The Different Types of Non-Experimental Research
- 2. TYPES OF NON- EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH Observes and describes variables without manipulation, providing insights into relationships and trends. It includes descriptive, survey, correlation, and causal-comparative methods for gathering insightful data.
- 3. Non-Experimental Research ✓ Observes phenomena as they occur naturally, without manipulating variables, often exploring relationships or describing characteristics.
- 4. Types of Non-Experimental Research Non-Experimental Research Descriptive Survey Correlational Causal- Comparative
- 5. Descriptive ✓ Describes characteristics or behaviors of a population without examining relationships or causes. ✓ Provides a snapshot of current conditions or attitudes.
- 6. Descriptive ✓ Gathers information and create an overview of a particular phenomenon, population, or condition. ✓ Answers: what, where, when, and how, but not why
- 7. Example ✓ What is the current level of awareness and perceived effectiveness of the school’s official FB page for class announcements and suspensions among the high school students of Prenza NHS during the academic year 2025- 2026?
- 8. Design ✓ A researcher surveys to document their level of perception on class announcements and suspensions without trying to influence them. The findings would simply describe the observed perception.
- 9. Example ✓ Among high school teachers in selected public schools within Marilao, Bulacan, what are the most frequently used online platform media for disseminating timely class announcements and suspensions, and what are their perceived advantages and disadvantages of using these platforms during the 2025-2026 school year?
- 10. Example ✓ To what extent do college students in Marilao, Bulacan, primarily rely on and trust official social media accounts of their respective academic institutions for timely announcements on class suspensions and resumptions during the current academic year (2025-2026)?
- 11. Remember ✓ The researcher observes and describes something without influencing it. ✓ You report what you find out.
- 12. Survey ✓ Collects data from a sample of individuals through questionnaires or interviews to gather information about their attitudes, opinions, behaviors, or characteristics.
- 13. Survey ✓ Gathers data from a large sample, allowing researchers to make inferences about the larger population.
- 14. Advantages of Survey Research ✓ Cost-effective and time efficient for large sample sizes ✓ Provides structured data that is easy to analyzed statistically
- 15. Disadvantages of Survey Research ✓ Limited depth, as responses are often restricted to options ✓ Potential for response bias, participants may not answer truthfully
- 16. Example ✓ How do STEM students in public schools in Marilao, Bulacan, recognize the role of technology and innovation in improving recycling processes within their local community, during the first semester of the 2025-2026 academic year?
- 17. Design ✓ The researchers identify the sample size to explore the students’ ideas on how technology could enhance recycling efforts.
- 18. Example ✓ What is the level of awareness on the "Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000 (RA 9003)" and its implications for household recycling among senior high school STEM students in Marilao, Bulacan, as of July 2025?
- 19. Example ✓ What are the preferred entrepreneurial skills and qualities perceived as most important for success by ABM senior high school students at schools in Bulacan, as of the first semester of the 2025- 2026 academic year?
- 20. Correlational ✓ examines the statistical relationship (or association) between two or more variables. It determines if and how variables are related, but it does not imply causation (or cause and effect).
- 21. Types of Correlation ✓ Positive – as one variable increases, the other also increases ✓ Negative – as one variable increases, the other decreases ✓ Zero or No Correlation – no association or relationship
- 22. Example ✓ Is there a correlation between the frequency of exposure to science- themed media and the critical thinking skills of STEM senior high school students in Marilao, Bulacan, as assessed by a standardized test?
- 23. Design ✓ Is there a significant correlation between the level of participation in business-related extra-curricular activities (e.g., Junior Achievement, business clubs, stock market simulations) and the self-assessed entrepreneurial intentions among ABM senior high school students in Marilao, Bulacan,?
- 24. Example ✓ Is there a significant correlation between the level of participation in business-related extra-curricular activities (e.g., Junior Achievement, business clubs, stock market simulations) and the self-assessed entrepreneurial intentions among ABM senior high school students in Marilao, Bulacan,?
- 25. Causal-comparative (or ex post facto) ✓ attempts to determine the cause- and-effect relationship after the fact. The IV has already occurred and cannot be manipulated. ✓ The researcher looks for potential causes by comparing groups that differ on a pre-existing characteristic.
- 26. Features ✓ No manipulation of the IVs (it’s already happened) ✓ Involves comparing two or more groups ✓ Attempts to explain why differences exist between groups where direct manipulation is unethical, impractical and impossible.
- 27. Limitations ✓ Other unmeasured factors might also differ between the groups.
- 28. Example ✓ Does the awareness of a key's eco- friendly origin influence users' willingness to recommend the product more significantly than traditional keys among environmentally-conscious consumers in Marilao, Bulacan?
- 29. Example ✓ Does the awareness of a key's eco- friendly origin influence users' willingness to recommend the product more significantly than traditional keys among environmentally-conscious consumers in Marilao, Bulacan?
- 30. Design ✓ The researchers select communities in Marilao that provide a specific, localized context for data collection.
- 31. Example ✓ Is there a significant difference in the ease of creating business presentations between ABM students in select high Schools in Marilao, Bulacan, who predominantly use Microsoft PowerPoint versus those who predominantly use Canva for their reporting needs in class?
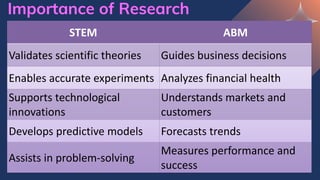
- 33. Importance of Research Quantitative research plays a crucial role in both STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) and ABM (Accountancy, Business, and Management) because it provides objective, data-driven insights that support decision-making, problem- solving, and innovation.
- 34. Importance of Research STEM ABM Validates scientific theories Guides business decisions Enables accurate experiments Analyzes financial health Supports technological innovations Understands markets and customers Develops predictive models Forecasts trends Assists in problem-solving Measures performance and success