Title Lorem Ipsum [Autosaved].pptx
- 1. DESIGN SCIENCE IN INFORMATION SYSTEMS RESEARCH By : Yassen Hadhoud
- 2. Abstract Two paradigms characterize much of the research in the Information Systems discipline : 1. behavioral science : The behavioral approach seeks to develop and verify theories explaining human or organizational behavior. • For example: Technology acceptance theory explains how people accept new tech. 2. design science The design approach seeks to expand capabilities by creating new innovations and artifacts. For example: Designing an AI application for medical diagnosis.
- 3. Introduction 1. Purpose of Information Systems (IS): - Implement IS to enhance organizational effectiveness and efficiency. - Success depends on system capabilities and organizational characteristics. 2. Researcher's Role in IS: - Researchers in IS contribute to knowledge for productive IT application in organizations. - Focus on both managing information technology and using it for organizational purposes. 3. Two Paradigms: - Behavioral Science: Rooted in natural science, develops theories explaining organizational and human phenomena in IS. - Design Science: Originating from engineering, creates innovations for effective IS development and usage. 17/07/1445
- 4. Introduction 4. Importance of Design: - Design is crucial in IS literature, with the relevance of IS research tied to practical applicability. 5. Integration of Technology and Behavior: - Calls for a complementary research cycle between design science and behavioral science. - Technology and behavior are inseparable in an information system. 6. IS Research Realm: - IS research focuses on the convergence of people, organizations, and technology. - IT artifacts include constructs, models, methods, and instantiations. 17/07/1445
- 5. Introduction 7. Illustrative Examples: - Design-science research examples include Executive Information Systems (EISs) and systems supporting emerging knowledge processes (EKPs). 8. Behavioral Science Focus: - Behavioral research often evaluates system use, perceived usefulness, and impact. - Limited focus on evaluating models in the management science literature. 9. Design Science Evaluation: - Design science creates and evaluates IT artifacts to solve organizational problems. - Artifacts represented in structured forms, allowing various types of quantitative evaluations. 17/07/1445
- 6. Introduction 10. Primary Goal of the Paper: - Inform IS researchers and practitioners on conducting, evaluating, and presenting design science research. 11. Guidelines for Design-Science Research: - Describes boundaries within the IS discipline. - Conceptual framework and guidelines provided for conducting and evaluating design-science research. 12. Focus Areas: - Primarily on technology-based design. - Acknowledgment of the exploration of organizations, policies, and work practices as designed artifacts. 17/07/1445
- 7. Introduction What Is Design Science Research? ◦ Design science research is a research paradigm in which a designer answers questions relevant to human problems via the creation of innovative artifacts, thereby contributing new knowledge to the body of scientific evidence. The designed artifacts are both useful and fundamental in understanding that problem. ◦ The fundamental principle of design science research is that knowledge and understanding of a design problem and its solution are acquired in the building and application of an artifact. ◦ The term artifact is used to describe something that is artificial, or constructed by humans, as opposed to something that occurs naturally (Simon 1996). Such artifacts must improve upon existing solutions to a problem or perhaps provide a first solution to an important problem. IT artifacts, which are the end-goal of any design science research project, are broadly defined as follows: ◦ • Constructs (vocabulary and symbols) ◦ • Models (abstractions and representations) ◦ • Methods (algorithms and practices) ◦ • Instantiations (implemented and prototype systems) ◦ • Better design theories 17/07/1445
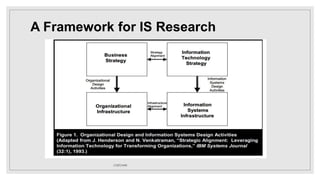
- 8. A Framework for IS Research 1. Nature of Information Systems and Organizations: - Complex, artificial, and purposefully designed. - Components include people, structures, technologies, and work systems. 2. Work Emphasis: - IS practitioners and managers, in general, are extensively involved in design work. - Design is viewed as the purposeful organization of resources for goal achievement. 5. References: - Cites sources like Alter (2003), Bunge (1985), and Simon (1996) for foundational concepts. 17/07/1445
- 9. A Framework for IS Research 17/07/1445
- 10. A Framework for IS Research 17/07/1445