.g., add an “ENDIF” for every “IF” – Java makes a separate category for if-else vs. if: IfThenStatement If (Expr) Statement IfThenElseStatement If (Expr) StatementNoShortIf else Statement StatementNoShortIf contains everything except IfThenStatement, so the else always goes with the IfThenElse statement not the IfThenStatement • Use precedence on symbols
- 14. Alternative to BNF • The use of regular expressions is an alternate way to express a language
- 15. Regex to EBNF • The book uses some deviations from “standard” regular expressions in Extended Backus Naur Format (defined in a few slides) { M } means zero or more occurrences of M ( M | N) means one of M or N must be chosen [M] means M is optional Use “{“ to mean the literal { not the regex {
- 16. RegEx Examples • Booleans – “true” | “false” • Integers – (0-9)+ • Identifiers – (a-zA-Z){a-zA-Z0-9} • Comments (letters/space only) – “//”{a-zA-Z }(“r” | “n” | “rn”) • Regular expressions seem pretty powerful – Can you write one for the language anbn? (i.e. n a’s followed by n b’s)
- 17. Extended BNF • EBNF – variation of BNF that simplifies specification of recursive rules using regular expressions in the RHS of the rule • Example: – BNF rule Expr Term | Expr + Term | Expr – Term Term Factor | Term * Factor | Term / Factor – EBNF equivalent Expr Term { [+|-] Term } Term Factor { [* | / ] Factor } • EBNF tends to be shorter and easier to read
- 18. EBNF • Consider: Expr Term{ (+|-) Term } Term Factor { (* | / ) Factor } Factor Identifier | Literal | (Expr) Parse for X+2*Y
- 19. BNF and Lexical Analysis • Lexicon of a programming language – set of all nonterminals from which programs are written • Nonterminals – referred to as tokens – Each token is described by its type (e.g. identifier, expression) and its value (the string it represents) – Skipping whitespace or comments or punctuation
- 20. Categories of Lexical Tokens • Identifiers • Literals Includes Integers, true, false, floats, chars • Keywords bool char else false float if int main true while • Operators = || && == != < <= > >= + - * / % ! [ ] • Punctuation ;.{}() Issues to consider: Ignoring comments, role of whitespace, distinguising the < operator from <=, distinguishing identifiers from keywords like “if”
- 21. A Simple Lexical Syntax for a Small Language, Clite Primary → Identifier [ "["Expression"]" ] | Literal | "("Expression")" | Type "("Expression")" Identifier → Letter { Letter | Digit } Letter → a | b | … | z | A | B | … Z Digit → 0 | 1 | 2 | … | 9 Literal → Integer | Boolean | Float | Char Integer → Digit { Digit } Boolean → true | false Float → Integer . Integer Char → ‘ ASCIICHAR ‘
- 22. Major Stages in Compilation • Lexical Analysis – Translates source into a stream of Tokens, everything else discarded • Syntactic Analysis – Parses tokens, detects syntax errors, develops abstract representation • Semantic Analysis – Analyze the parse for semantic consistency, transform into a format the architecture can efficiently run on • Code Generation – Use results of abstract representation as a basis for generating executable machine code
- 23. Lexical Analysis & Compiling Process Difficulties: 1 to many mapping from HL source to machine code Translation must be correct Translation should be efficient
- 24. Lexical Analysis of Clite • Lexical Analysis – transforms a program into tokens (type, value). The rest is tossed. • Example Clite program: // Simple Program int main() { int x; x = 3; } Result of Lexical Analysis:
- 25. Lexical Analysis (2) Result of Lexical Analysis: 1 Type: Int Value: int 2 Type: Main Value: main 3 Type: LeftParen Value: ( // Simple Program 4 Type: RightParen Value: ) int main() { 5 Type: LeftBrace Value: { int x; 6 Type: Int Value: int x = 3; 7 Type: Identifier Value: x } 8 Type: Semicolon Value: ; 9 Type: Identifier Value: x 10 Type: Assign Value: = 11 Type: IntLiteral Value: 3 12 Type: Semicolon Value: ; 13 Type: RightBrace Value: } 14 Type: Eof Value: <<EOF>>
- 26. Lexical Analysis of Clite in Java public class TokenTester { public static void main (String[] args) { Lexer lex = new Lexer (args[0]); Token t; int i = 1; do { t = lex.next(); System.out.println(i+" Type: "+t.type() +"tValue: "+t.value()); i++; } while (t != Token.eofTok); } } The source code for how the Lexer and Token classes are arranged is the topic of chapter 3
- 27. Lexical to Concrete • From the stream of tokens generated by our lexical analyzer we can now parse them using a concrete syntax
- 28. Concrete EBNF Syntax for Clite Program → int main ( ) { Declarations Statements } Declarations → { Declaration } Declaration → Type Identifier [ "["Integer"]" ] { , Identifier ["["Integer"]"] }; Type → int | bool | float | char Statements →{ Statement } Statement → ; | Block | Assignment | IfStatement | WhileStatement Block → { Statements } Assignment → Identifier ["["Expression"]" ] = Expression ; IfStatement → if "(" Expression ")" Statement [ else Statement ] WhileStatement → while "("Expression")" Statement Concrete Syntax; Higher than lexical syntax!
- 29. Concrete EBNF Syntax for Clite Expression → Conjunction { || Conjunction } Conjunction →Equality { && Equality } Equality → Relation [ EquOp Relation ] EquOp → == | != Relation → Addition [ RelOp Addition ] RelOp → < | <= | > | >= References lexical Addition → Term { AddOp Term } syntax AddOp → + | - Term → Factor { MulOp Factor } MulOp → * | / | % Factor → [ UnaryOp ] Primary UnaryOp → - | ! Primary → Identifier [ "["Expression"]" ] | Literal | "("Expression")" | Type "(" Expression ")"
- 30. Syntax Diagram • Alternate way to specify a language • Popularized with Pascal • Not any more powerful than BNF, EBNF, or regular expressions
- 31. Linking Syntax and Semantics • What we’ve described so far has been concrete syntax – Defines all parts of the language above the lexical level • Assignments, loops, functions, definitions, etc. • Uses BNF or variant to describe the language • An abstract syntax links the concrete syntax to the semantic level
- 32. Abstract Syntax • Defines essential syntactic elements without describing how they are concretely constructed • Consider the following Pascal and C loops Pascal C while i<n do begin while (i<n) { i:=i+1 i=i+1; end } Small differences in concrete syntax; identical abstract construct
- 33. Abstract Syntax Format • Defined using rules of the form – LHS = RHS • LHS is the name of an abstract syntactic class • RHS is a list of essential components that define the class – Similar to defining a variable. Data type or abstract syntactic class, and name – Components are separated by ; • Recursion naturally occurs among the definitions as with BNF
- 34. Abstract Syntax Example • Loop Loop = Expression test ; Statement body – The abstract class Loop has two components, a test which is a member of the abstract class Expression, and a body which is a member of an abstract class Statement • Nice by-product: If parsing abstract syntax in Java, it makes sense to actually define a class for each abstract syntactic class, e.g. class Loop extends Statement { Expression test; Statement body; }
- 35. Abstract Syntax of Clite Program = Declarations decpart; Statements body; Declarations = Declaration* Declaration = VariableDecl | ArrayDecl VariableDecl = Variable v; Type t ArrayDecl = Variable v; Type t; Integer size Type = int | bool | float | char Statements = Statement* Statement = Skip | Block | Assignment | Conditional | Loop Skip = Block = Statements Conditional = Expression test; Statement thenbranch, elsebranch Loop = Expression test; Statement body Assignment = VariableRef target; Expression source Expression = VariableRef | Value | Binary | Unary
- 36. Abstract Syntax of Clite VariableRef = Variable | ArrayRef Binary = Operator op; Expression term1, term2 Unary = UnaryOp op; Expression term Operator = BooleanOp | RelationalOp | ArithmeticOp BooleanOp = && | || RelationalOp = = | ! | != | < | <= | > | >= ArithmeticOp = + | - | * | / UnaryOp = ! | - Variable = String id ArrayRef = String id; Expression index Value = IntValue | BoolValue | FloatValue | CharValue IntValue = Integer intValue FloatValue = Float floatValue BoolValue = Boolean boolValue CharValue = Character charValue
- 37. Java AbstractSyntax for Clite class Loop extends Statement { Expression test; Statement body; } Class Assignment extends Statement { // Assignment = Variable target; Expression source Variable target; Expression source; } … Much more… see the file (when available)
- 38. Abstract Syntax Tree • Just as we can build a parse tree from a BNF grammar, we can build an abstract syntax tree from an abstract syntax • Example for: x+2*y Expression = Variable | Value | Binary Binary = Operator op ; Expression term1, term2 Binary node Expr
- 39. Sample Clite Program • Compute nth fib number
- 40. Abstract Syntax for Loop of Clite Program
- 41. Concrete and Abstract Syntax • Aren’t the two redundant? – A little bit • The concrete syntax tells the programmer exactly what to write to have a valid program • The abstract syntax allows valid programs in two different languages to share common abstract representations – It is closer to semantics – We need both!
- 42. What’s coming up? • Semantic analysis – Do the types match? What does this mean? char a=‘c’; int sum=0; sum = sum = a; • Can associate machine code with the abstract parse – Code generation – Code optimization
Editor's Notes
- #15: RegExpr for CS A331, MM/DD/YY or MM/DD/YYYY














![Regex to EBNF
• The book uses some deviations from “standard”
regular expressions in Extended Backus Naur
Format (defined in a few slides)
{ M } means zero or more occurrences of M
( M | N) means one of M or N must be chosen
[M] means M is optional
Use “{“ to mean the literal { not the regex {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-120423165500-phpapp01/85/Syntax-15-320.jpg)

![Extended BNF
• EBNF – variation of BNF that simplifies
specification of recursive rules using regular
expressions in the RHS of the rule
• Example:
– BNF rule
Expr Term | Expr + Term | Expr – Term
Term Factor | Term * Factor | Term / Factor
– EBNF equivalent
Expr Term { [+|-] Term }
Term Factor { [* | / ] Factor }
• EBNF tends to be shorter and easier to read](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-120423165500-phpapp01/85/Syntax-17-320.jpg)


![Categories of Lexical Tokens
• Identifiers
• Literals
Includes Integers, true, false, floats, chars
• Keywords
bool char else false float if int main true while
• Operators
= || && == != < <= > >= + - * / % ! [ ]
• Punctuation
;.{}()
Issues to consider: Ignoring comments, role of whitespace,
distinguising the < operator from <=, distinguishing
identifiers from keywords like “if”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-120423165500-phpapp01/85/Syntax-20-320.jpg)
![A Simple Lexical Syntax for a Small
Language, Clite
Primary → Identifier [ "["Expression"]" ] | Literal | "("Expression")"
| Type "("Expression")"
Identifier → Letter { Letter | Digit }
Letter → a | b | … | z | A | B | … Z
Digit → 0 | 1 | 2 | … | 9
Literal → Integer | Boolean | Float | Char
Integer → Digit { Digit }
Boolean → true | false
Float → Integer . Integer
Char → ‘ ASCIICHAR ‘](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-120423165500-phpapp01/85/Syntax-21-320.jpg)




![Lexical Analysis of Clite in Java
public class TokenTester {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Lexer lex = new Lexer (args[0]);
Token t;
int i = 1;
do
{
t = lex.next();
System.out.println(i+" Type: "+t.type()
+"tValue: "+t.value());
i++;
} while (t != Token.eofTok);
}
}
The source code for how the Lexer and Token classes are arranged
is the topic of chapter 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-120423165500-phpapp01/85/Syntax-26-320.jpg)

![Concrete EBNF Syntax for Clite
Program → int main ( ) { Declarations Statements }
Declarations → { Declaration }
Declaration → Type Identifier [ "["Integer"]" ] { , Identifier ["["Integer"]"] };
Type → int | bool | float | char
Statements →{ Statement }
Statement → ; | Block | Assignment | IfStatement | WhileStatement
Block → { Statements }
Assignment → Identifier ["["Expression"]" ] = Expression ;
IfStatement → if "(" Expression ")" Statement [ else Statement ]
WhileStatement → while "("Expression")" Statement
Concrete Syntax;
Higher than lexical
syntax!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-120423165500-phpapp01/85/Syntax-28-320.jpg)
![Concrete EBNF Syntax for Clite
Expression → Conjunction { || Conjunction }
Conjunction →Equality { && Equality }
Equality → Relation [ EquOp Relation ]
EquOp → == | !=
Relation → Addition [ RelOp Addition ]
RelOp → < | <= | > | >= References lexical
Addition → Term { AddOp Term } syntax
AddOp → + | -
Term → Factor { MulOp Factor }
MulOp → * | / | %
Factor → [ UnaryOp ] Primary
UnaryOp → - | !
Primary → Identifier [ "["Expression"]" ] | Literal | "("Expression")" |
Type "(" Expression ")"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntax-120423165500-phpapp01/85/Syntax-29-320.jpg)




































































































